Assessment of Bacterial Contamination and Biofilm Formation in Popular Street Foods of Biskra, Algeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Strategy and Food Selection for Microbial Analysis in Street Food
- ⮚
- Satisfactory: Test results indicating good microbiological quality (CFU < 102 CFU/g)
- ⮚
- Acceptable: Results reflecting borderline microbial quality (CFU between 102–104 CFU/g).
- ⮚
- Unsatisfactory: Indicating potential hygiene issues that may necessitate further inspection (CFU > 104 CFU/g).
- ⮚
- Unacceptable/potentially hazardous: N/A: Not applicable—this category is not defined for the corresponding microorganism.
2.2. Microbiological Analysis
2.2.1. Identification of Pathogenic Bacteria
2.2.2. Species Characterization and Antibiotic Resistance
2.2.3. Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of Biofilm
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Contamination Levels and Bacteria Isolates from Different Meat-Based Street Food
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Profile of Isolates
3.3. Slime and Biofilm Production Among Strains
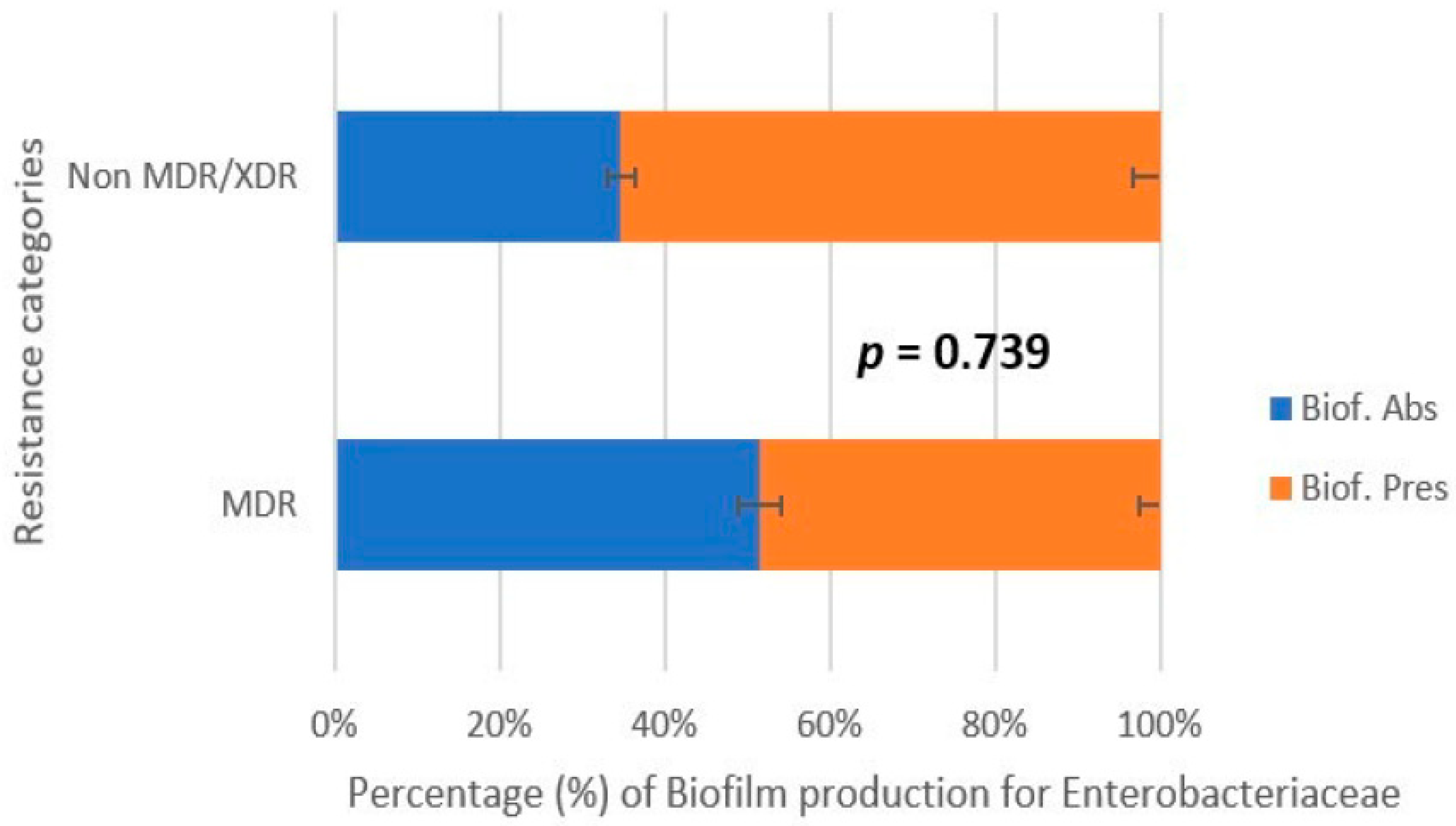
3.4. Correlation Between Biofilm Production and Antibiotic Resistance
3.5. Fed-Batch Mode Enhances Biofilm Formation Compared to Batch Culture
3.5.1. Enterobacterales
3.5.2. Staphylococcus
4. Discussion
Limitation of Strain-Level Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CoNS | Coagulase-negative staphylococci |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| CRA | Congo red agar |
| MDR | Multidrug resistance |
| XDR | Extensively drug resistant |
| MTP | Microtiter plate method |
References
- Alimi, B.A. Risk factors in street food practices in developing countries: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algeria Press Service Intoxication Alimentaire: Augmentation de 105 Cas Durant le 1er Semestre de 2021. Available online: https://www.aps.dz/sante-science-technologie/125713-intoxication-alimentaire-augmentation-de-105-cas-durant-le-1er-semestre-de-2021 (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Deepanjali, S.; Jharna, M.; Chanaveerappa, B.; Sarumathi, D.; Gopichand, P.; Anupriya, K. An outbreak of Salmonella enteritidis food poisoning following consumption of chicken shawarma: A brief epidemiological investigation. F1000Research 2022, 10, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banna, H.; Nawas, T. Salmonella: A Common Contaminant of Chicken Shawarma in RasBeirut Restaurants. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2016, 10, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, C.; Miranda-Madera, V.; Serrano-Silva, N.; Bernal, J.E.; Ríos-Montes, K.; González-Jiménez, F.E.; Ojeda-Juárez, D.; Sarria-Guzmán, Y. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Isolated from Street Foods: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmi, M.; Ansari, W.; Islam, M.; Sobur, M.; Rahman, M.; Rahman, M. Antibiotic resistance patterns of Staphylococcus spp. isolated from fast foods sold in different restaurants of Mymensingh, Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2021, 8, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Lee, H.; Ahn, J. Characteristics of Biofilm Formation by Selected Foodborne Pathogens. J. Food Saf. 2011, 31, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulášová, M.; Valáriková, J.; Dušinský, R.; Chovanová, R.; Belicová, A. Multiresistance of Staphylococcus xylosus and Staphylococcus equorum from Slovak Bryndza cheese. Folia Microbiol. 2014, 59, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/53728.html (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food Safety Risk Analysis: A Guide for National Food Safety Authorities; World Health Organization; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewska, J.; Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W. Biofilm Formation Ability and Presence of Adhesion Genes among Coagulase-Negative and Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci Isolates from Raw Cow’s Milk. Pathogens 2020, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Bonaventura, G.D.; Djukić, S.; Ćirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: Overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by Staphylococci. APMIS 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudagidan, M.; Ozalp, V.C.; Öztürk, O.; Yurt, M.N.Z.; Yavuz, O.; Tasbasi, B.B.; Ucak, S.; Mavili, Z.S.; Coban, A.; Aydin, A. Bacterial surface, biofilm and virulence properties of Listeria monocytogenes strains isolated from smoked salmon and fish food contact surfaces. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuler, M.L.; Kargi, F. Bioprocess Engineering: Basic Concepts, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chisti, Y. Fermentation Technology. In Industrial Biotechnology: Sustainable Growth and Economic Success; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, O.E.; Sauer, K. Escaping the biofilm in more than one way: Desorption, detachment or dispersion. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 30, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjersted, J.L.; Henson, M.A.; Mahadevan, R. Genome-scale analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolism and ethanol production in fed-batch culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, G.T. Principles of microbe and cell cultivation, S. John Pirt, Halsted Press, Division of John Wiley and Sons, New York, 274 pages, $34.00. AIChE J. 1976, 22, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanè, T.; Shimizu, S. Fed-Batch Techniques in Microbial Processes. In Bioprocess Parameter Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 147–194. [Google Scholar]
- Koumassa, O.A.B.; Ouétchéhou, R.; Hounsou, M.; Zannou, O.; Dabadé, D.S. Factors influencing street-vended foods quality and safety in developing countries: A review. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreten, V.; Giampà, N.; Schuler-Schmid, U.; Teuber, M. Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Coagulase-negative Staphylococci Isolated from Food. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 21, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Othman, F.A.; Bahareth, T.O.; Al-Sogair, A.M.; Sawaya, W.N. Microbiological Quality of Shawarma in Saudi Arabia. J. Food Prot. 1985, 48, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Abbas, S.; Butt, Z.A.; Ali, A.S.; Mahmood, R.; Ahmad, M.; Farhan, M.; Wahid, A.; Nawaz, M.; Iftikhar, A. Bacterial Contamination in Processed Chicken Shawarma (Meat) Sold in Various Parts of Lahore, Pakistan. Pak. J. Nutr. 2013, 12, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Gamel, A.; Khalifa, A.; AbdElHady, H.; Zeid, M. Microbial Status of Shawerma Sandwiches in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 51, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soran University; Saeed, W.Q.; Mohammad, I.M. University of Duhok Comparison between Chicken and Red Meat Shawarma Food for Bacterial Contamination. J. Duhok Univ. 2021, 24, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. Sci. Rep. 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.G.; El Naghy, W.S.; Shahbab, A.A.; Hassan, A.M. Evaluation of antagonistic activity of an Egyptian probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum against bacteria isolated from ready-to-eat meat products. Tanta Med. J. 2023, 51, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achek, R.; Hotzel, H.; Cantekin, Z.; Nabi, I.; Hamdi, T.M.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Emerging of antimicrobial resistance in staphylococci isolated from clinical and food samples in Algeria. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, A.L.; Lakhdara, N.; Rodriguez, E.E.; Kabouia, R.; Moreno, E.; García, M.E.; Koutchoukali, H.; Guerraichi, L.; Bouaziz, O. Prevalence of microbial contamination of fresh seafood product sold in Constantine, Algeria. Environ. Skept. Crit. 2014, 3, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Mourad, H.; Khelaf, S.; Reguia, N.; Halima, S.B.; Abdelhamid, F.; Ali, B. Microbiological quality of Merguez in some retailing meat shops in the region of MSila (Algeria). Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 11, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samira, Z.; Rachida, H.; Norhene, F. Control of bacterial contamination in three types of fish selected from the coastal and inland regions of Tipaza (Algeria). Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2024, 7, e74375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Liang, J.; Li, Q.; Lin, H.; Lin, C.; Liu, H.; Zhou, D.; Lu, W.; Sun, Z.; et al. Characterization of florfenicol resistance genes in the coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (CoNS) isolates and genomic features of a multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus lentus strain H29. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Naas, T.; Poirel, L. Global Spread of Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1791–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Shokri, F.; Rostamnezhad, M.; Khoshnood, S.; Mortazavi, S.M.; Sholeh, M.; Kouhsari, E. Fosfomycin: A look at its various aspects. Gene Rep. 2020, 19, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepperell, C.; Kus, J.V.; Gardam, M.A.; Humar, A.; Burrows, L.L. Low-virulence Citrobacter species encode resistance to multiple antimicrobials. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3555–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggoune, N.; Tali-Maamar, H.; Assaous, F.; Benamrouche, N.; Naim, M.; Rahal, K. Emergence of plasmid mediated carbapenemase OXA-48 in a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain in Algeria. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2014, 2, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaalal, N.; Touati, A.; Bakour, S.; Aissa, M.A.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Pantel, A. Spread of OXA-48 and NDM-1-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST48 and ST101 in Chicken Meat in Western Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekar, F.M.; Granier, S.A.; Touati, A.; Millemann, Y. Occurrence of Third-Generation Cephalosporins-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Fresh Fruits and Vegetables Purchased at Markets in Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudjerda, D.; Lahouel, M. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from chicken meat, beef, and raw milk. Austral J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 54, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamendjari, S.; Saidani, K.; Chaib, L.; Aggad, H.; Bouzebda, Z.; Bouzebda, F.A. Hygienic quality of food from animal origin and antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli in a border region of Algeria. Rev. Cient. Cienc. Veter. 2024, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guergueb, N. Fosfomycin Escherichia coli Resistance in Poultry Meat Associated with the Excessive use of Biocides During COVID-19. Folia Vet. 2024, 68, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, S.; Darwish, W.; Tharwat, A.; Said, M.; ElAtriby, D.; Seliem, M.; Alfifi, A.; Ghareeb, W.; Gad, T. Prevalence and antibiogram of shigatoxin-producing E. coli in camel meat and offal. Open Vet. J. 2024, 14, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaatout, N.; Al-Mustapha, A.I.; Bouaziz, A.; Ouchene, R.; Heikinheimo, A. Prevalence of AmpC, ESBL, and colistin resistance genes in Enterobacterales isolated from ready-to-eat food in Algeria. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 2205–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khennouchi, N.C.e.H.; Loucif, L.; Boutefnouchet, N.; Allag, H.; Rolain, J.-M. MALDI-TOF MS as a Tool To Detect a Nosocomial Outbreak of Extended-Spectrum-β-Lactamase- and ArmA Methyltransferase-Producing Enterobacter cloacae Clinical Isolates in Algeria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 6477–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouria, L.; Hafida, H.; Fréderic, R.; Richard, B.; Djamel-Eddine, A. Prevalence and molecular typing of extended-spectrum -lactamases in Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae and Citrobacter freundii isolates from Laghouat Hospital, Algeria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeffal, S.; Mamache, B.; Elgroud, R.; Hireche, S.; Bouaziz, O. Prevalence and risk factors for Salmonella spp. contamination in broiler chicken farms and slaughterhouses in the northeast of Algeria. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merati, R.; Boudra, A. Detection and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Salmonella spp. Isolated from Commercial Eggs in Tiaret Province, Algeria. World’s Vet. J. 2023, 13, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.J.I.; Islam, K.B.M.S.; Adnan, M.R.; Sadi, A.H.; Islam, M.; Drlica, K. Antibiotic-Resistant Salmonella enteritidis in Raw Chicken Meat of Dhaka City, Bangladesh. Int. J. Microbiol. 2025, 2025, 5654730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajmorak, F.; Ghasemian, S.O.; Gholami-Ahangaran, M. Isolation, genotyping and antibiotic resistance analysis in Salmonella species isolated from turkey meat in Isfahan, Iran. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, R.; Cantekïn, Z.; Khelef, D.; Ergün, Y.; Solmaz, H.; Kaidi, R. Cezayir’de İnek Mastitislerinden İzole Edilen Stafilokokların Antibiyotik Direncinin Fenotipik ve Moleküler Yöntemlerle Belirlenmesi. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2015, 21, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.; Waked, R.; Choucair, J.; Aubry, A.; Laurent, F.; Simoes, P.M.; Dupieux-Chabert, C.; Haddad, E. Linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus capitis isolate. Infect. Dis. Now 2022, 52, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoe, J.A.T.; Kerr, K.G.; Reynolds, G.W.; Jain, S. Staphylococcus capitis endocarditis: Two cases and review of the literature. Heart 1999, 82, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crepin, D.M.; Chavignon, M.; Verhoeven, P.O.; Laurent, F.; Josse, J.; Butin, M.; Forrest, G.N. Staphylococcus capitis: Insights into epidemiology, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance of a clinically relevant bacterial species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0011823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berends, M.S.; Luz, C.F.; Ott, A.; Andriesse, G.I.; Becker, K.; Glasner, C.; Friedrich, A.W. Trends in Occurrence and Phenotypic Resistance of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) Found in Human Blood in the Northern Netherlands between 2013 and 2019. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijałkowski, K.; Peitler, D.; Karakulska, J. Staphylococci isolated from ready-to-eat meat—Identification, antibiotic resistance and toxin gene profile. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 238, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Riegel, P.; Prévost, G. Is Staphylococcus lugdunensis Significant in Clinical Samples? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, L.; Stegger, M.; Söderquist, B. Staphylococcus lugdunensis: Antimicrobial susceptibility and optimal treatment options. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 38, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillotson, G.S. Trojan Horse Antibiotics–A Novel Way to Circumvent Gram-Negative Bacterial Resistance? Infect. Dis. Res. Treat. 2016, 9, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, Z.; Ghssein, G. Towards new antibiotics classes targeting bacterial metallophores. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 182, 106221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoffone, V.C.; Barbieri, G.; Irudal, S.; Trespidi, G.; Buroni, S. New Antimicrobial Strategies to Treat Multi-Drug Resistant Infections Caused by Gram-Negatives in Cystic Fibrosis. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shresthar, L.B.; Bhattarai, N.R.; Khanal, B. Comparative evaluation of methods for the detection of biofilm formation in coagulase-negative staphylococci and correlation with antibiogram. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh Sheikh, A.; Dezfuli, A.A.Z.; Navidifar, T.; Fard, S.S.; Dehdashtian, M. Association between biofilm formation, structure and antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from neonatal septicemia in southwest Iran. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadu, M.G.; Ferrari, M.; Mazzarello, V.; Zanetti, S.; Kushkevych, I.; Rittmann, S.K.-M.R.; Stájer, A.; Baráth, Z.; Szabó, D.; Urbán, E.; et al. No Correlation between Biofilm-Forming Capacity and Antibiotic Resistance in Environmental Staphylococcus spp.: In Vitro Results. Pathogens 2022, 11, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medis, S.; Dissanayake, T.; Kottahachchi, J.; Namali, D.; Gunasekara, S.; Wijesinghe, G.; Dilrukshi, N.; Weerasekera, M. Biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance among Coagulase Negative Staphylococcus species isolated from central venous catheters of intensive care unit patients. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 42, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepas, V.; López, Y.; Muñoz, E.; Rolo, D.; Ardanuy, C.; Martí, S.; Xercavins, M.; Horcajada, J.P.; Bosch, J.; Soto, S.M. Relationship Between Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A Review of Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Regulation Mechanism. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Rawat, S. A genetic regulatory see-saw of biofilm and virulence in MRSA pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1204428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.M.S.; Ferreira, F.A.; Beltrame, C.O.; Côrtes, M.F. The role of biofilms in persistent infections and factors involved inica-independent biofilm development and gene regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 602–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Oh, T.; Baek, S.-Y. Multidrug Resistance, Biofilm Formation, and Virulence of Escherichia coli Isolates from Commercial Meat and Vegetable Products. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño-Arriba, A.; González-Machado, C.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R. Antibiotic Resistance and Biofilm-Forming Ability in Enterococcal Isolates from Red Meat and Poultry Preparations. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beshiru, A.; Igbinosa, I.H.; Enabulele, T.I.; Ogofure, A.G.; Kayode, A.J.; Okoh, A.I.; Igbinosa, E.O. Biofilm and antimicrobial resistance profile of extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) and AmpC β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales in vegetables and salads. LWT 2023, 182, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.; Lukowicz, R.; Merchant, S.; Valquier-Flynn, H.; Caballero, J.; Sandoval, J.; Okuom, M.; Huber, C.; Brooks, T.D.; Wilson, E.; et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment Methods for Biofilm Growth: A Mini-review. Res. Rev. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 6, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, F.; Lima, C.A.; Brás, S.; França, Â.; Cerca, N.; Rumbaugh, K. Evidence for inter- and intraspecies biofilm formation variability among a small group of coagulase-negative staphylococci. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hunt, S.M.; Werner, E.M.; Huang, B.; Hamilton, M.A.; Stewart, P.S. Hypothesis for the Role of Nutrient Starvation in Biofilm Detachment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 7418–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Leonhard, M.; Schneider-Stickler, B. Evaluation of culture conditions for mixed biofilm formation with clinically isolated non- albicans Candida species and Staphylococcus epidermidis on silicone. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerca, N.; Pier, G.; Vilanova, M.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. Influence of batch or fed-batch growth on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger, O.; Charilaou, C.C.; Cundy, K.R. Comparison of the API Staph-Ident and DMS Staph-Trac systems with conventional methods used for the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1984, 19, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampimon, O.; Zadoks, R.N.; De Vliegher, S.; Supré, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Barkema, H.; Sol, J.; Lam, T. Performance of API Staph ID 32 and Staph-Zym for identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine milk samples. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burriel, A.R. A comparison of the micromethods API Staph and ID32 STAPH in the identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from sheep. J. Microbiol. Methods 1997, 28, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasone, I.; Kinjo, T.; Yamane, N.; Kisanuki, K.; Shiohira, C.M. Laboratory-based evaluation of the colorimetric VITEK-2 Compact system for species identification and of the Advanced Expert System for detection of antimicrobial resistances: VITEK-2 Compact system identification and antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 58, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

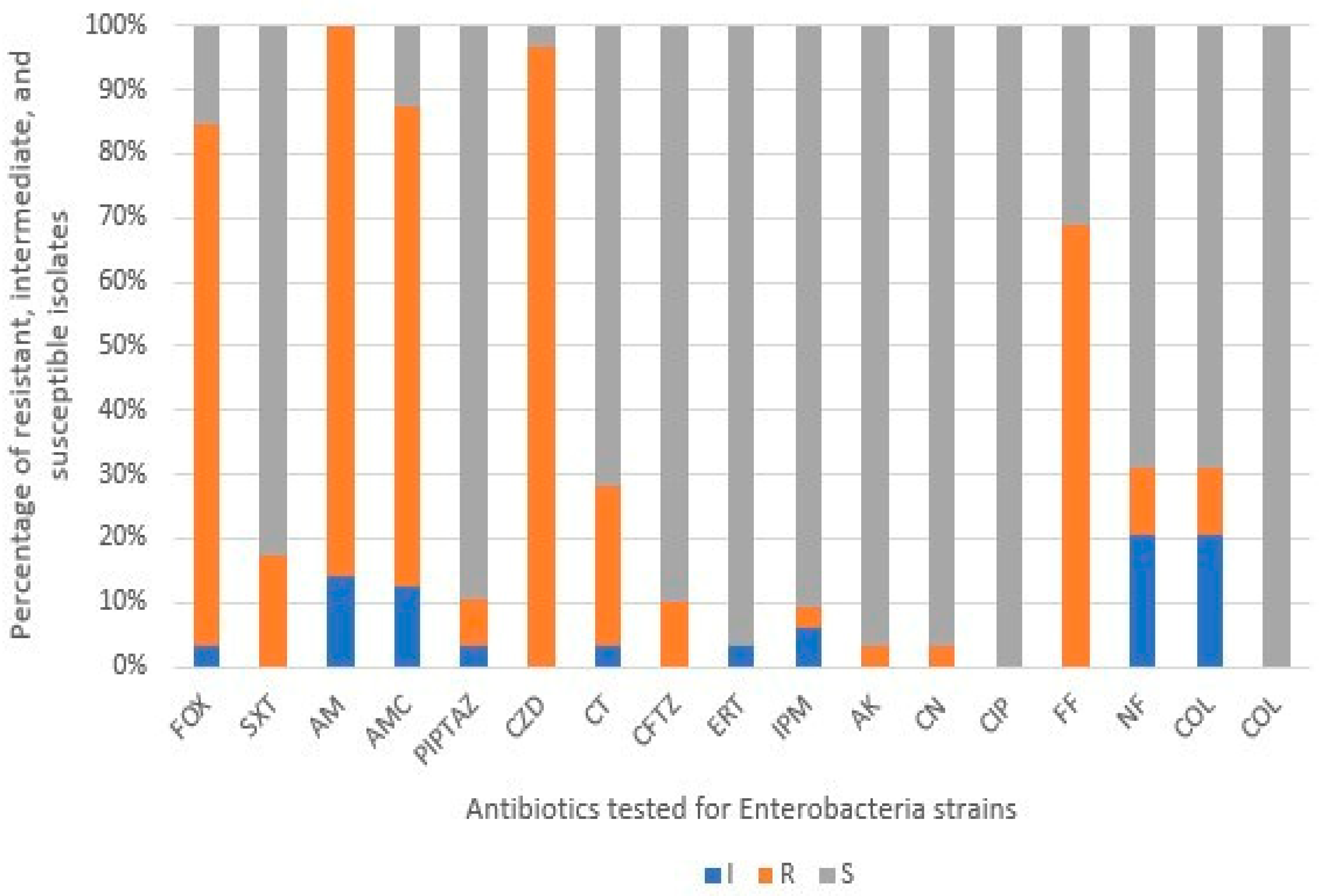

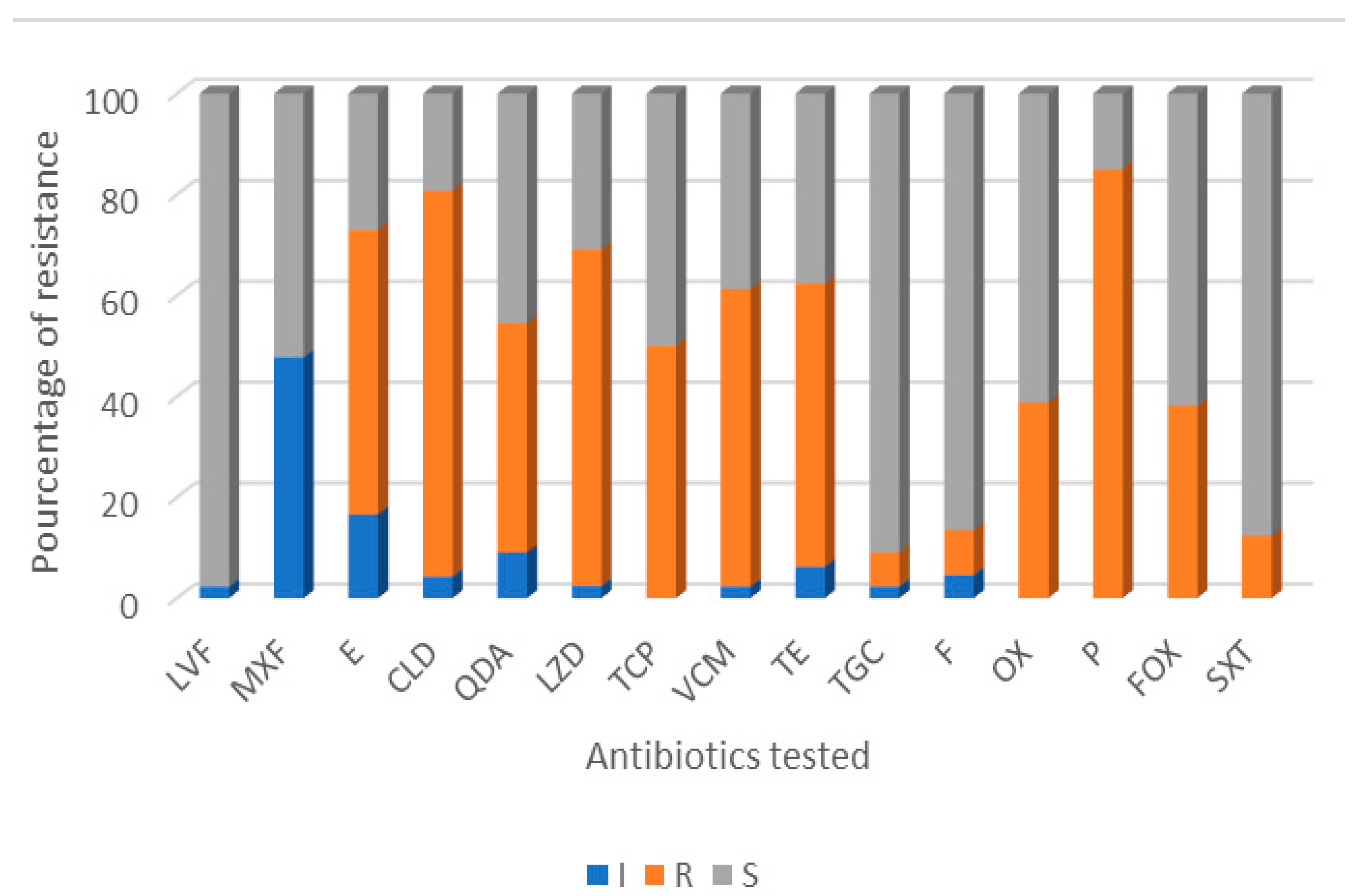
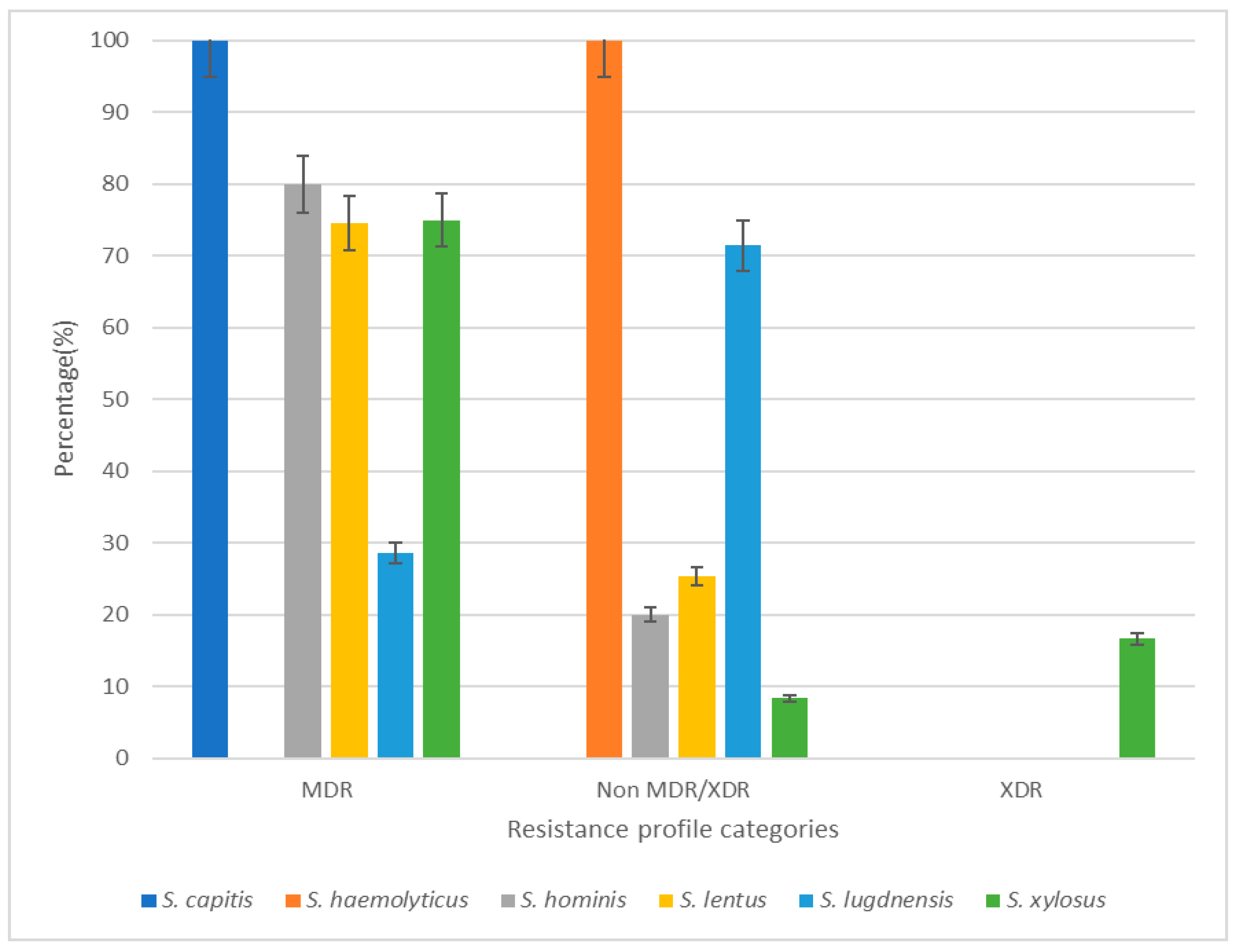
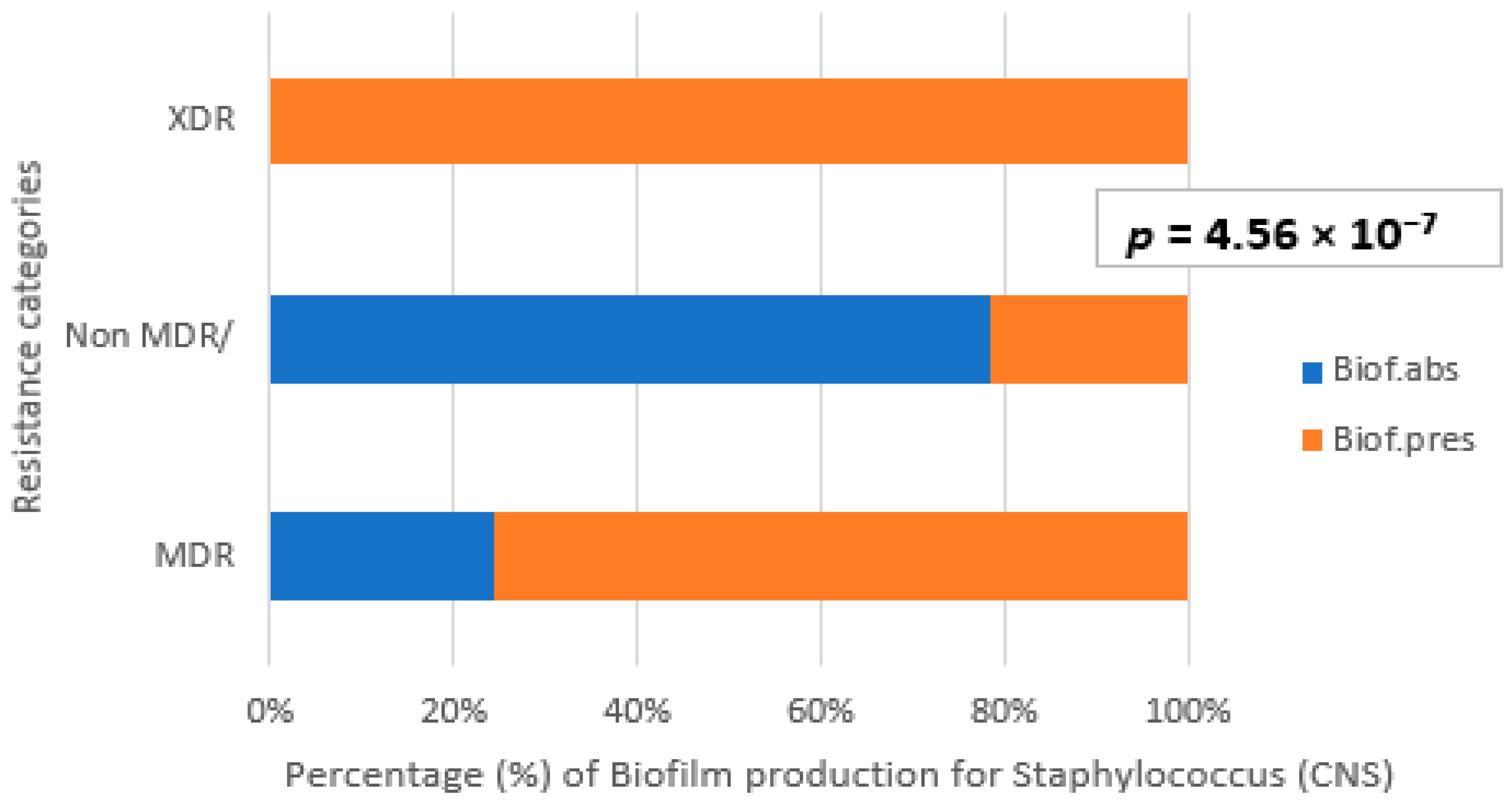

| Type of Food | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial diversity | Mutton Brochettes | Chicken Brochettes | Shawarma Sheep | Shawarma Chicken |
| Percentage (%) | ||||
| Citrobacter freundii | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Escherichia coli | 11.1 | 0 | 0 | 7.1 |
| Enterobacter cloacae | 66.7 | 50 | 85 | 64.3 |
| Klebsiella pneumonia | 0 | 12.5 | 10 | 0 |
| Salmonella | 0 | 12.5 | 0 | 0 |
| Enterobacter sakazakii | 11.1 | 25 | 0 | 7.2 |
| Seratia liquefaciens | 11.1 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 |
| Staphylococcus lentus | 50 | 52.6 | 64.7 | 46 |
| Staphylococcus xylosus | 28.6 | 31.6 | 23 | 34 |
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 14.3 | 10.5 | 8.3 | 16 |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| Staphylococcus hominis | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| Bacteria Group | Bacteria Strain | CRA | Biofilm After 24 h | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absence | Production | Absence | Production | ||
| STAPHYLOCOCCUS | 30% | 70% | 16.66% | 83.33% | |
| S. capitis | 66.66% | 33.33% | 22.22% | 77.77% | |
| S. haemolyticus | 33.33% | 66.66% | 66.66% | 33.33% | |
| S. hominis | 60% | 40% | 20% | 80% | |
| S. lentus | 5% | 95% | 5% | 95% | |
| S. lugdnensis | 42.85% | 57.14% | 52.38% | 47.61% | |
| S. xylosus | 41.66% | 58.33% | 0% | 100% | |
| ENTEROBACTERALES | 12.5% | 87.5% | 48.95% | 51.04% | |
| C. freunidi | 0% | 100% | 0% | 100% | |
| E. coli | 0% | 100% | 50% | 50% | |
| E. cloacae | 10% | 90% | 61.66% | 38.33% | |
| E. sakazakii | 25% | 75% | 50% | 50% | |
| K. pneumonia | 0% | 100% | 33.33% | 66.66% | |
| Salmonella | 100% | 0% | 0% | 100% | |
| S. liquefaciens | 0% | 100% | 0% | 100% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Hellenic Society for Microbiology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boulmaiz, S.; Ayachi, A.; Bouguenoun, W. Assessment of Bacterial Contamination and Biofilm Formation in Popular Street Foods of Biskra, Algeria. Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030032
Boulmaiz S, Ayachi A, Bouguenoun W. Assessment of Bacterial Contamination and Biofilm Formation in Popular Street Foods of Biskra, Algeria. Acta Microbiologica Hellenica. 2025; 70(3):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030032
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoulmaiz, Sara, Ammar Ayachi, and Widad Bouguenoun. 2025. "Assessment of Bacterial Contamination and Biofilm Formation in Popular Street Foods of Biskra, Algeria" Acta Microbiologica Hellenica 70, no. 3: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030032
APA StyleBoulmaiz, S., Ayachi, A., & Bouguenoun, W. (2025). Assessment of Bacterial Contamination and Biofilm Formation in Popular Street Foods of Biskra, Algeria. Acta Microbiologica Hellenica, 70(3), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030032






