Journal Description
Infectious Disease Reports
Infectious Disease Reports
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on infectious diseases published bimonthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 33.5 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Infectious Diseases)
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Benefits of Publishing: We aim to be a leading journal on infectious diseases and to be in the top 20 journals listed in the Journal Citation Report (JCR) in this specific category in the near future.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Sex Differences in Outcomes of Critically Ill Adults with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Pneumonia: A Retrospective Exploratory Cohort Study
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 151; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060151 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia is an underrecognized cause of critical illness in adults. However, the influence of biological sex on intensive care unit (ICU) outcomes in this population remains unclear. Due to limited case numbers and incomplete covariate data, this study
[...] Read more.
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia is an underrecognized cause of critical illness in adults. However, the influence of biological sex on intensive care unit (ICU) outcomes in this population remains unclear. Due to limited case numbers and incomplete covariate data, this study was designed as exploratory and hypothesis-generating. Methods: We conducted a retrospective exploratory cohort study using the MIMIC-IV database and identified 105 adult ICU patients with laboratory-confirmed RSV pneumonia. Clinical variables included sex, age, ICU length of stay, use of mechanical ventilation, and weaning status. Exploratory multivariable logistic regression was performed to assess associations with in-hospital mortality and weaning success, acknowledging substantial missingness of comorbidity data, severity scores, and treatment variables. This limited adjustment for confounding and statistical power. Results: Overall, in-hospital mortality was 33.3%. Mortality was significantly higher among women than men (51.6% vs. 7.0%; p < 0.001), although the absolute number of deaths in men was very small. In adjusted models, female sex (OR 14.6, 95% CI 1.58–135.3, p = 0.018), reflecting model instability due to sparse events, as well as longer ICU stay (OR 1.22 per day, p = 0.001) were independently associated with higher mortality. Female sex was also associated with lower odds of successful weaning (OR 0.07, 95% CI 0.01–0.63, p = 0.018). These effect estimates must be interpreted cautiously due to the very small number of deaths in men and the resulting wide confidence intervals. Age and ventilation duration were not significant predictors. Conclusions: In this preliminary ICU cohort, female sex and prolonged ICU stay were linked to higher mortality and lower weaning success in adults with RSV pneumonia. However, given the very small number of events—particularly among male patients—together with the modest sample size, limited covariate availability, and unstable effect estimates, the findings should be viewed as exploratory rather than confirmatory. Larger, well-powered, prospective multicenter studies are needed to validate and further characterize potential sex-related differences in outcomes of RSV-associated critical illness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Beyond the Spike Glycoprotein: Mutational Signatures in SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins
by
Emil Tonon, Riccardo Cecchetto, Virginia Lotti, Anna Lagni, Erica Diani, Asia Palmisano, Marco Mantoan, Livio Montesarchio, Francesca Palladini, Giona Turri and Davide Gibellini
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 150; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060150 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants represents a major public health concern. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables genomic surveillance, facilitating the detection and monitoring of mutations that impact viral evolution. Methods: In this study, full-length SARS-CoV-2 genomes were analyzed between February 2022 and
[...] Read more.
Background: The continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants represents a major public health concern. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables genomic surveillance, facilitating the detection and monitoring of mutations that impact viral evolution. Methods: In this study, full-length SARS-CoV-2 genomes were analyzed between February 2022 and March 2024 as part of routine genomic surveillance conducted in Verona, Italy. Mutations in the envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) structural proteins were investigated. Only substitutions with a total prevalence of greater than 1% in the study dataset were considered. Results: A total of 178 mutations were identified across the three proteins (E: 16; M: 33; N: 129), of which 18 met the inclusion threshold (E: 3; M: 5; N: 10). Mutations were classified according to temporal dynamics as fixed, emerging, or transient. Throughout the study period, fixed mutations were consistently prevalent, emerging mutations appeared later but persisted with an ascending trend, while transient mutations displayed a single frequency peak before disappearing. Several mutations were reported with potential structural or functional relevance based on the existing literature, while others remain of unknown significance. Conclusions: The mutational patterns detected in this study broadly reflect global evolutionary trends of SARS-CoV-2. These findings emphasize the importance of continued genomic surveillance and underline the need for integrated experimental approaches to clarify the biological and epidemiological impact of poorly characterized mutations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
►▼
Show Figures
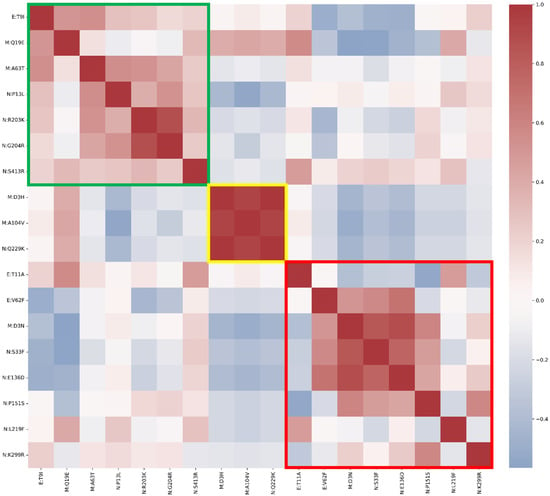
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Factors Associated with Condomless Anal Sex and Absence of Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Use Among Brazilian Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Laelson Rochelle Milanês Sousa, Patrícia Thais Cardoso da Silva, Allan Araujo Rodrigues, Márcio José dos Santos Silva, José Carlos Vinícius Jansen de Paz, Breno da Silva Oliveira, Daniel de Macêdo Rocha, Maria Wiklander, Elucir Gir and Renata Karina Reis
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 149; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060149 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM) in Brazil remain disproportionately affected by HIV. Combination prevention strategies, including Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), are critical, yet adherence remains a challenge. This study aimed to identify factors associated with the simultaneous practice of condomless anal
[...] Read more.
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM) in Brazil remain disproportionately affected by HIV. Combination prevention strategies, including Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), are critical, yet adherence remains a challenge. This study aimed to identify factors associated with the simultaneous practice of condomless anal sex and non-use of PrEP among Brazilian MSM. Methods: A national cross-sectional study was conducted in 2020 via an online questionnaire disseminated on social media and dating apps. The outcome was defined as reporting condomless anal sex and no PrEP use in the previous year. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed. Results: Among 1357 MSM participants, a high proportion (69.4%) reported condomless anal sex without PrEP use. Factors significantly associated with this behavior included being younger (18–28 years; AOR: 2.59), identifying as homosexual (AOR: 6.04), bisexual (AOR: 5.30), or pansexual (AOR: 8.67), having a steady partner (AOR: 4.57), engaging primarily in receptive or insertive anal sex, and having a prior STI diagnosis (AOR: 1.49). Conclusions: The confluence of condomless sex and PrEP non-use reveals a significant vulnerability profile among young MSM in Brazil, even within steady relationships. These findings highlight the originality of examining this combined behavioral outcome and underscore the urgent need for targeted, culturally sensitive prevention strategies that address risk perception and enhance PrEP uptake to meet the UNAIDS 2030 goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Containment Strategies of Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology, Surveillance and Prophylaxis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence in Ocular Toxoplasmosis Detection: A Scoping Review on Diagnostic Models, Data Challenges, and Future Directions
by
Dodit Suprianto, Loeki Enggar Fitri, Ovi Sofia, Akhmad Sabarudin, Wayan Firdaus Mahmudy, Muhammad Hatta Prabowo and Werasak Surareungchai
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 148; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060148 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ocular Toxoplasmosis (OT), a leading cause of infectious posterior uveitis, presents significant diagnostic challenges in atypical cases due to phenotypic overlap with other retinochoroiditides and a reliance on expert interpretation of multimodal imaging. This scoping review systematically maps the burgeoning application of artificial
[...] Read more.
Ocular Toxoplasmosis (OT), a leading cause of infectious posterior uveitis, presents significant diagnostic challenges in atypical cases due to phenotypic overlap with other retinochoroiditides and a reliance on expert interpretation of multimodal imaging. This scoping review systematically maps the burgeoning application of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning, in automating OT diagnosis. We synthesized 22 studies to characterize the current evidence, data landscape, and clinical translation readiness. Findings reveal a field in its nascent yet rapidly accelerating phase, dominated by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) applied to fundus photography for binary classification tasks, often reporting high accuracy (87–99.2%). However, development is critically constrained by small, imbalanced, single-center datasets, a near-universal lack of external validation, and insufficient explainable AI (XAI), creating a significant gap between technical promise and clinical utility. While AI demonstrates strong potential to standardize diagnosis and reduce subjectivity, its path to integration is hampered by over-reliance on internal validation, the “black box” nature of models, and an absence of implementation strategies. Future progress hinges on collaborative multi-center data curation, mandatory external and prospective validation, the integration of XAI for transparency, and a focused shift towards developing AI tools that assist in the complex differential diagnosis of posterior uveitis, ultimately bridging the translational chasm to clinical practice.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
When Fever Strikes Twice: A Case Report of Streptococcus pneumoniae Myelitis with Delayed-Onset Reactive Arthritis
by
Rosario Luca Norrito, Sergio Mastrilli, Felice Fiorello, Giuseppe Taormina, Lucia Di Giorgi, Grazia Mery Anna Ruggirello, Carlo Domenico Maida, Aurelio Piazza and Fabio Cartabellotta
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 147; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060147 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background:Streptococcus pneumoniae is a well-known pathogen responsible for respiratory and invasive diseases; however, central nervous system (CNS) involvement in the form of bacterial myelitis is exceedingly rare, particularly in immunocompetent adults. Moreover, the association between pneumococcal infections and reactive arthritis is scarcely
[...] Read more.
Background:Streptococcus pneumoniae is a well-known pathogen responsible for respiratory and invasive diseases; however, central nervous system (CNS) involvement in the form of bacterial myelitis is exceedingly rare, particularly in immunocompetent adults. Moreover, the association between pneumococcal infections and reactive arthritis is scarcely documented. We report an unusual case of pneumococcal myelitis complicated by reactive arthritis in an elderly patient with no evident immunosuppression. Case Presentation: A 68-year-old man with a medical history of hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia, multiple disc herniations, and a resected pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour presented to the emergency department with acute urinary retention and fever (38.5 °C). The neurological examination revealed lower limb weakness and decreased deep tendon reflexes. Spinal magnetic resonance demonstrated T2 hyperintense lesions suggestive of longitudinally transverse myelitis. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis showed pleocytosis with elevated protein levels; the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test resulted positive result for Streptococcus pneumoniae. The patient received intravenous antimicrobial and corticosteroid therapy with partial neurological improvement. Within days, he developed acute monoarthritis of the right ankle. Joint aspiration revealed sterile inflammatory fluid, negative for crystals and cultures, supporting a diagnosis of reactive arthritis. The articular symptoms resolved with the use of prednisone. An extensive immunological work-up was negative, and no other infectious or autoimmune triggers were identified. The patient underwent a structured rehabilitation program with gradual improvement in motor function over the following weeks. Conclusions: This case illustrates a rare clinical scenario of pneumococcal myelitis associated with reactive arthritis in a patient without overt immunosuppression. It highlights the importance of considering bacterial aetiologies in cases of acute transverse myelitis and the potential for unusual systemic immune responses such as reactive arthritis. Early recognition and the administration of appropriate antimicrobial and supportive therapies are crucial for improving neurological and systemic outcomes. To our knowledge, this is one of the first reported cases describing the co-occurrence of these two conditions in the context of S. pneumoniae infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bacterial Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
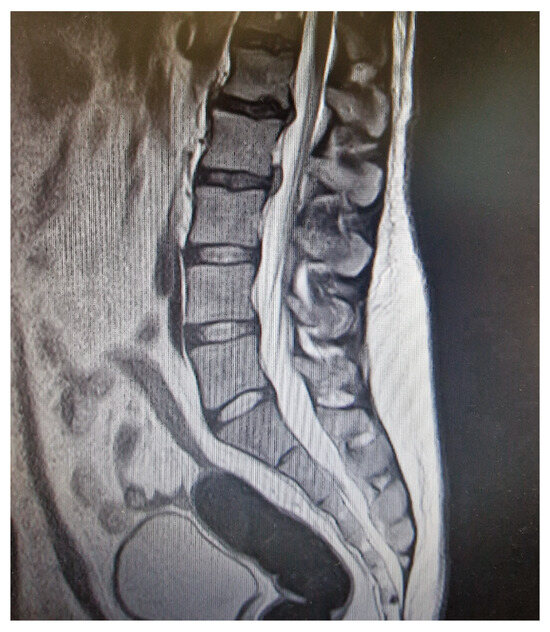
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Integration Models for Delivering COVID-19 Vaccines Through HIV Services in Low-and Middle-Income Countries: A Scoping Review
by
Nyanyiwe Masingi Mbeye, Roselyn Chipojola, Susan Banda, Prince Kaude, Aaron Mdolo, Charles Nwosisi and Sandra Mounier-Jack
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 146; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060146 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) remains a major global public health issue. People living with HIV (PLHIV) are among the vulnerable groups facing a higher risk of severe outcomes. Combining COVID-19 vaccination with HIV services can improve access and utilization of the
[...] Read more.
Background: The Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) remains a major global public health issue. People living with HIV (PLHIV) are among the vulnerable groups facing a higher risk of severe outcomes. Combining COVID-19 vaccination with HIV services can improve access and utilization of the vaccine among PLHIV although effective methods of delivery are yet to be ascertained. We conducted a scoping review to identify and describe models for delivering COVID-19 vaccines through HIV care services in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Methods: We used PRISMA-ScR guidelines to conduct the review. On 3rd and 4th February 2025, we searched PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE for studies on integrated COVID-19 vaccine delivery for PLHIV. Results: Three studies from sub-Saharan Africa reported call-back strategy, diverse partnership, and mixed service delivery models for implementing COVID-19 vaccination in HIV care services. Key strategies that were used included building capacity, generating demand, managing the supply chain, and involving stakeholders. The outcomes showed significant increases in vaccination coverage among PLHIV and reduced vaccine wastage. Conclusions: Integrating COVID-19 vaccination into HIV services is practical and effective in LMICs. It makes use of current infrastructure, partnerships, and local innovations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiological Profile and Diagnostic Outcomes of Blood Donors Following Hepatitis B Screening at the Largest Blood Bank in the State of Pará, Brazil
by
Núbia Caroline Costa de Almeida, Beatriz Monteiro Rodrigues Coelho, Camila Fonseca Barroso, Carlos Eduardo de Melo Amaral, Renata Bezerra Hermes de Castro, Letícia Martins Lamarão, Jacqueline Cortinhas Monteiro, Lucimar Di Paula dos Santos Madeira and Igor Brasil-Costa
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 145; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060145 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Serological and molecular screening for Hepatitis B virus (HBV) has been essential in reducing the risk of transfusion-transmitted infection, particularly in regions of high endemicity. This retrospective study aimed to analyze the epidemiological profile and laboratory outcomes of 259 blood donors deemed
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Serological and molecular screening for Hepatitis B virus (HBV) has been essential in reducing the risk of transfusion-transmitted infection, particularly in regions of high endemicity. This retrospective study aimed to analyze the epidemiological profile and laboratory outcomes of 259 blood donors deemed ineligible after initial reactive or inconclusive screening for HBV markers. Methods: Donors were summoned for revaluation at the HEMOPA Foundation, in Belém, Pará, between February 2015 and July 2016. Demographic data, risk factors, and results for HBsAg, anti-HBc, anti-HBs, and HBV DNA obtained at the donation and return time points were collected. Results: The mean age was 37 ± 11.25 years, with a predominance of males (56.8%) and first-time donors (76%). At the return time point, 63.7% presented a profile indicative of resolved HBV infection and 3.5% of active infection, 6.6% were susceptible to HBV infection, and 1.9% presented vaccine-induced HBV immunity. Cases of Occult Hepatitis B Infection (OBI, 0.4%) and Window Period (WP, 0.4%) were also identified. Conclusions: The findings reveal a high prevalence of resolved HBV infection among ineligible donors, particularly first-time donors, and reinforce the importance of combined serological and molecular screening, as well as the need for vaccination and health education strategies for at-risk populations. As a public blood bank located in the Amazon region, we highlight that local epidemiological specificities must be considered in the formulation of public health policies that are sensitive to the regional context.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Repurposing Agents as Anti-Infective Therapeutics to Aid in the Treatment of Candida auris Infections
by
Nazary Nebeluk and James B. Doub
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 144; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060144 - 27 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Candida auris is an emerging nosocomial fungal pathogen whose inherent multidrug resistance and ability to form biofilms make treatment extremely difficult. Given the limited number of therapeutic options available and the poor clinical outcomes associated with current therapeutics, this study evaluated the
[...] Read more.
Background: Candida auris is an emerging nosocomial fungal pathogen whose inherent multidrug resistance and ability to form biofilms make treatment extremely difficult. Given the limited number of therapeutic options available and the poor clinical outcomes associated with current therapeutics, this study evaluated the potential of repurposing existing agents to treat C. auris infections. Methods: Six clinical C. auris isolates from a single tertiary care center were tested for in vitro susceptibility to topical agents (hypochlorous acid, chlorhexidine gluconate, sodium hypochlorite) and systemic agents (N-acetylcysteine, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, ethyl pyruvate). Furthermore, these six isolates were allowed to form biofilms and the ability of repurposed agents to disrupt C. auris biofilms was measured. Results: All agents except N-acetylcysteine demonstrated inhibitory activity against planktonic C. auris. With respect to C. auris biofilms, these were characterized using electron microscopy and all six agents showed statistically significant (p < 0.05) ability to disrupt biofilms over controls. Moreover, the ability to disrupt biofilms was also statistically significant (p < 0.05) when compared to use of either normal saline or amphotericin B. Discussion: These findings support the potential clinical utility of repurposing existing agents, such as Ethyl Pyruvate or EDTA, for systemic C. auris infections, or hypochlorous acid for C. auris wound infections. Yet, further studies are needed to optimize dosing parameters and evaluate in vivo efficacy and tolerability.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Atypical Blistering Manifestation of Secondary Syphilis: Case Report and Review of Reported Cases
by
Agnieszka Markiewicz, Aleksandra Skórka and Agnieszka Owczarczyk-Saczonek
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 143; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060143 - 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Secondary syphilis typically presents with a non-pruritic maculopapular rash. However, vesicular and bullous manifestations are exceedingly rare in adults and may mimic autoimmune blistering diseases. The objective of this report is to describe atypical presentation of secondary syphilis with predominant vesiculobullous lesions
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Secondary syphilis typically presents with a non-pruritic maculopapular rash. However, vesicular and bullous manifestations are exceedingly rare in adults and may mimic autoimmune blistering diseases. The objective of this report is to describe atypical presentation of secondary syphilis with predominant vesiculobullous lesions and to emphasize the importance of including syphilis in the differential diagnosis of blistering skin diseases. Methods: We describe the case of a 46-year-old bisexual man with syphilis of unknown duration who presented with recurrent polymorphic skin eruptions, predominantly bullous and vesicular in nature. Clinical examination, serologic testing, and histopathologic evaluation were performed to establish the diagnosis. Results: Serologic tests confirmed active syphilis infection. A brief review of similar reported cases was conducted to highlight the clinical variability of vesiculobullous syphilis. Conclusions: Atypical vesiculobullous presentations of secondary syphilis pose significant diagnostic challenges and may be mistaken for autoimmune blistering disorders. Clinicians should maintain a high index of suspicion for syphilis in patients with polymorphic or blistering eruptions, particularly in those with risk factors for sexually transmitted infections. Awareness of these uncommon manifestations can facilitate timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Waning Protection Against Severe COVID-19 Following Vaccination: A Longitudinal IPTW Analysis of Emergency Department Encounters
by
Yuying Xing and Amit Bahl
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 142; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060142 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: The duration of protection that COVID-19 vaccination provides against severe outcomes remains uncertain. Accurately defining this timeframe is critical for informing effective vaccination policies and booster strategies. This investigation aimed to quantify the length and durability of vaccine-conferred protection against severe disease,
[...] Read more.
Background: The duration of protection that COVID-19 vaccination provides against severe outcomes remains uncertain. Accurately defining this timeframe is critical for informing effective vaccination policies and booster strategies. This investigation aimed to quantify the length and durability of vaccine-conferred protection against severe disease, delivering evidence to guide public health decision-making. Methods: We conducted a multi-site cohort study to evaluate the relationship between time since last COVID-19 vaccination and the risk of severe infection among emergency department (ED) patients with a principal diagnosis of COVID-19. Vaccination status was categorized by time since the last documented dose: unvaccinated, 0–6 months, 7–12 months, 13–18 months, and 19–24 months. The primary outcome was severe COVID-19, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or in-hospital death. Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting (IPTW) was used to adjust for baseline confounding based on age group, sex, race, comorbidity burden, immunocompromised status, and calendar time period (pre-2023 vs. post-2023). Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) for each vaccination interval compared to unvaccinated patients. Results: Between 1 December 2021, and 20 July 2024, 42,124 ED encounters were included in the analysis. In IPTW-weighted models, vaccination within 0–6 months (aHR 0.73, 95% CI 0.64–0.83), 7–12 months (aHR 0.72, 95% CI 0.64–0.82), and 13–18 months (aHR 0.67, 95% CI 0.57–0.79) was associated with a significantly reduced risk of severe outcomes. However, no significant protection was observed at 19–24 months (aHR 0.95, 95% CI 0.80–1.14). In age-stratified analyses, protection persisted longer in individuals aged ≥65 years than in those aged 50–64. Older age, male sex, comorbidities, and immunocompromised status were also associated with increased risk. Conclusions: COVID-19 vaccination provides sustained protection against severe outcomes for up to 18 months, after which effectiveness declines substantially. These findings support booster dose strategies based on time since last vaccination and targeted prioritization for high-risk populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Immunology and Vaccines)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Comparison of the Risk of Viral Load Blips in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Patients on Two-Drug Versus Three-Drug Antiretroviral Regimens
by
Kimihiro Yamaguchi, Masashi Ishihara, Yoshikazu Ikoma, Hitomi Sugiyama, Daichi Watanabe, Kei Fujita, Shin Lee, Tetsuji Morishita, Nobuhiro Kanemura, Masahito Shimizu and Hisashi Tsurumi
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 141; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060141 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The objective of this retrospective, multicenter cohort study was to compare the incidence of viral load blips between two-drug and three-drug antiretroviral therapy regimens in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients. Methods: A total of 121 patients were included, with 44
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The objective of this retrospective, multicenter cohort study was to compare the incidence of viral load blips between two-drug and three-drug antiretroviral therapy regimens in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients. Methods: A total of 121 patients were included, with 44 receiving two-drug regimens (e.g., dolutegravir/lamivudine) and 77 receiving three-drug regimens (e.g., bictegravir/tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine) at the time of analysis. The primary outcome was the occurrence of viral blips, defined as transient HIV-RNA elevations ≥ 50 copies/mL; a sensitivity analysis used ≥20 copies/mL. Results: Generalized estimating equation models adjusted for clinical covariates showed no significant difference in the odds of blip occurrence comparing three-drug with two-drug regimens, both for blips ≥ 50 (odds ratio [OR]: 2.64; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.91–7.70; p = 0.075) and ≥20 (OR: 1.76; 95% CI: 0.76–4.08; p = 0.190). In the two- and three-drug groups, the predicted probabilities of blips were 1.4% and 3.7% (p = 0.075) for blips ≥ 50, and 6.9% and 11.5% (p = 0.190) for ≥20, respectively. No virologic failure was observed. Conclusions: These findings suggest that two-drug regimens provide virologic control comparable to three-drug regimens and may be a viable clinical option due to fewer drug interactions, lower toxicity, and reduced cost.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Rare Case of Disseminated Nocardia transvalensis in an Immunocompetent Host
by
Branavan Ragunanthan, Kevin Wunderly, James Kleshinski and Caitlyn Hollingshead
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 140; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060140 - 12 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Nocardia are a group of bacteria known to cause pulmonary, cutaneous, neurologic, or disseminated diseases, usually in immunocompromised hosts. Within the Nocardia family is Nocardia transvalensis, a rarely encountered and underreported organism in the clinical literature. Case: Here, we
[...] Read more.
Background: Nocardia are a group of bacteria known to cause pulmonary, cutaneous, neurologic, or disseminated diseases, usually in immunocompromised hosts. Within the Nocardia family is Nocardia transvalensis, a rarely encountered and underreported organism in the clinical literature. Case: Here, we report the case of an immunocompetent patient presenting with lumbar pain diagnosed and treated for disseminated Nocardia transvalensis infection. Our patient underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), demonstrating possible abscess and subtle osteomyelitis of the L3-L4 facet joint and transverse process; a subsequent biopsy and culture resulted in Nocardia transvalensis. Further imaging with a computed tomography (CT) scan of the head revealed a 9 mm enhancing supratentorial lesion. The patient was treated with empiric antibiotics, but this was narrowed to levofloxacin, linezolid, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole after antibiotic sensitivities cropped up. Conclusions: Within this case, we extensively discuss the clinical pathogenesis of Nocardia transvalensis in an unusual host, the diagnostic approach to confirming active Nocardia infection, and the susceptibility patterns in a relatively unstudied organism.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bacterial Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Epidemiological and Clinical Changes in RSV-Associated Pneumonia in Children in Mexico Before and During the COVID 19 Pandemic
by
Ilen Adriana Diaz-Torres, Isamu Daniel Cabrera-Takane, Fanny Yasmin Ortega-Vargas, Aldo Agustin Herrera-González, Miguel Leonardo Garcia-León, Patricia Bautista-Carbajal, Daniel E. Noyola, Maria Susana Juárez-Tobías, Pedro Antonio Martínez-Arce, María del Carmen Espinosa-Sotero, Verónica Tabla-Orozco, Gerardo Martínez-Aguilar, Fabian Rojas-Larios and Rosa María Wong-Chew
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 139; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060139 - 8 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) significantly affects young children. In 2020, at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, widespread public health measures temporarily interrupted RSV transmission. However, by mid-2021, an atypical resurgence of RSV was observed. The objective of this study was to
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) significantly affects young children. In 2020, at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, widespread public health measures temporarily interrupted RSV transmission. However, by mid-2021, an atypical resurgence of RSV was observed. The objective of this study was to compare the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of RSV infections in children before and during the second half of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in Mexico. Methods: A comparative ambispective longitudinal epidemiological study was conducted using two distinct cohorts: one from 2010 to 2013 and another from 2021 to 2023. The study included children under five years of age diagnosed with RSV-related pneumonia. Statistical analyses included Student’s t-tests, chi-square tests, and logistic regression to identify risk factors associated with severe pneumonia. Incidence density was calculated as the number of RSV-positive pneumonia cases per 10 new pneumonia admissions per month. Results: The mean age of affected children increased from 10 to 15 months. RSV activity began earlier in 2021, emerging during the summer months, and showed a higher incidence than in previous seasons. RSV type B was significantly more common during the pandemic period (58.5% vs. 3.8%), and the proportion of co-infections also increased (60% vs. 39%), indicating a change in the viral landscape. Conclusions: These findings indicate a shift in RSV seasonality toward summer and autumn, increased case incidence, and infections in older children. These observations underscore the need for ongoing surveillance to better understand evolving RSV patterns, especially in the context of complex public health scenarios like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Viral Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology and Prevention Through Vaccination)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of COVID-19 on Health-Related Quality of Life and Mental Health Among Employees in Health and Social Services—A Longitudinal Study
by
Claudia Peters, Madeleine Dulon, Anja Schablon, Jan Felix Kersten and Albert Nienhaus
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 138; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060138 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Healthcare and social workers were at increased risk of infection during the COVID-19 pandemic, and were therefore also at increased risk of long-term physical and mental health consequences due to infection. This study aimed to investigate the course of health-related quality of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Healthcare and social workers were at increased risk of infection during the COVID-19 pandemic, and were therefore also at increased risk of long-term physical and mental health consequences due to infection. This study aimed to investigate the course of health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and mental health, in terms of depression and anxiety. Methods: A longitudinal study surveyed employees in health and social services diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 in 2020 over a period of three years. Results: A total of 834 individuals participated in all four surveys. The mean age was 50.2 years (SD 5.8), with 82.3% of the participants being female. Mixed-model analyses were performed to examine the development over time. The results showed significant impairments in physical and mental HRQoL, as well as in mental health. Factors influencing physical HRQoL were gender, age, and pre-existing conditions. Pre-existing mental health conditions and self-reported health prior to infection were found to be predictors of mental HRQoL and symptoms of depression and anxiety. Those with persistent symptoms reported a significantly lower quality of life than those who had recovered. The mean physical HRQoL among participants with ongoing symptoms was 38.6, compared with 50.0 for those without symptoms, and the mean mental HRQoL was 40.4 versus 50.1 (p < 0.001). Conclusions: These findings suggest that health-related quality of life and mental health should continue to be monitored to prevent long-term psychological distress.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Difficult-to-Treat Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Caused by Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-Producing Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Case Series
by
Luca Pipitò, Chiara Vincenza Mazzola, Giulio D’Agati, Eleonora Bono, Raffaella Rubino, Silvia Bonura, Claudia Gioè, Teresa Fasciana and Antonio Cascio
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 137; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060137 - 3 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) has emerged as a genetically distinct lineage from healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA), often producing Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) and causing severe skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) in otherwise healthy individuals. Methods: We describe five cases of
[...] Read more.
Background: Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) has emerged as a genetically distinct lineage from healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA), often producing Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) and causing severe skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) in otherwise healthy individuals. Methods: We describe five cases of PVL-positive CA-MRSA SSTIs admitted to the Infectious Diseases Unit of the University Hospital “Paolo Giaccone,” Palermo, Italy, between 2024 and 2025. Case inclusion followed the CDC criteria for CA-MRSA. Microbiological identification was performed using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing followed EUCAST standards. PVL gene presence was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction. Results: Clinical management included surgical drainage, systemic antibiotic therapy, and decolonization of both patients and close contacts. Long-acting lipoglycopeptides (oritavancin or dalbavancin) were evaluated as therapeutic options to achieve clinical resolution. Conclusions: PVL-positive CA-MRSA infections are characterized by recurrence, intrafamilial clustering, and frequent therapeutic failure with standard oral agents. Effective management requires an integrated approach combining prompt surgical drainage; systemic therapy, preferably including long-acting lipoglycopeptides; and comprehensive decolonization of all close contacts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging and Re-Emerging Infections: Surveillance, Diagnostics, and Global Health Impacts)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Six-Year Surveillance of Nasal Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Colonization on Intensive Care Unit Admission: Do We Need Screening?
by
Esma Eryilmaz Eren, Nursel Karagöz, Esma Saatçi, İlhami Çelik and Emine Alp Meşe
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 136; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060136 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonization is a risk factor for potential staphylococcal infection and outbreaks. Although it is recommended to obtain a swab culture to detect nasal colonization its necessity in low-prevalence countries is debated. The aim of this study was to
[...] Read more.
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) colonization is a risk factor for potential staphylococcal infection and outbreaks. Although it is recommended to obtain a swab culture to detect nasal colonization its necessity in low-prevalence countries is debated. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of MRSA nasal colonization, the rate of invasive infection development, and the risk factors for invasive infections in patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study included patients who were followed up in one of the adult intensive care units at Kayseri City Training and Research Hospital between 1 January 2019 and 31 December 2024 (6 years) and from whom a culture was taken at the time of hospital admission to detect MRSA colonization in the nose. MRSA carriers were examined for the development of any invasive infection caused by MRSA within 28 days of their relevant admission. Results: Over a total period of six years, nasal swab samples were collected from 22,913 patients, and MRSA colonization was detected in 939 (4.0%). Of the patients with MRSA colonization, 32 (3.4%) were excluded from the analysis because they already had invasive MRSA infection. Additionally, 431 patients (45.8%) were excluded from the analysis because they were discharged or died within the first seven days of their admission. Consequently, invasive MRSA infection developed within 28 days in 29 of the 476 patients with MRSA colonization (6.0%). Patients who developed invasive infection had a higher rate of chronic renal failure (p < 0.001), hemodialysis (p < 0.001), central venous catheter (p = 0.028), staying in nursing home (p = 0.001), and a history of hospitalization within the last 90 days (p = 0.015). In the multivariable regression analysis, routine hemodialysis (OR: 5.216, p = 0.015), nursing home stay (OR: 3.668, p = 0.014), and a history of hospitalization within the last 90 days (OR: 2.458, p = 0.028) were found to be risk factors for developing invasive infection. The most common invasive infections were ventilator-associated pneumonia (n = 9), surgical site infection (n = 7), and catheter-related bloodstream infection (n = 6). All 29 strains were susceptible to vancomycin, linezolid, and daptomycin, while one strain was resistant to teicoplanin (3.5%). Conclusions: MRSA colonization has been detected in 4% of patients admitted to the intensive care unit. Screening should be performed because MRSA colonization may be a risk factor for invasive infections; however, screening all patients would be prohibitively expensive and labor-intensive. Instead, it may be more appropriate to identify risk factors and then screen select patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Healthcare-Associated Infections)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Molecular Characterization of Chlamydia trachomatis Infection and Its Impact on Sperm Characteristics of Moroccan Infertile Men
by
Mariame Kabbour, Modou Mamoune Mbaye, Bouchra Ghazi, Achraf Zakaria, Rajaa Ait Mhand, Noureddine Louanjli and Moncef Benkhalifa
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 135; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060135 - 22 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Infections of the urogenital tract have experienced renewed interest in recent years, due to their frequency and also their impact on sperm parameters and the fertilizing quality of spermatozoa. Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) represents an intracellular microorganism responsible for sexually transmitted infections
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Infections of the urogenital tract have experienced renewed interest in recent years, due to their frequency and also their impact on sperm parameters and the fertilizing quality of spermatozoa. Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) represents an intracellular microorganism responsible for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in men and women. A reliable method of diagnosing this infection is therefore necessary because of the rapid onset of infection and the increase in STI-related diseases and their treatment costs. Methods: We analyzed 2371 semen samples from infertile men and detected the presence anti-CT IgG antibodies by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA), followed by real-time PCR confirmation of CT DNA whose target is the lipopolysaccharide (LPS). We assessed the effect of CT infections on characteristic parameters of sperm quality, including concentration, motility, viability, and morphology. The impact on sperm DNA quality was assessed by DNA fragmentation index (S) and decondensation of chromatin index (SDI) by the TUNEL technique. Results: Analysis of the results showed significant differences in mobility, concentration, and morphology (p < 0.05) between the control group, positive CT infection with normal spermiogram status (CT+/Normal SG) group, and positive CT infection with abnormal spermiogram status (CT+/Abnormal SG) group. A significant increase in the DFI and the SDI was found between the control group and the case groups, respectively (p < 0.01). Conclusions: Our results confirm that CT infection is associated with significant alterations in sperm parameters and sperm DNA quality. Regular CT screening by qPCR should be encouraged in couples suffering from unexplained infertility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge, Attitude and Practices of Primary Care Physicians Regarding Infection Control of Tuberculosis in Primary Health Care Centers, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
by
Yasser Alhazzani, Abdulaziz Nasser Alahmari, Bandar K. AlRabiah, Khalid F. Alsadhan, Abdulaziz Yahya Sahhari and Fahad Alrabieah
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(5), 134; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17050134 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a public health concern in Saudi Arabia, where primary care physicians play a crucial role in early detection and infection control. This study assessed physicians’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) regarding TB infection control in Riyadh. Methods: A cross-sectional
[...] Read more.
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a public health concern in Saudi Arabia, where primary care physicians play a crucial role in early detection and infection control. This study assessed physicians’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) regarding TB infection control in Riyadh. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 205 physicians in primary healthcare centers using a validated electronic questionnaire. Knowledge scores were classified as good (≥8/14 correct) or poor (<8). Descriptive statistics and chi-square/t-tests were applied. Results: The mean knowledge score was 8.5 (SD = 2.1); 57.1% of physicians demonstrated good knowledge. Knowledge was significantly associated with specialization (p = 0.049), position (p = 0.031), and monthly patient load (p = 0.031). While 92.7% correctly identified airborne transmission, only 30.7% knew when a TB patient becomes noninfectious. Most participants (80%) had not received TB-related training in the past year. Conclusions: Primary care physicians in Riyadh show moderate knowledge and positive attitudes, but important gaps remain in diagnostic clarity and infection control timelines. Strengthening continuous medical education and integrating TB-specific modules into the Saudi national TB control program are essential to standardize practices and improve patient outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
Open AccessBrief Report
Common Superficial Bacterial Skin Infections Self-Reported by 1047 Greek Competitive Swimmers: A 2021 Retrospective Study
by
Eleni Sfyri, Niki Tertipi, Vasiliki Kefala, Vasiliki-Sofia Grech and Efstathios Rallis
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(5), 133; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17050133 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Superficial bacterial skin infections are common, particularly among athletes. In swimming, data on folliculitis, impetigo, and pitted keratolysis are limited. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of superficial bacterial skin infections in young competitive swimmers from Greek clubs. Methods: An anonymous
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Superficial bacterial skin infections are common, particularly among athletes. In swimming, data on folliculitis, impetigo, and pitted keratolysis are limited. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of superficial bacterial skin infections in young competitive swimmers from Greek clubs. Methods: An anonymous questionnaire was distributed to all swimming clubs through the Hellenic Swimming Federation, with a request to forward it to their members. It was completed by 1047 swimmers or their parents. Data collection included skin conditions along with explanatory notes, as well as additional information such as gender, swimming age category, season of occurrence, training routine details, and hygiene-related behaviors. Results: The study showed that 2.7% of participants reported being affected by folliculitis, 10.9% by impetigo, and 3.2% by pitted keratolysis. Infections were significantly correlated with age categories. Folliculitis and pitted keratolysis were less frequent and were mainly reported by adolescent and adult swimmers. In contrast, impetigo was more common and primarily affected younger age groups. Specific behaviors—such as placing towels and clothes on locker room benches—were significantly associated with pitted keratolysis (p = 0.036) and impetigo (p < 0.001). Sharing equipment was associated with all three infections. Conclusions: This study highlights the high prevalence of bacterial skin infections in Greek swimmers, likely due to moisture exposure, shared equipment, and specific hygiene habits.
Full article
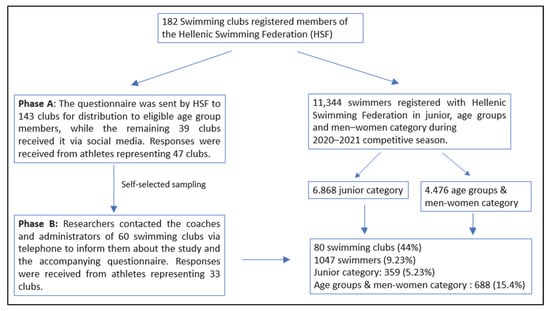
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Distribution and Factors Associated with Neisseria gonorrhoeae Cases in Kampala, Uganda, 2016–2020
by
Fahad Lwigale, Conrad Tumwine, Reuben Kiggundu, Patrick Elungat, Hope Mackline, Dathan M. Byonanebye, Andrew Kambugu and Francis Kakooza
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(5), 132; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17050132 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: Gonorrhoea is a common sexually transmitted infection with serious health consequences if not well-treated. Resistance to common therapeutic agents and limited diagnostics further heighten its burden on sexual and reproductive health. This study determined the positivity level, spatial distribution and factors
[...] Read more.
Background: Gonorrhoea is a common sexually transmitted infection with serious health consequences if not well-treated. Resistance to common therapeutic agents and limited diagnostics further heighten its burden on sexual and reproductive health. This study determined the positivity level, spatial distribution and factors influencing test positivity for Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Kampala, Uganda. Methods: Clinical data and urethral swabs were primarily collected from men with urethritis at 10 high-volume surveillance facilities. Laboratory analysis followed conventional microbiology techniques. Statistical analysis was conducted using R 4.4.3. Results: Among 1663 participants, 923 (56%, 95% CI: 53–58%) tested positive for N. gonorrhoeae, with comparable levels in Kampala divisions. Co-positivity of HIV and N. gonorrhoeae ranged from 5–27%. At bivariable analysis, there was a lower risk of testing positive for N. gonorrhoeae among participants aged above 24 years. Individuals who never use condoms or infrequently use them were marginally at a higher risk for positivity compared to routine users. Only age was the independent predictor for positivity with N. gonorrhoeae (aPR = 0.93, 95% CI: 0.87–0.99, p-value = 0.017), with men aged above 24 years being less likely to test positive for N. gonorrhoeae. Conclusions: Spatial distribution of N. gonorrhoeae positivity in Kampala was found not to be significantly influenced by location in any of the five divisions. Public health interventions should be tailored to focus on the high-risk groups such as men aged below 25 years, incorporating targeted education and prevention programs, particularly emphasizing consistent condom use among sexually active individuals to improve sexual and reproductive health in Kampala and greater Uganda.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Infectious Disease Reports, Insects, IJERPH, Pathogens, TropicalMed, Zoonotic Diseases
Vector-Borne Disease Spatial Epidemiology, Disease Ecology, and Zoonoses
Topic Editors: Chad L. Cross, Louisa Alexandra MessengerDeadline: 31 December 2026
Topic in
IJERPH, TropicalMed, Microorganisms, Infectious Disease Reports, Pathogens
Genetic, Environmental, and Climatic Drivers of Emerging Arboviruses and Public Health Implications
Topic Editors: André Ricardo Ribas Freitas, Pedro María Alarcón-Elbal, Luciano Pamplona de Góes CavalcantiDeadline: 20 January 2027
Topic in
Diseases, Epidemiologia, Infectious Disease Reports, Medicina, TropicalMed
Surveillance Systems and Predictive Analytics for Epidemics
Topic Editors: Georgia Kourlaba, Elisavet StavropoulouDeadline: 31 January 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Epidemiology, Prevention and Research on Dengue Virus
Guest Editor: Alessandro BartoloniDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Containment Strategies of Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology, Surveillance and Prophylaxis
Guest Editors: Giovanni Boccia, Gianluigi Franci, Enrica SerretielloDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Healthcare-Associated Infections
Guest Editor: Emine Alp MeşeDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Infections in Vulnerable Populations
Guest Editors: Botond Lakatos, Francesco Di GennaroDeadline: 30 June 2026












