- Review
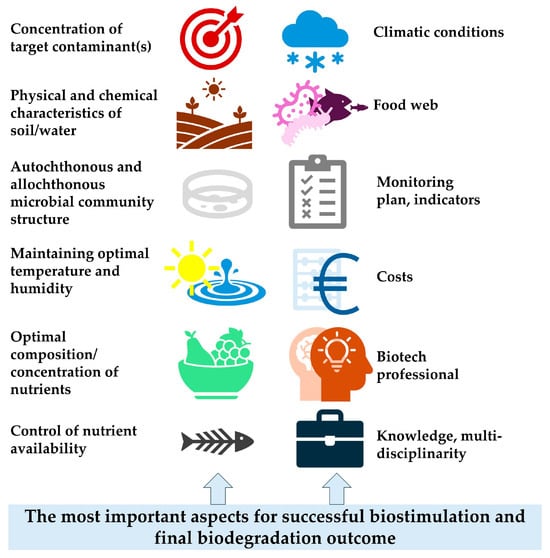
The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of the main trends and progress in the biostimulation approach, which represents a crucial component of the broader multi-factor bioremediation process. A comprehensive search was carried out in the Scopus database. The stimulating roles of individual and complex nutrient amendments are reviewed, with particular emphasis on plant extracts, molasses, and surfactants. Methodological approaches for optimising nutrient formulations and conditions to strengthen the biostimulation effect are analysed, taking into account microbial ecology and physiology. Aspects of interspecies microbial interactions, such as cross-feeding connections, are discussed. The roles of directed evolution, starvation, and statistical optimisation in enhancing microbial activity are also highlighted. Overall, substantial theoretical knowledge on this topic has been accumulated in the scientific literature. However, data from long-term field studies remain scarce. Looking forward, modern methodological approaches may bridge these knowledge gaps by enabling the prediction of microbial activity, interactions, and cross-feeding, supported by comprehensive monitoring. In particular, artificial intelligence tools for the statistical optimisation of biostimulation conditions are expected to significantly improve process performance. This review summarises recent scientific papers alongside findings from our own long-term studies.
2 December 2025