Journal Description
Logistics
Logistics
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal of logistics and supply chain management published quarterly online by MDPI. The first issue has been released in December 2017.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), RePEc, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 25.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Operations Research and Management Science) / CiteScore - Q1 (Information Systems and Management)
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
3.6 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.8 (2024)
Latest Articles
An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Customers’ Intentions to Switch to Smart Lockers as a Trending Last-Mile Logistics Channel
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 177; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040177 - 11 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: nowadays, traditional delivery options are challenging to the urban last-mile logistics and sustainability goals. The purpose of this study is to investigate the practical factors that drive frequent e-shoppers to actively switch their intention from conventional delivery options to utilizing smart
[...] Read more.
Background: nowadays, traditional delivery options are challenging to the urban last-mile logistics and sustainability goals. The purpose of this study is to investigate the practical factors that drive frequent e-shoppers to actively switch their intention from conventional delivery options to utilizing smart lockers. Methods: the hypothetical framework tested integrating constructs from the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), and supplementary constructs such as privacy and convenience. Data were collected via a structured online questionnaire from 513 respondents in major Egyptian cities, including Alexandria and Cairo. The framework was tested using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) via SmartPLS 4.0 software to assess the relationship between constructs and switching intention. Results: the analysis confirms that switching intention to use smart lockers is positively driven by Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, Convenience, Privacy, and Perceived Behavioral Control. Notably, a positive attitude towards smart lockers was found to have a non-significant effect on the intention to switch in the Egyptian context. Conclusions: this research contributes to addressing the gap in the extant literature by focusing on analyzing the unique contextual determinants in the emerging last-mile logistics within a developing market context.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Last Mile, E-Commerce and Sales Logistics)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Balancing Exploration and Exploitation: How Green Knowledge Integration Drives Supplier Performance in Sustainable Supply Chains
by
Shahid Khalil and Seyed Mohammadreza Ghadiri
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 176; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040176 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: This study examines how Green Knowledge Integration Capability (GKIC) influences supplier performance within sustainable supply chains by balancing exploration (acquiring new knowledge) and exploitation (refining existing knowledge) strategies. Methods: Based on Social Exchange Theory, Relationship Motivation Theory, and Absorptive Capacity Theory, a
[...] Read more.
Background: This study examines how Green Knowledge Integration Capability (GKIC) influences supplier performance within sustainable supply chains by balancing exploration (acquiring new knowledge) and exploitation (refining existing knowledge) strategies. Methods: Based on Social Exchange Theory, Relationship Motivation Theory, and Absorptive Capacity Theory, a conceptual model was developed and tested using cross-sectional survey data collected from 398 managers representing 240 multinational corporations (MNCs) operating in Pakistan. Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) was employed to analyse the relationships among exploration and exploitation focus, Green Management Innovation (GMI), GKIC, Green Absorptive Capacity (GAC), and supplier performance. Results: The findings indicate that exploration and exploitation strategies significantly enhance supplier performance, with GKIC acting as a mediating mechanism linking strategic focus and innovation to performance outcomes. Moreover, GAC strengthens the impact of the exploration and exploitation focus on performance but exhibits limited moderating effects for GMI and GKIC pathways. Conclusions: The results highlight GKIC’s critical role in translating strategic and innovation initiatives into supplier performance gains. This study contributes to the sustainable supply chain literature and provides actionable insights for managers and policymakers to enhance sustainability outcomes through knowledge integration and absorptive capacity development.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancing Circular Supply Chains: Integrating Logistics, Supply Chain Management and Circular Economy Practices)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Procurement Barriers in Indonesian Food Manufacturing SMEs: An ISM–Fuzzy MICMAC Analysis
by
Ilyas Masudin, Intan Dwi Lestari, Amelia Khoidir and Dian Palupi Restuputri
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 175; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040175 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: This study aims to examine the barriers hindering the implementation of sustainable procurement in Indonesian small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and to identify their hierarchical relationships. Methods: A mixed-method approach was adopted, employing Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) to map the
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aims to examine the barriers hindering the implementation of sustainable procurement in Indonesian small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and to identify their hierarchical relationships. Methods: A mixed-method approach was adopted, employing Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) to map the causal structure of barriers and Fuzzy MICMAC analysis to classify them according to their influence and dependence. Data were collected through expert evaluations and secondary sources, providing both empirical depth and contextual validity. Results: The results reveal that financial constraints, particularly funding limitations, are the most critical and independent barrier driving the entire system of obstacles. The analysis further shows that systemic linkage barriers, such as minimal government incentives, limited availability of eco-friendly raw materials, and high import dependency, create a self-reinforcing cycle that amplifies cost challenges for SMEs. Dependent barriers, including regulatory inadequacies and weak supplier collaboration, are identified as outcomes of these structural constraints, while autonomous barriers like limited consumer awareness remain less influential but still significant. Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that sustainable procurement barriers are not isolated but interconnected, with financial viability acting as the foundational challenge. The study contributes to the literature by providing a relational perspective on sustainable procurement barriers, offering managerial insights for policy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Supplier, Government and Procurement Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Prioritization Model for the Location of Temporary Points of Distribution for Disaster Response
by
María Fernanda Carnero Quispe, Miguel Antonio Daza Moscoso, Jose Manuel Cardenas Medina, Ana Ysabel Polanco Aguilar, Irineu de Brito Junior and Hugo Tsugunobu Yoshida Yoshizaki
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 174; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040174 - 29 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Disasters generate abrupt surges in humanitarian demand, requiring response strategies that balance operational performance with vulnerability considerations. This study examines how temporary Points of Distribution (PODs) can be planned and activated to support timely and equitable resource distribution after a high-magnitude earthquake.
[...] Read more.
Background: Disasters generate abrupt surges in humanitarian demand, requiring response strategies that balance operational performance with vulnerability considerations. This study examines how temporary Points of Distribution (PODs) can be planned and activated to support timely and equitable resource distribution after a high-magnitude earthquake. Methods: A two-stage framework is proposed. First, a modular p-median model identifies POD locations and allocates modular capacity to minimize population-weighted distance under capacity constraints; travel-distance percentiles guide the selection of p. Second, a SMART-based multi-criteria model ranks facilities using operational metrics and vulnerability indicators, including seismic and economic conditions and the presence of at-risk groups. Results: Evaluation of p values from 3 to 30 shows substantial reductions in travel distances as PODs increase, with an elbow at
(This article belongs to the Section Humanitarian and Healthcare Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Supply Chain in the Age of Industry 4.0: A Literature Review
by
Samia Haman, Anass Ben Abdelouahab, Younes El Bouzekri El Idrissi, Safae Merzouk and Aniss Moumen
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 173; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040173 - 29 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The rapid digital transformation driven by Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping manufacturing supply chains, yet comprehensive insights into how these technologies are integrated remain limited. Methods: This study addresses this research gap by conducting a systematic bibliometric analysis and literature review of
[...] Read more.
Background: The rapid digital transformation driven by Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping manufacturing supply chains, yet comprehensive insights into how these technologies are integrated remain limited. Methods: This study addresses this research gap by conducting a systematic bibliometric analysis and literature review of integrating Industry 4.0 technologies in the manufacturing supply chain. We used different scientific databases, Scopus and Web of Science, to elaborate this study. Results: Using advanced bibliometric methods, this study examines the evolution of academic discourse, identifies key themes, and maps the intellectual structure of this transformative research field. By leveraging bibliometric tools, the study names the most prolific authors, countries, and journals contributing to this domain. The findings of the first phase reveal the growing focus on topics like supply chain resilience and real-time decision-making, while also finding gaps in the literature related to technology integration. In the second phase, the literature review identified the most used adoption models in empirical studies such as resource-based view, dynamic capabilities view, and technology acceptance model, we also categorized the adoption drivers into technological, organizational, and environmental. Conclusions: This review emphasizes that although research on Industry 4.0 has expanded significantly, the majority of studies predominantly concentrate on technology adoption and quantitative analysis, with little examination of integration, contextual factors, and longitudinal effects.
Full article
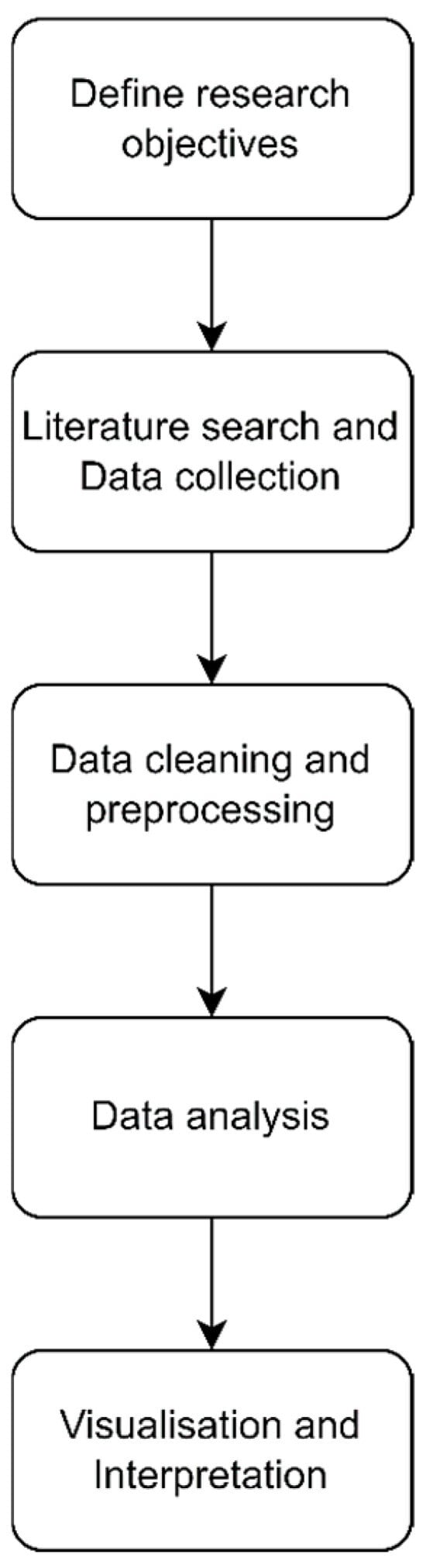
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Agent-Based Simulation Modeling of Multimodal Transport Flows in Transportation System of Kazakhstan
by
Alisher Khussanov, Botagoz Kaldybayeva, Oleksandr Prokhorov, Zhakhongir Khussanov, Doskhan Kenzhebekov, Mukhamediyar Yevadilla and Dauren Janabayev
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 172; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040172 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Kazakhstan’s transport system plays a key role in Eurasian logistics due to its position along the Middle Corridor. However, multimodal freight transport remains under-optimized due to infrastructure bottlenecks, uneven cargo flows, and limited digital tools for forecasting and planning. Methods: This study
[...] Read more.
Background: Kazakhstan’s transport system plays a key role in Eurasian logistics due to its position along the Middle Corridor. However, multimodal freight transport remains under-optimized due to infrastructure bottlenecks, uneven cargo flows, and limited digital tools for forecasting and planning. Methods: This study presents the development of an agent-based simulation model for analyzing multimodal transportation in Kazakhstan. The model integrates railway, road, and maritime components, simulating cargo flows across export, import, and transit scenarios. Key agents include orders, transport vehicles, logistics hubs, and border checkpoints. The model is implemented in AnyLogic 8.9 and calibrated using a mix of official statistics, industry data, and field estimates. Results: The simulation replicates key logistics processes, identifies congestion points, and evaluates delivery performance under different scenarios. Experiments demonstrate how bottlenecks at terminals and border crossings affect delivery times, vehicle utilization, and hub load. The model allows testing infrastructure development options and scheduling policies. Conclusions: The approach enables a dynamic assessment of logistics efficiency under uncertainty and can support decision-making in transport planning. The novelty lies in the integrated simulation of multimodal freight flows with infrastructure constraints. The model serves as a foundation for digital twin applications and scenario-based planning.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence, Logistics Analytics, and Automation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
System Dynamics Modeling of the Jute Stick Charcoal (JSC) Supply Chain: Logistics and Policy Strategies for Sustainable Rural Industrialization in Bangladesh
by
Mohammad Shamsuddoha, Ahamed Ismail Hossain, Irma Dewan and Kazi Farzana Nur
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 171; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040171 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Jute, recognized as the ‘golden fiber’ of Bangladesh, produces a substantial amount of stick left over (waste), a byproduct of the fiber. Usually, unused jute sticks (JS) are thrown away or burned, since they are treated as landfill or unusable waste.
[...] Read more.
Background: Jute, recognized as the ‘golden fiber’ of Bangladesh, produces a substantial amount of stick left over (waste), a byproduct of the fiber. Usually, unused jute sticks (JS) are thrown away or burned, since they are treated as landfill or unusable waste. Noteworthy research gaps exist in the farming process, infrastructure, [supply chains], unfavorable policies, government interference, and insufficient farmers’ knowledge of the export market. This research examines the potential of jute stick charcoal (JSC) as a sustainable and value-added product within the circular economy framework. Methods: This study employs a system dynamics (SD) modeling approach to examine how various factors, including agricultural output, supply chain process efficiency, trade flows, and relevant variables, influence JSC supply chain performance. Considering technologies, logistics, and policy variables, this study constructed a simulation model with three scenarios: current, worst-case, and improved, using Vensim DSS to identify system behavior under changing conditions. Results: The simulation indicates that optimizing idle jute resources, enhancing supply chain processes, and expanding markets can increase economic returns, reduce waste, and create more rural jobs, particularly for women. Conclusions: Enhanced coordination, technologies, and logistics can reduce carbon emissions, benefit farmers, support rural industries, and contribute to SDGs 8, 12, and 13.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Inventory Management and Its Influence on the Supply of High-Value Products: Case Study Evidence
by
Ângela Silva, Márcia Silva and Ana Cristina Ferreira
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 170; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040170 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: In the context of increasing supply chain complexity, efficient inventory management has become important in enhancing the performance of logistics systems and sustaining the competitiveness of companies. Real-time visibility, tracking, and control over stock levels ensure responsiveness, reduce waste, and support
[...] Read more.
Background: In the context of increasing supply chain complexity, efficient inventory management has become important in enhancing the performance of logistics systems and sustaining the competitiveness of companies. Real-time visibility, tracking, and control over stock levels ensure responsiveness, reduce waste, and support strategic decision-making. Decision support systems that integrate demand analysis with inventory policies play a pivotal role in improving operational efficiency. This paper addresses the need for more efficient stock management to optimize purchasing and inventory costs within a manufacturing environment. Methods: Production planning processes were analyzed to determine material requirements, and a representative product was selected. The study involved ABC classification based on the average annual stock value of purchased parts, complemented by an XYZ analysis to evaluate demand variability. Afterwards, stock management policies were tested, namely, continuous and periodic review models. Each item was assessed to determine the most suitable inventory management method based on its consumption profile. Results: A comparison with the company’s existing approach revealed that for 9 out of the 13 materials studied, the application of stock management models led to improvements. Conclusions: The results show a potential cost reduction of 33% for the nine materials to which stock policies were successfully applied.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Supply Chains and Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Logistical and Economic Feasibility in the Cheese Production Chain: A Study Using Monte Carlo Simulation
by
Gustavo Alves de Melo, Luiz Gonzaga de Castro Júnior, Maria Gabriela Mendonça Peixoto, José Willer do Prado, Andre Luiz Marques Serrano and Thiago Henrique Nogueira
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 169; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040169 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Agricultural production plays a vital role in the global economy by integrating different sectors and promoting capital circulation across industries. In this context, the dairy sector emerges as a promising avenue for investment. This study aims to assess the economic feasibility
[...] Read more.
Background: Agricultural production plays a vital role in the global economy by integrating different sectors and promoting capital circulation across industries. In this context, the dairy sector emerges as a promising avenue for investment. This study aims to assess the economic feasibility of establishing a dairy plant for the production of parmesan and mozzarella cheeses in Lavras, MG, considering both deterministic and probabilistic scenarios. Methods: The analysis was conducted in three stages: data collection, deterministic economic feasibility analysis using traditional financial indicators (NPV, IRR, profitability rate, and payback), and a probabilistic assessment using the Monte Carlo simulation with 100,000 iterations to incorporate uncertainty into the model. Results: The deterministic results indicated a positive Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR) exceeding the Minimum Attractiveness Rate (MAR), and a profitability rate above 1.5, validating the investment’s viability. The probabilistic analysis reinforced these findings, with over 80% of simulated scenarios resulting in a positive NPV and over 77% showing IRR above the MAR. Key variables influencing profitability included market share, Class AB cheese consumer percentage, parmesan markup, operational costs, and per capita cheese consumption. Conclusions: The study confirms the economic feasibility of implementing the proposed dairy plant. The integration of Monte Carlo Simulation enhanced the robustness of the analysis by accounting for uncertainty, providing valuable insights for strategic decision-making. The project presents strong potential for regional development, job creation, and income generation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Bridging Theory and Practice: A Comprehensive Framework for Digital Supply Chain Orchestration Through Big Data Analytics
by
Samrena Jabeen, Mudassar Khan, Sabeen Hussain Bhatti, Nohman Khan, Mohammad Falahat and Muhammad Imran Qureshi
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 168; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040168 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Digital supply chain transformation research exhibits a critical gap, examining technologies in isolation rather than as integrated ecosystems. Methods: This study addresses this limitation by developing a comprehensive orchestration frame-work through PRISMA-guided systematic review of 96 publications (2012–2024) using bibliometric
[...] Read more.
Background: Digital supply chain transformation research exhibits a critical gap, examining technologies in isolation rather than as integrated ecosystems. Methods: This study addresses this limitation by developing a comprehensive orchestration frame-work through PRISMA-guided systematic review of 96 publications (2012–2024) using bibliometric analysis, structural topic modeling, and thematic synthesis across Scopus and Web of Science databases. Results: Analysis revealed three distinct research clusters: Supply Chain Management (centrality: 14.95), Digital Transformation (centrality: 9.50, density: 101.05), and Big Data Analytics (density: 113.22), with substantial negative correlations (−0.48 to −0.54) indicating organizational evolution from fragmented adoption toward integration. Conclusions: Publications increased 78% year-over-year during 2021–2022, while Supply Chain Management dominated topic prevalence (41%) and Big Data Analytics declined from 0.9 to 0.15 as practices normalized. The Digital Supply Chain Orchestration Framework conceptualizes transformation as multi-layered with hierarchical relationships between foundational domains, technological enablers, integration mechanisms, and value creation dimensions. This framework provides structured approaches for organizations to assess digital maturity, identify technological gaps, and develop strategic roadmaps aligned with Sustainable Development Goals, bridging theory and practice for integrated, value-driven digital transformation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
RFID-Enhanced Modified Two-Bin System for Reducing Excess Inventory of FMCG Industry
by
Shuvojit Das, Gazi Md. Mahbubul Alam Rajin, Md. Nazmul Hasan Sarker, Md. Mahraj Uddin, Golam Sakaline and Edit Süle
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 167; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040167 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Globally, in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry, excess inventory results from the bullwhip effect. Earlier, barcode-based two-bin systems were limited by manual scanning; hence, a more responsive system is needed to align the inventory with real-time demand. Prior studies have
[...] Read more.
Background: Globally, in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry, excess inventory results from the bullwhip effect. Earlier, barcode-based two-bin systems were limited by manual scanning; hence, a more responsive system is needed to align the inventory with real-time demand. Prior studies have predominantly concentrated on mitigating demand fluctuations and employed comparatively low-efficiency systems, hindering excess inventory (EI) reduction. Methods: This study proposes identifying research gaps, considering the distributor-manufacturer relationship, and developing an RFID-based modified two-bin system and mathematical model to reduce EI and control over manufacturers’ excessive cost. Results: This study tested through Python-based simulation using historical data from an FMCG manufacturer, and the proposed model achieved a reduction in 67% EI and 73% month-wise holding costs. Moreover, the integration of the Artificial Bee Colony algorithm optimizes rework rates within budget, including reworking shop-floor and holding costs, contributing to a monthly excessive cost reduction of 34–48%, alongside a corresponding 41–44% cumulative excessive cost reduction. Conclusions: Bringing significant implications on digitalized SCM, this study offers a practical and scalable solution for perishable FMCG items facing demand variability and budget constraints. Collectively, this novel perspective bridges research gaps and motivates future research for embedding trend-aligned parameters, enhancing the model’s performance through diverse SCM contexts like safety stock and backorder cost optimization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges and Solutions in the Turbulent World)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Probabilistic Analysis of Meat Distribution Logistics: Application of Monte Carlo Simulation
by
Gustavo Alves de Melo, Luiz Gonzaga de Castro Júnior, Maria Gabriela Mendonça Peixoto, Samuel Borges Barbosa, André Luiz Marques Serrano, Caroline Cambraia Furtado Campos, Matheus Vanzela and Ana Paula Dalmagro Delai
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 166; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040166 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The food sector plays a critical role in promoting population well-being and contributes significantly to economic, social, and environmental development. However, inefficiencies in distribution logistics often result in elevated operational costs, potentially compromising the viability of enterprises in this sector. This
[...] Read more.
Background: The food sector plays a critical role in promoting population well-being and contributes significantly to economic, social, and environmental development. However, inefficiencies in distribution logistics often result in elevated operational costs, potentially compromising the viability of enterprises in this sector. This study focuses on evaluating the economic feasibility of a fresh beef and pork distribution center in the southern region of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Methods: A case study methodology with a quantitative approach was adopted. Methodological triangulation was applied by combining a traditional Economic Feasibility Analysis (EFA) with a Monte Carlo Simulation to incorporate uncertainty in key input variables. This approach enabled a comprehensive assessment of project viability under both deterministic and probabilistic conditions. Results: The results indicated that distribution price per kilogram, market share, population growth, and per capita meat consumption had a positive correlation with profitability. The economic analysis confirmed the viability of the proposed distribution center, with high expected profitability and a short payback period. The Monte Carlo Simulation revealed that market share, unit price, and consumption levels are the most influential drivers of financial performance, while logistics costs represent the main limiting factor. Conclusions: This study provides a robust, data-driven framework for investment decision-making in food logistics infrastructure. It demonstrates the value of integrating deterministic and probabilistic analyses to improve risk management and strategic planning in the food distribution sector.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
On the Optimality of State-Dependent Base-Stock Policies for an Inventory System with PH-Type Disruptions
by
Davide Castellano
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 165; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040165 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The management of inventory under realistic supply chain disruptions, which are often non-exponential, challenges classical control theory. This study addresses the critical question of whether the optimality of simple base-stock policies holds under the combined influence of non-exponential disruptions and random yield.
[...] Read more.
Background: The management of inventory under realistic supply chain disruptions, which are often non-exponential, challenges classical control theory. This study addresses the critical question of whether the optimality of simple base-stock policies holds under the combined influence of non-exponential disruptions and random yield. Methods: We model the system as a Piecewise Deterministic Markov Process (PDMP) with impulse control, using Phase-Type (PH) distributions to capture non-memoryless event timings. The analysis involves proving the existence of a solution to the Average Cost Optimality Equation (ACOE) via a vanishing discount approach, and the framework is validated with a numerical experiment. Results: Our primary finding is a rigorous proof that a state-dependent base-stock policy is optimal, a significant generalisation of classical theory. We establish this by demonstrating the value function’s convexity. The numerical experiment quantifies the significant cost penalties (over 12%) incurred by using simpler, memoryless models for supply disruptions. Conclusions: The study provides a crucial theoretical justification for the robustness of simple threshold-based control policies in complex, realistic settings. It highlights for managers the importance of modelling the variability of disruptions, not just their average duration, to avoid costly strategic errors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Data-Driven Framework for Agri-Food Supply Chains: A Case Study on Inventory Optimization in Colombian Potatoes Management
by
Daniel Muñoz Rojas, Jairo R. Montoya-Torres and Diana M. Ayala Valderrama
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 164; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040164 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Mitigating the negative impacts of climate change and ensuring food security are critical challenges for sustainable development. Potato crops play a key role in global food security, and optimizing their supply chains can improve yields, reduce waste, and stabilize farmer incomes. This
[...] Read more.
Background: Mitigating the negative impacts of climate change and ensuring food security are critical challenges for sustainable development. Potato crops play a key role in global food security, and optimizing their supply chains can improve yields, reduce waste, and stabilize farmer incomes. This study focuses on the potato supply chain in Boyacá, Colombia, aiming to maximize profitability for smallholder farmers through a data-driven approach. Methods: We developed a hybrid framework combining the newsvendor model, Monte Carlo simulation, and machine learning to optimize inventory decisions under uncertain demand and price conditions. Historical data on potato demand and prices were analyzed to fit probability distributions, and simulation scenarios were run for three main potato varieties. Results: The results show that integrating these methods improves inventory decision-making, with the Criolla Colombia variety yielding positive profitability, while the Diacol Capiro and Pastusa Suprema varieties incur losses under current market conditions. The machine learning model enhances predictive accuracy and supports dynamic planning. Conclusions: The findings demonstrate the potential of advanced analytics to reduce waste, support sustainable practices, and inform agricultural policy. The proposed methodology offers a practical decision-support tool for stakeholders and can be adapted to other crops and regions facing similar operational challenges.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence, Logistics Analytics, and Automation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Engineering Vehicle Scheduling in Shipbuilding and Repair Yards Based on the Dual-Cycle Strategy
by
Jianhua Zhou, Haifei Wu, Hailong Weng, Lijun He, Wenfeng Li and Taiwei Yang
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 163; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040163 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: As a labor-, capital-, and technology-intensive sector, shipbuilding supports water transportation, international trade, and marine development, driving economic growth and employment. Yet rising raw material/labor costs now bottleneck enterprise performance, making cost reduction and efficiency improvement urgent for shipbuilding and repair firms.
[...] Read more.
Background: As a labor-, capital-, and technology-intensive sector, shipbuilding supports water transportation, international trade, and marine development, driving economic growth and employment. Yet rising raw material/labor costs now bottleneck enterprise performance, making cost reduction and efficiency improvement urgent for shipbuilding and repair firms. It is an effective way to improve logistics transportation efficiency for reducing the cost of shipbuilding and repair firms. However, there are still few methods specifically designed for logistics transportation scheduling in shipbuilding and repair firms. Methods: In this paper, a “dual-cycle” strategy is proposed to optimize material transportation and cut logistics vehicles’ empty-load rate in the shipbuilding and repair process. A mixed-integer programming model is built to minimize total empty travel time, considering task priorities and time windows. A genetic algorithm-based scheduling method is proposed to solve this complex scheduling model. Results: Simulation with real shipyard logistics data shows the proposed model and algorithm can effectively address the shipbuilding logistics vehicle scheduling problem. In addition, the proposed algorithm performs better than two other compared algorithms in handling the studied problem. Conclusions: This study aids shipbuilding and repair logistics managers in making scheduling plans and determining optimal vehicle numbers, supporting cost-efficiency improvement.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Modal Distribution Diversification and Intermodal Transport Analysis in Europe: A Comprehensive Investigation of Freight Transport Patterns
by
Ana Castro, Gabriel Ludke, Vânia Dias, Sónia Longras, Edit Sule, Estela Vilhena and António Rocha
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 162; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040162 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: This study analyzes modal distribution patterns across Europe and 28 European countries, employing clustering analysis to identify trends in transport mode utilization. The research quantifies logistics diversification, examining extreme cases and addressing gaps in understanding modal transitions affecting environmental and economic
[...] Read more.
Background: This study analyzes modal distribution patterns across Europe and 28 European countries, employing clustering analysis to identify trends in transport mode utilization. The research quantifies logistics diversification, examining extreme cases and addressing gaps in understanding modal transitions affecting environmental and economic performance. Methods: Statistical testing using compositional data transformations revealed significant differences between modal distributions (p < 0.001), justifying country-specific and European-level assessments. K-means clustering was applied to identify groups of countries with similar modal distribution patterns. Results: Maritime and road transport constitute the predominant modes across all analyzed countries in the study period. Among terrestrial modes, road transport dominates universally, exhibiting systematic growth, while rail transport experienced a corresponding decline. This trend directly contradicts European sustainability objectives promoting modal shift toward environmentally superior alternatives. Romania demonstrates the highest logistics diversification with the most balanced modal distribution, while Portugal exhibits the lowest diversification due to maritime transport dominance. K-means clustering positioned Portugal within a maritime-dominated group alongside Greece, Cyprus, and Ireland, reflecting similar geographical constraints and distribution patterns. Conclusions: The findings reveal critical aspects requiring further investigation concerning European modal distribution trends that challenge current policy effectiveness, highlighting the divergence between observed transport patterns and stated sustainability goals. These results provide essential insights for addressing persistent modal shift challenges in European transport systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges and Solutions in the Turbulent World)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Impact of IoT-Enabled Routing Optimization on Waste Collection Distance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Rafael R. Maciel, Adler Diniz de Souza, Rodrigo M. A. Almeida and João Paulo R. R. Leite
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 161; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040161 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Waste collection is a critical logistical challenge in urban management, and while Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are increasingly used to optimize collection routes, a systematic, quantitative synthesis of their impact is lacking. This study aims to bridge this gap by
[...] Read more.
Background: Waste collection is a critical logistical challenge in urban management, and while Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are increasingly used to optimize collection routes, a systematic, quantitative synthesis of their impact is lacking. This study aims to bridge this gap by quantifying the effect of IoT-enabled routing optimization on waste collection distances. Methods: We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis following the PRISMA protocol, searching the Scopus, IEEE Xplore, and ACM Digital Library databases. This process yielded 11 eligible studies, providing 21 distinct samples for quantitative synthesis. Results: The analysis reveals that IoT-enabled routing optimization reduces collection distance by a combined average of 21.51%. A significant disparity was found between study types, with simulation-based approaches reporting higher reductions (−39.79%) compared to real-world deployments (−12.37%). No statistically significant performance differences were observed across different routing algorithm categories or Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) variants. Conclusions: These findings provide robust quantitative evidence of the significant efficiency gains from implementing IoT-based smart waste management systems. The gap between simulated and real-world results underscores the need for practitioners to set realistic expectations, while our analysis supports the adoption of these technologies for more sustainable urban logistics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimizations and Operations Management of Modern Logistic Systems and Supply Chains)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Agent-Based Simulation of Digital Interoperability Thresholds in Fragmented Air Cargo Systems: Evidence from a Developing Country
by
Siska Amonalisa Silalahi, I Nyoman Pujawan and Moses Laksono Singgih
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 160; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040160 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: This study investigates how varying levels of digital interoperability affect coordination and performance in Indonesia’s decentralized air cargo system, reflecting the inefficiencies typical of fragmented digital infrastructures in developing economies. Methods: An Agent-Based Model (ABM) was developed to simulate interactions among shippers,
[...] Read more.
Background: This study investigates how varying levels of digital interoperability affect coordination and performance in Indonesia’s decentralized air cargo system, reflecting the inefficiencies typical of fragmented digital infrastructures in developing economies. Methods: An Agent-Based Model (ABM) was developed to simulate interactions among shippers, freight forwarders, airlines, ground handlers, and customs agents along the CGK–SIN/HKG export corridor. Six simulation scenarios combined varying levels of digital adoption, operational friction, and behavioral adaptivity to capture emergent coordination patterns and threshold dynamics. Results: The simulation identified a distinct interoperability threshold at approximately 60%, beyond which performance improvements became non-linear. Once this threshold was surpassed, clearance times decreased by more than 40%, and capacity utilization exceeded 85%, particularly when adaptive decision rules were implemented among agents. Conclusions: Digital transformation in fragmented logistics systems requires both technological connectivity and behavioral adaptivity. The proposed hybrid framework—integrating Autonomous Supply Chains (ASC), Graph-Based Digital Twins (GBDT), and interoperability thresholds—provides a simulation-based decision-support tool to determine when digitalization yields system-wide benefits. The study contributes theoretically by linking behavioral adaptivity and digital interoperability within a unified modeling approach, and practically by offering a quantitative benchmark for policymakers and practitioners seeking to develop efficient and resilient logistics ecosystems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic New Technological Solutions, Research Methods, Simulation and Analytical Models That Support the Development of Modern Transport Systems, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Applying Lean Six Sigma DMAIC to Improve Service Logistics in Tunisia’s Public Transport
by
Mohamed Karim Hajji, Asma Fekih, Alperen Bal and Hakan Tozan
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 159; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040159 - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: This study deploys the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC framework to achieve systemic optimization of the school subscription process in Tunisia’s public transport service, a critical administrative operation affecting efficiency and customer satisfaction across the urban mobility network. Methods: Beyond conventional
[...] Read more.
Background: This study deploys the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC framework to achieve systemic optimization of the school subscription process in Tunisia’s public transport service, a critical administrative operation affecting efficiency and customer satisfaction across the urban mobility network. Methods: Beyond conventional applications, the research integrates advanced analytical and process engineering tools, including capability indices, measurement system analysis (MSA), variance decomposition, and root-cause prioritization through Pareto–ANOVA integration, supported by a structured control plan aligned with ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 31000:2018 risk-management standards. Results: Quantitative diagnosis revealed severe process instability and nonconformities in information flow, workload balancing, and suboptimal resource allocation that constrained effective capacity utilization. Corrective interventions were modeled and validated through statistical control and real-time performance dashboards to institutionalize improvements and sustain process stability. The implemented actions led to a 37.5% reduction in cycle time, an 80% decrease in process errors, a 38.5% increase in customer satisfaction, and a 38.9% improvement in throughput. Conclusions: This study contributes theoretically by positioning Lean Six Sigma as a data-centric governance framework for stochastic capacity optimization and process redesign in public service systems, and practically by providing a replicable, evidence-based roadmap for operational excellence in governmental organizations within developing economies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Optimizations and Operations Management of Modern Logistic Systems and Supply Chains)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Logistics Hub Location for High-Speed Rail Freight Transport—Case Ottawa–Quebec City Corridor
by
Yong Lin Ren and Anjali Awasthi
Logistics 2025, 9(4), 158; https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040158 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: This paper develops a novel, interdisciplinary framework for optimizing high-speed rail (HSR) freight logistics hubs in the Ottawa–Quebec City corridor, addressing critical gaps in geospatial mismatches, static optimization limitations, and narrow sustainability scopes found in the existing literature. Methods: The research
[...] Read more.
Background: This paper develops a novel, interdisciplinary framework for optimizing high-speed rail (HSR) freight logistics hubs in the Ottawa–Quebec City corridor, addressing critical gaps in geospatial mismatches, static optimization limitations, and narrow sustainability scopes found in the existing literature. Methods: The research methodology integrates a hybrid graph neural network-reinforcement learning (GNN-RL) architecture that encodes 412 nodes into a dynamic graph with adaptive edge weights, fractal accessibility (α = 1.78) derived from fractional calculus (α = 0.75) to model non-linear urban growth patterns, and a multi-criteria sustainability evaluation framework embedding shadow pricing for externalities. Methodologically, the framework is validated through global sensitivity analysis and comparative testing against classical optimization models using real-world geospatial, operational, and economic datasets from the corridor. Results: Key findings demonstrate the framework’s superiority. Empirical results show an obvious reduction in emissions and lower logistics costs compared to classical models, with Pareto-optimal hubs identified. These hubs achieve the most GDP coverage of the corridor, reconciling economic efficiency with environmental resilience and social equity. Conclusions: This research establishes a replicable methodology for mid-latitude freight corridors, advancing low-carbon logistics through the integration of GNN-RL optimization, fractal spatial analysis, and sustainability assessment—bridging economic viability, environmental decarbonization, and social equity in HSR freight network design.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Computers, Informatics, Information, Logistics, Mathematics, Algorithms
Decision Science Applications and Models (DSAM)
Topic Editors: Daniel Riera Terrén, Angel A. Juan, Majsa Ammuriova, Laura CalvetDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Economies, Sustainability, World, Digital, Logistics
Sustainable Supply Chain Practices in A Digital Age
Topic Editors: Atour Taghipour, Youssef Tliche, Jomana Leroux, Hamdi RadhouiDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Drones, Infrastructures, Logistics, Modelling, Energies, Technologies, Future Transportation
New Technological Solutions, Research Methods, Simulation and Analytical Models That Support the Development of Modern Transport Systems, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Artur Kierzkowski, Tomasz Nowakowski, Agnieszka A. Tubis, Franciszek Restel, Tomasz Kisiel, Anna Jodejko-Pietruczuk, Mateusz Zaja̧c, Viktoria Ivannikova, Michał Stosiak, Andrija VidovićDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
Logistics, Sustainability, World
Research on Public Procurement for Sustainability
Topic Editors: Paul Davis, David McKevittDeadline: 31 March 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Logistics
Advancements in Building Resilient Reverse Supply Chains: Strategies, Technologies, and Sustainable Practices
Guest Editors: P. Carmona Marques, Marcele Elisa Fontana, Wesley Douglas SilvaDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Logistics
Investment, Risk, and Sustainability in Maritime Logistics and Supply Chain
Guest Editors: Amir Alizadeh, Haiying Jia, David MenachofDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Logistics
Advancing Circular Supply Chains: Integrating Logistics, Supply Chain Management and Circular Economy Practices
Guest Editors: Selman Karagöz, Derya Deliktas, Ramez Kian, Emrah BilgicDeadline: 5 January 2026
Special Issue in
Logistics
Multi-Criteria Decision-Making and Its Application in Sustainable Smart Logistics—2nd Edition
Guest Editors: Mladen Krstić, Željko Stević, Snežana TadićDeadline: 31 January 2026









