- Communication
Molecular and Phylogenetic Characterization of Parvovirus B19 Strains Detected in the Pediatric Population of the Greater Thessaloniki Region in Greece During March–April 2024
- Evangelia Giosi,
- Ifigeneia Dimopoulou and
- Georgia Gioula
- + 10 authors
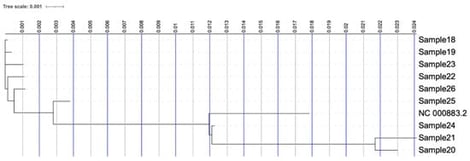
Parvovirus B19 is a DNA virus. Most parvoviruses infect animals; Parvovirus B19 infects humans. Parvovirus B19 is mainly transmitted through respiratory droplets during close contact, but additional routes such as transmission through contaminated blood products and vertical transmission from mother to fetus have also been documented. Infections occur throughout the year, with a seasonal increase between late winter and early summer. Clinical symptoms depend on age, and on patients’ immune status. Healthy, immunocompetent individuals experience asymptomatic or mild infections including a febrile rash; serious complications rarely appear, such as rheumatoid-like arthritis or acute myocarditis. Clusters of myocarditis cases following Parvovirus B19 infections appeared in a daycare in Thessaloniki in 2024. To molecularly and phylogenetically characterize Parvovirus B19 strains detected during a pediatric outbreak associated with elevated troponin levels and myocarditis in Northern Greece, and to compare these strains with isolates from adult cases with mild symptoms in order to explore potential associations between viral genetic variability and cardiac involvement. MinION sequencing protocol was performed for nine whole blood samples, seven belonging to children with myocarditis, and two to adults presenting mild symptoms. Statistical analysis was performed with QualiMap 2.3 and relevant tools. Phylogenetic analysis identified distinct viral groups originating from the samples investigated. A distinct branch was formed by the reference genome and the ones of the adults’ samples, while samples from children with myocarditis provided discrete branches differing from the reference one. The findings demonstrate a clear association between Parvovirus B19 infection and myocarditis in the pediatric cases analyzed. The detected viral strains, including variants identified in several samples, support the role of Parvovirus B19 as a contributing factor in post-infectious cardiac involvement. Although these results reinforce the clinical relevance of Parvovirus B19 in childhood myocarditis, expanding the sample size would allow for a more robust characterization of circulating strains and confirmation of the observed patterns.
30 January 2026