- Case Report
Percutaneous Retrieval of an Embolized Catheter Fragment in Right Heart Chambers in Pinch-Off Syndrome and Subsequent Reimplantation: Nurse’s Role in Interventional Cardiology—A Case Report
- Alessandro Faraci,
- Salvatore Evola and
- Alfredo Ruggero Galassi
- + 6 authors
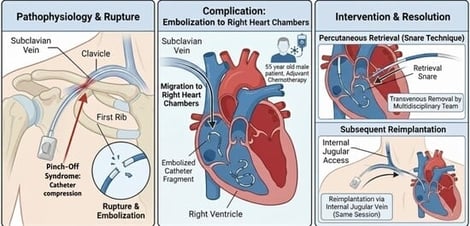
“Pinch-Off Syndrome,” first described by Hinke, is a mechanical complication of totally implantable central venous catheters inserted via subclavian venous access. It occurs when the catheter is compressed between the clavicle and the first rib. Compression can cause transient catheter obstruction and may result in rupture or even complete resection and embolization of the catheter. In this case report, we describe our experience of percutaneous transvenous removal of an embolized port-a-cath fragment within the right heart chambers following a rupture. We used the “retrieval snare” technique and subsequent reimplantation through internal jugular access. The intervention occurred in the same session and involved a multidisciplinary team for a 55-year-old man in need of adjuvant chemotherapy.
2 February 2026