Abstract
A key requirement in containing contagious diseases, like the COVID-19 pandemic, is the ability to efficiently carry out mass diagnosis over large populations, especially when testing resources are limited and rapid identification is essential for outbreak control. Some of the leading testing procedures, such as those utilizing qualitative polymerase chain reaction, involve using dedicated machinery which can simultaneously process a limited amount of samples. A candidate method to increase the test throughput is to examine pooled samples comprised of a mixture of samples from different patients. In this work, we study pooling-based tests which operate in a one-shot fashion, while providing an indication not solely on the presence of infection, but also on its level, without additional pool-tests, as often required in COVID-19 testing. As these requirements limit the application of traditional group-testing (GT) methods, we propose a multi-level GT scheme, which builds upon GT principles to enable accurate recovery using much fewer tests than patients, while operating in a one-shot manner and providing multi-level indications. We provide a theoretical analysis of the proposed scheme and characterize conditions under which the algorithm operates reliably and at affordable computational complexity. Our numerical results demonstrate that multi-level GT accurately and efficiently detects infection levels, while achieving improved performance and less pooled tests over previously proposed oneshot COVID-19 pooled-testing methods. Our simulations show that the efficient method proposed in this work can correctly identify the infected items and their infection levels with high probability at the known upper bound (for a maximum likelihood decoder in GT) on the number of tests. We also show that the method works well in practice when the number of infected items is not assumed to be known in advance.
1. Introduction
The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic forced lockdowns all over the globe, and claimed more than seven million lives worldwide [1]. In order to handle and contain pandemics, and particularly COVID-19, large portions of the population should be frequently tested [2]. One of the main difficulties in doing so stems from the limited testing resources and the lengthy duration required to identify the presence of an infection [3,4]. In particular, the main diagnosis tool for COVID-19 tests is based on Ribonucleic acid (RNA) extraction via qualitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Although various technological alternatives have been proposed [5,6], such as the rapid lateral-flow antigen tests, and rapid lateral-flow tests based on Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) gene-editing technology [7] and the Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (RT-LAMP) [8], the qualitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) process remains the most accurate method for COVID-19 testing. The output of this procedure represents an estimate of the viral load in the tested sample [9]. This estimation indicates the infection process and progress (when it exists and starts), e.g., for Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the cell and between cells [10]. The more efficient the virus is at entering and replicating in cells, the faster the viral load builds up. In practice, viral load analysis (when it is detected) is a complicated phenomenon that is widely considered in the medical and biological community, and there are certain factors impacting it, such as the presence/absence of specific Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) mutations in an individual or the specific mutations accumulated in the S-protein of SARS-CoV-2. These factors are crucial to learn and conclude on the viral infection. In this work, we focus on efficient viral load detection from tested samples. We refer to the literature for more information on the viral load analysis [11,12]. Now, the main bottleneck associated with this form of COVID-19 testing follows from the fact that each qualitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) machine can simultaneously process a fixed number of samples, and its procedure tends to be quite lengthy, on the order of a few hours for each test [13,14]. Computational and algorithmic methods have shown great promise in alleviating these challenges, especially during the time of limited testing resources [15].
A promising method to tackle this lengthy measurement procedure and thus to increase the efficiency of COVID-19 tests is based on pooling [16,17]. Here, each sample processed, i.e., each input to the qualitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) machine, is comprised of a mixture of several samples taken from different patients. When the infected patients constitute a small subset of the overall tested individuals, pooling-based schemes allow accurate recovery using a number of tests which is notably smaller than the number of patients [18]. Several recovery schemes for pooled COVID-19 tests have been recently proposed [17,19,20,21,22,23,24,25], which can be divided according to the two main mathematical frameworks for such recovery procedures: The first is group-testing theory, originally derived for detecting infections in large populations [26], used in [16,17,19]. Group testing (GT) was first suggested to identify syphilis-infected draftees during World War II [26], and has been long studied and utilized in many fields, such as computational biology [27], biology and chemistry [28,29], communications [30,31,32], sensor networks [33], pattern matching [34], web services [35], and cyber security [36,37,38]. The second framework is compressed sensing, which deals with the recovery of sparse signals [39], and was utilized for pooled COVID-19 tests in [20,21,22,23,24,25]. Another interesting recovery method, which can be seen as an extension of classical group testing (GT), is the Semi-Quantitative Group Testing (SQGT) scheme [40]. This method assumes that varying material can be extracted from different items, resulting in discrete non-binary pooling matrices. This scheme can be useful for conflict resolution in multiple access channels and genotyping [40].
One of the main differences between classical group testing (GT) and compressed sensing (CS) is that GT deals with group detection problems, which results in binary variables. Specifically, in GT, each subject can either be infected or not infected [18], while compressed sensing (CS)-based methods result in real-valued variables. GT is traditionally adaptive, requiring multiple sequential tests [26] in order to achieve a minimal number of overall tests from which the presence of infection can be inferred. Nonetheless, GT can also be applied in a one-shot (non-adaptive) manner [41], avoiding the need to mix new samples during the testing procedure. CS focuses on the one-shot recovery of sparse real-valued vectors from lower-dimensional linear projections, and thus each subject can take any real value number [39]. The additional domain knowledge of GT, namely, the more restricted binary domain over which it operates compared to CS, allows it in some applications to operate using fewer measurements compared to CS, as shown in [42,43] in the context of quantization of sparse signals.
When testing for contagious diseases, and particularly for COVID-19, one is often interested in obtaining some score on the level of the viral load of the patients due to its epidemiological value [21,44,45]. This score is called the infection level. The infection level can correspond to an estimate of the viral load, which in turn can map to the threshold cycle value of RT-qPCR testing. For example, [46] uses viral loads to determine the effectiveness of different quarantine methods. This can be achieved using CS tools. The fact that GT and CS have their own pros and cons for pooled testing motivates the design of a recovery method which combines GT with one-shot operation and multi-level detection, as in CS.
Neither GT nor CS fully address the challenges posed by the need to identify infection levels during an ongoing pandemic of a large scale. In this work, we propose a multi-level GT recovery scheme for pooled testing. Our proposed GT-based method is designed to account for the unique characteristics of pooled tests for contagious diseases, and particularly those arising in COVID-19 testing. The proposed technique extends GT schemes to detect multiple levels of viral load, building upon our previous results on combining GT with CS concepts and multi-level discretization in [42]. The resulting multi-level GT scheme operates in a one-shot manner, and is designed to avoid dilution due to mixing too many samples in each pool [4]. This is a novel approach that identifies the non-binary infection levels, as opposed to classical GT, while requiring significantly less pooled tests than CS-based approaches. In fact, we demonstrate that our method achieves the upper bound on the number of tests of a maximum likelihood (ML) decoder, while having significantly lower complexity than a maximum likelihood (ML) decoder. All of these characteristics, alongside the proven low complexity regime in which our method works in the context of COVID-19, makes it particularly attractive for large-scale infection level detection among large populations. A comparison between the methods is available in Table 1. Note that our proposed multi-level GT method can be readily altered to return viral loads instead of infection levels, by removing the quantization at the end.

Table 1.
Comparison of testing methods.
We begin by identifying the specific requirements which arise from the setup of pooled COVID-19 testing. From these requirements, we derive the multi-level GT method. Our scheme is comprised of a dedicated testing matrix, determining which patients are pooled together into each test; and a GT-based recovery method operating in a two-stage manner, by first identifying the defective patients building upon classic GT tools, followed by a dedicated mechanism for characterizing the level of infection for the identified patients.
We theoretically analyze the proposed multi-level GT scheme. We first characterize its associated computational complexity, which is shown to be dominated by the identification of the defective subjects in the first stage of the proposed algorithm. As the complexity formulation results in a random quantity which depends on the statistical modeling of the measurement procedure, we derive the expected computational burden, and show that it results in a number of computations which is of the same order as that of low-complexity CS-based methods. Next, we derive sufficient conditions for the algorithm to yield a unique solution. While similar guarantees are also available for CS-based methods, we numerically demonstrate that our proposed scheme achieves improved accuracy over CS-based pooled recovery. While GT has been shown to be effective in real settings, and for COVID-19 in particular [47,48,49], obtaining real-world data can be challenging [50]. We therefore conduct our experimental results using the model proposed in [21] for pooled RT-qPCR testing. For these setups, we demonstrate that our multi-level GT scheme reliably recovers the infection levels, while operating at a limited computational burden, and achieves improved accuracy over existing CS-based approaches.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 reviews the system model, focusing on pooled COVID-19 testing and identifies the unique requirements of this procedure. Section 3 presents the proposed multi-level GT scheme. In Section 4, we analyze our approach, identifying sufficient conditions for it to reliably detect the level of infection of each patient, and characterize its complexity. Section 5 details the simulation study, and Section 6 provides concluding remarks.
Throughout the paper, we use boldface lower-case letters for vectors, e.g., . Matrices are denoted with boldface upper-case letters, e.g., . Let denote the element at the i-th row and j-th column of . Sets are expressed with calligraphic letters, e.g., , and is the n-th order Cartesian power of . The stochastic expectation is denoted by , ⋁ and ⊕ are the Boolean OR and XOR operations, respectively, and is the set of non-negative real numbers.
2. System Model
In this section, we present the system model for which we derive the recovery algorithm in Section 3. We begin by identifying the specific characteristics of pooled COVID-19 tests in Section 2.1, based on which we present our problem formulation in Section 2.2.
2.1. Pooled COVID-19 Tests
The common approach in testing for the presence of COVID-19 is based on the RT-qPCR method. Here, a sample is collected, most commonly based on nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs or saliva. The presence of infection is then examined by Ribonucleic acid (RNA) extraction via RT-qPCR measurements, quantifying the viral load in the sample. The RT-qPCR process is quite time consuming (on the typical order of several hours), and can simultaneously examine up to a given number of m inputs (commonly on the order of several tens of samples). This results in a major bottleneck, particularly when the number of patients, denoted by n, is much larger than m.
A candidate approach to reduce the test duration, which is considered in this paper, utilizes pooling [16]. Pooling mixes the samples of groups of patients together, forming m mixed samples out of the overall n patients. Then, the presence of COVID-19 for each of the tested individuals is recovered from the mixed RT-qPCR measurements, either directly, i.e., in a one-shot fashion, or in an adaptive manner involving additional tests [51]. Some characteristics of COVID-19 tests are the following:
Assumption 1.
The number of infected measurements, denoted by k, is much smaller than the number of tested individuals n. Typically, up to 10% of the tested population is infected.
Assumption 2.
One is interested not only in identifying whether a subject is infected, but also in some discrete score on the viral load. For example, possible outputs are no (no virus), low (borderline), mid (infected), and high (highly infected).
Assumption 3.
The RT-qPCR measurements are noisy, i.e., some level of random distortion is induced in the overall process, encapsulating the randomness in the acquisition of the samples, their mixing, and the RT-qPCR reading.
Assumption 4.
One-shot tests are preferable, where we fully identify all subjects from a single RT-qPCR operation, without having to carry out additional tests based on the results.
Assumption 5.
There is a limit, denoted by , on the number of subjects which can be mixed together in a single measurement. A typical limit on the number of subjects mixed together is [16]. Furthermore, the portion taken from each sample for the pooled measurements is identical, e.g., one cannot mix 30% from one patient with 70% from another patient into a single pool.
While the characteristics are identified for swab-based RT-qPCR tests, they also hold for other forms of contagious disease testing, including, e.g., serological tests [52]. Assumption 5 is crucial when dealing with a pandemic, as extracting different samples from different items can be cumbersome for laboratory technicians, impractical in many cases, and prone to human errors. We note that Assumption 5 is violated in the Semi-Quantitative Group Testing (SQGT) scheme.
An illustration of the overall flow of pooled RT-qPCR-based COVID-19 testing along with the desired one-shot recovery operation is depicted in Figure 1. On the left side of the figure, we show the true viral loads of all n items, where the first item is infected in a medium level, the fourth item is infected in a low level, and all other items are not infected. Next, pooling is conducted based on a testing matrix, which is generated prior to obtaining the samples. For example, the first pooled test involves samples from the first, third, and fifth items. This results in a measurement vector, denoted by . This vector is fed to the recovery algorithm, which is able to tell in one shot that the first item is infected in a medium level, the fourth item is infected in a low level, and all other items are not infected.
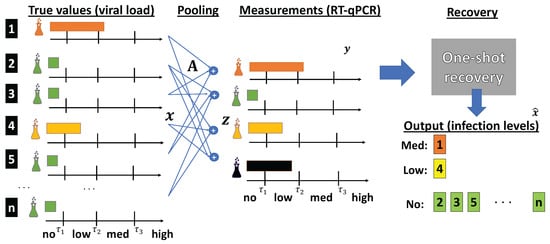
Figure 1.
Pooled RT-qPCR testing with one-shot recovery.
2.2. Problem Formulation
Based on the characteristics of pooled COVID-19 tests detailed above, we consider the following problem: Let be a vector whose entries are the viral loads of the n patients. By Assumption 1, it holds that is k-sparse, i.e., . The pooling operation is represented by the matrix . Let denote the number of subjects mixed together in the i-th individual pool, . This implies that the i-th row of , denoted by , is -sparse by Assumption 5. The viral loads of the pooled samples are represented by the vector , whose entries are given by , where the factor and the structure of guarantee that identical portions are taken from each sample in a pool-test, as required in Assumption 5. The RT-qPCR measurements, denoted by , are given by some stochastic mapping applied to . This mapping represents the distortion detailed in Assumption 3, and we write the measurements as , where is carried out element-wise.
To formulate our objective, we note that by Assumption 2, we are interested in recovering a discrete representation of the viral load. We thus define the discretization mapping , where is a finite set containing the possible decisions, e.g., . The decision regions are defined by the pre-specified thresholds , such that a value not larger than is treated and not infected, while, e.g., a value in the range is treated as a low level of infection. Our goal is to design an algorithm which maps the RT-qPCR measurements into an estimate of the discretized viral loads, denoted by . We wish to minimize the error probability, defined as . The fact that is obtained directly from indicates that the algorithm operates in a one-shot fashion, as required in Assumption 4. By Assumption 1, we have prior knowledge of a reliable upper bound on the number of infected patients k. Such a bound is often obtained by pooling asymptomatic subjects, for which the infection ratio is typically low, on the order of 1% [20]. When k is not known or the given bound is expected to be loose, one of the methods proposed in the GT literature to approximate this number within tests can be used, e.g., [53,54].
To summarize, for the subset of k infected items of a total of n inspected patients, the goal in multi-level pooled testing is to design an one-shot pooling pattern and a corresponding recovery algorithm for reconstructing from . The measurement matrix should guarantee that, at most, L subjects are mixed in each pool-test. We aim to identify the subset of infected items and their discrete representation of the viral load using the recovery algorithm from .
3. Multi-Level Group Testing
In this section, we provide an efficient scheme which implements GT with multiple decisions. Our design builds upon the fact that the sparsity Assumption 1 implies that the recovery of pooled RT-qPCR tests can be treated as a sparse recovery problem, which is typically studied under either the framework of GT [18], or that of CS [39]. Broadly speaking, GT deals with sparse recovery of binary variables, i.e., it can recover whether a subject is infected or not. In order to evaluate the actual levels of each tested subject, as requested in Assumption 2, one would have to re-run the RT-qPCR test, violating requirement Assumption 4. The alternative approach of CS operates over the domain of real numbers, namely, it attempts to identify the exact cycle threshold or viral load for each subject, and thus tends to be less accurate compared to GT, as it does not exploit the fact that one is only interested in a discrete grade value by Assumption 2. This motivates the derivation of a dedicated algorithm for pooled COVID-19 recovery, which harnesses the strength of GT theory while extending it to the multi-level domain. The proposed multi-level GT method is presented in Section 3.1, followed by a discussion in Section 3.2.
3.1. Pooled-Testing Algorithm
Multi-level GT is comprised of two components: the design of the testing matrix , which determines the pooling operation; and the recovery algorithm which determines the discrete level associated with each subject based on the results of the pooled tests. We next elaborate on each of these components.
3.1.1. Pooling Procedure
To determine , we first fix the number of the pool-tests m. In principle, m should satisfy (where the is often omitted for ease of read), for some , as this is the sufficient number of pool-test for reliable recovery in GT using the optimal maximum likelihood (ML) decoder [55,56]. The parameter controls the probability of error of the procedure [55], as we illustrate in Section 5. In practice, the number of pools-tests is often dictated by the measurement setup, e.g., it may be constrained to be an integer multiple of the number of inputs accepted by an RT-qPCR machine. Unless stated otherwise, we assume that , and in Section 4, we prove that this number of samples is sufficient to detect the infection levels using the proposed algorithm.
Once m is fixed, we proceed to setting , whose binary entries dictate which patient is mixed into which pool. The traditional GT method of generating draws its elements in an i.i.d. fashion according to a Bernoulli distribution with parameter p. A common choice for p is , for which the probability of each element in to be zero is . We note that an approximation of is often used [57]. This approximation yields an error term of the order of ; hence, it is negligible for sufficiently large values of k. When k is unknown, p is chosen using a rough approximation of k. A major drawback of this approach is that Assumption 5 is not necessarily satisfied, and there is some chance that too many patients will be mixed into the same pool, causing dilution. We therefore consider an alternative method, which forces the columns of , as well as the rows of , to be “typical”. That is, we want every column/row to have exactly and ones, respectively. This ensures that with high probability, half of the elements of are zero, which, in turn, reduces the required pooled tests, as demonstrated in Section 5. This requirement cannot be guaranteed in the non-asymptotic regime by generating the elements of in an i.i.d. fashion; hence, we force to be typical.
Since in practical testing setups, one is interested in using a fixed deterministic matrix rather than having to work with random matrices, we generate once before the pooling starts. A typical matrix is not unique, and in fact, there are many typical matrices. Generating a typical matrix that satisfies Assumption 5 and the number of required pool-tests for recovery can be performed readily. The same testing matrix can be used for multiple pooling experiments.
3.1.2. Recovery Algorithm
The proposed recovery algorithm is given in Algorithm 1. It operates in two main steps: The first step treats the recovery as a GT setup, and thus aims to divide the patients into infected and non-infected. The second step accounts for the multi-level requirement Assumption 2, and uses decisions made in the first step to determine the infection levels.
Step 1: Detection of Defective Subjects. The first part of the algorithm identifies efficiently all of the definitely defective items in two stages, without determining the infection levels. It does so by treating the problem, in which the observations and the viral loads take continuous non-negative values in general, as a GT setup which operates over binary variables. Hence, in this step, we use a binary representation of the real-valued , denoted , where divides each measured pool into infected and non-infected. Recalling that the viral level decisions are defined by the thresholds , the i-th element of , denoted , is given by
| Algorithm 1 Multi-level GT recovery. | |
| Input: | |
| Output: | ▹ contains index and infection level tuples |
| 1: | |
| Step 1: Detection of defective subjects | |
| 2: | ▹ contains PD items |
| 3: | ▹ contains DD items |
| 4: | |
| Step 2: Infection level recovery | |
| Option 1: Least squares method | |
| 5: Solve least squares (LS) problem (3) | |
| 6: for all i s.t. do | |
| 7: | |
| 8: end for | |
| Option 2: Iterative method | |
| 9: | |
| 10: while do | |
| 11: for all i s.t. do | |
| 12: index s.t. | |
| 13: | |
| 14: | |
| 15: | ▹ From line 12 |
| 16: | |
| 17: end for | |
| 18: end while | |
| Definitely Not Defective (DND) [41] | |
| 19: procedure DND() | |
| 20: | |
| 21: for all i s.t. do | |
| 22: for all j s.t. do | |
| 23: | |
| 24: end for | |
| 25: end for | |
| 26: return | |
| 27: end procedure | |
| Maximum Likelihood (ML) [55] over Possibly Defective (PD) subjects | |
| 28: procedure ML() | |
| 29: return | |
| 30: end procedure | |
In the first stage of the first step, the definitely not defective (DND) algorithm [58] is used (lines 2 and 19–27). This stage removes all items which are definitely not defective, resulting only in a smaller possibly defective set . Recall that the number of pool-tests m, dictated by the testing matrix , is fixed to allow maximum likelihood (ML) detection. The definitely not defective (DND) algorithm attempts to match the columns of with the vector . In particular, if column j of has a non-zero entry while the corresponding element in is zero, the column is assumed not to correspond to a defective subject. This algorithm finds most of the subjects that are definitely not defective (DND) and drastically reduces the number of possible defective (PD) items. The set of subjects declared as possible defective (PD) after this stage, denoted by , is shown to be indeed much smaller than the number of patients n; this is proved rigorously in Section 4, and demonstrated empirically in our numerical study in Section 5. In particular, in Section 4, we give a precise expression for the expected size of . We show that in the non-asymptotic regime that is of interest for COVID-19 pooled testing, and numerically assert these claims, showing that, typically, . The remaining subjects are declared not defective.
The fact that the number of possible defective (PD) subjects is notably smaller than the overall number of patients is exploited in the second stage of the first step, which determines the set of definitely defective (DD) patients. Here, the Boolean ML algorithm [55] is used only over the smaller set of PD subjects , to identify exactly the set of k definitely defective (DD) subjects (lines 3 and 28–30). We use ML over the subset rather than over all the patients, allowing us to carry out this typically computationally prohibitive method at affordable complexity, as we show in Section 4.5. The ML algorithm looks for a collection of k columns in , for which is most likely. The ML decision rule is given by
In the ML rule, we denote by the set of defective subjects, and by the set of combinations of k defective subjects in . While the formulation here is given with the true number of infected patients k, in practice, it is carried out with k (which is unknown) replaced by an approximation or an available upper bound on it.
Step 2: Infection Level Recovery. The output of the first step is a division of the patients into infected and non-infected, encapsulated in the set of identified defective subjects . In the second step, the algorithm estimates the infection level of each subject in . We provide two methods to do so:
Option 1—least squares: The first option uses least squares (LS) estimation [59] to identify the viral loads of all definitely defective (DD) items (line 5):
where denotes the matrix created by taking the columns of from . The output of the algorithm is the infected items, and the quantized infection levels (line 10) using the threshold-based quantization mapping defined in Section 2.2, where a value of “not infected” is given to all items not in . For the LS solution in (3) to be unique, we should have . In this case, (3) is given by
When the measurement process induces some known non-linearity, it can be incorporated into (3), resulting in a non-linear LS formulation. The LS operation outputs a real-valued vector, while the discrete levels are obtained by quantizing the entries of (4). Note that has to be non-negative; thus, one can compute the LS in (3) while constraining the entries of to be non-negative. Here, we omit this constraint; the simulations conducted in Section 5 show that omitting this constraint does not affect the performance of the algorithm in the case studied in this paper. However, in the general setting, this constraint can be easily included if needed [60]. We choose this method in our analyses below, namely, the complexity analysis and the theoretical performance guarantees characterized in the sequel consider Algorithm 1 implemented with the LS recovery option. Nonetheless, we also provide an additional method to recover the infection levels based on iterative detection.
Option 2—iterative detection: An alternative approach is to iteratively estimate the viral loads using pools containing a single patient whose viral load was not yet recovered, and to update the measurements accordingly. In contrast to option 1, which jointly maps the entries of into an estimate of the viral loads, here, we iteratively search for the pools which represent a single unknown value, identifying their corresponding infection levels separately, and then canceling their contribution on the remaining pools. This approach facilitates recovery in setups where not only the infection levels, but also the viral loads themselves are discrete.
The iterative method for recovering the infection levels from is summarized in lines 9–18 of Algorithm 1. Here, we let be the i-th element of . For a test in which only one infected subject participates according to the testing matrix (lines 11–12) (note that ∑ here represents addition over integers and not Boolean OR), the algorithm can recover the viral load directly from the measurement (lines 13–14). To obtain a discrete score, the measured value is quantized using a threshold-based mapping . Then the algorithm subtracts the viral load of that subject from all the tests in which it participates (lines 15–16), and repeats until it recovers the infection levels of all declared infected subjects (line 10).
In Section 5, we compare the performance of the algorithm with the LS method vis-à-vis the iterative method. In our numerical results, which focus on a scenario with continuous-valued viral loads, the LS method is shown to achieve more accurate recovery. This follows from its ability to mitigate the effects of the noise induced in the measurement process, allowing it to retrieve viral loads that are close enough to the true viral loads. Option 2, in which detected pools are iteratively subtracted from non-detected ones, is more sensitive to noise and inaccurate identifications made in previous iterations, whose error may propagate to subsequent decisions. Note that increasing the granularity of the quantization can move us from discrete scores to continuous scores. We also would like to note that in the discussed regime of COVID-19, where there are strict limitations on how many tests can be combined (see Section 2), both options are feasible in terms of computational complexity and running time. Finally, viral load analysis is a complicated phenomenon whose study falls beyond the scope of this paper, as discussed in Section 1 and Section 6.
3.2. Discussion
The novelty of the multi-level GT algorithm stems from its two-step procedure; the first step utilizes efficient GT methods to notably reduce the number of examined patients, while the second step inspects the remaining patients and applies dedicated mechanisms to recover their level of infection. Here, we note a few remarks arising from the proposed scheme.
In Section 3.1, we describe how the matrix is generated. The description involves random generation, for which the resulting matrix is not guaranteed to satisfy Assumption 5. The motivation for using such randomization stems from its provable performance guarantees in GT theory [18]. In practice, once a typical testing matrix satisfying Assumption 5 is selected, one does not have to generate a new matrix for each group of n patients.
For n i.i.d. tested individuals, the probability of finding the infected items (though not necessarily their levels) is maximized by the ML rule. However, its complexity is burdensome, as it has to consider options [61,62]. An efficient alternative is the DND algorithm, also known as column matching [41,58,63], whose time complexity is [56]. However, it requires a greater amount of pooled measurements compared to ML in order to reliably identify the detective items. The first step of our proposed multi-level GT method combines the concepts of DND with the ML algorithm, while the second step extends them to operate over non-binary fields, i.e., recover multiple levels rather than just identifying which subject is defective. Performing DND on all n items using the number of tests set to allow ML detection, i.e., as opposed to the number of tests required for DND, which is [41], results in a smaller set of PD subjects . This, in turn, notably reduces the complexity of the recovery method. In Section 4, we give exact expressions for after performing DND. Given , the ML decoder has to consider significantly less options, which is likely to be computationally feasible and considerably faster than considering all () combinations, as discussed in the complexity analysis in Section 4.5. It is important to note that () options are considered only during the second stage of the first step (the ML stage). In the second step, the infection levels are produced only once (using either the LS option or the iterative detection option), after the most likely set of infected items have been generated.
Algorithm 1 requires two conditions to hold. First, the number of PD items, i.e., , should be relatively small, preferably close to k, so that the ML algorithm is feasible. Furthermore, for the LS recovery method to have a unique solution, it should hold that . If the solution is not unique, the algorithm may produce an undesirable output of different decisions when applied to the same pooled measurements. Both these requirements are numerically asserted to hold in the experimental scenarios considered in the paper, and their validity is also theoretically studied in the following section.
We note that in this paper, we assume that the binary quantization of the tests does not have any error. If this does not hold, one can use the noisy variants of the DND and the ML algorithms of Step 1, as known in the GT literature [41,55]. We leave this case for future work.
In our numerical evaluations of multi-level GT, we demonstrate its ability to achieve error-free detection when the number of measurements m satisfies the upper bound on this quantity for which the computationally prohibitive ML GT is guaranteed to approach zero error, i.e., for some [55]. Furthermore, in the case where it is possible to identify the number of infected subjects in a pool-test by observing its measurement, i.e., when one can separately tell for each element of how many defective patients are mixed into it (though not necessarily their infection level), we notice empirically that it is possible to achieve the lower bound number of pool-tests suggested for GT using the ML algorithm, i.e., [41,55] (for further details, see Section 5). We leave the analysis of this case for future work.
3.3. Unknown k
It is commonly assumed in the GT literature that the number of infected items k is known in advance [62], or that it can be estimated correctly within tests [53,54]. We mainly study this scenario in this paper to focus on the novel aspects of our proposed method. However, in practical scenarios, let alone during a pandemic, this assumption can be restrictive, and the estimations may suffer from errors, especially in the pooled tests that are noisy. In this section, we assume that the estimated number of infected items is different than the actual number of infected items k. We propose an adaptation to the proposed method that can handle this mismatch. Recall that our method is comprised of two main steps: designing the pooling procedure and executing the recovery algorithm.
Designing the pooling procedure boils down to designing the pooling matrix . We propose to use the estimate when constructing the pooling matrix, i.e., . We break the analysis for the two possible mismatches.
- : In this case, the DND step will result in fewer PD items than if we designed the pooling matrix with the correct estimation for k. In the non-asymptotic regime discussed in this paper, such mismatch is likely to result in the DND step correctly identifying all the infected items, as the number of tests required to correctly identify all infected items using the DND algorithm is [41,58].
- : In this case, the DND step is likely to generate more PD items since this estimation is equivalent to lowering in the number of tests m. Assuming the error in the estimation is not severe, the modified ML step can identify the correct infected items with manageable complexity, as we next discuss. For a numerical example, see the discussion in Section 4.1.
It is worth mentioning that once the pooling matrix is set, the DND step does not require knowledge of the number of infected items. Hence, the DND step remains unchanged.
The ML step in Algorithm 1 assumes that the number of infected items is known in advance. If k is not known in advance, one can alter the ML procedure of Algorithm 1 (starting at Line 28) to look for any set of defective items. The objective is to find the smallest number of infected items that would explain the output results . This changes the ML procedure to the one given in Algorithm 2. The adapted version of the algorithm is still able to find the infected items correctly with high probability. This is also supported by our simulations.
We do note that in the case where the number of infected items k is known in advance, declaring that k items are infected is equivalent to declaring that the rest items are not infected. However, in the case where k is unknown, the ML step identifies the smallest set of items that are declared infected among the PD items. In this case, we cannot say for certain that the rest of are not infected. We also empirically show that the infected items are identified correctly with high probability, and there may be some false positives among the non-infected items. Recall that in the context of COVID-19, falsely identifying non-infected items as infected is not as severe an error as false negatives, where infected items are declared as not infected.
| Algorithm 2 Maximum Likelihood (ML) over PD subjects , unknown k |
|
4. Theoretical Analysis
In this section, we provide a theoretical analysis of the proposed multi-level GT scheme. In particular, we characterize two key components of Algorithm 1: the expected number of PD subjects, which dominates the computational complexity of the algorithm, and guarantees for LS recovery to have a unique solution. We then proceed to analyze the complexity of Algorithm 1, and show it is computationally efficient in the regimes of interest in the context of COVID-19. Our theoretical results are given as a function of the system parameters, i.e., the overall number of patients n and the number of infected ones k (assumed in this section to be the true number of infected patients and not a bound on it), as well as using those of the pooling pattern, namely, the number of measurements m and the Bernoulli distribution parameter p. While our theoretical measures are given using the true number of infected patients, we recall that Algorithm 1 can be applied using an approximation or an upper bound on this quantity. For the analysis in this section, we assume that is drawn according to an i.i.d. Bernoulli distribution with parameter p. It is known in the literature that there is approximately a 10% performance gap between picking a typical and an i.i.d. one, so this can serve as a bound on the performance [64]. We also empirically demonstrate this result in Section 5.2.
In our analysis of the expected number of PD subjects, we consider different models of the noise in Step 1. Following conventional GT terminology [55], the cases we treat are as follows:
- Noiseless case—here, the noise induced by the measurement process does not affect the ability to identify whether or not a pool contains a defected subject. Namely, .
- Additive noise—here, the presence of noise may result in a pool not containing any defected subject being measured as an infected pool. This implies that for each .
- Dilution noise—dilution implies that pools containing infected subjects may be falsely measured as non-defective. In this case, for each .
These cases are studied individually in Section 4.1, Section 4.2 and Section 4.3, respectively, for arbitrary settings of the parameters ; conditions for uniqueness of the LS solution are stated in Section 4.4, and the complexity of Algorithm 1 is characterized in Section 4.5.
4.1. Noiseless Case
We first calculate how many items are declared PD after running DND in Algorithm 1 in the noiseless setting. Recall that in this stage, we use the DND algorithm to declare the PD subjects. In the noiseless setting, all defective k items are declared PD, and there is some probability that each non-defective item is declared PD by the DND algorithm. For Algorithm 1 to run in reasonable time, it is essential that is small enough, so the number of options to be considered by the ML decoder is not exponentially large. In the noiseless setting, the expected number of PD subjects is stated in the following theorem:
Theorem 1.
The expected number of items declared PD by the DND algorithm (first stage of the first step of Algorithm 1) in the noiseless setting is given by
The proof is given in Appendix A.1.
Theorem 1 characterizes the exact expected number of PD items declared by DND in the noiseless setting. This characterization holds regardless of the fact that the outputs of the DND method are later used for identifying infection levels. Note that the second part of (5) is similar to a known result on the DND algorithm, e.g., [65] (Equation (8)). The main difference is that it is traditionally used to bound the probability of error of the algorithm using a union bound, whereas we use this expression to calculate the exact expected number of PD items.
To affirm and numerically evaluate Theorem 1, we depict in Figure 2a the expected number of items declared PD, computed via (5), plotted as the dashed lines, as a function of the number of defective items k. This theoretical quantity is compared to the empirical expected number of items declared PD, averaged over Monte-Carlo simulations. The number of tests are chosen to match the upper ML bound , as described in Section 5. We observe in Figure 2a that the simulation results agree with the theoretical values dictated by Theorem 1. The figure also shows that in the non-asymptotic regime, which is of interest for applications such as COVID-19 pooled testing, the expected number of PD items is significantly smaller than the number of patients n, and in particular, often lies in . This means that the second part of Step 1 of Algorithm 1, which uses an ML decoder, has to consider much less combinations compared to that needed without the prior DND subject identification. Similar observations are reported in Figure 3a, which considers the same comparison as in Figure 2a, only with a significantly larger number of items n. The figure shows that the average number of PD items after DND is substantially smaller than n, indicating that the gains of using DND in reducing the computational burden are more dominant as the number of patients grows. In Figure 2b and Figure 3b, we empirically show that, using the results of [66], the probability that the number of PD items is significantly larger than the calculated expected value is small. Namely, we show that is small for , as we show in Figure 2a and Figure 3a, where g is a selected threshold. This ensures that the complexity associated with carrying out the ML step is manageable. The complexity can be controlled and further reduced by increasing the number of pooled tests m.
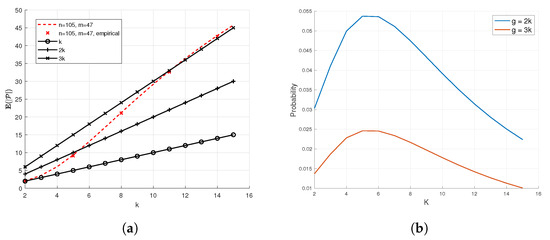
Figure 2.
Empirical demonstration of Theorem 1, , and , matching the ML upper bound (See Section 5). In (a), we see that the expected number of PD items is low. In (b), we see that it is unlikely that the the number of PD items will be significantly higher than the expected number of PD items. (a) Simulated and theoretical number of elements declared PD by DND in the noiseless case. (b) .
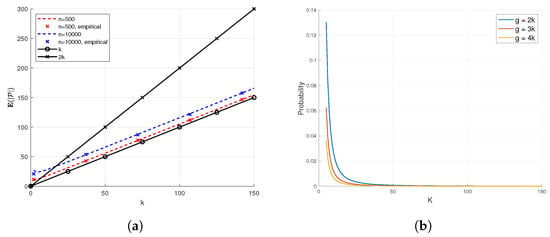
Figure 3.
Empirical demonstration of Theorem 1, for a high number of n, and . The number of tests m satisfies . In (a), we see that the expected number of PD items is close to k for different values of n. In (b), we see that the it is unlikely that the the number of PD items will be significantly higher than the expected number of PD items. (a) Simulated and theoretical number of elements declared PD by DND in the noiseless case. (b) .
This paper studies GT-based methods to identify patients infected with COVID-19 using the RT-qPCR method. As such, the regime in mind is a non-asymptotic regime (see Assumption 5). However, in the GT literature, the analysis is often conducted in the asymptotic regime, where are large and . In this regime, the number of non-defective items declared PD by the DND step goes to zero for (see Appendix A.2 for further details). This demonstrates the trade off between the desired complexity of the ML step and the number of tests m.
Figure 2a,b also show that it is feasible to perform the ML step in the case of a mismatch between the actual number of infected items and the estimated number of infected items (as elaborated in Section 3.3). In Figure 2a, the number of pooled tests m is designed for the case where there are infected items and . We see that when the true number of infected items k exceeds 5, the expected number of PD items is small enough, and Figure 2b shows it will not be too far from with high probability. For example, when the actual number of infected items is k = 7, the DND step returns = 16 PD items on average. The number of combinations considered by the ML step, assuming all the infected items are correctly identified, is equal to , which is a feasible number of combinations to consider by the ML step. Figure 2b shows that the probability to exceed = 16 items is bounded above by 0.05.
4.2. Additive Noise
In the additive noise model, a test may be positive even if no defective items participate in it [55]. This case reflects the possibility of false positives in traditional binary GT. This happens with probability q, i.i.d. between different tests. That is, we define a set of i.i.d. random variables , such that obeys a Bernoulli distribution with parameter q. The binarized test results of the i-th test are here modelled as a Boolean OR function of the test result without additive noise and i.e., . It follows from [55] that the DND algorithm can still guarantee accurate recovery of the PD subjects when the number of tests is increased by a factor of at least with respect to the noiseless scenario. We expand the results of Theorem 1 in the following theorem:
Theorem 2.
Let q be the probability that a test without infected items comes out positive. The expected number of items declared PD by DND algorithm (first stage of the first step of Algorithm 1) in the additive noise setting is given by
The proof is given in Appendix A.3.
Theorem 2 extends Theorem 1 to the case of additive noise. Note that when , i.e., the effect of the additive noise vanishes, we obtain the corresponding expected value derived in Theorem 1 for the noiseless case.
To exemplify the difference between the expected number of PD subjects for noiseless and noisy setups, we next evaluate (6) with the parameters used in Figure 2a for the noiseless case. Specifically, we set , and focus on defective items. In the presence of additive noise with Bernoulli parameter , we obtain that , as opposed to in the noiseless case. This demonstrates the importance of adjusting the number of tests in the additive noise scenario: when we use a number of tests that corresponds to the noiseless case, DND, on average, outputs that most of the items are PD.
4.3. Dilution Noise
In the dilution noise model, a test may come negative even if defective items participate it [55]. This case reflects the possibility of false negatives in traditional binary GT, which are often more severe than false positives, especially in the context of COVID-19. In particular, if a defective item is declared DND in Step 1 of Algorithm 1, then it will not be detected as infected by the algorithm.
To model the presence of dilution noise, we let each defective item be diluted with probability u, independently of other defective items in the test. In order to handle the presence of dilution noise, the DND algorithm has to be adjusted. In the modified DND algorithm, a patient is declared PD if it participates in at least tests that come out positive [41,65]. As a result, the number of positive tests that an item participates in is distributed according to a binomial distribution with m trials. The probability to participate in a test depends on whether the item is infected or not. We denote the probability that an infected/non-infected item participates in a positive result by , respectively. Consequently, the number of positive tests an infected/non infected item participates in is distributed according to , , respectively. Here, is the binomial distribution with a trials and probability of success b.
In the presence of dilution noise, we are no longer guaranteed that a defective item would always be declared as PD. We define as the set of all defective/non-defective items that are marked PD, respectively, i.e., while is an empty set. The extension of Theorem 1 to the presence of dilution noise is given in the following theorem:
Theorem 3.
Let u denote the dilution probability of a defective item in each test, and τ be the threshold used by the modified DND algorithm. Then, the set subjects declared PD is comprised of the distinct sets which satisfy ,
and thus
.
The proof is given in Appendix A.4.
Theorem 3 characterizes the overall number of PD items, as performed in Theorems 1 and 2 for the noiseless and additive noise setups, respectively. In addition to expressing , Theorem 3 also identifies the expected number of patients which are not defective but are identified as PD by the DND algorithm. Unlike the models used in deriving Theorems 1 and 2, under the dilution noise model, we are no longer guaranteed that a defective item is declared DD. Thus, there is a non-zero probability that some of the k infected patients are not assigned into by the DND algorithm, and thus .
4.4. Uniqueness of LS Recovery
Next, we identify sufficient conditions under which the LS solution is unique. Step 2 recovers the infection levels based on the output of Step 1, i.e., . Therefore, to provide a lower bound on the probability that this output enables recovery of infection levels via LS followed by discretization of the values, in the following, we focus on the case where all the infected items have been identified by the first step of the algorithm.
Once the set of infected items, whose indices are denoted by , has been identified by the GT procedure in Step 1, the infection levels of those subjects are recovered by quantizing the LS solution to (3). Notice that since we are left with k subjects to resolve, it holds that , and . When solving (3), we treat as a real matrix rather than a matrix over the binary field. A unique solution exists to the LS problem in this scenario if is of full rank, namely . When this holds, the unique solution to the LS procedure is used to estimate viral loads. Our proposed Algorithm 1 recovers the infection levels by quantizing these estimates, which is numerically demonstrated to yield accurate identification of the infection levels in Section 5. The following theorem bounds the probability that is rank-deficient:
Theorem 4.
Let the number of tests satisfy for some , and the Bernoulli parameter p satisfy . Then, the probability that the solution of (3) is not unique is bounded as
The proof is given in Appendix A.5.
Theorem 4 guarantees that Step 2 of Algorithm 1 uses a unique LS estimate with high probability, assuming that Step 1 of the algorithm has successfully identified the infected items. The resulting probability depends on the number of pools m via the parameter . In Section 5, we assess in simulation that the high probability of having a full rank in Step 2 results in identifying the correct infection levels.
4.5. Complexity Analysis
One of the key features of the proposed multi-level GT methods is its reduced complexity compared to ML-based GT. To fully analyze this aspect of Algorithm 1, we give the following proposition which characterizes its complexity, focusing on the implementation with LS recovery.
Proposition 1.
Let be a design parameter. The overall complexity of Algorithm 1, when used with , is given by
Proof.
The complexity of DND is [56]. Once PD items are identified, the complexity of the ML algorithm is , as we have to compute a Boolean OR of k vectors of size m, and compare it with . The complexity of LS depends on the dimensions of , but also on the specific implementation. Since , LS involves operations [67]. We note that it is likely that the matrix is sparse [39], and it becomes more sparse as p decreases. Efficient algorithms for solving LS are known in the literature when the matrix is sparse, e.g., LSQR [68]. Substituting as the number of tests, we obtain (8), thus proving the proposition. □
The complexity expression in Proposition 1 includes three terms, as the algorithm has three main components: the DND algorithm, which identifies the subset of PD items ; the ML search in (2) on ; and the recovery of the infection levels using LS. The computational complexity of the ML stage is dictated by the set , which is a random quantity depending on the observations. As shown in the previous subsections, the expected cardinality of the PD set can be computed in closed form depending on the assumed noise model.
To analyze the dominant part of the algorithm in terms of complexity, we consider the values that are used in Section 5, which are representative values when testing for COVID-19 using pooled RT-qPCR measurements [21]. In this regime, it holds that , and so the third component (representing the LS complexity) is negligible. To quantify the complexity associated with ML, which is dictated by the random set , we adopt here the noiseless model for the binary measurements. In this case, when the number of tests is set to , which corresponds to the upper bound on the number of tests required for ML decoding, we have that (see Figure 2a). Under these settings and when replacing with its expected value, the ML decoder has to consider combinations. This overhead is much lower than that required in order to apply ML directly to the measurements, which involves a search over different combinations. As is greater than n, the dominant complexity factor corresponds to that required by the ML decoder. This complexity term is not prohibitive in the considered regime, and is of the same order as low complexity CS-based recovery, such as the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit algorithm, which typically requires operations (after plugging in the number of tests m) [69].
5. Numerical Evaluations
In this section, we numerically evaluate the performance of the proposed multi-level GT method recovering COVID-19 infection levels from pooled RT-qPCR measurements.
5.1. Experimental Setup
We consider the model used in [21] for representing the RT-qPCR operation, i.e., the element-wise mapping which yields . In particular, the RT-qPCR measurement operation is modeled via
where q is a constant and is a set of i.i.d. zero-mean Gaussian random variables with variance .
The elements of the test matrix are chosen such that the rows and columns of are typical, and satisfy requirement Assumption 5 with , by generating matrices according to a Bernoulli i.i.d. distribution until a typical matrix is obtained. Unless stated otherwise, Algorithm 1 implements recovery in Step 2 via LS, and the number of patients considered is , out of which are infected. The viral load of each defective subject is drawn from a uniform distribution within , as in [21]. The infection level score is based on a division of this interval into four regions with thresholds , namely, = no; = low (borderline); = mid; and >700 = high. The threshold of 300 is the recommended threshold according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines [16]. We average over 1000 Monte-Carlo simulations. We choose and .
The recovery performance of the proposed Algorithm 1 is compared to upper and lower bounds on ML recovery in GT theory. These bounds represent the necessary and the sufficient number of test pools m one has to use in order to be able to guarantee accurate detection of which of the subjects are infected, respectively, assuming a noiseless GT model as detailed in Section 4.1 [55]. The ML lower bound is
while the upper bound is given by
for any . The bounds in (10) and (11) guarantee detecting the presence of infection using computationally prohibitive ML-based GT; we are interested not only in detecting which patients are defective, but also in characterizing their infection levels. In addition to the ML bounds, we also compare the performance of Algorithm 1 to that reported in [20,21].
5.2. Results
We first evaluate the success probability of Algorithm 1 as a function of the number of pool-tests m. In particular, we evaluate the algorithm using two forms of success probability: finding defective items, for which an error is declared when there is at least a single defective subject who is not detected out of a set of n patients; and finding infection levels, where an error implies that there is at least one patient whose infection level is not correctly recovered. The resulting error probabilities are depicted in Figure 4a, and compared to the ML lower/upper bound on the number of tests m computed via (10) and (11), respectively. From the plot, we see that the success probability of finding the defective items and the success probability of finding the infection levels coincide. That is, whenever the defective set was recovered successfully, the correct infection levels were also estimated successfully, indicating the validity of Step 2 of Algorithm 1. We also see that when the number of tests is at the ML upper bound, the probability of success approaches one.
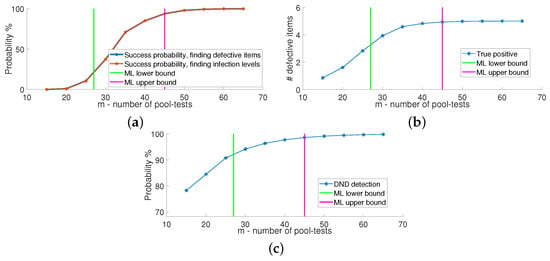
Figure 4.
Performance evaluation of multi-level GT over 200 iterations, with , and with 4 infection levels. (a) Success probability of multi-level GT. (b) True positives detected in multi-level GT. (c) Detected non-defectives at DND stage.
Figure 4b shows the number of true positives, i.e., the number of defective subjects that are declared defective. We observe that when m matches the ML upper bound, we have no false negatives with high probability. In the context of COVID-19, false negatives are the worst outcomes of a test. Figure 4c illustrates the probability of the detected non-defective subjects after the DND stage in Algorithm 1. This is calculated as the number of non-defective items declared by the DND algorithm, divided by the total number of non-defective items . We see that when the number of tests satisfies the ML upper bound, DND identifies of the subjects as non-defective, i.e., . These will be candidates to be tested in the second stage as PD, demonstrating the notable complexity reduction achieved by the two-step process. Similar results are obtained when the non-negativity constraint is enforced on in the LS formulation.
The results in Figure 4a–c evaluate the error probability, but do not capture which types of errors are produced. We thus report in Figure 5 the confusion matrix for the considered scenario, as well as when repeating the setup with a much larger amount of patients of (and with the same number of infected patients ), using merely pool-tests. We observe in Figure 5 that the algorithm rarely classifies infected items as non-infected, and vice versa. For example, for , only 0.1% of infected items are declared non-infected, akin to the results achieved in [21] for the same parameters. This behavior is more notable when jointly testing subjects in Figure 5b,c, where, for example, for (Figure 5b), no false negatives are reported. Comparing these results to [21], it is noted that multi-level GT achieves improved false positive and false negative probabilities with only test-pools compared to that achieved using all CS methods examined in [21] with test-pools. For instance, for [21] reported false positive probabilities varied from 0.1% to 0.8%. This indicates the potential of multi-level GT in facilitating pooled testing of large numbers of subjects.
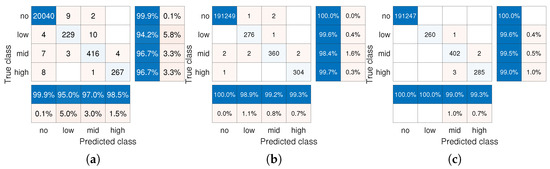
Figure 5.
Confusion matrices of one-shot multi-level GT with LS method. (a) , . (b) , . (c) , .
The gains noted in Figure 5a stem from the combination of GT tools (Step 1 in Algorithm 1) with LS-based recovery (Step 2) which identifies the infection levels and handles the presence of noise in the DD subjects. To quantify the gains of using LS recovery, we repeat the same simulation where the iterative method (Option 2 for Step 2 in Algorithm 1) is used, reporting the confusion matrices are in Figure 6. We note that here, LS outperforms the iterative method. The iterative method does not attempt to denoise the measured viral loads; thus, it is more susceptible to noise. This problem is mitigated by the LS method, which inherently tries to estimate viral loads that would minimize the sum of squared errors between the measured viral loads and the estimated ones.
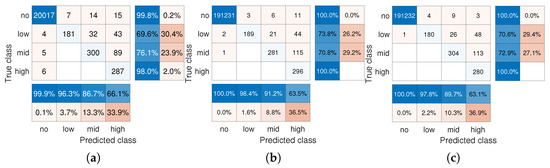
Figure 6.
Confusion matrices of one-shot multi-level GT with iterative method. (a) , . (b) , . (c) , .
In Figure 7, we depict the performance of multi-level GT as a function of different numbers of infected items and total items. The results presented are for the upper bound of the required number of pool-tests, , using an ML decoder as given in (11). It can be clearly seen that the number of pool-tests scales linearly with k and logarithmic with n. In Figure 8, we demonstrate the linear trend showing the error probability using Algorithm 1 over 200 iterations, with and k varied from 2 to 9. In Figure 9, we demonstrate the logarithmic trend for and n varying from 30 to 1000.
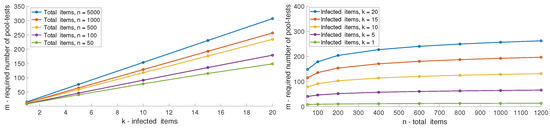
Figure 7.
Required pool-tests m of multi-level GT for different values of n and k, with .
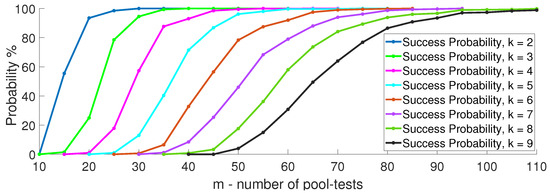
Figure 8.
Success probability of multi-level GT over 200 iterations, with and k varying from 2 to 9.
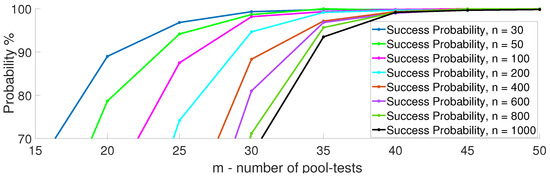
Figure 9.
Success probability of multi-level GT over 200 iterations, with and n varying from 30 to 1000.
Next, we compare the performance achievable when using the typical and random pool-testing matrices described in Section 3. Figure 10 plots the success probability of multi-level GT using both generation methods with . We see that when is typical, one can identify the infected items with about 21% fewer pool-tests, and that the performance achieved with random also holds with typical .
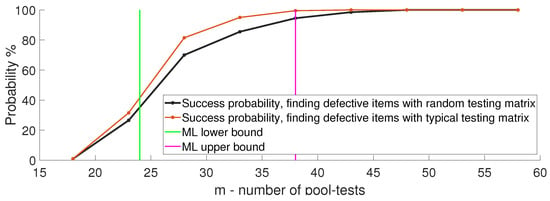
Figure 10.
Success probability comparison of multi-level GT using typical and i.i.d. testing matrices with .
In Section 3, we describe how in the first GT-based step of Algorithm 1, the measured pooled viral loads are represented using the mapping . We use this quantity for each pooled test as an indication to whether it includes an infected item or not; nonetheless, we do not have a similar indication regarding the number of infected items in a pooled test. We next explore how Algorithm 1 fares when given access to such an indication on how many infected items participate in each pooled test. While not being the main focus of this paper, this scenario may be useful if we are able to output the number of infected items in each pooled test. When the number of infected items in a pooled test can be estimated in the recovery process, we may utilize such knowledge to reduce the number of pooled tests to the known lower bound for ML decoding of GT [55]. Figure 11 plots the success probability measures as in Figure 4a versus m, when the number of infected items in a test is either known (in teal circles) or unknown (in orange exes). The number of infected items and total number of items , similar to the experiment reported in [20]. Figure 11 shows that like [20], multi-level GT is able to correctly identify the infected items. Unlike [20], multi-level GT is also able to recover the correct infection level of the infected items, when the number of tests is set according to the upper bound for ML decoding. Moreover, if the number of infected items in each pooled test is revealed, multi-level GT also achieves the lower bound required for ML detection, namely, it can operate reliably with the minimal necessary number of test pools dictated by GT theory. Note that without this additional information, i.e., the number of infected items in each test, no existing solution in the literature achieves this lower bound.
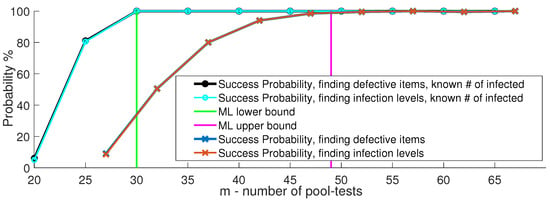
Figure 11.
Success probability of multi-level GT when the decoder can identify the number of infected subjects in a pool.
In Section 3.3, we discussed how the proposed method can be modified to handle the case where the number of infected items k is not assumed to be known in advance. Figure 12 shows the probability to correctly identify the infected items using the version of the ML decoder (Algorithm 2) that does not assume the number of infected items in advance. In this example, and the pooling matrix is designed assuming the number of infected items is . The figure shows that the proposed method can successfully identify the infected items with high probability, even without prior knowledge of the number of infected items k. As previously discussed, this version of the ML step cannot guarantee that the remaining PD items are not infected. Figure 13 shows that when , the DND step declares more non-infected items as PD. These items may result in false positives, which is not the severe type of error in the context of COVID-19 identification. We also see that when , the DND step successfully identifies all the infected items and does not produce any additional PD items. This is expected since this case corresponds to enlarging , hence reducing the probability of error.
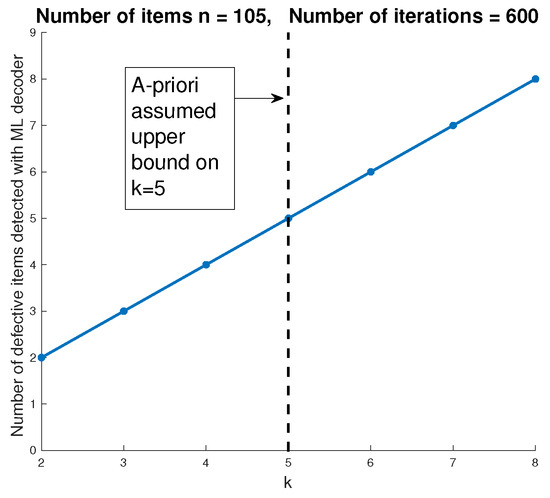
Figure 12.
Number of correctly identified infected items using the modified version of the ML decoder in Algorithm 2, when the true number of the infected patients is unknown.
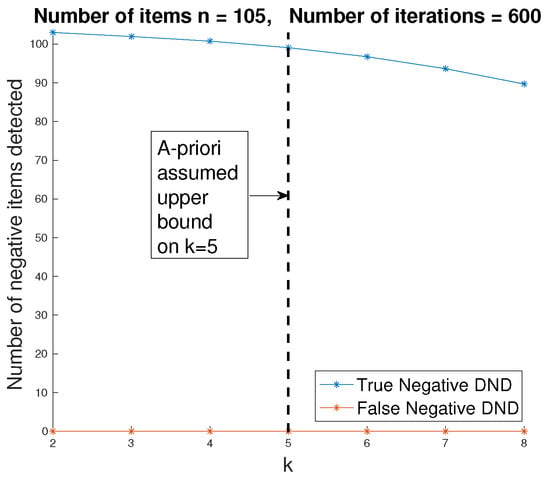
Figure 13.
Number of true and false negative items declared after the DND step. In this case, there are infected items, and the estimated number of infected items is . The number of pooled tests is , which corresponds to the lower bound of ML with .
6. Conclusions
In this work, we proposed multi-level GT for one-shot pooled COVID-19 tests. We first identified the unique characteristics and requirements of RT-qPCR-based tests. Based on these requirements, we designed multi-level GT to combine traditional GT methods with one-shot operation and multi-level outputs, while implementing a preliminary DND detection mechanism to facilitate recovery at reduced complexity. We provided theoretical analysis of the algorithm, and identified conditions under which it operates with feasible complexity, which include the regimes of interest in the context of COVID-19. We numerically demonstrate that multi-level GT reliably identifies the infection levels when examining far fewer samples compared to the number of tested subjects. These results highlight the applicability of our method in real-world scenarios where testing speed, resource constraints, and infection quantification are all critical—making it particularly suited for large-scale outbreaks like COVID-19.
Future work could explore different noise models that are known in the literature and mentioned in the paper, as noise arises naturally in practical testing scenarios during pandemics. The assumption that infected items are not correlated may not be realistic, though omitting it can be an interesting venue of further research, e.g, as considered recently for Boolean GT in [66]. Incorporating prior biological or epidemiological information—such as typical viral load distributions or population-level infection patterns—into the multi-level GT framework is another promising avenue for future research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; methodology, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; software, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; validation, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; formal analysis, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; investigation, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; resources, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; data curation, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; writing—review and editing, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; visualization, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; supervision, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; project administration, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E.; funding acquisition, A.S., A.C., N.S., and Y.C.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Miel de Botton and Jean and Terry de Gunzburg Coronavirus Research, by the Manya Igel Centre for Biomedical Engineering and Signal Processing, by the QuantERA grant number C’MON-QSENS!, by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program grant number 646804-ERC-COG-BNYQ, and by the Israel Science Foundation grant number 0100101.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Muriel Médard for fruitful discussions and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Proof of Theorem 1
In our proof, we use to denote the event that the i-th item is declared PD at the j-th test/all of the tests, respectively. There are only two disjoint events in which a non-defective item i is declared PD in test j. For that to happen, either item i does not participate in test j, or item i participates in test j, but at least one of the defective items participates in test j as well. Consequently, the only case in which item i is declared DND at test j is if it participates at test number j, while none of the defective items participate in that test.
The probability is calculated as
using the fact that the elements of are chosen independently, and denotes the complement of A, recall that denotes the set of actual defective items. Observe that does not depend on , and that , where we use the fact that the tests are independent. Note that does not depend on i. Let be the indicator function of the event that the i-th (non-defective) item is declared PD, and thus, . Let D denote the number of non-defective items that are declared PD by the DND algorithm. Then, . The expected number of non-defective items that are declared PD by the DND algorithm, , is
Since DND declares all defective items as PD, the expected number of items declared PD is .
Appendix A.2. The Number of Non-Defective Items Declared PD by the DND Step
In this section, we assume that are asymptotically large and that (recall Assumption 1). Let . We also use the commonly used approximation of [57]. Using the fact that , we get that the number of non-defective items declared PD by the DND step is given by
and goes to 0 for as n grows.
Appendix A.3. Proof of Theorem 2
In the presence of additive noise, we have to adjust the calculation of . The event can now happen without the presence of defective items in test number j with probability q. In other words,
Akin to the proof of Theorem 1, we get that and that . This concludes the proof of (6).
Appendix A.4. Proof of Theorem 3
Let be the number of defective items that participate in test j, and i be an index of a non-defective item. Note that . We calculate as
If i is a defective item, the i-th item has to participate in the test. The modified probability is
which is not a function of i. By plugging , we get the noiseless case. Unlike previous cases, in the dilution model, the DND algorithm does not declare an item as PD if it comes out PD at each of the m tests. Instead, item i is declared PD if it comes PD at a sufficient amount of tests. Formally, let be the number of times item i comes out PD by DND algorithm. We say that item i is PD, i.e., is true, if , where is a threshold. As different tests are independent, and item i comes out PD at test j with probability , we conclude that , as a sum of i.i.d. Bernoulli random variables. As a result, . In a similar fashion to before, we get that and
Appendix A.5. Proof of Theorem 4
We first prove the following lemma, then prove Theorem 4 by plugging into it .
Lemma A1.
Let be the Bernoulli parameter of , the number of defective items, and the number of tests, respectively, where and . Let be a submatrix formed by taking the k columns of that correspond to the k true defective items. Then,
Proof.
To prove the lemma, we start with that contains no columns, and gradually add k columns. Let be the set of all columns in before adding the i-th column. Before adding the i-th column, we assume that all previously added columns are linearly independent. Define as all the binary columns spanned by , namely,
and the addition is performed over the real field . Observe that , as some combinations of may result in columns that do not belong to . At each step, we add a column of length m whose elements are drawn from i.i.d. Bernoulli distribution with parameter p, and ask whether the added column is within the binary span of the previous columns or not, i.e., if . Note that is satisfied if, at every step, we add a column that is not in the span of the previously added columns, namely . For example, in the first step, we need to add a column that is not in the span of zero previously added columns. Second, we note that for every i, which is the most likely column among all columns that lie in the span (since we assume that ). The probability of choosing the zero column is given by . As a result, the probability that the newly added column does not lie within the span of previously selected columns is bounded below by .
We can readily bound the probability that is of full rank by repeating this argument k times and getting
, thus
where we use the fact that the columns are chosen independently, and the geometric series formula. □
The lemma gives a lower bound on the probability of finding a unique solution to (3), which is a part of Step 2, for a general selection of . The proof is concluded by plugging in .
References
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Deaths Dashboard; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Salathé, M.; Althaus, C.L.; Neher, R.; Stringhini, S.; Hodcroft, E.; Fellay, J.; Zwahlen, M.; Senti, G.; Battegay, M.; Wilder-Smith, A.; et al. COVID-19 epidemic in Switzerland: On the importance of testing, contact tracing and isolation. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, E.J.; Persad, G.; Upshur, R.; Thome, B.; Parker, M.; Glickman, A.; Zhang, C.; Boyle, C.; Smith, M.; Phillips, J.P. Fair allocation of scarce medical resources in the time of Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.; Cho, M.; Wu, X.; Mudumbai, R.; Xu, W. Optimal Pooling Matrix Design for Group Testing with Dilution (Row Degree) Constraints. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.01944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, C.; Federico, P.B.; Alejandra, G.C. An ultrasensitive, rapid, and portable coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 sequence detection method based on CRISPR-Cas12. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Assa, N.; Naddaf, R.; Gefen, T.; Capucha, T.; Hajjo, H.; Mandelbaum, N.; Elbaum, L.; Rogov, P.; Daniel, K.A.; Kaplan, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 On-the-Spot Virus Detection Directly From Patients. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, M.J.; Parker, R.; Larremore, D.B. Rethinking COVID-19 test sensitivity—A strategy for containment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Herbst, K.; Boerner, K.; Meurer, M.; Kremer, L.P.; Kirrmaier, D.; Freistaedter, A.; Papagiannidis, D.; Galmozzi, C.; Stanifer, M.L.; et al. A colorimetric RT-LAMP assay and LAMP-sequencing for detecting SARS-CoV-2 RNA in clinical samples. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eabc7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.; Hands, R.E.; Bustin, S.A. Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1559–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wu, Z.; Nie, X.; Du, L. Polymorphisms and mutations of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 genes are associated with COVID-19: A systematic review. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, D. Structural implications of SARS-CoV-2 Surface Glycoprotein N501Y mutation within receptor-binding domain [499-505]–computational analysis of the most frequent Asn501 polar uncharged amino acid mutations. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2023, 37, 2206492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranbat, D.; Schneider, L.; Kantor, R.; Beckwith, C.G.; Bazerman, L.; Gillani, F.; Sahu, S.; Rapoza, K.; Sam, S.; Novitsky, V.; et al. DirectDetect SARS-CoV-2 direct real-time RT-PCR study using patient samples. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4945–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Nolan, T. RT-qPCR testing of SARS-CoV-2: A primer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Yu, P.S. A survey on applications of artificial intelligence in fighting against COVID-19. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUr) 2021, 54, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelin, I.; Aharony, N.; Tamar, E.S.; Argoetti, A.; Messer, E.; Berenbaum, D.; Shafran, E.; Kuzli, A.; Gandali, N.; Shkedi, O.; et al. Evaluation of COVID-19 RT-qPCR test in multi-sample pools. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, R.; Thurner, S. Boosting test-efficiency by pooled testing strategies for SARS-CoV-2. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A.C.; Iwen, M.A.; Strauss, M.J. Group testing and sparse signal recovery. In Proceedings of the 2008 42nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 26–29 October 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1059–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ami, R.; Klochendler, A.; Seidel, M.; Sido, T.; Gurel-Gurevich, O.; Yassour, M.; Meshorer, E.; Benedek, G.; Fogel, I.; Oiknine-Djian, E.; et al. Large-scale implementation of pooled RNA extraction and RT-PCR for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shental, N.; Levy, S.; Skorniakov, S.; Wuvshet, V.; Shemer-Avni, Y.; Porgador, A.; Hertz, T. Efficient high throughput SARS-CoV-2 testing to detect asymptomatic carriers. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Agarwal, R.; Rehan, M.A.; Pathak, S.; Agarwal, P.; Gupta, Y.; Consul, S.; Gupta, N.; Ritika, R.; Goenka, R.; et al. A Compressed Sensing Approach to Pooled RT-PCR Testing for COVID-19 Detection. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2021, 2, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Mudumbai, R.; Xu, W. Low-Cost and High-Throughput Testing of COVID-19 Viruses and Antibodies via Compressed Sensing: System Concepts and Computational Experiments. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05759. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, H.B.; Bah, B.; Jung, P. Practical High-Throughput, Non-Adaptive and Noise-Robust SARS-CoV-2 Testing. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.09171. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, J.; Cho, M.; Wu, X.; Xu, W.; Mudumbai, R. Error Correction Codes for COVID-19 Virus and Antibody Testing: Using Pooled Testing to Increase Test Reliability. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.14919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Rivera, K.; Baron, D. Noisy Pooled PCR for Virus Testing. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfman, R. The detection of defective members of large populations. Ann. Math. Stat. 1943, 14, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourad, R.; Dawy, Z.; Morcos, F. Designing pooling systems for noisy high-throughput protein-protein interaction experiments using Boolean compressed sensing. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2013, 10, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Hwang, F.K.; Hwang, F. Combinatorial Group Testing and Its Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2000; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Macula, A.J. Probabilistic nonadaptive group testing in the presence of errors and DNA library screening. Ann. Comb. 1999, 3, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, M.K. Group detection for synchronous Gaussian code-division multiple-access channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1995, 41, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghchi, M.; Karbasi, A.; Mohajer, S.; Saligrama, V. Graph-constrained group testing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2012, 58, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wei, S.; Wang, Y.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Yuan, J. Partition information and its transmission over boolean multi-access channels. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 61, 1010–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajwa, W.U.; Haupt, J.D.; Sayeed, A.M.; Nowak, R.D. Joint source–channel communication for distributed estimation in sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 3629–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, R.; Efremenko, K.; Porat, E.; Rothschild, A. k-mismatch with don’t cares. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Algorithms, Eilat, Israel, 8–10 October 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, W.T.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Z.; Bai, X.; Huang, H.; Paul, R. Testing web services using progressive group testing. In Proceedings of the Advanced Workshop on Content Computing, Zhenjiang, China, 15–17 November 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Cormode, G.; Muthukrishnan, S. What’s new: Finding significant differences in network data streams. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2005, 13, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Shin, I.; Thai, M.T.; Znati, T. Detecting application denial-of-service attacks: A group-testing-based approach. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2009, 21, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, M.T.; Atallah, M.J.; Tamassia, R. Indexing information for data forensics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, New York, NY, USA, 7–10 June 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 206–221. [Google Scholar]
- Eldar, Y.C.; Kutyniok, G. Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Emad, A.; Milenkovic, O. Semiquantitative group testing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 4614–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.L.; Jaggi, S.; Saligrama, V.; Agnihotri, S. Non-adaptive group testing: Explicit bounds and novel algorithms. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 3019–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Shlezinger, N.; Salamatian, S.; Eldar, Y.C.; Médard, M. Serial Quantization for Sparse Time Sequences. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 3299–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Shlezinger, N.; Salamatian, S.; Eldar, Y.C.; Médard, M. Distributed Quantization for Sparse Time Sequences. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 5580–5584. [Google Scholar]
- Beldomenico, P.M. Do superspreaders generate new superspreaders? A hypothesis to explain the propagation pattern of COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, L.M.; Wan, L.; Xiang, T.X.; Le, A.; Liu, J.M.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.; Zhang, W. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Cai, Z. Quantifying the effect of quarantine control and optimizing its cost in COVID-19 pandemic. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2022, 21, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbantoglu, O.U. Group testing performance evaluation for SARS-CoV-2 massive scale screening and testing. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2020, 20, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, I.; Jain, A.; Singh, M.; Balakrishnan, A.; Dhodapkar, R.; Borkakoty, B.; Ashok, M.; Das, P.; Biswas, D.; Kalawat, U.; et al. Pooled testing for COVID-19 diagnosis by real-time RT-PCR: A multi-site comparative evaluation of 5-& 10-sample pooling. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 152, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Storto, A.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Collin, G.; André, B.; Mallory, A.; Dangla, R.; Descamps, D.; Visseaux, B.; Gossner, O. High-sensitivity SARS-CoV-2 group testing by digital PCR among symptomatic patients in hospital settings. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 141, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehudi, Y.; Hughes-Noehrer, L.; Goble, C.; Jay, C. COVID-19: An exploration of consecutive systemic barriers to pathogen-related data sharing during a pandemic. Data Policy 2025, 7, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Oliver, J.M.; Swallow, W.H. A two-stage adaptive group-testing procedure for estimating small proportions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1994, 89, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Verkerke, H.; Owens, J.; Saeedi, B.; Boyer, D.; Shin, S.; Roback, J.; Neish, A.; Stowell, S. Serum pooling for rapid expansion of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing capacity. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2021, 28, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaschke, P.; Muhammad, A.S. Competitive group testing and learning hidden vertex covers with minimum adaptivity. Discret. Math. Algorithms Appl. 2010, 2, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaschke, P.; Muhammad, A.S. Bounds for nonadaptive group tests to estimate the amount of defectives. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Combinatorial Optimization and Applications, Kailua-Kona, HI, USA, 18–20 December 2010; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Atia, G.K.; Saligrama, V. Boolean compressed sensing and noisy group testing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2012, 58, 1880–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Cohen, A.; Gurewitz, O. Secure group testing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 16, 4003–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, M.; Baldassini, L.; Gunderson, K. Almost separable matrices. J. Comb. Optim. 2017, 33, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aldridge, M.; Baldassini, L.; Johnson, O. Group testing algorithms: Bounds and simulations. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 3671–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekking, F.M.; Kraaikamp, C.; Lopuhaä, H.P.; Meester, L.E. A Modern Introduction to Probability and Statistics: Understanding Why and How; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, C.L.; Hanson, R.J. Solving Least Squares Problems; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Coja-Oghlan, A.; Gebhard, O.; Hahn-Klimroth, M.; Loick, P. Information-theoretic and algorithmic thresholds for group testing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2020, 66, 7911–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, M.; Johnson, O.; Scarlett, J. Group testing: An information theory perspective. Found. Trends® Commun. Inf. Theory 2019, 15, 196–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, W.; Singleton, R. Nonrandom binary superimposed codes. IEEE Tran. Inf. Theory 1964, 10, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, O.; Aldridge, M.; Scarlett, J. Performance of group testing algorithms with near-constant tests per item. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2018, 65, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.L.; Che, P.H.; Jaggi, S.; Saligrama, V. Non-adaptive probabilistic group testing with noisy measurements: Near-optimal bounds with efficient algorithms. In Proceedings of the Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Monticello, IL, USA, 28–30 September 2011; pp. 1832–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy, A.C.; Cohen, A. Non-Adaptive Multi-Stage Algorithm for Group Testing with Prior Statistics. In Proceedings of the 2024 60th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, Urbana, IL, USA, 24–27 September 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.; Boyd, S.P.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Paige, C.C.; Saunders, M.A. LSQR: An algorithm for sparse linear equations and sparse least squares. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 1982, 8, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y. Efficient Implementations for Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. Electronics 2020, 9, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).