Journal Description
COVID
COVID
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on the study of coronaviruses, coronavirus-related diseases and global impact, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Immunology and Microbiology (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 20.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.4 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.0 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.0 (2024)
Latest Articles
Developing a Long COVID Case Definition: Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Long COVID Based on Symptom Presentation
COVID 2025, 5(12), 205; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120205 (registering DOI) - 14 Dec 2025
Abstract
Efforts have been made to develop a case definition for Long COVID, with results differing on whether the case definition should be specific and exclusive, or broad and easily generalizable. Each of these methods has been subject to limitations. As most efforts have
[...] Read more.
Efforts have been made to develop a case definition for Long COVID, with results differing on whether the case definition should be specific and exclusive, or broad and easily generalizable. Each of these methods has been subject to limitations. As most efforts have focused on symptoms, inclusion criteria have often relied on the binary occurrence of a symptom. The current study uses a more detailed measure that considers the frequency and severity of symptoms in a sample of individuals with Long COVID and matched controls who recovered from acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. Patients were diagnosed with Long COVID in a systematic process involving their completion of quantitative questionnaires, qualitative interviews, a physical examination, and general laboratory testing to rule out other diagnoses. Since samples were comparatively small given the number of symptoms investigated, Leave One Out Cross-Validation (LOOCV) was used to develop LASSO regression models to determine which symptoms best distinguished Long COVID from recovered controls. An ideal threshold for classifying Long COVID based on symptomatology was developed using a receiver operator characteristics (ROC) curve. The model presented in this article identified Long COVID with high accuracy. The importance of smell/taste was lessened in the current study, and gastrointestinal symptoms took on greater prominence in our study. It is possible to achieve high accuracy in differentiating those with Long COVID from those who have recovered. It is important to specify criteria of Long COVID and to measure symptoms comprehensively to identify those with Long COVID. Reliably identifying those who have developed Long COVID will help in the formulation of treatment strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Long COVID: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management)
Open AccessArticle
Association Between Methylprednisolone and the Increase of Respiratory Infections in COVID-19 Patients in the Intensive Care Unit
by
Eduardo Tuta-Quintero, Alirio Bastidas, Esteban García-Gallo, Emilio Díaz, María Bodí, Jordi Solé-Violán, Ricard Ferrer, Antonio Albaya-Moreno, Lorenzo Socias, Ángel Estella, Ana Loza-Vazquez, Ruth Jorge-García, Isabel Sancho, Ignacio Martin-Loeches, Alejandro Rodriguez and Luis Felipe Reyes
COVID 2025, 5(12), 204; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120204 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to assess whether methylprednisolone treatment, while effective in reducing COVID-19 mortality, increases the risk of intensive-care-unit-acquired respiratory tract infections (RTI-ICU) in critically ill patients. Methods: This was a multicenter prospective cohort study conducted in ten countries across Latin America
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aimed to assess whether methylprednisolone treatment, while effective in reducing COVID-19 mortality, increases the risk of intensive-care-unit-acquired respiratory tract infections (RTI-ICU) in critically ill patients. Methods: This was a multicenter prospective cohort study conducted in ten countries across Latin America and Europe. It included patients over 18 years of age with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who required ICU admission. A multivariable logistic regression analysis and propensity score matching (PSM) were performed to determine the association between methylprednisolone treatment and RTI-ICU. Results: A total of 3239 patients were included, of whom 1527 patients (47.1%) were treated with methylprednisolone. Methylprednisolone treatment was associated with a higher risk of developing RTI-ICU (OR = 1.59; 95% CI: 1.33–1.91). Patients with RTI-ICU had a significantly higher average number of days on invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) (24.6, SD: 15.9 vs. 9.5, SD: 11.7; p < 0.001), longer hospital stays (40 days, SD: 24.9 vs. 24.4 days, SD: 18.7; p < 0.001), and higher ICU mortality (39.2%, 259/660 vs. 29.2%, 754/2579; p < 0.001). Conclusions: Methylprednisolone treatment is associated with an increased risk of RTI-ICU in critically ill patients with COVID-19. RTI-ICU was linked to higher mortality, a greater need for invasive mechanical ventilation, prolonged ICU stay, elevated leukocyte and C-reactive protein levels, and a higher comorbidity burden. However, methylprednisolone may not be the sole factor explaining these differences, as residual confounding related to baseline disease severity and comorbidities could have influenced the outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue COVID and Public Health)
►▼
Show Figures
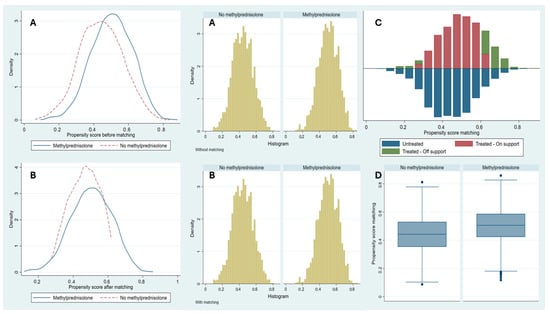
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Temporal Profiling of SARS-CoV-2 Variants Using BioEnrichPy: A Network-Based Insight into Host Disruption and Neurodegeneration
by
Sreelakshmi Kalayakkattil, Ananthakrishnan Anil Indu, Punya Sunil, Haritha Nekkanti, Smitha Shet and Ranajit Das
COVID 2025, 5(12), 203; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120203 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, disrupts human cellular pathways through complex protein–protein interaction, contributing to disease progression. As the virus has evolved, emerging variants have exhibited differences in transmissibility, immune evasion, and pathogenicity, underscoring the need to investigate their distinct molecular interactions
[...] Read more.
SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19, disrupts human cellular pathways through complex protein–protein interaction, contributing to disease progression. As the virus has evolved, emerging variants have exhibited differences in transmissibility, immune evasion, and pathogenicity, underscoring the need to investigate their distinct molecular interactions with host proteins. In this study, we constructed a comprehensive SARS–CoV–2–human protein–protein interaction network and analyzed the temporal evolution of pathway perturbations across different variants. We employed computational approaches, including network-based clustering and functional enrichment analysis, using our custom-developed Python (v3.13) pipeline, BioEnrichPy, to identify key host pathways perturbed by each SARS-CoV-2 variant. Our analyses revealed that while the early variants predominantly targeted respiratory and inflammatory pathways, later variants such as Delta and Omicron exerted more extensive systemic effects, notably impacting neurological and cardiovascular systems. Comparative analyses uncovered distinct, variant-specific molecular adaptations, underscoring the dynamic and evolving nature of SARS-CoV-2–host interactions. Furthermore, we identified host proteins and pathways that represent potential therapeutic vulnerabilities, which appear to have co-evolved with viral mutations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications for Developing the Diagnosis of COVID-19, 3rd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Evaluation of Self-Collected Mouth Rinse Specimens for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Testing: A Pilot Study
by
Kento Fukano, Junko S. Takeuchi, Azusa Kamikawa, Wataru Sugiura, Junko Terada-Hirashima and Moto Kimura
COVID 2025, 5(12), 202; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120202 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Saliva specimens are widely used for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) testing using RT-qPCR due to their advantages over nasopharyngeal swabs of being non-invasive and self-collectable. However, saliva collection can be time-consuming in individuals with reduced saliva secretion, including those with diabetes, diseases involving
[...] Read more.
Saliva specimens are widely used for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) testing using RT-qPCR due to their advantages over nasopharyngeal swabs of being non-invasive and self-collectable. However, saliva collection can be time-consuming in individuals with reduced saliva secretion, including those with diabetes, diseases involving salivary glands such as Sjögren’s syndrome, and older adults. In this study, we evaluated the diagnostic performance of mouth rinse specimens, which can be easily collected even from individuals with reduced saliva secretion, as an alternative to saliva for RT-qPCR COVID-19 testing. Among the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) positive specimens analyzed, 88.2% were derived from patients possessing risk factors associated with reduced salivary secretion, including diabetes, use of medications such as anticholinergics or antihistamines, smoking, and older age. The analysis results of mouth rinse specimens demonstrated 96.7% overall agreement with those of saliva specimens, with a sensitivity of 94.1% and specificity of 100%; however, the viral load in the mouth rinse specimens was lower than that in saliva because of sample dilution. These findings suggest that mouth rinse specimens are a practical, versatile, and reliable alternative specimen for RT-qPCR COVID-19 testing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Clinical Manifestations and Management)
►▼
Show Figures
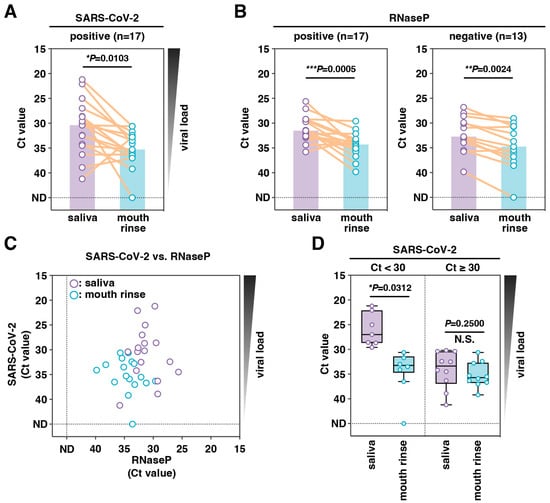
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Functioning, Disability and Rehabilitation After Mild Infection in Concern to Previous Health Status: A Lithuanian Online Survey Study
by
Dovilė Važgėlienė, Raimondas Kubilius and Indre Bileviciute-Ljungar
COVID 2025, 5(12), 201; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120201 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
Objective: To compare self-reported functioning, disability, and health care-seeking behavior of previously healthy and unhealthy participants after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Design: Cross-sectional design conducted in 2021–2022. Subjects/Patients: Participants 18 years or older were asked to participate in an anonymous survey after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection
[...] Read more.
Objective: To compare self-reported functioning, disability, and health care-seeking behavior of previously healthy and unhealthy participants after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Design: Cross-sectional design conducted in 2021–2022. Subjects/Patients: Participants 18 years or older were asked to participate in an anonymous survey after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection (at least 28 days passed). Methods: The survey was conducted using an Internet-based questionnaire distributed through Lithuanian websites, including Facebook groups, city/town/district hospitals, and media outlets. Results: The final cohort consisted of 1945 participants, almost 90% being women with higher education and approximately 89% working at the time of survey. The mean age was 43 years. Among them, 53% reported to be healthy before SARS-CoV-2 infection and 5% were hospitalized during acute infection. Individuals with chronic diseases prior to infection rated their health status significantly lower but reported similar functional capacity before infection. After infection, they reported more restricted activities and more often sought health care due to remaining symptoms. In total, 16% of the cohort applied for rehabilitation services and only 7% were accepted, more often those with chronic diseases before infection. Conclusions: Results indicate a small proportion of participants receiving rehabilitation services, more often these with prior chronic diseases. The results increase awareness of rehabilitation needs after infection, particularly for previously unhealthy people.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue How COVID-19 and Long COVID Changed Individuals and Communities 2.0)
Open AccessBrief Report
Maternal Mortality During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Tamaulipas, Mexico: A Retrospective Study
by
Hadassa Yuef Martínez-Padrón, Ariadne Guadalupe Quintero-Zapata, Ares Duvaliere Buenfild-Saldivar, Jorge Luis Valdéz-Báez, Elsa Verónica Herrera-Mayorga and Rodrigo Vargas-Ruiz
COVID 2025, 5(12), 200; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120200 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Women are at increased risk of developing severe morbidity and mortality during pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium, especially in developing countries. In Mexico, during 2020, 27.5% of maternal deaths were attributed to COVID-19. The aim of this study was to describe the
[...] Read more.
Background: Women are at increased risk of developing severe morbidity and mortality during pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium, especially in developing countries. In Mexico, during 2020, 27.5% of maternal deaths were attributed to COVID-19. The aim of this study was to describe the sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of maternal deaths among patients with and without COVID-19 in the state of Tamaulipas. Materials and Methods: A non-probabilistic sampling approach was used in this observational, cross-sectional, descriptive, retrospective study of obstetric patients. Results: One hundred and six obstetric patient records were evaluated. Eleven patients died directly from COVID-19 complications. The mean age of the population was 29.5 years, with 7.54% suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus and 5.66% systemic arterial hypertension. Obstetric complications were late surgical puerperium (11.32%), physiological puerperium (9.43%), and obstetric hemorrhage (7.54%). Lung complications were community-acquired pneumonia (20.75%), of which 50% were due to COVID-19 (10.37%) and respiratory distress syndrome (15.09%). Systemic complications were hypovolemic shock (16.98%), septic shock (15.09%), and multiple organ failure (12.26%). Conclusions: Mortality from COVID-19 in obstetric patients was 10.37%, and 89.63% died from gynecological, lung, and systemic complications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue COVID and Public Health)
►▼
Show Figures
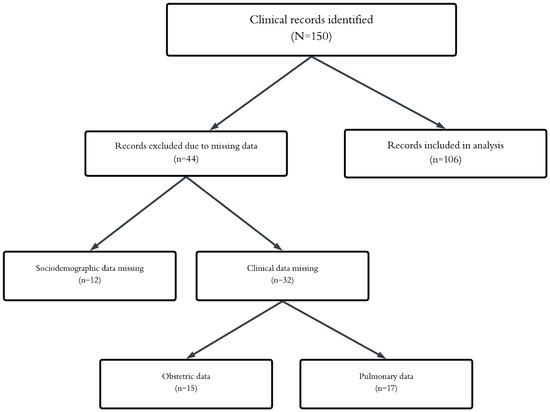
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Documenting Clinical Outcomes Assessed in Outpatients with COVID-19: A Scoping Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
by
Chia Siang Kow, Dinesh Sangarran Ramachandram, Barbara R. Conway and Syed Shahzad Hasan
COVID 2025, 5(12), 199; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120199 - 30 Nov 2025
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic initially focused clinical efforts on hospitalized patients. However, as the pandemic progressed, attention shifted to outpatients who often experience milder symptoms yet still contribute to viral transmission. This scoping review aimed to document and evaluate the clinical outcomes assessed in
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially focused clinical efforts on hospitalized patients. However, as the pandemic progressed, attention shifted to outpatients who often experience milder symptoms yet still contribute to viral transmission. This scoping review aimed to document and evaluate the clinical outcomes assessed in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving outpatients with COVID-19, identifying gaps and areas for improvement in trial design. This review followed the PRISMA-ScR guidelines. A comprehensive search of four electronic databases (PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane CENTRAL, and Web of Science) was conducted for RCTs published between December 2019 and December 2023. Studies were included if they involved outpatients with confirmed COVID-19 and reported clinical outcomes. Data were extracted from eligible studies, and outcomes were categorized using the COMET taxonomy. A total of 91 studies were included, representing a wide geographical distribution, with the USA, Iran, and Brazil contributing the most studies. The most frequently investigated treatments included hydroxychloroquine, fluvoxamine, convalescent plasma, and ivermectin. Key outcomes focused on hospitalization rates, symptom resolution, and disease progression. Mortality, although less common in outpatients, was reported in 65 studies, underscoring the importance of outpatient interventions. This review highlights the need for standardized outcome measures in outpatient COVID-19 trials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Clinical Manifestations and Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Does Low-Dose Oral Naltrexone Alleviate Symptoms of Long COVID? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Aung Du and Andrew Dang Khai Nguyen
COVID 2025, 5(12), 198; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120198 - 29 Nov 2025
Abstract
Long COVID, a condition marked by persistent symptoms following COVID-19 infection, poses significant challenges in regard to clinical management. While emerging pharmacological treatments have demonstrated limited benefits in isolated studies, clinical experience and the literature suggest that low-dose naltrexone (LDN) may be a
[...] Read more.
Long COVID, a condition marked by persistent symptoms following COVID-19 infection, poses significant challenges in regard to clinical management. While emerging pharmacological treatments have demonstrated limited benefits in isolated studies, clinical experience and the literature suggest that low-dose naltrexone (LDN) may be a promising therapeutic option. Therefore, in this systematic review, we aim to synthesise findings from the available literature and evaluate the overall safety and efficacy of LDN as a potential treatment for long COVID. A literature search was conducted using a combination of key terms—‘COVID’, ‘COVID-19’, ‘SARS-COV-2’, and ‘Naltrexone’— and the following databases: MEDLINE, Web of Science (Clavirate), Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Cumulative Index in Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL). The methodology is available on the PROSPERO database (CRD42025630362). Screening identified five eligible articles. Four studies were included, but only two provided comparable data suitable for meta-analysis. Meta-analysis demonstrated statistically significant improvements in fatigue, brain fog, and headaches. Preliminary evidence suggests LDN has potential benefits in the treatment of long COVID, particularly with respect to fatigue, brain fog, and headaches, but more robust studies, such as randomised controlled trials, are urgently needed to confirm LDN’s safety and efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Long COVID: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Factors Associated with the Presence of Post-COVID Syndrome in Older Patients with Arterial Hypertension
by
Venera Kudabaeva, Timur Tastaibek, Almagul Mansharipova, Arystan Seidalin and Nargiza Nassyrova
COVID 2025, 5(12), 197; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120197 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Diagnosing post-COVID syndrome (PCS) in older adults with hypertension is difficult due to heterogeneity and multimorbidity. We aimed to identify factors associated with PCS. Methods: An observational study was conducted from June 2024 to April 2025. Patients aged 60–89 years with arterial
[...] Read more.
Background: Diagnosing post-COVID syndrome (PCS) in older adults with hypertension is difficult due to heterogeneity and multimorbidity. We aimed to identify factors associated with PCS. Methods: An observational study was conducted from June 2024 to April 2025. Patients aged 60–89 years with arterial hypertension were enrolled; PCS was verified according to the national protocol. Between-group comparisons used standard tests. Multivariable logistic regression with pre-specified clinical predictors estimated independent associations. Results: A total of 291 patients with arterial hypertension were included in the study. Patients were grouped by PCS status (PCS = 101; controls = 190). In multivariable analysis, female sex (OR 3.64; 95% CI 1.22–10.82), younger age (OR 0.93; 95% CI 0.89–0.98), lower systolic blood pressure (SBP) (OR 0.98; 95% CI 0.96–1.00), and rhythm disturbances (OR 2.63; 95% CI 1.07–6.49) were associated with PCS; other predictors were not significant. Model discrimination was moderate (AUC 0.728; 95% CI 0.668–0.787; Brier score 0.193) with positive net benefit across thresholds ~0.10–0.65. Conclusions: In older hypertensive adults, female sex, younger age, lower SBP, and rhythm disturbances indicate higher PCS likelihood, supporting risk-stratified monitoring and management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Long COVID: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessStudy Protocol
Therapeutic Potential of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) in Long COVID: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocol
by
Nilihan E. M. Sanal-Hayes, Kate Slade, Marie Mclaughlin, Ethan Berry, Emma Swift and Lawrence D. Hayes
COVID 2025, 5(12), 196; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120196 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
The cumulative global incidence of long COVID is around 400 million individuals, yet effective treatment options remain limited. A recent systematic review published in 2025 highlighted promising results for non-invasive brain stimulation in alleviating long COVID symptoms. Given the growing use of repetitive
[...] Read more.
The cumulative global incidence of long COVID is around 400 million individuals, yet effective treatment options remain limited. A recent systematic review published in 2025 highlighted promising results for non-invasive brain stimulation in alleviating long COVID symptoms. Given the growing use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for people with long COVID, a focused meta-analysis on the therapeutic effectiveness of rTMS is warranted. To address this gap, this protocol outlines the planned procedures for a systematic review and meta-analysis. A comprehensive search will be conducted across CINAHL Ultimate, MEDLINE, ScienceDirect, and Scopus. Retrieved studies will be managed using Rayyan, with two independent reviewers screening titles and abstracts, followed by full-text review. Data extraction will follow PRISMA and Cochrane guidelines using a standardised form, with dual independent extraction and reconciliation of discrepancies. Risk of bias will be assessed using Cochrane RoB 2.0. Meta-analytical procedures will include calculation of standardised effect sizes (e.g., Hedges’ g), use of random-effects models, and assessment of heterogeneity via I2, Cochran’s Q, and tau2. Subgroup and moderator analyses will explore variations in rTMS protocols, participant characteristics, and symptom domains. Sensitivity analyses and meta-regression will be conducted where data permit. Results will be visualised using forest and funnel plots, and the GRADE framework will be used to assess the quality of evidence.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Long COVID: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management)
Open AccessArticle
The Class Gap in Pandemic Attitudes and Experiences
by
Claus Rinner
COVID 2025, 5(12), 195; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120195 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Attitudes towards COVID-19 and lived experiences during the pandemic depended greatly on people’s level of education. This study extends a previous analysis of vaccine hesitancy as a function of formal education and examines additional indicators from the COVID-19 Trends and Impacts Survey for
[...] Read more.
Attitudes towards COVID-19 and lived experiences during the pandemic depended greatly on people’s level of education. This study extends a previous analysis of vaccine hesitancy as a function of formal education and examines additional indicators from the COVID-19 Trends and Impacts Survey for the United States during 2021–2022. The monthly values for social and health-related activities and constraints, testing and vaccination decisions, and information-seeking behaviours, as well as trust and beliefs, often varied markedly between education-defined classes. Many indicators present a significant gap between the attitudes and experiences of better-educated groups, represented by college/university graduates and those with post-graduate studies, on the one hand, and less-educated groups, including those with only high school or some college education, on the other hand. These patterns suggest that the academic and professional-managerial classes, which supply the vast majority of societal decision-makers, may be ill-equipped to understand and respect the needs and worries of the working class in an emergency situation such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Given growing concerns about the benefit–harm balance of many government policies, a more inclusive pandemic response could have been achieved by respecting and adopting the common sense, scepticism, and outright opposition of the less-educated groups vis-a-vis restrictions and public health measures.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Public Health and Epidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Retrospective Look at Early COVID-19 Treatment and Outcomes in Two Tertiary Centers in Türkiye and Bosnia & Herzegovina
by
Rahima Jahic, Mustafa Asim Demirkol, Sefika Umihanic, Jasmina Smajic, Sekib Umihanic, Alma Trnacevic, Amra Adrovic Yildiz, Kamber Kasali, Ayhan Olcay, Nejra Selak and Onur Yolay
COVID 2025, 5(12), 194; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5120194 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
During the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, treatment protocols varied substantially among countries and even between hospitals. This study compared the clinical characteristics, management strategies, and outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients treated in tertiary centers in Türkiye and Bosnia and Herzegovina. We
[...] Read more.
During the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, treatment protocols varied substantially among countries and even between hospitals. This study compared the clinical characteristics, management strategies, and outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients treated in tertiary centers in Türkiye and Bosnia and Herzegovina. We retrospectively analyzed 1338 adults hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection: 657 patients in Tuzla (Bosnia and Herzegovina, June–December 2020) and 681 in İstanbul (Turkiye, April–May 2020). Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data, treatment details (including favipiravir use), need for invasive or non-invasive mechanical ventilation, and in-hospital mortality were extracted from medical records. Patients in Bosnia and Herzegovina were older (61.6 ± 14.4 vs. 56.9 ± 15.8 years; p < 0.001) and had longer hospital stays (9.0 ± 5.5 vs. 7.7 ± 6.1 days; p < 0.001). In the Bosnian cohort, leukocyte, neutrophil, platelet, ferritin, CRP, troponin, creatinine, AST, and ALT levels were significantly higher, whereas hemoglobin and D-dimer levels were lower. The need for ventilatory support was greater in Bosnia and Herzegovina (15.1% vs. 12.2%, p < 0.001), and overall mortality was higher (25.7% vs. 9.3%, p < 0.001). No mortality difference was observed between patients treated and not treated with favipiravir. Despite similar inclusion criteria, patients in Bosnia and Herzegovina exhibited more severe disease, greater organ involvement, and higher mortality than those in Turkiye. Favipiravir use did not influence survival. Inter-country comparisons highlight how differing patient profiles and treatment protocols may impact COVID-19 outcomes; however, interpretation should consider that the two centers contributed data from different phases of the 2020 pandemic, and that country-level differences in circulating variants, healthcare capacity, hospital strain, and evolving clinical guidelines may also have influenced the observed patterns.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Clinical Manifestations and Management)
Open AccessArticle
Long-Term Myocardial Involvement and Outcome in the Post-COVID-19 Condition
by
Miltiadis Georgiadis, Nuriye Akyol, Lars Kamper, Nima Nadem-Boueini, Athanasios Ziakos, Patrick Haage, Melchior Seyfarth and Nadine Abanador-Kamper
COVID 2025, 5(11), 193; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110193 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
After SARS-CoV-2 infection, a subset of patients experience persistent cardiac symptoms, yet data on long-term cardiac involvement and clinical outcomes in the post-COVID-19 condition remain limited. This study aimed to investigate myocardial abnormalities using advanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging techniques in patients
[...] Read more.
After SARS-CoV-2 infection, a subset of patients experience persistent cardiac symptoms, yet data on long-term cardiac involvement and clinical outcomes in the post-COVID-19 condition remain limited. This study aimed to investigate myocardial abnormalities using advanced cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging techniques in patients with ongoing cardiac symptoms for at least three months following COVID-19 diagnosis, and to assess their clinical outcomes. Between January 2021 and March 2022, 94 post-COVID-19 patients were examined at a median of 99 days (IQR 92–110) after diagnosis and compared to 100 controls. The CMR assessment included the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), myocardial T2 signal, late gadolinium enhancement (LGE), and myocardial strain parameters. Follow-up for major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) was conducted at a median of 269 days (IQR 144–352). While no significant differences in LVEF were observed, post-COVID-19 patients demonstrated significantly reduced peak radial and circumferential strain values, suggesting subclinical myocardial dysfunction. Additionally, these patients exhibited a higher event rate compared to controls (0.063 vs. 0; p = 0.029). These findings indicate that patients with cardiac symptoms following COVID-19 may exhibit subtle but measurable myocardial changes and an increased risk of adverse outcomes. The observed alterations in myocardial strain most likely reflect mild, subclinical myocardial involvement within the spectrum of post-COVID-19 effects, rather than a direct cause of persistent symptoms. Further research is warranted to determine the prognostic significance of these findings.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Long COVID and Post-Acute Sequelae)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nasopharyngeal Proteomic Profiles from Patients Hospitalized Due to COVID-19 in Manaus, Amazonas, Brazil
by
Cláudia P. M. Araújo, Carolina M. Vieira, Ketlen C. Ohse, Alessandra S. Silva, Sofia A. Cavalcante, Felipe G. Naveca, Fernanda N. Oliveira, James L. Crainey, Marcus V. G. Lacerda, Gisely C. Melo, Vanderson S. Sampaio, Michel Batista, Amanda C. Camillo-Andrade, Marlon D. M. Santos, Diogo B. Lima, Juliana de S. G. Fischer, Paulo C. Carvalho and Priscila F. Aquino
COVID 2025, 5(11), 192; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110192 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
This study investigated proteomic differences in nasopharyngeal swabs of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients from Manaus (Brazil) who were hospitalized during the devastating first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, before the emergence of the deadly P1 SARS-CoV-2 strain. LC-MS/MS proteomic analysis compared 16 matched COVID-19 patient
[...] Read more.
This study investigated proteomic differences in nasopharyngeal swabs of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients from Manaus (Brazil) who were hospitalized during the devastating first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, before the emergence of the deadly P1 SARS-CoV-2 strain. LC-MS/MS proteomic analysis compared 16 matched COVID-19 patient profiles: eight survivors and eight fatalities. A total of 1604 proteins were identified in fatality swabs, and 981 in the swabs of survivors. Our study provides new insights into the cellular mechanisms underlying first-wave COVID-19 deaths from Manaus and identifies hypoxia-related HYOU1, endothelial injury-associated S100A10, and some viral replication proteins (DDX1/17, XPO1) as potential biomarkers of fatal infections. The proteomic profiles of the swabs taken from patients that died collectively suggest that many of the first wave COVID-19 fatalities in Manaus suffered immune-system collapse. Survivor patient swabs showed elevated levels of immune defense proteins (FN1, C4BPA, IGKV1-5), indicating effective antiviral responses. Gene ontology analysis revealed dysregulated secretory pathways in fatalities and did not detect the defense-response pathways in fatality-group datasets that were observed in survivor protein datasets. Interestingly, the NOS2 protein, previously associated with first-wave fatalities, was found exclusively in our fatality swabs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Host Genetics and Susceptibility/Resistance)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploratory, Cross-Sectional Observations on Post-COVID-19 Respiratory Symptoms: A Multivariable Analysis
by
Patchareeya Amput, Arunrat Srithawong, Ajchamon Thammachai and Sirima Wongphon
COVID 2025, 5(11), 191; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110191 - 8 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: This cross-sectional study reports exploratory observations on respiratory symptom patterns in individuals with prior coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), evaluating associations with exercise habits, number of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection episodes, vaccine doses received, body mass index (BMI), age, sex,
[...] Read more.
Background: This cross-sectional study reports exploratory observations on respiratory symptom patterns in individuals with prior coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), evaluating associations with exercise habits, number of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection episodes, vaccine doses received, body mass index (BMI), age, sex, and comorbidities. Methods: A total of 240 participants were assessed for age, sex, height, weight, BMI, comorbidities, SARS-CoV-2 infection episodes, vaccine doses received, and exercise habits; the self-reported duration of symptomatic periods was summarized descriptively and was not modeled as an exposure or outcome. Results: Compared with the first SARS-CoV-2 infection episode (reference), patients who experienced a second episode had higher odds of dyspnea (adjusted odds ratio; OR = 7.61; 95% confidence interval CI = 1.54–37.66). In univariate analysis, patients who received three vaccine doses had lower odds of dyspnea than those who received two doses (OR = 0.39; 95% CI = 0.16–0.98), but this association was not significant after adjustment (adjusted OR = 0.46; 95% CI = 0.13–1.63). After adjustment, patients who exercised had lower odds of secretion compared with those who did not (adjusted OR = 0.30; 95% CI = 0.12–0.73). Conclusions: These cross-sectional, hypothesis-generating observations suggest higher adjusted odds of dyspnea among individuals with repeat infection and lower adjusted odds of sputum among those reporting regular exercise; estimates are imprecise and subject to residual confounding due to unbalanced group sizes. Confirmation in larger, longitudinal cohorts is required.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Clinical Manifestations and Management)
Open AccessArticle
Determining the Impact of Exogenous Factors in Acute Respiratory Infections Using a Mathematical Epidemiological Model—Case Study of COVID-19 in a Peruvian Hospital
by
Pedro I. Pesantes-Grados, Emma Cambillo-Moyano, Erasmo H. Colona-Vallejos, Libertad Alzamora-Gonzales, Dina Torres Gonzales, Giannina Tineo Pozo, Elena Chamorro Chirinos, Cynthia Lorenzo Quito, Elias E. Aguirre-Siancas, Eliberto Ruiz-Ramirez and Roxana López-Cruz
COVID 2025, 5(11), 190; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110190 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
In this study, we develop and analyze an extended SEIR-type compartmental model that incorporates vaccination and treatment to describe the dynamics of acute respiratory infection transmission. The model subdivides the infectious population into several symptomatic stages and an asymptomatic class, which allows the
[...] Read more.
In this study, we develop and analyze an extended SEIR-type compartmental model that incorporates vaccination and treatment to describe the dynamics of acute respiratory infection transmission. The model subdivides the infectious population into several symptomatic stages and an asymptomatic class, which allows the evaluation of control strategies across different levels of infection severity. The basic reproduction number
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Analysis of Modeling and Statistics for COVID-19, 2nd edition)
►▼
Show Figures
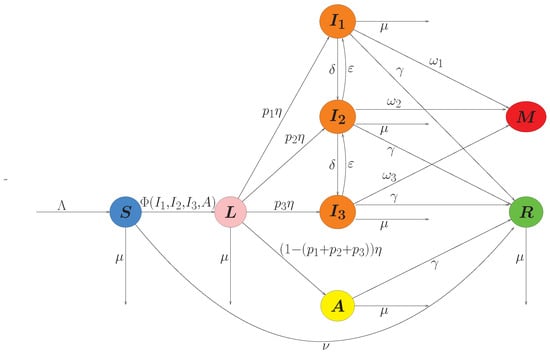
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mental Health in Primary School Children Before and During the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Benito León-del-Barco, María-Isabel Polo-del-Río, Santiago Mendo-Lázaro, Víctor-María López-Ramos, Carolina Bringas-Molleda and Julián Álvarez-Delgado
COVID 2025, 5(11), 189; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110189 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
The health crisis caused by COVID-19 led to a series of restrictive measures worldwide. Amongst them, a period of lockdown that resulted in a decrease in social contact, which had a series of effects at the emotional, educational, and social levels, the greatest
[...] Read more.
The health crisis caused by COVID-19 led to a series of restrictive measures worldwide. Amongst them, a period of lockdown that resulted in a decrease in social contact, which had a series of effects at the emotional, educational, and social levels, the greatest concern being the mental health effects in minors. The aim of this study is to analyse mental health disorders affecting Primary Education students before and during the pandemic, at emotional, social and behavioural levels. A total of 1045 students from different educational centres, in 5th and 6th year of Primary Education, of both sexes and aged between 10 and 12 years old, took part in the study. The instrument used was the “Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire, SDQ”, which measures mental health disorders in minors. The results indicate that during the pandemic there was an increase in emotional problems among minors, alongside a decrease in hyperactivity, conduct problems, and peer-related problems. Social distancing during the pandemic may have acted as a key mediating variable in the observed outcomes. It is concluded that these results are important in preventing psychological effects on the mental health of minors in crisis situations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Public Health and Epidemiology)
Open AccessArticle
COVID-19 Post-Pandemic Adaptation and Resilience: A Cross-Cultural Study of China and Canada
by
Sarah-Mei Chen, Junru Yan, Fan Yang, Clara B. Rebello, Angelie M. Ignacio, Chao S. Hu and Gerald C. Cupchik
COVID 2025, 5(11), 188; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110188 - 2 Nov 2025
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic altered individuals’ worldviews. This study examined how cultural values shaped the ways students navigated stress and adapted after the COVID-19 pandemic. Drawing on Conservation of Resources (COR) Theory and cultural psychology frameworks of individualism and collectivism, we hypothesized that university
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic altered individuals’ worldviews. This study examined how cultural values shaped the ways students navigated stress and adapted after the COVID-19 pandemic. Drawing on Conservation of Resources (COR) Theory and cultural psychology frameworks of individualism and collectivism, we hypothesized that university students in two culturally distinct contexts—China and Canada—would demonstrate resilience differently. Chinese students would display collectivistic coping strategies (e.g., social responsibility and perspective-taking), while Canadian students would show resilience through individualistic strategies (e.g., personal reflection and self-efficacy). A total of 814 students completed a mixed-methods survey assessing resilience, cognitive reflection, and post-pandemic adaptations. Quantitative data were analyzed using factor analysis and stepwise regression to identify predictors. Qualitative responses were thematically analyzed for context. Results revealed cultural differences in resilience and adaptation, with social responsibility, healthy habits, and third-person perspective-taking predicting the responses of Chinese students, whereas internal emotional processing and personal moral reflection predicting it for Canadian students. This study enhances cross-cultural understanding of resilience and adaptation after collective trauma.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Public Health and Epidemiology)
Open AccessArticle
Mental Health Outcomes Among Physicians Following the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
Politimi Kellartzi, Constantine Anetakis, Anna-Bettina Haidich, Vasileios Papaliagkas, Stella Mitka, Maria Anna Kyriazidi, Maria Nitsa and Maria Chatzidimitriou
COVID 2025, 5(11), 187; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110187 - 1 Nov 2025
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the fragility of global health systems, as physicians faced extremely challenging conditions including excessive workloads, infection risk, and high patient mortality. We conducted a cross-sectional survey that aimed to assess the post-pandemic prevalence of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed the fragility of global health systems, as physicians faced extremely challenging conditions including excessive workloads, infection risk, and high patient mortality. We conducted a cross-sectional survey that aimed to assess the post-pandemic prevalence of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in a sample of Greek physicians who worked on the frontline during the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic. An online survey was conducted between 1 March and 31 July 2023, in which 200 Greek physicians were invited via e-mail to voluntarily answer a confidential online questionnaire, and 58 of them responded. The survey included two clinically validated tools: the Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4) and the Impact of Event Scale—Revised (IES-R). Univariate correlations of 26 exposure variables with anxiety, depression, combined anxiety/depression, and PTSD were performed. In total, 58 eligible physicians (46.6% female) participated in this study. The rates of anxiety, depression, combined anxiety/depression, and PTSD were 27.5% (95% CI: 16.7–40.9), 31.0% (19.5–44.5), 22.4% (12.5–35.3), and 24.1% (13.9–37.2), respectively. Notably none of the physicians working in a laboratory developed any mental health symptoms. The following factors were found to be associated with the development of higher mental health symptoms: age ≤ 30, employment in healthcare ≤ 10 years, working in COVID-19 wards, working in intensive care units or COVID-19 wards, a history of mental health symptoms, a history of physical conditions, shortages of materials and equipment for diagnosing or treating patients, development of a disease other than COVID-19, and the development of a new mental health condition during the pandemic (p < 0.05 for all associations). Our findings highlight the need to better prepare physicians with adequate materials, infrastructure, and psychological support such that, in a potential future health crisis, they will not be at such high risk of mental health problems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Public Health and Epidemiology)
Open AccessArticle
The Impact of Fear of COVID-19 on Mood and Health During the First COVID-19 Lockdown Period in The Netherlands
by
Pantea Kiani, Pauline A. Hendriksen, Dana M. Dijkgraaf, Agnese Merlo, Maureen N. Zijlstra, Johan Garssen, Gillian Bruce, Andrew Scholey and Joris C. Verster
COVID 2025, 5(11), 186; https://doi.org/10.3390/covid5110186 - 1 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Fear of COVID-19 has been associated with adverse mental and physical health outcomes, yet evidence from The Netherlands is limited. This study investigated associations between fear of COVID-19, mood, quality of life, immune fitness, and related health variables during the first Dutch
[...] Read more.
Background: Fear of COVID-19 has been associated with adverse mental and physical health outcomes, yet evidence from The Netherlands is limited. This study investigated associations between fear of COVID-19, mood, quality of life, immune fitness, and related health variables during the first Dutch national lockdown and identified key predictors of fear. Methods: In June–July 2020, n = 1020 Dutch adults completed an online survey assessing demographics, personality, mental resilience, pain sensitivity, pain catastrophizing, alcohol use, immune fitness, and mood. Retrospective ratings were provided for the pre-pandemic period (January–March 2020) and the first lockdown (March–May 2020). Fear of COVID-19 was measured using a modified Fear of COVID-19 Scale. Results: Overall, 13.2% of participants reported significant fear of COVID-19, which was associated with poorer mood, reduced quality of life, lower immune fitness, more severe COVID-19 symptoms, greater pain sensitivity, and higher levels of pain catastrophizing. Regression analysis explained 19.6% of the variance, with pre-pandemic anxiety (8.7%) and poorer immune fitness (3.4%) as the strongest predictors of fear of COVID-19, followed by lower psychoticism, lower mental resilience, older age, greater helplessness, and greater extraversion. Discussion: These findings suggest that a minority experienced high levels of fear of COVID-19 with substantial consequences, including negative effects on mood, immune fitness, and quality of life. The strong association with pre-existing anxiety and immune fitness highlights the need for early identification and targeted interventions for vulnerable groups to reduce psychological and physical health impacts in future public health crises.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section COVID Public Health and Epidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures
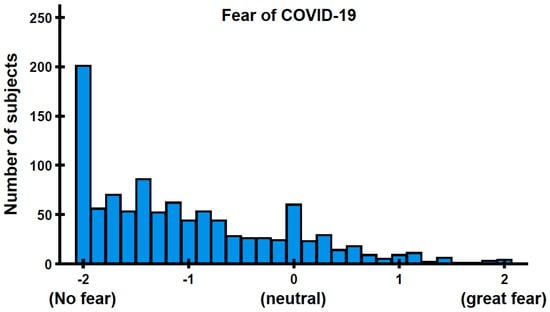
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Special Issues
Special Issue in
COVID
COVID and Public Health
Guest Editor: Anna Puigdellívol-SánchezDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
COVID
Analysis of Modeling and Statistics for COVID-19, 2nd edition
Guest Editors: Martin Kröger, Reinhard SchlickeiserDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
COVID
Cardiovascular Effects of COVID-19: Acute and Chronic
Guest Editor: Timothy D. HenryDeadline: 31 January 2026
Special Issue in
COVID
Long COVID: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management
Guest Editors: Lawrence D. Hayes, Nilihan Sanal HayesDeadline: 31 January 2026








