- Review
Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Mechanisms in Klebsiella pneumoniae: Understanding for Better Interventions
- Assefa Asnakew Abebe,
- Alemayehu Godana Birhanu and
- Tesfaye Sisay Tessema
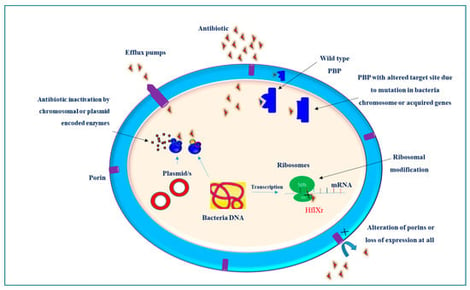
Klebsiella pneumoniae is a prominent pathogen implicated in a wide range of infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and septicemia. Its ability to acquire and disseminate antibiotic resistance, coupled with the rising prevalence of hypervirulent strains, represents a significant public health threat. Understanding the molecular basis of drug resistance can guide the design and development of effective treatment strategies. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in these bacteria is a complicated process and cannot be attributed to a single resistance mechanism. K. pneumoniae develops resistance to antibiotics through a variety of mechanisms, ranging from single molecular mechanisms to complex interactions, where molecular synergy exacerbates resistance. This review summarizes the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms that contribute to the drug resistance and virulence of this pathogen. Key antibiotic resistance mechanisms include drug inactivation via B-lactamases and carbapenemases, membrane remodeling, efflux pump systems, such as AcrAB-TolC and OqxAB, and biofilm formation facilitated by quorum sensing. Additionally, the role of ribosomal changes in resistance is highlighted. This review also examines the mechanisms of virulence, emphasizing fimbriae, iron acquisition systems, and immune evasion strategies. Understanding these mechanisms of drug resistance and virulence is crucial for remodeling existing antibiotics and developing new therapeutic strategies.
2 February 2026