Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in Figure 2. The corrected Figure 2 appears below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
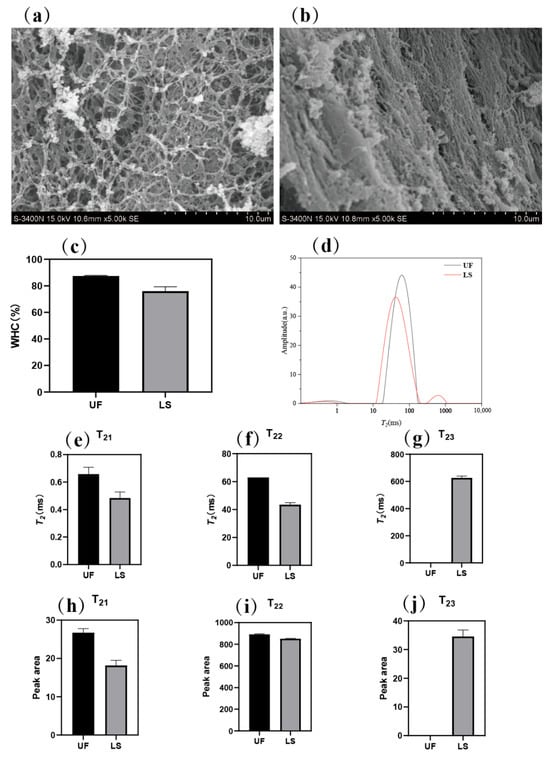
Figure 2.
Microstructure of unfermented (a) and fermented (b) giant squid; WHC (c) and T2 relaxation time distribution (d) of unfermented and fermented giant squid; T2 relaxation time (e–g) and peak area (h–j) of unfermented and fermented giant squid. UF and LS represent unfermented samples and fermented samples, respectively.
Reference
- Mu, H.; Weng, P.; Wu, Z. Mixed Inoculation with Lacticaseibacillus casei and Staphylococcus carnosus Improves Safety, Gel Properties and Flavor of Giant Squid Surimi Without Added Seasonings. Fermentation 2025, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).