An Overview of Fish Disease Diagnosis and Treatment in Aquaculture in Bangladesh
Abstract
1. Introduction
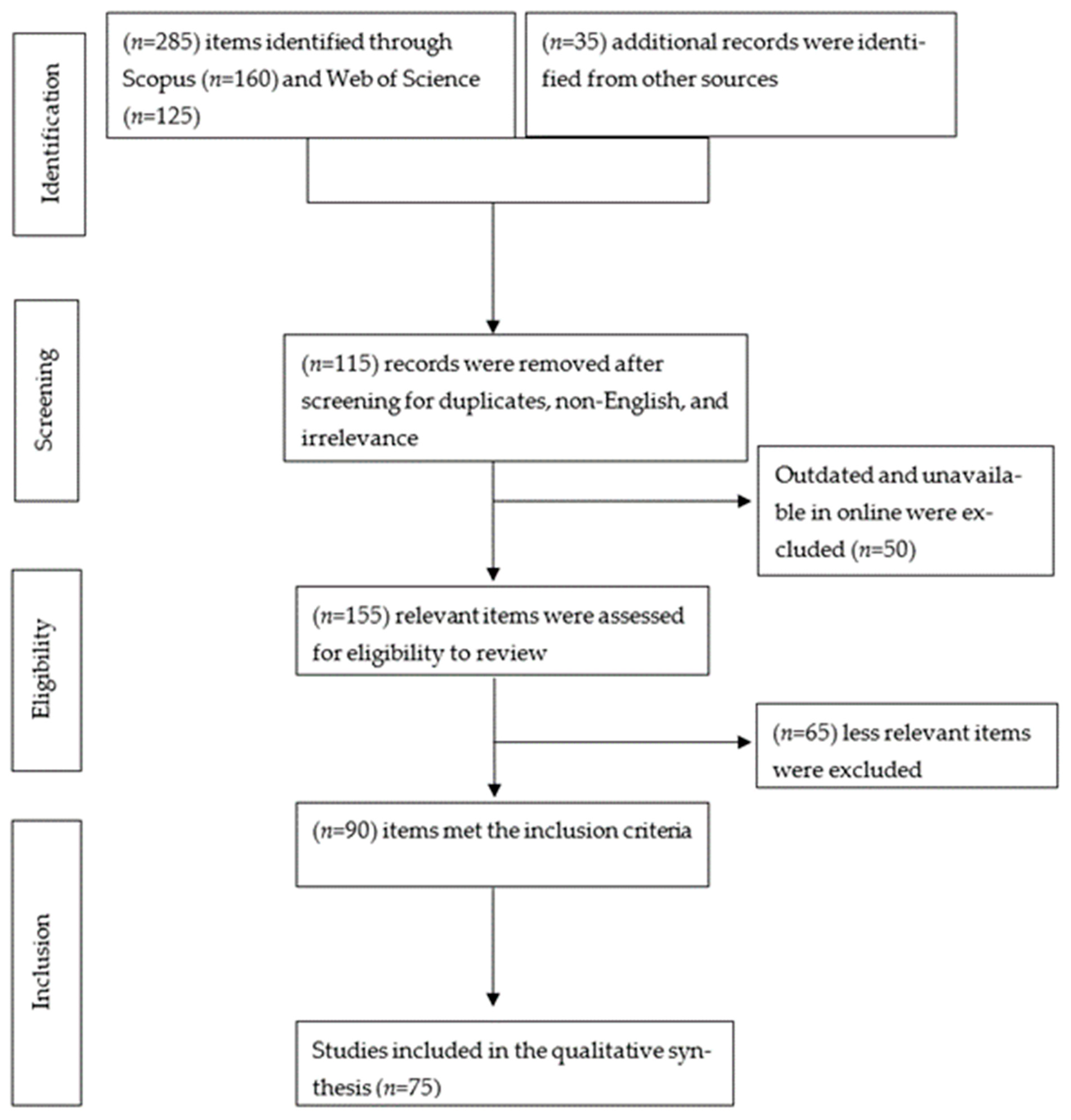
2. Methods
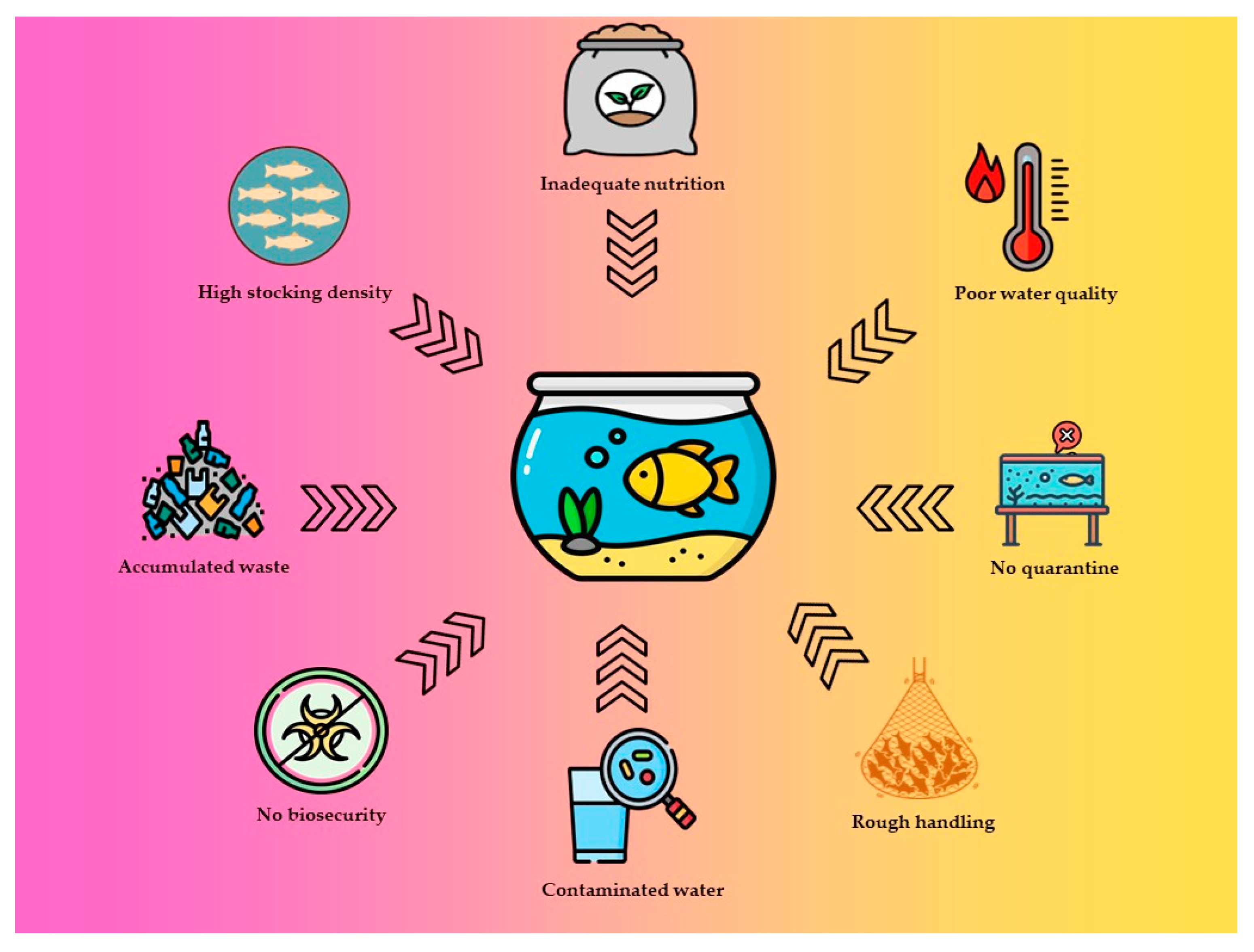
3. Common Fish and Shellfish Diseases in Bangladesh
| Categories | Name of Diseases | Etiological Agents | Signs and Symptoms * | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial diseases | Columnaris | Flavobacterium columnare | Ulcers and hemorrhagic patches are observed on the body, along with tail rot and red spots on the caudal peduncle. No visible lesions are found in the internal organs. The fish exhibits sluggish movement. | [33,63] |
| Edwardsiellosis | Edwardsiella tarda | Spiraling in circles, opercula flared (gill covers extended), visible skin lesions, pale gills, eye swelling, excessive mucus on the body surface, scale erosion, and ulcers in a few cases. | [29,64] | |
| Motile aeromonas septicemia (MAS) or Dropsy | Aeromonas hydrophila | Distended abdomen, straw-colored fluid in the body cavity, scale protrusion (dropsy-like appearance), exophthalmia, intestinal inflammation, swelling, and vacuolation of hepatocytes (liver cells). | [53,65,66] | |
| Fin rot | A. salmonicida | White patches and lesions along the fin edge, fraying and breakdown of soft tissue between fin rays, complete fin loss, and damage to the caudal fin. | [53,57,66,67] | |
| Vibriosis | Vibrio parahaemolyticus, V. anguillarum | Lethargic behavior, impaired balance, muscle necrosis, anorexia, irregular swimming, and hemorrhages on the body surface. Lesions and ulcers on the skin, and exophthalmia. | [68,69,70,71,72] | |
| Gill rot | Flavobacterium spp. or Aeromonas spp. | Discolored and necrotic gill tissues, often covered with excess mucus or foul-smelling patches. Infected fish display signs of respiratory distress, gasping at the surface, and reduced activity. | [57,66] | |
| Streptococcosis | Enterococcus spp. Streptococcus spp. | Unusual appearances were observed, characterized by multifocal pinpoint hemorrhages, abscesses, necrosis, and ascites affecting the skin, fins, muscles, liver, spleen, kidney, blood, and interstitial fluids, particularly involving the central nervous system and brain. | [40,73,74] | |
| Enteric Septicemia of Catfish | E. ichtaluri | Hemorrhages, swollen abdomen, pop-eye, and “hole-in-the-head” lesions. Affected fish show lethargy and erratic swimming, with high mortality in warm, crowded conditions. | [75,76] | |
| Bacterial Hemorrhagic Septicemia | Pseudomonas spp. | Affected fish show signs such as hemorrhagic patches on the skin and fins, body ulcers, fin and tail rot, and a swollen abdomen. In advanced cases, internal organs may show signs of congestion and necrosis, with affected fish becoming lethargic and losing appetite. | [77,78] | |
| Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease | V. parahaemolyticus | Primarily affects shrimp during the early culture period, typically within the first 30–35 days after stocking. Infected shrimp often show lethargy, anorexia, and gather near the edges of ponds. One of the most characteristic signs is a pale, shrunken, or atrophied hepatopancreas, accompanied by an empty gastrointestinal tract. In severe cases, shrimp may also exhibit soft shells, blackened gills, and high, sudden mortality. | [79] | |
| Fungal | EUS | Aphanomyces invadans | It is characterized by the appearance of red spots, hemorrhagic patches, and deep ulcers on the skin that can extend into the underlying muscle. Infected fish often exhibit lethargy, loss of appetite, and erratic swimming behavior. | [53,66] |
| Saprolegniasis | Saprolegnia paraisitca | Superficial fluffy colonies on skin and gills, hemorrhagic spots on the body, excess mucus secretion, discoloration, and damage to gill filaments. | [30,56] | |
| Branchiomycosis | Branchiomyces spp. Saprolegnia spp. | Grasping behavior, lethargy, anorexia, swollen opercula, frayed gill tissues, excessive mucus secretion, and damaged opercula. | [30,66] | |
| Achlya infection | Achlya spp. | Typically appears as white to grayish, cotton-like growths on the skin, fins, gills, or eyes. Affected fish may develop lesions, ulcers, or fin erosion around the infected areas. Behavioral symptoms include lethargy, loss of appetite, and rubbing against surfaces due to irritation. In hatcheries, Achlya can also infect fish eggs, leading to significant mortality. The disease often occurs under stress, injury, or poor water quality conditions. | [56,80] | |
| Viral | Tilapia lake virus disease (TiLVD) | Tilapia lake virus | Eye opacification, skin lesions and discoloration, lesions on the operculum, endophthalmia, and exophthalmia (bulging eyes). | [81,82] |
| Viral nervous necrosis diseases (VNND) | Viral nervous necrosis | Neural cell necrosis in the retina, necrosis in the brain, and the spinal cord. Affected fish also become lethargic, lose appetite, and may display darkened body coloration or exophthalmia. | [83] | |
| White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) disease | White spot syndrome virus | Rapid appearance of white spots or patches on the exoskeleton, especially on the carapace and appendages. Infected shrimp show lethargy, reduced feeding, reddish discoloration, and often high mortality. | [76,84,85] | |
| Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) disease | Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus | Growth retardation, bent or deformed rostrum, and cuticular abnormalities in shrimp, particularly P. monodon and P. vannamei. Affected juveniles exhibit reddish body coloration, poor molting, and slow movement. | [86] | |
| Monodon Baculovirus (MBV) disease | Monodon baculovirus | Primarily affects the hepatopancreas of shrimp, particularly the P. monodon species. Infected shrimp often exhibit reduced growth, lethargy, and pale or soft shells. One of the key visible signs is the presence of white or milky fecal strings. Internally, histological examination reveals large eosinophilic occlusion bodies within the nuclei of hepatopancreatic tubule cells. | [86] | |
| Hepatopancreatic parvovirus (HPV) disease | Hepatopancreatic parvovirus | HPV disease in shrimp primarily affects the hepatopancreas and midgut epithelium of post-larvae and juveniles. Infected shrimp often show growth retardation, reduced feed intake, and pale or atrophied hepatopancreas. In severe cases, the disease can lead to high mortality, especially when co-infected with other pathogens. | [86] | |
| Yellow head virus (YHV) disease | Yellow head virus | Infected shrimp often show a pale or yellowish cephalothorax due to the yellowing of the hepatopancreas and gills. Other symptoms include reduced feed intake, soft shell, discolored gills, and lethargic swimming near the surface or pond edges. The disease typically spreads rapidly and can result in 100% mortality within a few days in affected ponds. | [87] | |
| Parasitic diseases | Ichthyophthiriasis (Ich) disease | Ichthyophthirius multifiliis | Invades the epithelial tissue of gills, skin, or fins, causes small wounds, and forms visible white spots or nodules where the parasite encysts. | [28,40,88] |
| Trichodiniasis | Trichodina spp. | Commonly infest the skin, fins, and gills. Infected fish often exhibit excessive mucus production, frayed fins, and frequent rubbing or flashing against tank or pond surfaces due to irritation. Affected fish may also show signs of respiratory distress, such as gasping at the surface, along with lethargy and reduced appetite. In severe cases, the weakened condition of the fish can lead to secondary bacterial or fungal infections. | [28,89] | |
| Argulosis | Argulus spp. | Fish infected with Argulus parasites typically exhibit restlessness, flashing behavior (rubbing against objects), and frequent jumping due to skin irritation. Visible round, flat parasites may be seen attached to the skin, fins, or around the eyes. Affected areas often show redness, hemorrhages, or ulcers, leading to secondary infections. Infected fish may also show reduced feeding, lethargy, and, in severe cases, mortality, especially in young or stressed fish. | [28,58,90] | |
| Ichthyobodosis | Ichthyobodo necatrix | Excess mucus forms a blue-gray or white film on the body and gills, lethargy and listlessness, loss of appetite, and increased mortality. | [28,88,91] | |
| Fluke | Dactylogyrus spp., Gyrodactylus spp. | Fish infected with flukes often show increased mucus production, especially on the gills or skin, leading to a cloudy or slimy appearance. Common symptoms include flashing or rubbing against objects, frayed fins, and respiratory distress, such as gasping at the water surface when gills are affected. Infected fish may also display lethargy, poor growth, and loss of appetite. Heavy infestations can cause tissue damage, secondary infections, and even mortality, particularly in fingerlings or under stressful conditions | [28,92,93] | |
| Fish leech | Piscicola geometra | Fish infested with leeches often display restlessness, erratic swimming, and frequent rubbing or flashing against surfaces. Visible leeches may be found attached to the skin, fins, or gills, often surrounded by red, inflamed, or ulcerated areas. Infected fish may show anemia, lethargy, and reduced feeding due to blood loss. | [28,94] |
4. Advances in Disease Diagnosis in Bangladesh
4.1. Immunodiagnostic Techniques
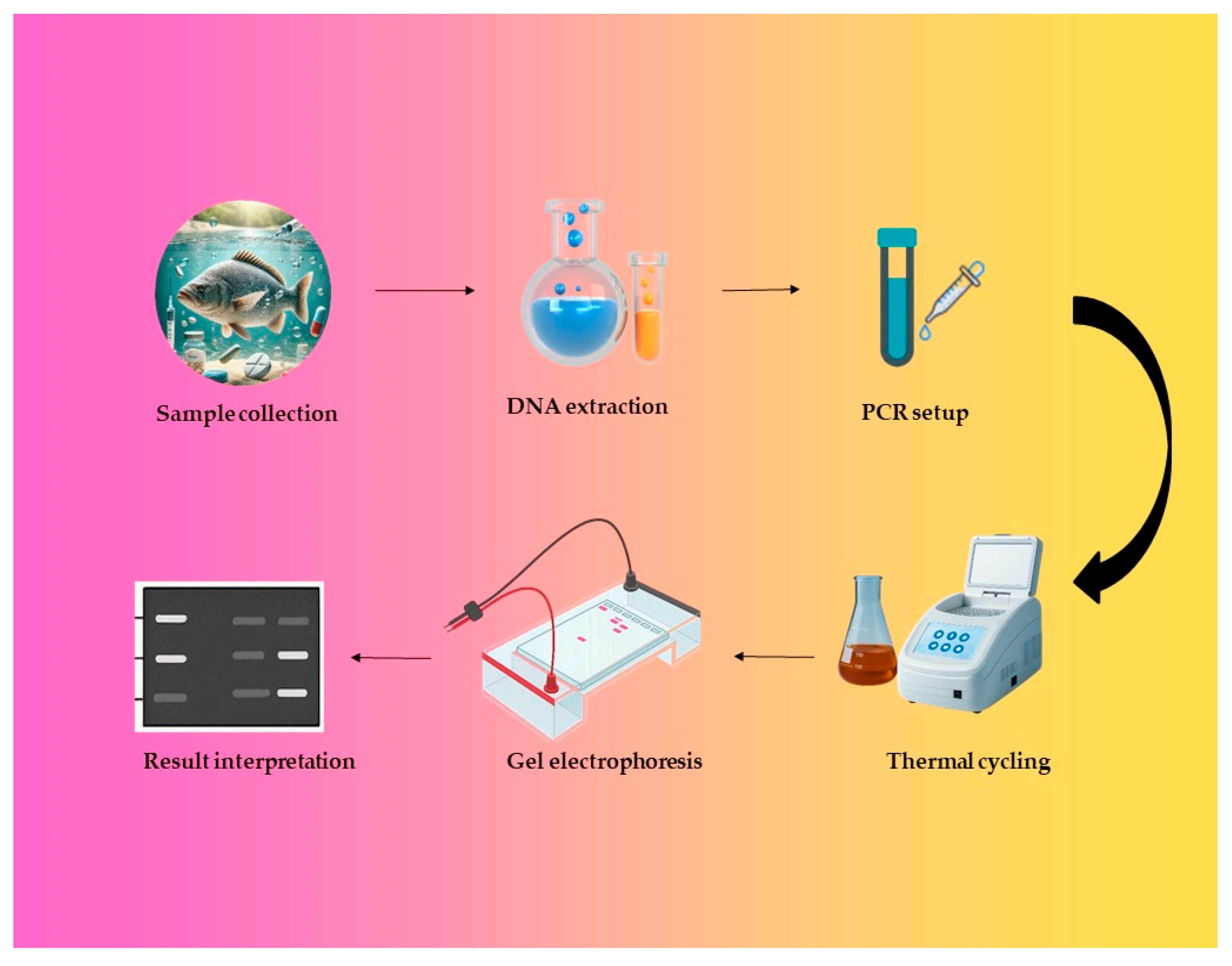
4.2. Molecular Diagnostics and PCR-Based Tools
4.3. Machine Learning (ML) Approaches
4.4. Nanoparticles (NPs) in the Diagnosis of Fish Pathogens
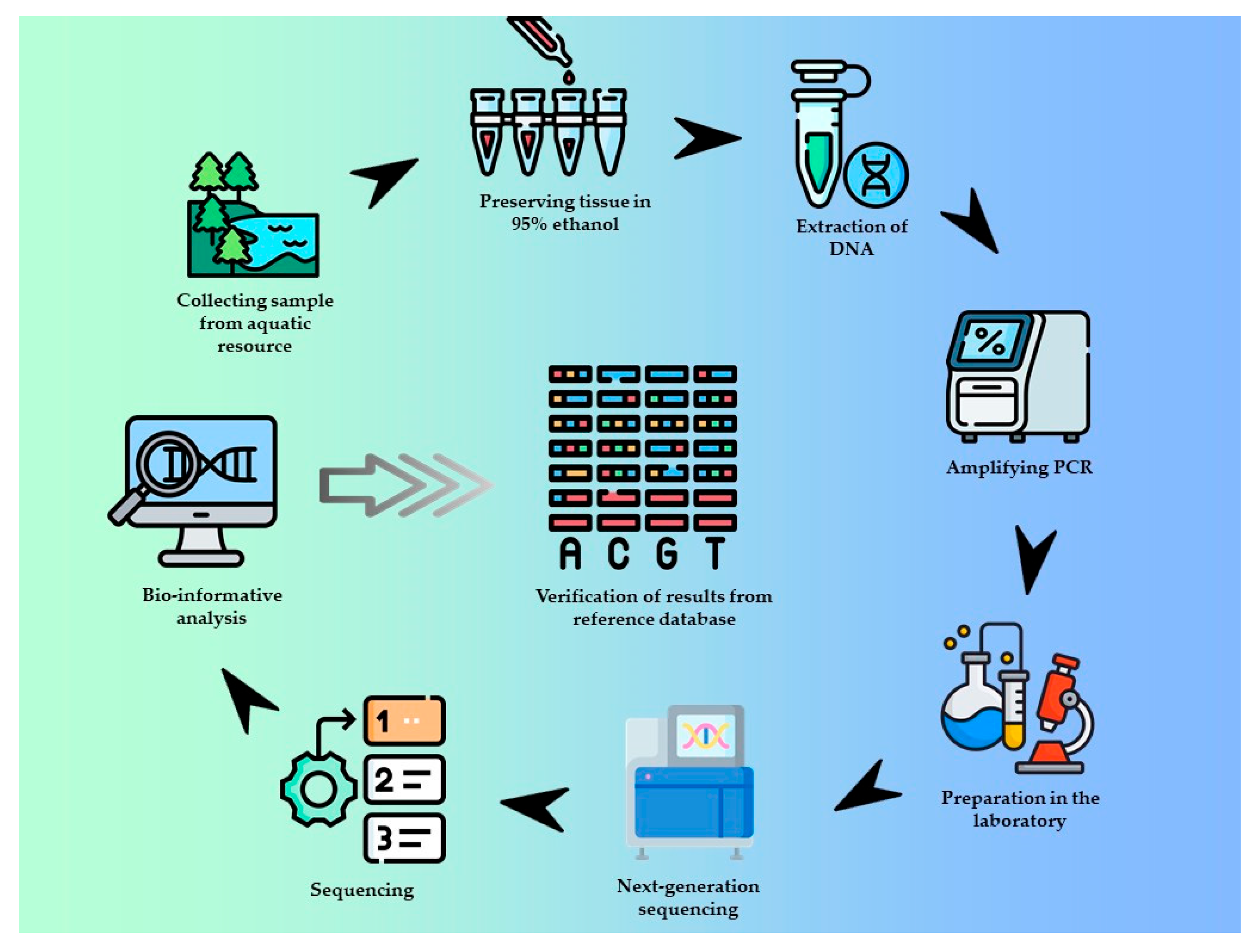
4.5. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
5. Treatments and Disease Management Strategies
| Management Practice | Type | Ingredient | Effectiveness | Purpose of Use | Degree of Implementation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use of probiotics | Growth promoter | Bacillus sp., Lactobacillus sp., Rhodopseudomonas sp., Rhodobacter sp., Rhodococcuss sp., Nitrobacter sp. | Moderate to High | Primarily, enhance fish immunity and improve gut health, leading to better growth performance and disease resistance. They also help maintain water quality by reducing pathogenic microbial loads in the culture environment. | Moderate, increasing in commercial farms, limited adoption in small-scale farms | [149,167,168] |
| Use of antibiotics | Therapeutic and prophylactic | Tetracycline, oxytetracycline, erythromycin, azithromycin, sulphadiazine, trimethoprim, florfenicol, sulphamethoxazole, amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, levofloxacin, and neomycin. | High | Primarily used in aquaculture to treat and control bacterial infections in fish and shellfish. | High, widespread during disease outbreaks, often without veterinary guidance | [41,148,153,169] |
| Vaccination | Preventive | Bacterial strains, especially Enterococcus faecalis, E. hirae, E. faecium, A. hydrophila, A. veronii | High | Used to prevent infectious diseases, boost fish immunity, and reduce reliance on antibiotics. It enhances survival rates and promotes sustainable fish health management, especially in intensive farming systems. | Low, mostly pilot projects and research trials, are rare in commercial farms | [157,158,170,171] |
| Liming | Preventive | Calcium carbonate (CaCO3), Calcium oxide (CaO), Calcium hydroxide (CaOH), Calcium magnesium carbonate (CaMg (CO3)2) | Moderate | Regulate water and soil pH, neutralize pond acidity, and enhance the availability of essential nutrients. It improves soil quality, promotes plankton growth, and creates a favorable environment for fish health and development by reducing the toxicity of harmful compounds, such as ammonia and hydrogen sulfide. | High, common practice in pond preparation and water pH regulation | [41,156,172,173] |
| Water quality monitoring | Preventive | N/A | Moderate to High | Prevents poor water conditions that lead to disease or mortality. Ensures optimal environment for fish health and growth and supports early detection of stress indicators (e.g., low DO, high ammonia). | Low to Moderate, regular in commercial or large farms, rare in smallholders | [65,174,175] |
| Biosecurity protocols | Preventive | N/A | Very High | Biosecurity protocols in aquaculture help reduce disease burden, improve farm and national fish health, and limit global disease spread. They also enhance socio-economic benefits and attract investment by ensuring safer, more sustainable aquaculture practices. | Low, practiced mainly in hatcheries, not in most grow-out farms | [24,49,164,165,166] |
| Use of immunostimulants | Health management | Glucans and polysaccharides, vitamins, minerals, vitamin-mineral premixes, enzymes, nucleic acids, and plant extracts. hemicellulose, mineral, amylase, amino acid, pectinase, lipase | High | To enhance immune competence and disease resistance in fish and shellfish, and related supplements help maintain overall health by reducing pathogen susceptibility and stress. They support growth, wound healing, stress response, and may influence lipid metabolism, collagen synthesis, and key cellular functions linked to neuromodulation, hormones, and the immune system | Moderate, growing interest but limited awareness among small farmers | [38,176] |
| Application of disinfectants | Preventive | Polgard Plus, Timsen, Virex, Biogaurd, Lenocide, Emsen, Aqua Cleaner Plus, Formalin and bleaching powder, Benzalkonium chloride (BKC), Pathonil, Micronil, Virocid, Potassium permanganate, Hydrogen peroxide, Sodium percarbonate, and chlorine. | High | Helps to eliminate pathogens and pollution, disinfect water and sediments between production cycles, and improve water quality by increasing dissolved oxygen and reducing ammonia and hardness. Additionally, they prevent bacterial, fungal, and viral infections while also maintaining hygienic conditions in ponds and equipment. | High, common during pond preparation and disease outbreaks | [38,41,153,169,177,178,179,180] |
| Use of pesticides | Pest removal | Ivermectin, Cypermethrin, L-ascorbic polyphosphate, Quinalphos, Deltamethrin, NaCl, Ethion, Trichlorfon 40%, CaCO3, Ca (OH)2, CaO, Active malathion, KMnO4, Oxalic Acid, Beta-glucan, Fenitrothion, Dextrose anhydrous USP 98% and ascorbic acid BP 2% | High | Primarily used to control ectoparasites like copepods and manage infestations such as Argulus. They are also effective in killing harmful aquatic insects, including backswimmers, dragonfly nymphs, and water scavenger beetles. Additionally, they help reduce fish stress, enhance disease resistance, and eliminate pathogens from cultured fish environments. | Moderate, applied selectively in farms, though regulated and discouraged | [153,181] |
6. Institutional and Policy Support
7. Challenges and Future Prospects
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miladinov, G. Impacts of Population Growth and Economic Development on Food Security in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries. Front. Hum. Dyn. 2023, 5, 1121662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfiko, Y.; Xie, D.; Astuti, R.T.; Wong, J.; Wang, L. Insects as a Feed Ingredient for Fish Culture: Status and Trends. Aquac. Fish. 2022, 7, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, N. A Review on Replacing Fish Meal in Aqua Feeds Using Plant Protein Sources N Daniel. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 164–179. [Google Scholar]
- Stankus, A. State of World Aquaculture 2020 and Regional Reviews: FAO Webinar Series; FAO Aquaculture Newsletter: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 978-92-5-138763-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, H. The World Now Produces More Seafood from Fish Farms than Wild Catch. Our World in Data 2019. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/rise-of-aquaculture (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- United Nations World Population Prospects. United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. 2019. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423). Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/assets/Files/WPP2019_Highlights.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Waite, R.; Beveridge, M.; Brummett, R.; Castine, S.; Chaiyawannakarn, N.; Kaushik, S.; Mungkung, R.; Nawapakpilai, S.; Phillips, M. Improving Productivity and Environmental Performance of Aquaculture: Creating a Sustainable Food Future, Installment Five; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- DoF. Yearbook of Fisheries Statistics of Bangladesh, 2022–2023. Fisheries Resources Survey System (FRSS); Department of Fisheries: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2023.
- Assefa, A.; Abunna, F. Maintenance of Fish Health in Aquaculture: Review of Epidemiological Approaches for Prevention and Control of Infectious Disease of Fish. Vet. Med. Int. 2018, 2018, 5432497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, S.C.; McMurtrie, J.; Temperton, B.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Mohan, C.V.; Tyler, C.R. Tilapia Aquaculture, Emerging Diseases, and the Roles of the Skin Microbiomes in Health and Disease. Aquac. Int. 2023, 31, 2945–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinn, A.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bron, J.; Paladini, G.; Brooker, E.E.; Brooker, A. Economic Impacts of Aquatic Parasites on Global Finfish Production. Glob. Aquac. Advocate 2015, 82–84. Available online: https://www.globalseafood.org/advocate/economic-impacts-of-aquatic-parasites-on-global-finfish-production/?headlessPrint (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Mohd-Aris, A.; Muhamad-Sofie, M.H.N.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Daud, H.M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y. Live Vaccines against Bacterial Fish Diseases: A Review. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshath, A.A.; Rajan, A.P.; Vimal, S.; Prabhakaran, V.-S.; Ganesan, R. Bacterial Pathogenesis in Various Fish Diseases: Recent Advances and Specific Challenges in Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2023, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalaikumar, E.; Lelin, C.; Sathishkumar, R.; Vimal, S.; Anand, S.B.; Babu, M.M.; Citarasu, T. Oral Delivery of PVAX-OMP and PVAX-Hly DNA Vaccine Using Chitosan-Tripolyphosphate (Cs-TPP) Nanoparticles in Rohu, (Labeo rohita) for Protection against Aeromonas hydrophila Infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 115, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buján, N.; Toranzo, A.; Magariños, B. Edwardsiella piscicida: A Significant Bacterial Pathogen of Cultured Fish. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2018, 131, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.S.; Rakesh, D.; Dhiman, M.; Choudhary, P.; Debbarma, J.; Sahoo, S.N.; Mishra, C.K. Present Status of Fish Disease Management in Freshwater Aquaculture in India: State-of-the-Art-Review. J. Aquac. Fish. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Mohanty, J.; Garnayak, S.K.; Mohanty, B.R.; Kar, B.; Prasanth, H.; Jena, J.K. Estimation of Loss Due to Argulosis in Carp Culture Ponds in India. Indian J. Fish. 2013, 60, 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Aich, N.; Paul, A.; Choudhury, T.G.; Saha, H. Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) Disease: Current Status of Understanding. Aquac. Fish. 2022, 7, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrick, R.; Batts, W.; Yun, S.; Traxler, G.; Kaufman, J.; Winton, J. Host and Geographic Range Extensions of the North American Strain of Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2003, 55, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurath, G.; Garver, K.A.; Troyer, R.M.; Emmenegger, E.J.; Einer-Jensen, K.; Anderson, E.D. Phylogeography of Infectious Haematopoietic Necrosis Virus in North America. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakaran, R.; Syed Musthaq, S.; Haribabu, P.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Gopal, C.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Experimental Transmission of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and Extra Small Virus (XSV) in Three Species of Marine Shrimp (Penaeus indicus, Penaeus japonicus and Penaeus monodon). Aquaculture 2006, 257, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapin, S.; Thaowbut, Y.; Gangnonngiw, W.; Chuchird, N.; Sriurairatana, S.; Flegel, T.W. Impact of Yellow Head Virus Outbreaks in the Whiteleg Shrimp, Penaeus Vannamei (Boone), in Thailand. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Rahman, T.; Rahmatullah, S.M.; Sarker, J.; Khanum, R.; Salim Mahadi, M. AL Biosecurity Status in Some Commercial Aquafarms of Kishoreganj and Mymensingh Districts. Bangladesh J. Fish. 2019, 31, 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Hatai, K. Diseases of Fish and Shellfish Caused by Marine Fungi; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 15–52. [Google Scholar]
- Muraosa, Y.; Lawhavinit, O.; Hatai, K. Lagenidium Thermophilum Isolated from Eggs and Larvae of Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus Monodon in Thailand. Fish Pathol. 2006, 41, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, G.; Mushtaq, S.; Singh, L.S.; Kumar Ganpatbhai, A.V. Fungal Diseases in Aquaculture: A Review. Pharma Innov. 2023, 12, 1959–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Faruk, M.A.R. Infectious Diseases Associated with Fish Parasite, 1st ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francic Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.M.; Sultana Chowdhury, F.; Ashrafuzzaman, M.; Al Nayem Chowdhury, M.; Rezwan Ul Haque, M.; Zinnah, K.; Mahbubur Rahman, M. Identification, Pathogenecity, Antibiotic and Herbal Sensitivity of Edwardsiella Tarda Causing Fish Disease in Bangladesh. Curr. Res. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 292–297. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, M.; Bashar, M.; Hussain, M.; Kibria, A. Fungal Disease of Freshwater Fishes in Natore District of Bangladesh. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2009, 7, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.R.; Rana, K.S.; Rahman, M.H.; Al-Amin; Jaman, A.; Mukti, S.S.; Siddiquee, M.M. Assessment of Aqua Farms in Mymensingh District: Perspective of Health Management and Probiotics Use. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2022, 10, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadia, Z.M.; Roy, P.; Rahman, T. Culture Practices and Health Management Issues in Selected Aquafarms of Rajbari, Bangladesh: A Preliminary Study. J. Agric. Food Environ. 2021, 2, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, M.A.R.; Alam, M.J.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Kabir, M.B. Status of Fish Disease and Health Management Practices in Rural Freshwater Aquaculture of Bangladesh. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 7, 2092–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Rahman, M.; Monir, M.; Haque, M.; Siddique, M.; Khasruzzaman, A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M. Isolation and Molecular Detection of Streptococcus Agalactiae from Popped Eye Disease of Cultured Tilapia and Vietnamese Koi Fishes in Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2021, 8, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reza, M.S.; Razu, A.; Haque, S.; Khan, M.; Kamal, M. Sources of Off-Flavor in High Nutrient-Load Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Ponds in North-Central Bangladesh. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2023, 12, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndashe, K.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Changula, K.; Yabe, J.; Samutela, M.T.; Songe, M.M.; Kefi, A.S.; Njobvu Chilufya, L.; Sukkel, M. An Assessment of the Risk Factors Associated with Disease Outbreaks across Tilapia Farms in Central and Southern Zambia. Fishes 2023, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.A.; Hossain, A.; Hamli, H.; Islam, S.; Kabir, S.L. Research Trends of Aqua Medicines, Drugs and Chemicals (AMDC) in Bangladesh: The Last Decade’s (2011–2020) Story to Tell. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 7, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, M.; Begum, M.; Anka, I. Use of Immunostimulants for Fish Health Management in Mymensingh District Of Bangladesh. SAARC J. Agric. 2021, 19, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammas, I.; Bitchava, K.; Gelasakis, A.I. Transforming Aquaculture through Vaccination: A Review on Recent Developments and Milestones. Vaccines 2024, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasul, M.N.; Hossain, M.T.; Sifat-un-nuri; Haider, M.N.; Hossain, M.T.; Reza, M.S. Disease Prevalence, Usage of Aquaculture Medicinal Products and Their Sustainable Alternatives in Freshwater Aquaculture of North-Central Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawsar, M.A.; Alam, M.T.; Pandit, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Mia, M.; Talukdar, A.; Sumon, T.A. Status of Disease Prevalence, Drugs and Antibiotics Usage in Pond-Based Aquaculture at Narsingdi District, Bangladesh: A Major Public Health Concern and Strategic Appraisal for Mitigation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangtip, S.; Sirikharin, R.; Sanguanrut, P.; Thitamadee, S.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Mavichak, R.; Proespraiwong, P.; Flegel, T.W. AP4 Method for Two-Tube Nested PCR Detection of AHPND Isolates of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Rep. 2015, 2, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougin, J.; Roquigny, R.; Travers, M.-A.; Grard, T.; Bonnin-Jusserand, M.; Le Bris, C. Development of a MreB-Targeted Real-Time PCR Method for the Quantitative Detection of Vibrio Harveyi in Seawater and Biofilm from Aquaculture Systems. Aquaculture 2020, 525, 735337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Hao, Y. Advanced Techniques for the Intelligent Diagnosis of Fish Diseases: A Review. Animals 2022, 12, 2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Monticelli, L.S.; Caruso, R.; Bergamasco, A. Development of a Fluorescent Antibody Method for the Detection of Enterococcus Faecium and Its Potential for Coastal Aquatic Environment Monitoring. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tserevelakis, G.J.; Pavlidis, M.; Samaras, A.; Barmparis, G.D.; Mavrakis, K.G.; Draganidis, I.; Oikonomou, A.; Fanouraki, E.; Tsironis, G.P.; Zacharakis, G. Hybrid Confocal Fluorescence and Photoacoustic Microscopy for the Label-Free Investigation of Melanin Accumulation in Fish Scales. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johny, T.K.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Sood, N.; Pradhan, P.K.; Lal, K.K. A Panoptic Review of Techniques for Finfish Disease Diagnosis: The Status Quo and Future Perspectives. J. Microbiol. Methods 2022, 196, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Huys, G.; Kühn, I.; Rahman, M.; Möllby, R. Prevalence and Transmission of Antimicrobial Resistance among Aeromonas Populations from a Duckweed Aquaculture Based Hospital Sewage Water Recycling System in Bangladesh. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2009, 96, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faruk, A.R.; Arjun, K.; Ali, N.; Shakil Rana, K. Status of Biosecurity in Commercial Aqua Farms in Mymensingh and Jashore Districts. Bangladesh J. Fish. 2019, 31, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ndebele-Murisa, M.; Mubaya, C.P.; Dekesa, C.H.; Samundengo, A.; Kapute, F.; Yossa, R. Sustainability of Aqua Feeds in Africa: A Narrative Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambelli, D.; Vairo, D.; Solfanelli, F.; Zanoli, R. Economic Performance of Organic Aquaculture: A Systematic Review. Mar. Policy 2019, 108, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Mahmud, M.N. Potential Role of Aquaculture in Advancing Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Bangladesh. Aquac. Res. 2025, 2025, 6035730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.; Khalil, S.; Sumon, T.A. Prevalence of fish diseases in different aquaculture farms in the north-eastern region of Bangladesh. J. Sylhet Agril. Univ. 2018, 5, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Oidtmann, B.; Peeler, E.; Lyngstad, T.; Brun, E.; Bang Jensen, B.; Stärk, K.D.C. Risk-Based Methods for Fish and Terrestrial Animal Disease Surveillance. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 112, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hamed, S.; Tavares Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.; Tachibana, L.; de Carla Dias, D.; Ishikawa, C.M.; Esteban, M.A. Fish Pathogen Bacteria: Adhesion, Parameters Influencing Virulence and Interaction with Host Cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahura, U.; Chaudhary, M.B.R.; Faruk, M.A.R. Fungal Infection in Freshwater Fishes of Mymensingh Bangladesh. Indian J. Fish. 2004, 51, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bagum, N.; Monir, M.; Khan, M. Present status of fish diseases and economic losses due to incidence of disease in rural freshwater aquaculture of bangladesh. J. Innov. Dev. Strategy 2013, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Aftabuddin, S.; Islam, M.N.; Bhuyain, M.A.B.; Mannan, M.A.; Alam, M.M. Fish Diseases and Strategies Taken by the Farmers in Freshwater Aquaculture at Southwestern Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Zool. 2016, 44, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.I.m.; Mazumder, T.; Kumar, R.; Salehin, A.N.; Debnath, S.; Ghosh, R.K.; Mandal, S.C. Aquaculture Status in Southern Bangladesh With Special Emphasis on Disease Induced Loss. Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 31, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder Shefat, S.H. Nutritional Fish Disease and Public Health Concern. Poult. Fish. Wildl. Sci. 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Faruk, M.; Anka, I.; Azad, M. Investigation on Fish Health and Diseases in Rural Pond Aquaculture in Three Districts of Bangladesh. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2013, 11, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifat, M.A.; Wahab, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Nahiduzzaman, M.; Mamun, A.-A. Nutritional Value of the Marine Fish in Bangladesh and Their Potential to Address Malnutrition: A Review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, B.; Sarker, M.G.A.; Khan, M.H.; Chowdhury, M.B.R. Incidence of Ulcer Type of Disease in Wild Fishes of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Fish. Res. 2001, 5, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Rashid, M.M. Isolation and Identification of Edwardsiella Tarda from Catla (Catla catla), Koi (Anabas testudineus) and Tilapia (Tilapia mosumbicus). J. Agrofor. Environ. 2024, 17, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Rashid, M.M.; Waheduzzaman, M.; Alam, M.S. Isolation and Identification of Aeromonas hydrophila from Carps, Catfishes, Perches, and an Eel from Mymensingh Region of Bangladesh. J. Agrofor. Environ. 2024, 17, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, B.K.; Hossain, M.M.M.; Bappa, S.B.; Akter, S.; Khondoker, S. Impact of Diseases on Fish Production of Baors in Jessore, Bangladesh. J. Fish. 2014, 2, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ferdowsy, H.; Kashem, M.A.; Foysal, M.J. Tail and Fin Rot Disease of Indian Major Carp and Climbing Perch in Bangladesh. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 10, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siddique, A.B.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ali, S.; Dewan, M.N.; Islam, M.R.; Islam, M.S.; Amin, M.B.; Mondal, D.; Parvez, A.K.; Mahmud, Z.H. Characterization of Pathogenic Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Isolated From Fish Aquaculture of the Southwest Coastal Area of Bangladesh. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 635539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Hossain, M.; Azad, A.B.; Siddique, A.B.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Amin, M.B.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Mondal, D.; et al. Diversity of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus in Marine Fishes of Bangladesh. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2539–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefat, S.H.T. Vibrio Anguillarum, the Causative Agent of Vibriosis. ACTA Sci. Microbiol. 2019, 2, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Monir, M.S.; Borty, S.C.; Bagum, N.; Rahman, M.K.; Islam, M.A.; Mahmud, Y. Identification of Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from Diseased Stinging Catfish, Shing (Heteropneustes fossilis) Cultured in Greater Mymensingh, Bangladesh. Asian-Australas. J. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Hossain, A.; Mandal, S.C.; Rahman, M.S.; Mahmud, Z.H. Prevalence, Characterization and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Isolated from Fishes and Shellfishes of Coastal Regions of Bangladesh. Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 24, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Akter, T.; Foysal, M.J.; Alam, M.; Ehsan, R.; Paul, S.I.; Momtaz, F.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Fotedar, R.; Gupta, S.K.; et al. Involvement of Enterococcus Species in Streptococcosis of Nile Tilapia in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.M.; Ehsan, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Haq, M.; Chowdhury, M.B.R. Transmission and Pathology of Streptococcus Inane in Monosex Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Aquaculture of Bangladesh. J. Fish. 2014, 2, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosharraf Hossain, M.M.; Saha, T.K.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Ansari, M.J.; Farid, M.A.; Farjana, N.; Afroz, R.; Moon, R.S.; Tanni, L.N.; et al. Molecular Identification, Genetic Diversity, and Antibiotic Resistance of Pathogenic Bacteria in Finfish Aquaculture Systems of Southwestern Bangladesh. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 207, 107910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S. Policy Framing for Control of Transboundary Aquatic Animal Diseases, 1st ed.; Giri, S.S., Ed.; SAARC Agriculture Centre, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khatun, H.; Hossain, M.; Jahan, S.; Khanom, D. Bacterial Infestation in Different Fish at Rajshahi. J. Sci. Found. 2011, 9, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goni, O.; Mahbub Alam, M.; Mohammed Ibrahim Khalil, S.; Mashequl Bari, S.; Md Ibrahim Khalil, S.; Hamom, A.; Parven, M.; Abdullah-Al-Mamun, M. Identification of Pathogenic Bacteria from Diseased Stringing Catfish Heteropneustis Fossilis with Their Sensitivity to Antibiotics. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2020, 8, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Eshik, M.M.E.; Punom, N.J.; Begum, M.K.; Khan, T.; Saha, M.L.; Rahman, M.S. Molecular Characterization of Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease Causing Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Strains in Cultured Shrimp Penaeus Monodon in South-west Farming Region of Bangladesh. Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 27, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.B.R.; Muniruzzaman, M.; Zahura, U.A.; Habib, K.Z.A.; Khatun, M.D. Ulcer Type of Disease in the Fishes of Small-Scale Farmer’s Pond in Bangladesh. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 6, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chaput, D.L.; Bass, D.; Alam, M.M.; Al Hasan, N.; Stentiford, G.D.; van Aerle, R.; Moore, K.; Bignell, J.P.; Haque, M.M.; Tyler, C.R. The Segment Matters: Probable Reassortment of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) Complicates Phylogenetic Analysis and Inference of Geographical Origin of New Isolate from Bangladesh. Viruses 2020, 12, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, P.P.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Jansen, M.D.; Phiwsaiya, K.; Dalia, A.; Hasan, M.A.; Senapin, S.; Mohan, C.V.; Dong, H.T.; Rodkhum, C. Two-year Surveillance of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) Reveals Its Wide Circulation in Tilapia Farms and Hatcheries from Multiple Districts of Bangladesh. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, A.T.; Rani, N.A.; Sharker, Y.A.; Ahammed, T.; Rahman, U.S.; Yasmin, S.; Ratul, I.H.; Joyoti, S.A.; Musa, M.S.; Rahaman, M.U.; et al. Computational Design and Evaluation of a Polyvalent Vaccine for Viral Nervous Necrosis (VNN) in Fish to Combat Betanodavirus Infection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, A.S.; Punom, N.J.; Eshik, M.M.E.; Begum, M.K.; Islam, H.M.R.; Hossain, Z.; Rahman, M.S. Molecular Identification of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) and Associated Risk Factors for White Spot Disease (WSD) Prevalence in Shrimp (Penaeus monodon) Aquaculture in Bangladesh. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 179, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bir, J.; Ray, S.; Sultana, S.; Mohammed, S.; Khalil, I. A Critical Review on White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV): A Potential Threat to Shrimp Farming in Bangladesh and Some Asian Countries. Int. J. Microbiol. Mycol. 2017, 6, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrobortty, D.; Ali, M.R.; Dey, B.K.; Gupta, N.; Islam, S.S.; Sui, L. Viral Contamination of Tiger Shrimp Penaeus Monodon Broodstock in Bangladesh. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 2161–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabuj, M.A.I.; Bairagi, T.; Asif, A.A.; Faruq, O.; Bari, M.R.; Neowajh, M.S. Shrimp Disease Investigation and Culture Strategies in Bagerhat District, Bangladesh. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 1, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delwer, M.D.; Hasan, A.; Haque, M.; Ali, M.; Ali, M.; Barman, A. Parasitic Diseases of Indian Major Carp in Rajshahi District of Bangladesh. J. Agrofor. Environ. 2010, 3, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kibria, M.M.; Asmat, G.S.M. An Addition of a Trichodinid Parasite (Ciliophora: Trichodinidae) from Cultured Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) (Linnaeus, 1758) in Bangladesh. I3 Biodivers. 2019, 6, 602. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Yeasmin, M.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Khan, S. Status, Occurrence, Intensity and Impact of Argulosis in Different Brood Stock Ponds. MOJ Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2019, 4, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, M.S.; Bagum, N.; Rahman, S.; Ashaf-Ud-Doulah, M.; Bhadra, A.; Chakra Borty, S. Parasitic Diseases and Estimation of Loss Due to Infestation of Parasites in Indian Major Carp Culture Ponds in Bangladesh. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Doulah, M.A.U.; Islam, S.M.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Rashid, M.H.O.; Razzak, M.A. Investigation of Parasite and Diseases at Cage Culture Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Southern Region of Bangladesh. Res. Agric. Livest. Fish. 2020, 6, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, K.J.; Jannat, M.S. Monogenean Gill Parasites of Indian Major Carps from Different Fish Farms of Mymensingh, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Fish. Res. 2002, 6, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, K. Fish Parasitological Studies in Bangladesh: A Review. J. Agric. Rural Dev. 2006, 4, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Hossain, M.D.; Rahman, M.H. Histopathology of Some Diseased Fishes. J. Life Earth Sci. 2007, 2, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, P.K.; Saurabh, S. Recent advances in fish disease diagnostics and health management with special reference to indian freshwater aquaculture. In Aquaculture in India; Tripathi, S.D., Lakra, W.S., Chadha, N.K., Eds.; Narendra Publishing House: Delhi, India, 2018; pp. 391–422. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Roy, S.; Kumar, A.; Barman, D. Immunoserological and Molecular Techniques Used in Fish Disease Diagnosis—A Mini Review. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2014, 1, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, S.; Putalun, W.; Vimolmangkang, S.; Phoolcharoen, W.; Shoyama, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Morimoto, S. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Quantitative/Qualitative Analysis of Plant Secondary Metabolites. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsalam, A.; Rajendran, K.V.; Kezhedath, J.; Godavarikar, A.; Sood, N.; Bedekar, M.K. Development of an Indirect ELISA Test for the Detection of Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) in Fish Tissue and Mucus Samples. J. Virol. Methods 2023, 315, 114707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibenge, M.; Opazo, B.; Rojas, A.; Kibenge, F. Serological Evidence of Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus (ISAV) Infection in Farmed Fishes, Using an Indirect Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2002, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millard, E.; Brenden, T.; LaPatra, S.; Marcquenski, S.; Faisal, M. Detection of Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus-IVb Antibodies in Sera of Muskellunge Esox Masquinongy Using Competitive ELISA. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 108, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaies, I.; Shah, F.A.; Qadiri, S.S.N.; Qayoom, I.; Bhat, B.A.; Dar, S.A.; Bhat, F.A.; Bhat, H.F.; Farooq, S.; Mandu, S.M. Diagnosis of Aeromoniasis in Common Carp Fish by Indirect ELISA Test through Antibody Detection. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2024, 45, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, S.; Riederer, M.; Zubkowski, T.; Trudel, M.; Rhodes, L. Interpreting Dual ELISA and QPCR Data for Bacterial Kidney Disease of Salmonids. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 91, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyam, K.U.; Kim, H.-J.; Kole, S.; Oh, M.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, W.-S. Antibody-Based Lateral Flow Chromatographic Assays for Detecting Fish and Shrimp Pathogens: A Technical Review. Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.Z.; Song, J.L.; Zhan, W.B. Development of a Colloidal Gold Immunochromatographic Test Strip for Detection of Lymphocystis Disease Virus in Fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, S.G.; Kim, D.; Hwang, J.; Choi, Y.; Hong, J.W.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.-H.; Hwang, M.P.; Choi, J. Enhanced Detection of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus via Lateral Flow Chip and Fluorometric Biosensors Based on Self-Assembled Protein Nanoprobes. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y. An Immunochromatographic Test Strip for Rapid Detection of Fish Pathogen Edwardsiella Tarda. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.-H.; Jeong, H.-N.; Shyam, K.U.; Oh, M.-J.; Kim, C.-S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.-S. Development and Validation of a Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assay for Specific Detection of Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus (VHSV, Genotype IVa) in Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 2021, 537, 736491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral Flow Assays: Principles, Designs and Labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Xu, X.; Zhan, W. Development and Application of Antibody Microarray for Lymphocystis Disease Virus Detection in Fish. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 189, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Jiang, Y. Development of Colloidal Gold Immunochromatographic Strip for Rapid Detection of Cyvirus Cyprinidallo 2. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2025, 161, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwer, M.G.; Rony, M.M.H.; Sharmin, M.S.; Chowdhury, A.K.J.; Bhowmik, S. ELISA Validation and Determination of Cut-off Level for Chloramphenicol (CAP) Residues in Shrimp and Fish. Our Nat. 2017, 15, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jaies, I.; Shah, F.A.; Qadiri, S.S.N.; Qayoom, I.; Bhat, B.A.; Dar, S.A.; Bhat, F.A. Immunological and Molecular Diagnostic Techniques in Fish Health: Present and Future Prospectus. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullis, K.; Faloona, F.; Scharf, S.; Saiki, R.; Horn, G.; Erlich, H. Specific Enzymatic Amplification of DNA In Vitro: The Polymerase Chain Reaction. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1986, 51, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzadnia, A.; Naeemipour, M. Molecular Techniques for the Detection of Bacterial Zoonotic Pathogens in Fish and Humans. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, H.; Ali, M.Y.; Shahiduzzaman, M.; Shams, F.I.; Sarower, M.G. Biochemical and PCR Assay for Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria at Shrimp and Shrimp Farms in Bangladesh. Fish. Aquac. J. 2015, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, I.M.; Siddique, M.A.; Hossain, A. PCR Based Detection of White Spot Syndrome Virus(WSSV) in Shrimp Post Larvae (PL) of Bangladesh. Int. J. Sci. Basic. Appl. Res. 2020, 51, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Aktar, S.; Parvez, M.S.; Islam, H.M.R.; Ahsan, M.N. Multiplex-PCR Protocol Development for Rapid Screening of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in Shrimp. J. Fish. 2020, 8, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, M.S.; Punom, N.J.; Eshik, M.M.E.; Ahmmed, S.; Rabbane, M.G.; Rahman, M.S. Investigation of Tilapia Mortality Events Targeting Tilapia Lake Virus Disease (TiLVD) in Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.P.; Dinh-Hung, N.; Taengphu, S.; Nguyen, V.V.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Senapin, S.; Vishnumurthy Mohan, C.; Dong, H.T.; Rodkhum, C. Tilapia Lake Virus Was Not Detected in Non-Tilapine Species within Tilapia Polyculture Systems of Bangladesh. J. Fish Dis. 2022, 45, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achariya, A.; Nasren, S.; Sujon, M.S.R.; Alam, M.M.M.; Khalil, S.M.I.; Mamun, M.A. Al Status of Biofloc Culture System in Sylhet, Bangladesh: Mass Mortality of Striped Snakehead, Channa striata (Bloch 1793) Due to Coinfections with Aeromonas veronii and Trematodes Cercariae. J. Aquat. Res. Sustain. 2025, 2, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, I.S.; Kellermann, M.; Mossotto, E.; Beattie, R.M.; MacArthur, B.D.; Ennis, S. A Systematic Review of the Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Autoimmune Diseases. npj Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Luna, S.A.; Siddique, Z. Machine-Learning-Based Disease Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.T.; Nigar, S.; Kanti, P.; Rana, A.; Kumar, M.; Ansari, M.K.; Hasan, S.W. Recent Advances and Future Prospects in the Fish Disease, Diagnosis and Their Treatment. Int. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2024, 13, 10–26. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Gupta, H.; Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, A.; Joshi, R.C.; Dutta, M.K. A Novel Pilot Study on Imaging-based Identification of Fish Exposed to Heavy Metal (Hg) Contamination. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.R.I.; Rahman, U.S.; Akter, T.; Azim, M.A. Fish Disease Detection Using Deep Learning and Machine Learning. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2023, 185, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayan, A.-A.; Saha, J.; Mozumder, A.N.; Mahmud, K.R.; Al Azad, A.K.; Kibria, M.G. A Machine Learning Approach for Early Detection of Fish Diseases by Analyzing Water Quality. Trends Sci. 2021, 18, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikder, J.; Sarek, K.I.; Das, U.K. Fish Disease Detection System: A Case Study of Freshwater Fishes of Bangladesh. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbongshi, A.; Shakil, R.; Akter, B.; Lata, M.A.; Joarder, M.M.A. A Comprehensive Analysis of Feature Ranking-Based Fish Disease Recognition. Array 2024, 21, 100329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.N.; Haque, M.M. Reassessing the Role of Nanoparticles in Core Fields of Aquaculture: A Comprehensive Review of Applications and Challenges. Aquac. Res. 2025, 2025, 6897333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K. Nanodiagnostics: Application of Nanotechnology in Molecular Diagnostics. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2003, 3, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, P.; Pereira, E.; Eaton, P.; Doria, G.; Miranda, A.; Gomes, I.; Quaresma, P.; Franco, R. Gold Nanoparticles for the Development of Clinical Diagnosis Methods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Soliman, H.; El-Matbouli, M. Gold Nanoparticles as a Potential Tool for Diagnosis of Fish Diseases. In Veterinary Infection Biology: Molecular Diagnostics and High-Throughput Strategies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.; Soliman, H.; Haenen, O.; El-Matbouli, M. Antibody-Coated Gold Nanoparticles Immunoassay for Direct Detection of Aeromonas salmonicida in Fish Tissues. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, G.C.; Sheng, L.P.; Rijiravanich, P.; Marimuthu, K.; Ravichandran, M.; Yin, L.S.; Lertanantawong, B.; Surareungchai, W. Gold-Nanoparticle Based Electrochemical DNA Sensor for the Detection of Fish Pathogen Aphanomyces Invadans. Talanta 2013, 117, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahariar, M.A.; Hossain, M.Z.; Urmi, J.F.; Hasan, M.M.; Masum, M.M.I.; Shah, A.K.M.A.; Hasan, M.; Rahman, Z.; Alam, M.S. Biosynthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and Its Impacts on Striped Dwarf Catfish (Mystus vittatus) as Feed Additives. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 39, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewel, A.S.; Haque, A.; Akter, N.; Akter, S.; Satter, A.; Sarker, P.K.; Marshall, D.J.; Paray, B.A.; Hossain, M.B. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Zn-Nanoparticles on the Growth Performance and Nutritional Quality of Asian Catfish, Clarias Batrachus. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1410557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Martinez-Agosto, J.A.; Rexach, J.; Fogel, B.L. Next Generation Sequencing in Clinical Diagnosis. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, S.; McPherson, J.D.; McCombie, W.R. Coming of Age: Ten Years of next-Generation Sequencing Technologies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Verma, D.; Kumar, S.; Ji, S.; Satkar, S.; Bhusare, S.; Kumar, N. Next generation sequencing: A revolution technology in fisheries and environmental DNA (eDNA) study. In Futuristic Trends in Agriculture Engineering & Food Sciences; Book 11; Iterative International Publisher; Selfypage Developers Pvt Ltd.: Chikkamagaluru, India, 2024; Volume 3, pp. 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, D.B.; dos Anjos, T.M.C.; De Los Santos, E.F.F.; Rodrigues, M.D.N.; Alegria, O.V.C.; Ramos, R.T.J. New Perspectives on Metagenomic Analysis for Pathogen Monitoring in Sustainable Freshwater Aquaculture Production: A Systematic Review. Front. Freshw. Sci. 2024, 2, 1459233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, M.J.; Momtaz, F.; Kawsar, A.Q.M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Gupta, S.K.; Tay, A.C.Y. Next-generation Sequencing Reveals Significant Variations in Bacterial Compositions across the Gastrointestinal Tracts of the Indian Major Carps, Rohu (Labeo rohita), Catla (Catla catla) and Mrigal (Cirrhinus cirrhosis). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Sadekuzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.; Siddique, M.; Uddin, M.; Haque, M.; Chowdhury, M.; Khasruzzaman, A.; Rahman, M.; Hossain, M.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of the Multidrug Resistant Aeromonas veronii Isolated for the First Time from Stinging Catfish (Shing Fish) in Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardis, E.R. Next-Generation DNA Sequencing Methods. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2008, 9, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Park, J.-E.; Chai, H.-H.; Jang, G.-W.; Lee, S.-H. Dajeong Next Generation Sequencing in Livestock Species—A Review. J. Anim. Breed. Genom. 2017, 1, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeler, E.J.; Taylor, N.G. The Application of Epidemiology in Aquatic Animal Health—Opportunities and Challenges. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Roy, S.; Meena, D.K.; Sarkar, U.K. Application of Probiotics in Shrimp Aquaculture: Importance, Mechanisms of Action, and Methods of Administration. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2016, 24, 342–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Rheman, S.; Debnath, N.; Delamare-Deboutteville, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Ghosh, S.; Parveen, S.; Islam, K.; Islam, M.A.; Rashid, M.M.; et al. Antibiotics Usage Practices in Aquaculture in Bangladesh and Their Associated Factors. One Health 2022, 15, 100445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.K.; Shahjahan, M.; Kari, Z.A.; Téllez-Isaías, G. Trends in the Use of Probiotics in Aquaculture of Bangladesh—Present State, Problems, and Prospects. Aquac. Res. 2023, 2023, 5566980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.T.; Ahmed, G.U.; Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.N. Study on the Effect of Aquaculture-Drugs and Chemicals on Health and Production of Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) in Narail, Bangladesh. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmed, G.U.; Hasan, M.T.; Faruk, M.A.R.; Rahman, M.K.; Hoque, M.N. Aqua-Drugs and Chemicals: Impact on Fish Health and Production in Mymensingh, Bangladesh. Res. Agric. Livest. Fish. 2015, 2, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Akanda, M.; Rahman, M.; Chowdhury, M. Evaluation of the Efficacies of Selected Antibiotics and Medicinal Plants on Common Bacterial Fish Pathogens. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2009, 7, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, U.; Shafiujjaman, M.; Al Zahid, M.; Faruque, M.H.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Hossain, A. Widespread Use of Antibiotics, Pesticides, and Other Aqua-Chemicals in Finfish Aquaculture in Rajshahi District of Bangladesh. Sustainability 2022, 14, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Paul, S.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Lively, J.A. Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria in Shrimp and Shrimp Farms of Bangladesh. Water 2022, 14, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornber, K.; Huso, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Biswas, H.; Rahman, M.H.; Brum, E.; Tyler, C.R. Raising Awareness of Antimicrobial Resistance in Rural Aquaculture Practice in Bangladesh through Digital Communications: A Pilot Study. Glob. Health Action 2019, 12, 1734735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra Pall, J.; Mondal, S.; Majumdar, P.R.; Hossain, M.A. Effect of Multi-Ownership on Pond Aquaculture Production in Bhola District, Bangladesh. Fish. Aquac. J. 2018, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, T.; Ehsan, R.; Paul, S.I.; Ador, M.A.A.; Rahman, A.; Haque, M.N.; Islam, M.T.; Rahman, M.M. Development of Formalin Killed Vaccine Candidate against Streptococcosis Caused by Enterococcus Sp. in Nile Tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 27, 101371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Hossain, M.T.; Siddique, M.P.; Haque, M.E.; Khasruzzaman, A.K.M.; Islam, M.A. Efficacy of Bi-Valent Whole Cell Inactivated Bacterial Vaccine against Motile Aeromonas Septicemia (MAS) in Cultured Catfishes (Heteropneustes fossilis, Clarias batrachus and Pangasius pangasius) in Bangladesh. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3881–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Hasan, N.A.; Eltholth, M.M.; Saha, P.; Mely, S.S.; Rahman, T.; Murray, F.J. Assessing the Impacts of In-Feed Probiotic on the Growth Performance and Health Condition of Pangasius (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) in a Farm Trial. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, T.; Sofi Uddin Mahamud, A.G.M.; Acharjee, T.K.; Hassan, R.; Akter Snigdha, T.; Islam, T.; Alam, R.; Khoiam, M.U.; Akter, F.; Azad, M.R.; et al. Probiotic Supplementations Improve Growth, Water Quality, Hematology, Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Morphology of Nile Tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Islam, M.; Biswas, M.; Das, P.; Arif, A. Effects of Probiotics on Growth and Production of Monosex Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Nylon Net Cages at Dekar Haor, Sunamganj, Bangladesh. J. Asiat. Soc. Bangladesh Sci. 2018, 44, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Farjana, K.; Mahamud, A.G.M.S.U.; Mondal, D.K.; Tabassum, T.; Khoiam, M.U.; Ahmed, F.F.; Rahman, T. Evaluation of the Dietary Supplementation of Autochthonous Bacteria on Growth, Survival and Resistance to Aeromonas veronii Challenge in Clarias batrachus and Heteropneustes fossilis. Aquac. Fish Fish. 2022, 2, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, A.A.; Haque, M.M.; Hossain, M.K.; Hasan, M.M.; Bashar, A.; Hasan, M.Z.; Shohan, M.H.; Farin, N.N.; Schneider, P.; Bablee, A.L. Effects of Commercial Probiotics on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Microbiota and Intestinal Histomorphology of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Reared in Biofloc Technology (BFT). Biology 2024, 13, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Luyten, W.; Paeshuyse, J. Disease Management and Biosecurity Adoption Status in Finfish Aquaculture: Insights from Bangladesh. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, R.M.; Shakil Rana, K.M.; Hashibur Rahman, M.; Sultana Mukti, S.; Jaman, A. Biosecurity Measures to Address Fish Health Management in Mymensingh District: A Baseline Survey. Int. J. Adv. Res. Dev. 2022, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, D.; Jahan, F.; Halim, K.M.A.; Ali, M.N.; Faruk, M.A.R. Biosecurity Practices in Hatcheries of High Value Fishes. Bangladesh J. Fish. 2022, 34, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, C.P.; Sultana Assistant Professor, S.; Kabiraj, M.; Sultana, S.; Shahin Hossain, S. Role of Probiotics in Aquaculture Practice of Satkhira Region of Bangladesh. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2019, 7, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Munni, M.J.; Akther, K.R.; Ahmed, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Roy, N.C. Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics as an Alternative to Antibiotics on Growth and Blood Profile of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2023, 2023, 2798279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajib Sharker, M.; Rukshana Sumi, K.; Jahangir Alam, M.; Mokhlasur Rahman, M.; Ferdous, Z.; Mohammad Ali, M.; Reaz Chaklader, M. Drugs and chemicals used in aquaculture activities for fish health management in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Int. J. Life Sci. Biotechnol. Pharma Res. 2014, 3, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, H.; Thomas, J. A Review on the Recent Advances and Application of Vaccines against Fish Pathogens in Aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1971–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muktar, Y.; Tesfaye, S. Present Status and Future Prospects of Fish Vaccination: A Review. J. Vet. Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Verdegem, M.C.J.; Khatoon, H.; Wahab, M.A.; van Dam, A.A.; Beveridge, M.C.M. A Comparison of Fertilization, Feeding and Three Periphyton Substrates for Increasing Fish Production in Freshwater Pond Aquaculture in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2002, 212, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Chandan, C.S.S.; Roy, P.; Hossain, M.I.; Bari, S.M. Inland Aquaculture and Fish Health Management: A Case Study of Sylhet District in Bangladesh. Aquac. Stud. 2021, 21, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemal, M.M.; Rahman, A.; Nurjahan; Islam, F.; Ahmed, S.; Kaiser, M.S.; Ahmed, M.R. An Integrated Smart Pond Water Quality Monitoring and Fish Farming Recommendation Aquabot System. Sensors 2024, 24, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalder, B.; Mahmud, M.N.; Basori, M.R.; Seba, M.I.J.; Shammi, M.A.B.H.; Siddique, M.A.B.; Ahammad, A.K.S.; Haque, M.M. Climate-Resilient Aquaculture: Recirculatory Aquaculture Systems–Based Seed Production for Heteropneustes fossilis in Bangladesh. Aquac. Fish. Fish. 2025, 5, e70066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastan, S.A. Use of Immunostimulants in Aquaculture Disease Management. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2015, 2, 277–280. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M. Status and Impact of Commercial Aqua Drugs and Chemicals on Fish Health at Farmer Level. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.A.; Rashid, M.M. Use of Aqua-Medicines and Chemicals in Aquaculture in Shatkhira District, Bangladesh. J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2014, 9, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, H.; Rico, A.; Murshed-e-Jahan, K.; Belton, B. An Assessment of Chemical and Biological Product Use in Aquaculture in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, R.K.; Rahman, M.; Asif, A. Al Present Status of Aqua-Medicines Used in Aquaculture at Jessore Sadar Upazila, Bangladesh. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 4, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Hoq, M.; Mazid, M. Use of Chemicals and Biological Products in Aquaculture in Bangladesh. Agric. 2010, 6, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.A.; Haque, M.M.; Hinchliffe, S.J.; Guilder, J. A Sequential Assessment of WSD Risk Factors of Shrimp Farming in Bangladesh: Looking for a Sustainable Farming System. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, M.N.; Ritu, F.Y.; Ansary, A.A.; Haque, M.M. Exploring Protein-Based Fishmeal Alternatives for Aquaculture Feeds in Bangladesh. Aquac. Nutr. 2025, 2025, 3198303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Criterion | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusion | Exclusion | |
| Time frame | After 2000 | Before 2000 |
| Type of Language | English | Non-English |
| Type of Literature | Peer-reviewed literature, government, and organizational reports | Non-peer-reviewed literature |
| Area of Content | Fish disease, disease diagnosis, and treatment methods in aquaculture | Non-aquaculture sectors |
| Publication Status | Published and available online | Published but not accessible |
| Geographic Coverage | Focus on Bangladesh, where aquaculture has a significant role | None |
| General Topics | Prevalence of fish diseases, diagnostic methods, treatment and management approaches, biosecurity, and policy interventions | None |
| Methodologies | Studies employing experimental trials, field surveys, laboratory validation, diagnostic tool development, or review/synthesis on diagnostics and treatments | Studies lacking methodological clarity or without a focus on the diagnosis and treatment of aquaculture diseases |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmud, M.N.; Ansary, A.A.; Ritu, F.Y.; Hasan, N.A.; Haque, M.M. An Overview of Fish Disease Diagnosis and Treatment in Aquaculture in Bangladesh. Aquac. J. 2025, 5, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5040018
Mahmud MN, Ansary AA, Ritu FY, Hasan NA, Haque MM. An Overview of Fish Disease Diagnosis and Treatment in Aquaculture in Bangladesh. Aquaculture Journal. 2025; 5(4):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5040018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmud, Md. Naim, Abu Ayub Ansary, Farzana Yasmin Ritu, Neaz A. Hasan, and Mohammad Mahfujul Haque. 2025. "An Overview of Fish Disease Diagnosis and Treatment in Aquaculture in Bangladesh" Aquaculture Journal 5, no. 4: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5040018
APA StyleMahmud, M. N., Ansary, A. A., Ritu, F. Y., Hasan, N. A., & Haque, M. M. (2025). An Overview of Fish Disease Diagnosis and Treatment in Aquaculture in Bangladesh. Aquaculture Journal, 5(4), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/aquacj5040018







