Economic Feasibility and Risk Analysis of Nile Tilapia Juveniles Reared in a Biofloc Technology System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
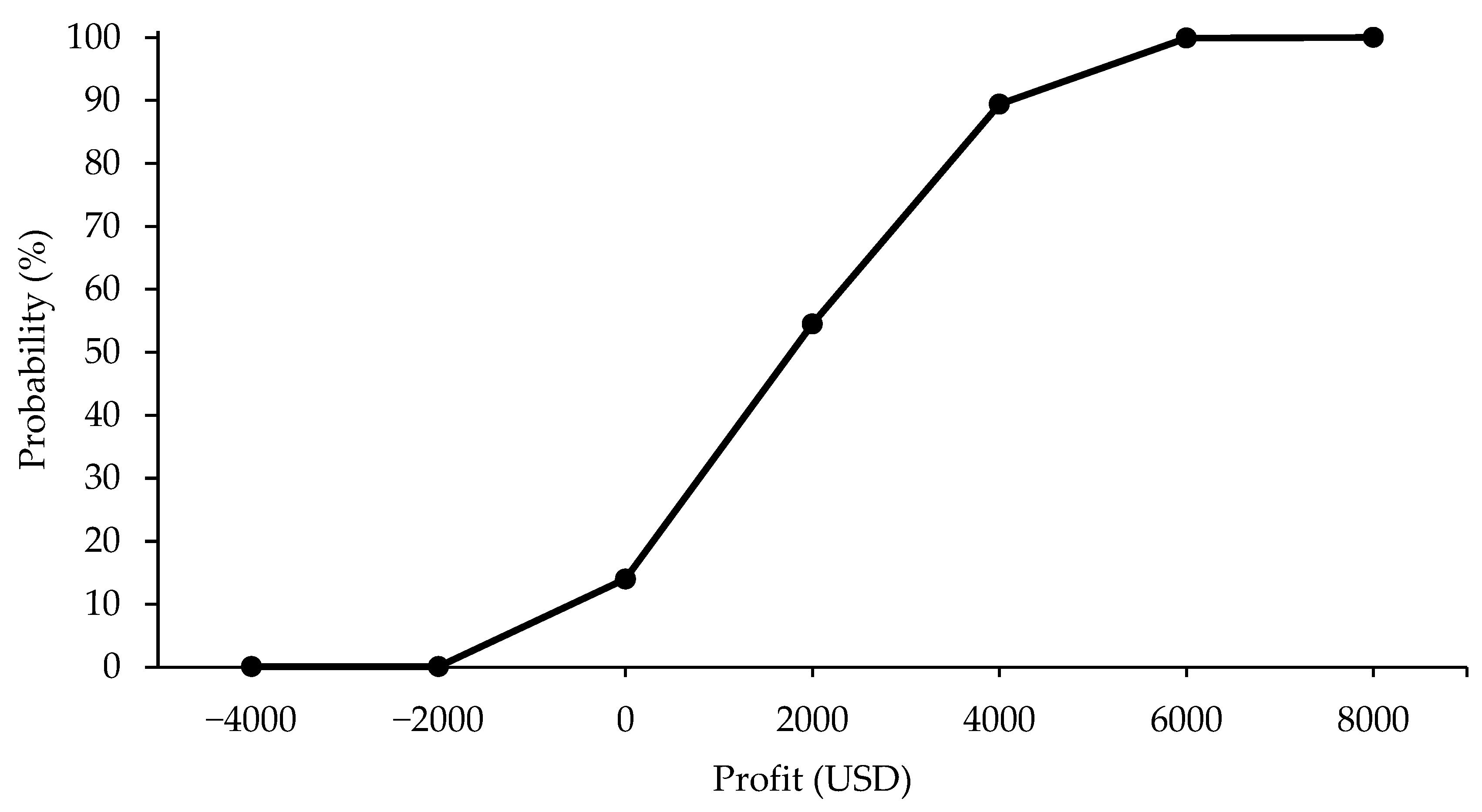
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO (Food and Agricultural Organization). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture—Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, A.F.M. Tilapia Culture; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, M.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Fountoulaki, E. Review on the use of insects in the diet of farmed fish: Past and future. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2015, 203, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixe, B.R. Anuário Brasileiro da Piscicultura; Peixe BR: São Paulo, Brazil, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, K.R.; Wasielesky, W., Jr.; Abreu, P.C. Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in the biofloc production of the pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2013, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y. Biofloc Technology—A Pratice Guide Book; The World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Biofloc production systems for aquaculture. SRAC 2013, 4503, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, P.C.M.; Abreu, J.L.; Silva, A.E.M.; Severi, W.; Galvez, A.O.; Brito, L.O. Nile tilapia fingerling cultivated in a low-salinity biofloc system at different stocking densities. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, e0612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Gao, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Sun, D.; Li, L.; Tan, H. Growth, digestive activity, welfare, and partial cost-effectiveness of genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) cultured in a recirculating aquaculture system and an indoor biofloc system. Aquaculture 2014, 422–423, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, H.; Barbosa, P.T.L.; Arruda, H.L.; Mattioli, C.C. Comparative study of growth, feed efficiency, and hematological profile of Nile tilapia fingerlings in biofloc technology and recirculating aquaculture system. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Alizadeh, M.; Sharifinia, M. Effects of different carbon sources on water quality, biofloc quality, and growth performance of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fingerlings in a heterotrophic culture system. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, H.; Pinheiro, V.R.; Losekann, M.E.; Moura e Silva, M.S.G. Effect of feeding frequency on water quality, growth, and hematological parameters of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus reared using biofloc technology. J. Appl. Aquac. 2020, 33, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.; Little, D.C. The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: Water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2008, 283, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, M.A.S.; Sabbag, O.J.; Soares, R.; Peixoto, S. Financial viability of inserting the biofloc technology in a marine shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei farm: A case study in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. Aquac. Int. 2016, 25, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woiler, S.; Mathias, W.F. Projetos: Planejamento, Elaboração e Análise; Atlas: São Paulo, Brazil, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Casarotto Filho, N.; Kopittke, B.H. Análise de Investimento; Atlas: São Paulo, Brazil, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ngoc, P.T.A.; Meuwissen, M.P.M.; Tru, L.C.; Bosma, R.H.; Verreth, J.; Lansink, A.O. Technical inefficiency of Vietnamese pangasius farming: A data envelopment analysis. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2018, 22, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, D.; Gouvea, A.C.F. Método de Monte Carlo aplicado a economicidade do cultivo de tilápia-do-Nilo em tanques-rede. Arch. Zootec. 2015, 64, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.M.; Timmons, M.B.; Bisogni, J.J. Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia–nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2006, 257, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, M.; Bemelmans, P.F.; Toledo, P.E.N.; Dulley, R.D.; Okawa, H.; Pedroso, I.A. Metodologia de custo de produção utilizada pelo IEA. Bol. Téc. Inst. Econ. Agríc. 1976, 23, 123–139. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, L.C.; Barreto, O.J.S.; Henriques, M.B. The economic viability for the production of live baits of White Shrimp (Litopenaeus schmitti) in recirculation culture system. Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, E.F.; Ehrhardt, M.C. Financial Management: Theory & Practice; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sontakke, R.; Haridas, H. Economic Viability of Biofloc Based System for the Nursery Rearing of Milkfish (Chanos chanos). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2960–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, F. Análise de Viabilidade Técnico-Econômica da Produção de Juvenis de Tilápia, Oreochromis niloticus, um Estudo de Caso. M.Sc. Thesis, Universidade Federal do Ceará, Fortaleza, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brande, M.R.; Santos, D.F.L.; Fialho, N.S.; Proença, D.C.; Ojeda, P.G.; Godói, F.C.M.; Roubach, R.; Bueno, G.W. Economic and financial risks of commercial tilapia cage culture in a neotropical reservoir. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, M.A.S.; Sabbag, O.J.; Soares, R.; Peixoto, S. Risk analysis of the insertion of biofloc technology in a marine shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei production in a farm in Pernambuco, Brazil: A case study. Aquaculture 2017, 469, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, B.O.; Hernández-Flores, A.; Adeogun, O.A.; Duarte, J.A.; Villanueva-Poot, R. Stochastic bioeconomic analysis of intensive African Catfish cultivation with three sources of uncertainty. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 2919–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, C.R. Aquaculture Economics and Financing: Management and Analyses; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hisano, H.; Parisi, J.; Cardoso, I.L.; Ferri, G.H.; Ferreira, P.M.F. Dietary protein reduction for Nile tilapia fingerlings reared in biofloc technology. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 51, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatobá, A.; Borges, Y.V.; Silva, F.A. BIOFLOC: Sustainable alternative for water use in fish culture. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. 2019, 71, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacout, D.M.M.; Soliman, N.F.; Yacout, M.M. Comparative life cycle assessment (LCA) of Tilapia in two production systems: Semi-intensive and intensive. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Items | Value (USD) | (%) | Life Cycle (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structures | |||
| Land (144 m2) | 425.00 | 4.41 | - |
| Greenhouse (12 × 12 m; 144 m2) | 2662.06 | 27.64 | 10 |
| Circular tank (80 m3) | 1373.83 | 14.26 | 5 |
| Equipment | |||
| Cleaning system a | 1198.88 | 12.45 | 10 |
| Power generator (6 kva three-phase) | 1444.67 | 15.00 | 10 |
| Submersible pump | 171.21 | 1.78 | 10 |
| Aeration system b | 735.14 | 7.63 | 10 |
| Digital oximeter | 333.44 | 3.46 | 5 |
| PPE c | 75.85 | 0.79 | 1 |
| Balance | 46.73 | 0.49 | 10 |
| Fishing tackle d | 204.45 | 2.13 | 2 |
| Documentation | |||
| Licensing e | 961.29 | 9.98 | - |
| Total | 9632.55 | 100.00 |
| Indicators | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Initial number of fish | fish | 60,000 |
| Starting average weight | g | 5 |
| Final average weight | g | 27 |
| Density | fish/m3 | 750 |
| Initial productivity | kg/m3 | 3.75 |
| Final productivity | kg/m3 | 16.18 |
| Survival | % | 80 |
| Average weight gain | g | 22 |
| Gain in biomass | kg | 994.38 |
| Feed consumption | kg | 1124 |
| Feed conversion rate | - | 1.13 |
| Unit | Quantity | Value (USD) | (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fingerlings | Fish | 60,000 | 2242.99 | 33.24 |
| Feed | kg | 1124 | 1512.67 | 22.42 |
| Energy | kWh | 1.49 | 100.63 | 1.49 |
| Agricultural lime | kg | 112.40 | 18.91 | 0.28 |
| Labor | Employee | 1 | 478.44 | 7.09 |
| Source of carbon (Sugar) | kg | 56.2 | 25.31 | 0.38 |
| Sea salt | kg | 240 | 50.22 | 0.74 |
| Water analysis | Kit | 1 | 50.45 | 0.75 |
| Technical assistance | Month | 2 | 299.07 | 4.43 |
| Interest (working capital) | 28.97 | 0.43 | ||
| EOC | 4807.67 | - | ||
| Depreciation | 190.90 | 2.83 | ||
| Pro labore | Month | 2 | 1702.54 | 25.23 |
| TOC | 6701.11 | - | ||
| Opportunity cost | 47.12 | 0.70 | ||
| TC | 6748.24 | 100.00 | ||
| Final production | kg | 241.94 | - | |
| Sale price | USD/kg | 6.58 | - | |
| Total revenue | USD/cycle | 8512.71 | - | |
| Gross margin (GM) | 3705.04 | - | ||
| Net margin (NM) | 1811.60 | - | ||
| Profit (P) | 1764.47 | - |
| Pessimistic | Realistic | Optimistic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD | |||
| Total Revenue (TR) | 5114.02 | 8590.44 | 12,785.05 |
| Effective Operating Cost (EOC) | 5106.71 | 4798.15 | 4056.54 |
| Total Operating Cost (TOC) | 7000.15 | 6691.59 | 5949.98 |
| Total Cost (TC) | 7047.27 | 6738.71 | 5997.10 |
| Gross Margin (GM) | 7.31 | 3792.29 | 8728.51 |
| Net Margin (NM) | −1886.13 | 1898.85 | 6835.07 |
| Profit (P) | −1933.25 | 1851.73 | 6787.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bezerra, G.A.; Pires, D.C.; Watanabe, A.L.; Buglione Neto, C.C.; Cardoso, A.J.d.S.; Simões, A.R.P.; Hisano, H. Economic Feasibility and Risk Analysis of Nile Tilapia Juveniles Reared in a Biofloc Technology System. Aquac. J. 2025, 5, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5020009
Bezerra GA, Pires DC, Watanabe AL, Buglione Neto CC, Cardoso AJdS, Simões ARP, Hisano H. Economic Feasibility and Risk Analysis of Nile Tilapia Juveniles Reared in a Biofloc Technology System. Aquaculture Journal. 2025; 5(2):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleBezerra, Gabriel Artur, Dara Cristina Pires, André Luiz Watanabe, Celso Carlos Buglione Neto, Alex Júnio da Silva Cardoso, Andre Rozemberg Peixoto Simões, and Hamilton Hisano. 2025. "Economic Feasibility and Risk Analysis of Nile Tilapia Juveniles Reared in a Biofloc Technology System" Aquaculture Journal 5, no. 2: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5020009
APA StyleBezerra, G. A., Pires, D. C., Watanabe, A. L., Buglione Neto, C. C., Cardoso, A. J. d. S., Simões, A. R. P., & Hisano, H. (2025). Economic Feasibility and Risk Analysis of Nile Tilapia Juveniles Reared in a Biofloc Technology System. Aquaculture Journal, 5(2), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5020009






