- Article
Task Offloading Based on Virtual Network Embedding in Software-Defined Edge Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
- Lixin Ma,
- Peiying Zhang and
- Ning Chen
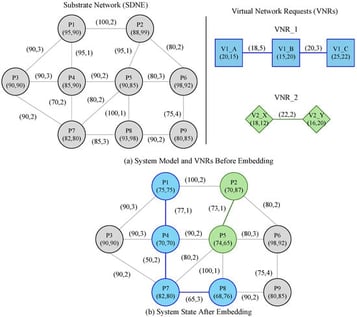
The advent of 5G/6G technologies and the pervasive deployment of IoT devices are driving the emergence of demanding applications that necessitate ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and significant computational power. Traditional cloud computing models fall short in meeting these stringent requirements. To address this, Software-Defined Edge Networks (SDENs) have emerged as a promising architecture, yet efficiently managing their heterogeneous and geographically distributed resources poses substantial challenges for optimal application provisioning. In response, this paper proposes a novel framework for intelligent task offloading, which reframes the intricate multi-component application task offloading problem as a Virtual Network Embedding (VNE) challenge within a SDEN environment. We introduce a comprehensive model where complex applications are represented as Virtual Network Requests (VNRs). In this model, each VNR consists of virtual nodes that demand specific computing and storage resources, as well as virtual links that demand specific bandwidth and must adhere to maximum tolerable delay constraints. To dynamically solve this NP-hard VNE problem in the face of stochastic VNR arrivals and dynamic network conditions, we leverage Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). Specifically, a Soft Actor-Critic (SAC) agent is employed at the SDN controller. This agent learns a sequential decision-making policy for mapping virtual nodes to physical edge servers and virtual links to network paths. To guide the agent towards efficient resource utilization, we define the reward for each successful embedding as the long-term revenue-to-cost ratio. By learning to maximize this reward, the agent is naturally driven to find economically viable allocation strategies. Comprehensive simulation experiments demonstrate that our SAC-based VNE approach significantly outperforms other baselines across key metrics, affirming its efficacy in dynamic SDEN environments.
10 March 2026




![Global population by broad age groups from 1950 to 2100, showing the projected significant increase in the 65+ age group. The growth of this demographic underscores the need for user-centered ICT systems that promote participation and independence in later life. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [2] © 2024 United Nations.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/information/information-17-00275/article_deploy/html/images/information-17-00275-ag-550.jpg)