- Article
Sponsorship Dynamics in Low-Media-Coverage Sports: An Examination of Norwegian Individual Athletes and Their Sponsors
- Mark Romanelli,
- Andrea Kjærstad and
- Louis Moustakas
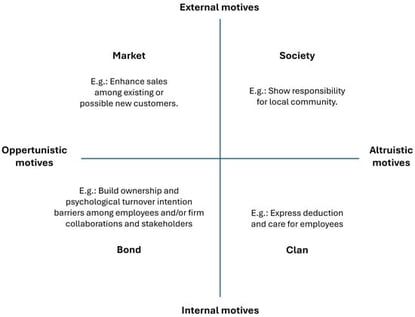
This study investigates why companies sponsor individual athletes in sports with low media coverage and how such athletes secure sponsorship agreements. While sport sponsorship research has predominantly focused on mainstream sports and event-based contexts, limited attention has been given to individual athletes in niche sports. Using a qualitative research design, semi-structured expert interviews were conducted with Norwegian sponsors and elite athletes in long-distance running, trail running, and orienteering. The data were analyzed through qualitative content analysis, informed by the Sponsorship Motive Matrix and the Model of Athlete Brand Image. The findings indicate that sponsorship decisions are primarily driven by market-related motives, complemented by bond and society motives, with cost-effectiveness, authenticity, and value alignment playing important roles. Sponsors prioritize athlete performance, personality, and social media presence, while athletes emphasize financial support and performance optimization. Sponsorship activation is generally limited, and agreements are predominantly in-kind or hybrid. The study concludes that sponsorships in low-media-coverage sports are relational and selective, relying heavily on athlete-driven outreach and social media visibility. These findings extend existing sponsorship frameworks to an underexplored context and offer practical insights for sponsors and athletes in niche sports.
6 February 2026