Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of autochthonous strains (Pediococcus pentosaceus 128b, Latilactobacillus sakei S15, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum S91, L. plantarum S24 and Staphylococcus carnosus G109) used as mono and mixed starter cultures on the quality attributes of traditionally produced sucuk, a Turkish dry fermented sausage, in a local small-scale facility. At the end of ripening, samples underwent comprehensive microbiological and physicochemical analyses. The use of autochthonous starter cultures (ASC) showed no statistically significant influence on thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances and water activity value. Lower pH values were observed in groups with autochthonous lactic acid bacteria strains (ALABS) compared to the control group. However, ALABS inhibited Micrococcus/Staphylococcus growth by rapidly lowering the pH, except in the groups with S. carnosus G109. The use of ASC led to an increase in the L* values of sucuk samples, except monoculture L. plantarum S91. The correlation heat map illustrating the relationships between the starter cultures and volatile compounds revealed that all groups containing L. plantarum S91 exhibit a volatile compound profile different from other single or mixed cultures. According to the results of the principal component analysis performed to determine the relationship between the chemical groups of the starter cultures and volatile compounds, the groups containing L. plantarum S91 differed from the other groups and showed positive correlations with phenols, furans, acids, terpenes, aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, nitrogenous compounds, esters, and aliphatic hydrocarbons.
1. Introduction
Fermentation is one of the oldest known methods of food preservation. This method relies on the biological activities of microorganisms. Metabolites formed during fermentation suppress the growth and viability of food-borne pathogens and spoilage microorganisms in foodstuffs [1]. Meat fermentation is defined as a microbial ecosystem in which bacteria, yeasts, and molds coexist. During fermentation, perishable substances such as meat and fat are improved adding sodium chloride, and through the effectiveness of the drying process are transformed into microbiologically stable final products [2]. Fermented sausages are gastronomically valuable products with a long history [3]. Fermentation plays a fundamental role in the production of these products. Although fermentation is performed by spontaneous lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in traditional production, starter cultures are commonly employed in industrial production. Choosing a starter culture suitable for the product type is a key production strategy [4]. Fermented sausages are produced by adding salt, sugars, nitrite, nitrate, and spices to a mixture of minced fat and lean meat, filling the batter into casings, and keeping the products in ripening chambers for several weeks, where they are hung vertically [5]. Traditional foods are important cultural heritage products that bridge a country’s past and present [6]. One of them is sucuk, the best-known traditional dry fermented meat product in Türkiye, made using beef and/or water buffalo meat, beef fat and/or sheep tail fat, sugar, salt, curing agents (nitrite and/or nitrate), and many spices. An important feature that distinguishes sucuk from other European sausages is that it is not smoked. Sucuk is prepared by filling small-diameter casings and subjecting them to a relatively short ripening process [7].
Food fermentation is a process driven by the adventitious microbiota naturally found in raw food ingredients and in the environment and has evolved over centuries towards the controlled use of starter cultures [8]. The choice of starter culture determines the characteristics and quality of fermented sausages. Starter cultures need to be well adapted and dominant in the meat environment and throughout the production process. Commercial starter cultures, which are widely used in fermented sausage production, are selected according to their fermentative, proteolytic, and lipolytic properties, but they may not always be preferred because they can cause the loss of some desirable sensory properties [9]. The addition of desirable microorganisms in the meat industry is used to ensure product safety by inhibiting pathogenic bacteria and prolonging the shelf life of the product by preventing undesirable changes caused by spoilage microorganisms or abiotic reactions, while also providing new sensory properties and beneficial health effects [10]. LAB and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) are the two main bacterial groups isolated from dry fermented sausages [11]. LAB decrease pH by producing lactic acid, thereby preventing the growth of undesirable bacteria and affecting protein coagulation. CoNS possess nitrate reductase and catalase activities [6]. Thus, they play a role in color formation and delaying lipid oxidation. They also contribute to flavor formation via lipolytic and proteolytic activities [12]. The use of autochthonous LAB originating from fermented meats offers several advantages such as better adaptation to meat fermentation conditions, control of the ripening process, and inhibition of the growth of spontaneous microorganisms [6,11,13].
Autochthonous starter cultures (ASC) can be used to produce typical regional fermented meat products, ensure new sensory properties, and improve product safety, stability, and shelf life [14]. Several studies have been conducted on the use of autochthonous strains as starter cultures for sucuk production [9,15,16,17,18,19,20]. These studies were conducted under controlled fermentation conditions. However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have investigated the applicability of autochthonous strains under small-scale facility conditions in the traditional production of sucuk. Traditional fermented sausage production often relies on the spontaneous microorganisms present in the raw materials and the production environment, resulting in an uncontrolled process. Unpredictable changes in the microbiota can occur even within the same batch, leading to inconsistencies in product flavor and safety. Consequently, ensuring uniformity and maintaining high quality in sausages can be challenging. The best solution to this problem is the selection and inoculation of appropriate starter cultures [21,22]. On the other hand, the use of mixed starter cultures consisting of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) is also recommended to achieve the desired characteristics in fermented sausages. Moreover, it is emphasized that the bacterial communities of fermented sausages have significant effects on their aroma and taste properties [21,22,23]. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the effects of selected autochthonous strains (Latilactobacillus sakei S15, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum S24, L. plantarum S91, Pediococcus pentosaceus 128b, and Staphylococcus carnosus G109) previously isolated and identified from sucuk [24], when applied as mono and mixed starter cultures under traditional processing conditions. For this purpose, ten different sucuk formulations, including a control group, were prepared and produced in a local small-scale facility using traditional techniques. Following ripening, the samples were subjected to comprehensive microbiological and physicochemical analyses to determine the influence of these starter cultures on the overall quality characteristics of traditionally produced sucuk.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
In this study, beef cuts from the round and chuck regions of the carcass were trimmed into smaller pieces and stored at −20 °C. Beef fat (intermuscular fat) was also obtained from the beef carcass, cut into small pieces, and stored at −20 °C.
Pediococcus pentosaceus 128b (KT327865), Latilactobacillus sakei S15 (KR025387), Lactiplantibacillus plantarum S91 (KT327838), L. plantarum S24 (KT327849), and Staphylococcus carnosus G109 (KY011911), isolated and identified through 16S rRNA gene sequencing from sucuk, were used as starter cultures [24]. L. sakei S15, L. plantarum S24, L. plantarum S91 and P. pentosaceus 128b were grown on de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe broth (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), whereas S. carnosus G109 was grown in Brain Heart Infusion broth (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) at 30 °C for 24 h.
2.2. Production of Sucuk
Sucuk production was carried out in a local small-scale facility using traditional techniques. Sucuk batter was prepared using, per kilogram of meat and fat mixture (80% lean beef and 20% beef fat), 25 g salt, 4 g sucrose, 7 g red pepper, 5 g black pepper, 9 g cumin, 2.5 g allspice, and 10 g garlic. Nine different starter culture formulations were prepared, as presented in Table 1. P. pentosaceus 128b, L. sakei S15, L. plantarum S24 and L. plantarum S91 were added to the sucuk batter at 7 log cfu/g, and S. carnosus G109 was added at 6 log cfu/g. Batches produced without starter cultures were used as the control group. After the sucuk batter was prepared, it was stuffed into collagen casings (38 mm, Naturin Darm, Germany) and ripened in a climate chamber (Özlü Makine, Zonguldak, Türkiye) (fermentation at 24 ± 1 °C for 24 h, followed by drying at 18 ± 2 °C for 7 days) under plant conditions.

Table 1.
Design of mono and mixed starter cultures.
2.3. Microbiological Analysis
Each 25 g sample portion was aseptically weighed, transferred into a sterile stomacher bag, and diluted with 225 mL of sterile physiological saline solution (0.85%). The mixture was homogenized for 2 min using a stomacher (Lab Stomacher Blender 400-BA 7021, Seward, UK), and the spread-plate method was used. Lactic acid bacteria counts were determined on de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe agar (MRS, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) under anaerobic conditions (Anaerocult A, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) at 30 °C for 48 h. Micrococcus/Staphylococcus were enumerated on Mannitol Salt Phenol Red agar (MSA, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. Mold/yeast counts were quantified using Rose Bengal Chloramphenicol agar (RBC, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) incubated at 25 °C for 72 h. Enterobacteriaceae were enumerated on Violet Red Bile Dextrose agar (VRBD, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) incubated at 30 °C for 48 h [25]. All microbial counts were reported as log10 colony-forming unit per g (log10 cfu/g).
2.4. pH and Water Activity (aw)
For pH analysis, 10 g of each sample was homogenized with 100 mL of distilled water (1:10 w/v) using an Ultra-Turrax homogenizer (IKA T25 basic, Staufen, Germany). The pH was subsequently measured with a calibrated digital pH meter (S220, Mettler-Toledo, Switzerland). Water activity (aw) was determined using a TH-500 aw Sprint apparatus (Novasina, Pfäffikon, Switzerland), with samples placed in the measuring chamber and analyzed at a constant temperature of 25 °C.
2.5. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS)
The TBARS values were determined according to the method described by Lemon [26], and the results were expressed as mg of malondialdehyde (MDA) per kg of sample.
2.6. Instrumental Color
The color parameters of the sucuk samples were evaluated using a Minolta colorimeter (CR-200, Minolta Co., Osaka, Japan). Color measurements were recorded according to the CIELAB color system as defined by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE), using the L*, a*, and b* coordinates [20]. In this system, L* represents sample lightness, a* indicates the degree of redness, and b* denotes the level of yellowness, reflecting a three-dimensional model of color assessment.
2.7. Volatile Compound Analysis
The method described by Kaban and Kaya [16] was employed for the analysis of volatile compounds in sucuk samples. Headspace volatile compounds were extracted using a solid-phase microextraction (SPME) device (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA). A 75 µm carboxen/polydimethylsiloxane (CAR/PDMS) fiber was utilized and placed in sealed vials for 2 h to allow adsorption of volatiles. Following extraction, the fiber was introduced into a gas chromatograph (GC; Agilent Technologies 6890N) in splitless mode, with injection at 250 °C for 6 min. The GC was coupled with a mass-selective detector (MS; Agilent Technologies 5973) to identify volatile compounds. Separation was achieved using a DB-624 capillary column (Agilent J&W Scientific, Santa Clara, CA, USA; 60 m length, 0.25 mm i.d., 1.4 µm film thickness). Helium was used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. The oven temperature program commenced at 40 °C (held for 5 min), followed by a gradual increase to 110 °C at 3 °C/min, to 150 °C at 4 °C/min, and finally to 210 °C at 10 °C/min, where it was held for 12 min. The total analysis time was 56.3 min, and the GC-MS interface temperature was maintained at 280 °C. Mass spectra were obtained using electron impact ionization at 70 eV, covering a mass range of 30–400 amu.
Compound identification was carried out by comparing the mass spectra with databases from the NIST, Flavor and Wiley, as well as by matching retention indices with those reported in the literature. Kovats indices were calculated using a reference standard (Supelco 44585-U, Bellefonte, PA, USA). The results were expressed as arbitrary units of area (AU × 106) and presented as mean values from three independent replicates.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Two independent manufacturing processes were carried out for each treatment on different days (two batters per treatment). Two random samples were taken from each treatment in each production for the analyses. The data obtained from analyses related to the use of starter cultures were statistically evaluated using a completely randomized design with two replicates. Differences between mean values were assessed using Duncan’s multiple range test, performed with SPSS version 24 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). To determine relationship between the starter cultures and volatile compounds, the correlation heatmap was applied using ChiPlot [27]. To determine the relationship between the starter cultures and chemical groups of volatile compounds, PCA was carried out using the Minitab 17.1.0 software (State College, PA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microbiological Results
The microbiological count results of sucuk produced with selected autochthonous starter cultures (ASCs) are shown in Figure 1. In the control group, spontaneous LAB exhibited good growth, and the addition of ASCs had no significant effect on LAB counts. Accordingly, the count of LAB was generally 8 log cfu/g at the end of the ripening period. The LAB strains used in this study showed good growth and quickly became dominant over time. These results indicate that spontaneous lactic acid bacteria exhibited good growth. Nevertheless, the composition of spontaneous microbiota is highly variable and influenced by numerous factors, making controlled fermentation inherently unpredictable. Therefore, the use of starter cultures is essential to ensure uniformity and maintain high product quality in sausages [10,21,22,28]. The main role of LAB in meat fermentation is to grow and survive under production conditions and to cause a rapid decrease in pH in the batter [29]. This result is consistent with those previously reported by Kaban and Kaya [15,30], Kaban et al. [19], and Akköse et al. [20].
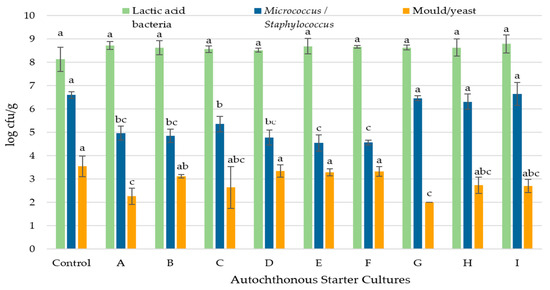
Figure 1.
The effects of starter cultures on microbiological properties of sucuk samples (Control: without starter culture, A: L. sakei S15, B: L. plantarum S91, C: P. pentosaceus 128b, D: L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, E: L. plantarum S24 + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, F: P. pentosaceus S128b + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, G: L. sakei S15 + S. carnosus G109, H: L. sakei S15 + L. plantarum S91 + S. carnosus G109, I: P. pentosaceus S128b + S. carnosus G109 + L. sakei S15). (a–c: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between autochthonous starter culture for each microbiological properties) (p < 0.05).
The use of ASC had a significant effect on the count of Micrococcus/Staphylococcus (p < 0.01). According to Duncan’s multiple range test, there was no statistical difference between the control group and the groups containing S. carnosus G109 in terms of Micrococcus/Staphylococcus (Figure 1). Due to the slow decrease in pH in the control group, spontaneous Micrococcus/Staphylococcus grew and reached 6 log cfu/g. In contrast, in the groups (A, B, C, D, E and F) using only autochthonous lactic acid bacteria strains (ALABS) as starter cultures, spontaneous Micrococcus/Staphylococcus counts remained lower due to rapid acidification (Figure 1). These results are due to the fact that Micrococcus/Staphylococcus are acid-sensitive microorganisms [16,30,31]. In the groups (G, H and I) containing both ALABS and S. carnosus G109, however, S. carnosus G109 maintained its viability and even exhibited slight growth despite the rapid acidification. Therefore, the Micrococcus/Staphylococcus count was higher in these groups compared to the other groups, except for the control group (Figure 1). These results show that S. carnosus G109 is a good starter culture candidate for sucuk. Corbiere et al. [32] found that S. carnosus survived under plant conditions in dry fermented sausages. In other studies on sucuk, it was reported that S. carnosus used as a starter culture significantly preserved its viability throughout the process, with Micrococcus/Staphylococcus counts of approximately 6 log cfu/g [19,30].
Enterobacteriaceae counts were below the detectable limit (<2 log cfu/g) during ripening in all sucuk groups produced with different starter cultures. The growth of Enterobacteriaceae is promoted by high initial water activity and pH, low concentrations of fermentable carbohydrates, low numbers of lactobacilli in the fresh sausage mixture, the absence of nitrate or nitrite, and sometimes insufficient ripening temperatures [33]. The fact that Enterobacteriaceae counts were below the detectable limit even in sausage batter indicates the hygienic quality of the raw material. Because bacteria belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family are sensitive to low pH (<5.3) and aw (<0.96) values, their numbers decrease during ripening [20]. Casquete et al. [34] emphasized that the addition of autochthonous starter cultures reduced the growth of Enterobacteriaceae at the beginning of the ripening process. Casaburi et al. [35] reported that after a 3-day ripening period, Enterobacteriaceae counts increased by approximately 2 log in the control sausage samples, whereas a decrease was observed in sausages with added starter cultures. This situation can be explained by the rapid decrease in pH following the addition of starter cultures. Bonomo et al. [5] reported that Enterobacteriaceae could not be detected in sausage samples containing ASC at the end of ripening. Similar results have been reported by Dominguez et al. [36].
The mold/yeast counts of the samples were found to be 102–103 cfu/g. Yeast/mold counts were significantly affected by the addition of starter cultures (p < 0.05). Groups A and G had lower yeast/mold counts than the control group (Figure 1). The yeast/mold counts of the other groups did not differ from those of the control group. Similarly, Palavecino Prpich et al. [37] reported that yeast/mold counts were not different from those of the control group.
3.2. pH, aw, and TBARS Values
The pH, aw, and TBARS values of the sucuk samples produced using ASC are shown in Table 2. The pH of the sucuk samples was very significantly affected by the addition of ASC (p < 0.01). The pH value, which was 5.53 in the control group, was found to be below 5.0 in all other groups (Table 2). Moreover, our findings were in good agreement with those of other researchers [36,38,39,40], who reported lower pH values in samples inoculated with starter cultures compared to the control. In the current study, groups B, D, E, F, and H, which used L. plantarum as a monoculture or mixed culture, exhibited statistically lower pH values than groups using other starter cultures. These results also indicate that L. plantarum S91 is better adapted to the environment of sucuk fermentation. On the other hand, Pragalaki et al. [41] determined that the separate use of autochthonous L. sakei 8416 and L. sakei 4413 strains did not affect the pH level. In dry fermented sausages such as sucuk, salami, and Rohwurst, the water-holding capacity of meat proteins decreases as the pH drops to around 5.3 during fermentation, thereby accelerating the drying of the product. With drying, part of the water is removed, and thus the aw value decreases. Acidification that occurs during fermentation and the consequent decrease in pH are extremely important for the development of color, flavor, and texture in meat products. In addition, a decrease in pH is important not only for the inhibition of spoilage microorganisms but also for the prevention of pathogenic microorganism growth [28].

Table 2.
The effects of starter cultures on pH, aw and TBARS values of sucuk samples (mean ± standard deviation).
The use of ASC did not cause a significant difference in aw values (p > 0.05) (Table 2). However, in a study it was revealed that aw decreases more rapidly in sucuk produced with LAB than in naturally fermented sucuk [16]. These differences are probably related to the composition of the spontaneous microbiota [10].
TBARS is an indicator of lipid oxidation in meat products. It has been reported that the deterioration of sausages is caused not only by spoilage microorganisms but also by lipid oxidation. Lipid oxidation, in turn, affects product quality by producing off-odors and by promoting the formation of peroxides that are harmful to human health [42]. The TBARS values of sucuk produced with ASC are listed in Table 2. The use of ASC did not cause a significant difference in TBARS values (p > 0.05). On the other hand, in a study conducted on sucuk, the use of L. sakei S15 as a monoculture increased the TBARS value at the end of the ripening period, whereas certain mixed cultures resulted in lower TBARS values, which was attributed to the antioxidant activity of S. carnosus [19]. As presented in Table 2, the mean TBARS values obtained in this study were below 1 mg MDA/kg. TBARS values lower than 1 mg MDA/kg generally indicate minimal lipid oxidation, suggesting that the product is unlikely to develop rancid flavors. Values ranging from 1 to 2 mg MDA/kg reflect a moderate degree of lipid oxidation. In contrast, TBARS values exceeding 2 mg MDA/kg are indicative of advanced oxidative deterioration, accompanied by noticeable flavor degradation and the development of off-flavors, particularly rancidity. It should be noted that TBARS levels can vary substantially depending on the specific processing conditions applied to the meat product. In fact, rancidity levels as high as 2–2.5 mg MDA/kg have been reported in certain processed meat products [43].
3.3. Color Values
The effects of the starter cultures on the color of the sucuk are shown in Figure 2. The results suggested that the use of starter cultures caused a statistical difference only in the L* value among the color parameters examined (p < 0.05). The lowest L* values were observed in the control group. However, the mean value of this group did not differ significantly from that of the group treated with only L. plantarum S91. These results indicate that starter culture inoculation had only a minor effect on the color characteristics of the products. Color formation and stability are important components of fermented sausage quality, and consumers often associate overall quality with color [44]. Kaban et al. [19] reported that sucuk samples containing ASC had higher L* values than the control group (p < 0.01). In addition, in the same study, ASC showed no significant effect on the a* value of the sucuk samples (p > 0.05). Van Ba et al. [45] reported lower L* values in sausage samples inoculated with S. carnosus + S. xylosus + D. hansenii + L. curvatus, and higher L* values in those inoculated with S. xylosus + L. plantarum (p < 0.05). On the other hand, Casaburi et al. [35] found no effect of starter inoculation or pH on color changes in fermented sausages.
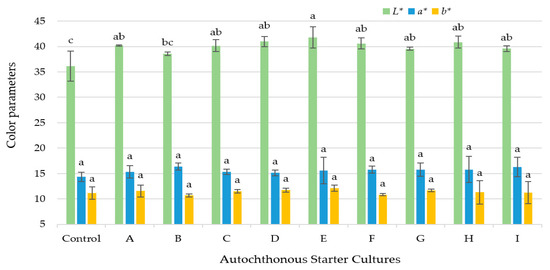
Figure 2.
The effects of starter cultures on color values of sucuk samples (Control: without starter culture, A: L. sakei S15, B: L. plantarum S91, C: P. pentosaceus 128b, D: L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, E: L. plantarum S24 + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, F: P. pentosaceus S128b + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, G: L. sakei S15 + S. carnosus G109, H: L. sakei S15 + L. plantarum S91 + S. carnosus G109, I: P. pentosaceus S128b + S. carnosus G109 + L. sakei S15). (a–c: Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between autochthonous starter culture for each color parameter) (p < 0.05).
3.4. Volatile Compounds
The formation of volatile compounds has been attributed to lipid oxidation, protein hydrolysis, and amino acid catabolism. During the ripening process of sausages, a wide array of volatile compounds is generated as a result of these biochemical and enzymatic reactions [46]. In this study, 68 compounds belonging to 12 different chemical groups were identified, including aldehydes, alcohols, sulfur compounds, aliphatic hydrocarbons, esters, acids, ketones, aromatic hydrocarbons, terpenes, furans, phenols, and nitrogenous compounds (Table 3). Many non-volatile compounds, such as peptides and amino acids, are produced by the degradation of meat proteins during the ripening of fermented sausages [47]. However, the sources of volatile compounds vary, and these compounds may also be generated through secondary reactions between substances produced by various catabolic processes [48]. It is known that flavor development in fermented sausages is influenced by spices in the formulation, process conditions, and the presence of starter cultures [15]. Proteolysis also plays an important role in the aroma of dry-fermented sausages. As a result of proteolytic reactions, the levels of volatile compound precursors, flavor-active free amino acids, and low-molecular-weight peptides (non-protein nitrogenous substances) increase [49,50,51]. Factors such as formulation, starter culture, and production conditions, which vary from product to product, are also known to influence proteolysis [52].

Table 3.
The effects of autochthonous strains on volatile compounds (AUx106) of sucuk (mean± standard deviation).
Aldehydes are typical products of lipid oxidation, with hexanal and nonanal being formed through lipid auto-oxidation and characterized by low threshold values. These compounds are considered major contributors to the flavor of processed meat products [53]. The use of ASC in sucuk samples showed no significant effect on hexanal and heptanal (p > 0.05) but had a significant effect on acetaldehyde, decanal, 3-phenyl-2-methylpropanal (p < 0.01), and octanal (p < 0.05) (Table 3). Changes in lipid content during ripening also significantly affect the sensory properties of the product [46,54]. Free fatty acids formed as a result of lipolysis are good substrates for autoxidation. The end products of autoxidation (aldehydes, alcohols, ketones, furans, etc.) are volatile compounds that play an important role in odor and flavor development. In these products, different factors such as product formulation, meat particle size, pH, salt, nitrite, spices, and antioxidants are known to affect lipid oxidation [46].
ASC treatment was significantly associated with benzeneethanol and 4-(1-methylethyl) benzenemethanol (p < 0.01). In this study, ethyl alcohol levels were significantly higher in the control group than in the other groups (p < 0.05) (Table 3). Alcohols are primarily derived from the reduction of methyl ketones, carbohydrate metabolism, amino acid catabolism, and lipid oxidation, and therefore play an important role in determining the flavor profiles of fermented sausages [22].
Sulfur compounds, with their low threshold values, can significantly affect the sensory properties of food, even in small amounts. These compounds may originate from garlic or may result from amino acid catabolism. The characteristic aroma of garlic is mainly attributed to diallyl disulfide and diallyl thiosulfinate [55]. In the present study, diallyl disulfide, methyl-2-propenyl disulfide, 3,3′-thiobis-1-propene (p < 0.01), allyl mercaptan, and di-2-propenyl disulfide (p < 0.05) were significantly affected by the addition of ASC (Table 3). In terms of 3,3′-thiobis-1-propene, the control group and groups A, G, and I, which did not contain L. plantarum, showed similar results (Table 3).
Ketones are characteristic flavor compounds in fermented sausages that contribute to floral, creamy, fatty, and fruity notes [56]. In this study, ASC inoculation in sucuk samples had a significant effect on 3-hydroxy-2-butanone (p < 0.01) and 2-nonanone (p < 0.05).
Fermentation and storage of meat lead to the production of various compounds, including acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, acetaldehyde, diacetyl, and acetoin, as a result of lactic acid metabolism [4]. Acetic acid, a product of carbohydrate metabolism, can also be formed via lipid or amino acid catabolism [49,57]. As can be seen from Table 3, acetic acid and propionic acid levels in sucuk samples were significantly affected by ASC inoculation (p < 0.01). Groups D, E, F, H, and I had higher acetic acid abundance than the other groups, including the control group. In groups B, D, F and H, high abundances were observed in terms of propionic acid (Table 3).
Esters in meat products are typically generated through the esterification of carboxylic acids and alcohols. Moreover, lactic acid bacteria and staphylococci are known to exhibit esterification activity as well [58]. In the present study, ethyl acetate, butyl propionate, propyl hexanoate, hexyl butanoate and benzoic acid 2-hydroxy-methyl ester were determined in the samples. Benzoic acid 2-hydroxy-methyl ester was only significantly affected by ASC addition (p < 0.01), and the groups B and I showed high abundance. However, the mean abundances of these groups did not differ from those of F, G, and H (Table 3).
1-methyl-1H-pyrrole, which is among the nitrogenous compounds, was affected by the use of ASC. The highest abundance was determined in groups F and H, which contain both L. sakei S15 and L. plantarum S91. However, no statistical difference was determined between these groups and groups B, C and E. Indeed, it is stated that microbial degradation of amino acids may be effective in the formation of compounds such as straight-chain sulfur compounds, pyrroles, pyrazines, and thiols [59].
In the present study, ASC use had no significant effect on the aliphatic hydrocarbon and furan compounds (p > 0.05) (Table 3). On the other hand, among aromatic hydrocarbons, 1-methyl-4-(1-methylethenyl)-benzene was affected by ASC at p < 0.01 level. On the other hand, of the three phenol compounds identified, ASC use showed a significant effect only on 4-methyl-phenol at the p < 0.05 level (Table 3), and the highest abundance was found in the groups E, F and H, which contain both L. sakei S15 and L. plantarum S91. However, no statistical difference was found between the mean values of these groups and the mean values of groups B, D, G and I (Table 3).
Terpenes primarily originate from spices used in the production of fermented sausages, as well as from the meat itself, which is influenced by animal nutrition [18]. In the present study, the use of ASC significantly affected α-thujene, α-pinene, α-phellandrene, 3-carene, terpinene-4-ol, α-terpinene and α-terpineol (p < 0.01), as well as β-phellandrene, D-limonene, linalool, camphene, phellandral, and caryophyllene (p < 0.05). Kaban and Kaya [16] and Kargozari et al. [9] also reported that ASCs influence many terpene compounds in sucuk. The highest mean abundances of α-thujene, β-phellandrene, and camphene were found in group B (L. plantarum S91), and this group was statistically different from the other groups. However, the lowest mean abundance of α-pinene were observed in the control group. The highest abundances of α-phellandrene, 3-carene, D-limonene, α-terpinene, linalool, and terpinene-4-ol were determined in groups containing both L. sakei S15 and L. plantarum S91. The lowest mean abundances of α-terpineol were found in groups A, C, and G. On the other hand, while the highest abundances of phellandral were found in group I, the use of mixed culture increased the caryophyllene content (Table 3). Terpenes are compounds that play a significant role in the volatile profile of sucuk [7]. These compounds may originate from spices, but they also have the potential to migrate into meat from animal feed. Additionally, studies on sucuk were determined that starter cultures affect terpene compounds [16,19,60], suggesting that this result may be due to terpene biotransformation by microorganisms. This study also determined that different ASC exhibited varying effects on many terpene compounds.
Figure 3 presents a correlation heat map illustrating the relationships between the starter cultures and volatile compounds. The analysis revealed differences among the starter cultures, with the use of different cultures resulting in the formation of two main distinct clusters. The use of different starter cultures resulted in significant differences in the volatile compound profiles. However, the most significant result is that all groups containing L. plantarum (B, D, E, F, and H) were clustered together in one cluster, indicating that L. plantarum, when used alone or with other microorganisms, produces a similar volatile profile (Figure 3).
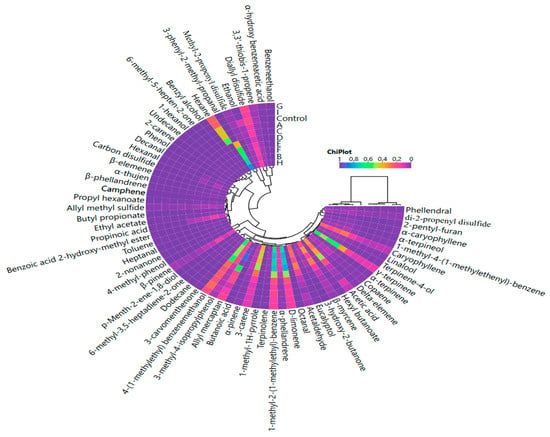
Figure 3.
Cluster analysis of the correlation heat map illustrating the relationships between starter cultures and volatile compounds(Control: without starter culture, A: L. sakei S15, B: L. plantarum S91, C: P. pentosaceus 128b, D: L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, E: L. plantarum S24 + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, F: P. pentosaceus S128b + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, G: L. sakei S15 + S. carnosus G109, H: L. sakei S15 + L. plantarum S91 + S. carnosus G109, I: P. pentosaceus S128b + S. carnosus G109 + L. sakei S15).
Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to assess the relationships among starter cultures and volatile compounds (Figure 4). The PC-1 explained 49.20% of the variation, and PC-2 explained 26.40% of the variation. The total variance was fully explained (75.60%) by the first two principal components. All groups containing L. plantarum (B, D, E, F and H) were located on the positive side of PC-1 and were separated from the other groups (control, A, C, G and I). Furthermore, phenols, furans, acids, terpenes, aromatic hydrocarbons, ketones, nitrogenous compounds, esters, and aliphatic hydrocarbons were located on the positive side of PC-1 and showed positive correlations with all groups containing L. plantarum. The groups without L. plantarum and the control group were on the negative side of PC1 and exhibited positive correlations with alcohols, aldehydes and sulfide compounds (Figure 4). In contrast, alcohols and aldehydes formed as a result of lipid oxidation showed negative correlations with groups containing L. plantarum. This result is thought to be due to the antioxidant properties of L. plantarum strains. Indeed, Mei et al. [61] reported that L. plantarum strains with antioxidant properties are effective in inhibiting lipid and protein oxidation and contribute to a better flavor in the sausage.
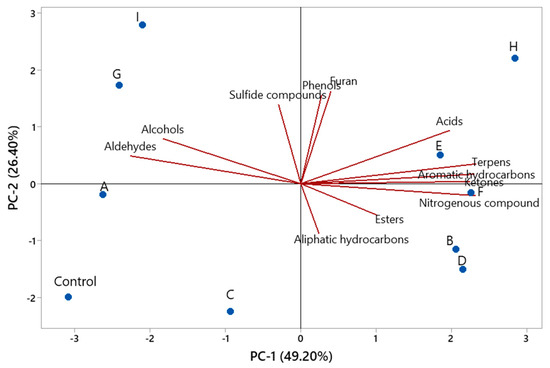
Figure 4.
PCA biplot of the relationships between starter cultures and volatile compounds (Control: without starter culture, A: L. sakei S15, B: L. plantarum S91, C: P. pentosaceus 128b, D: L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, E: L. plantarum S24 + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, F: P. pentosaceus S128b + L. plantarum S91 + L. sakei S15, G: L. sakei S15 + S. carnosus G109, H: L. sakei S15 + L. plantarum S91 + S. carnosus G109, I: P. pentosaceus S128b + S. carnosus G109 + L. sakei S15).
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that the incorporation of autochthonous starter cultures (ASCs) can play a decisive role in shaping the quality characteristics of traditionally produced sucuk under local small-scale facility conditions. The use of these strains, either as mono- or mixed-starter cultures, contributed to desirable changes in key physicochemical parameters. Moreover, the application of ASCs supported product safety by limiting the growth of undesirable microorganisms without adversely affecting lipid oxidation or water activity. In addition, groups containing L. plantarum were determined to be associated with a wider range of aromatic compounds, revealing their potential role in increasing the flavor complexity of sucuk. Taken together, these findings highlight the potential of ASCs as an effective tool for improving the quality and safety properties of artisanal fermented meat products, thereby providing a sustainable strategy to strengthen both product standardization and consumer appeal. However, sensory assessments are also required to confirm the impact of ASC-induced changes on consumer preference and product acceptance.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, B.S., K.Ç.T. and G.K.; methodology, M.K. and G.K.; investigation, M.K., B.S., K.Ç.T. and G.K.; writing—original draft preparation, B.S. and K.Ç.T.; writing—review and editing, M.K. and G.K.; conceptualization, M.K.; supervision, M.K.; project administration, M.K.; funding acquisition, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Republic of Türkiye Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry General Directorate of Agricultural Research and Policy (Project number: TAGEM/13/AR-GE/7).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ross, R.P.; Morgan, S.; Hill, C. Preservation and fermentation: Past, present and future. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 79, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocolin, L.; Dolci, P.; Rantsiou, K. Biodiversity and dynamics of meat fermentations: The contribution of molecular methods for a better comprehension of a complex ecosystem. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aro, J.M.A.; Nyam-Osor, P.; Tsuji, K.; Shimada, K.; Fukushima, M.; Sekikawa, M. The effect of starter cultures on proteolytic changes and amino acid content in fermented sausages. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionek, B.; Szydłowska, A.; Küçükgöz, K.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D. Traditional and new microorganisms in lactic lactic acid fermentation of food. Fermentation 2023, 9, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, M.G.; Ricciardi, A.; Salzano, G. Influence of autochthonous starter cultures on microbial dynamics and chemical-physical features of traditional fermented sausages of Basilicata region. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Tucci, P.; Del Matto, I.; Marino, L.; Amadoro, C.; Colavita, G. Autochthonous cultures to improve safety and standardize quality of traditional dry fermented meats. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaban, G. Sucuk and pastırma: Microbiological changes and formation of volatile compounds. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, D.; Puglisi, E.; Cocconcelli, P.S. Comparing natural and selected starter cultures in meat and cheese fermentations. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargozari, M.; Moini, S.; Basti, A.A.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Gandomi, H.; Martin, I.R.; Ghasemlou, M.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Effect of autochthonous starter cultures isolated from Siahmazgi cheese on physicochemical, microbiological and volatile compound profiles and sensorial attributes of sucuk, a Turkish dry-fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2014, 97, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lücke, F.-K. Utilization of microbes to process and preserve meat. Meat Sci. 2000, 56, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, L.; Ge, Y.; An, Y.; Sun, X.; Xue, K.; Xie, H.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Screening, identification, and application of superior starter cultures for fermented sausage production from Traditional Meat Products. Fermentation 2025, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Feng, M.-Q.; Sun, J. Influence of mixed starters on the degradation of proteins and the formation of peptides with antioxidant activities in dry fermented sausages. Food Control 2021, 123, 107743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talon, R.; Leroy, S.; Lebert, I.; Giammarinaro, P.; Chacornac, J.-P.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.; Vidal-Carou, C.; Zanardi, E.; Conter, M.; Lebecque, A. Safety improvement and preservation of typical sensory qualities of traditional dry fermented sausages using autochthonous starter cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 126, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baka, A.M.; Papavergou, E.J.; Pragalaki, T.; Bloukas, J.G.; Kotzekidou, P. Effect of selected autochthonous starter cultures on processing and quality characteristics of Greek fermented sausages. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Identification of lactic acid bacteria and Gram-positive catalase-positive cocci isolated from naturally fermented sausage (Sucuk). J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, M385–M388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus xylosus on the quality characteristics of dry fermented sausage “Sucuk”. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloğlu, A. Functional and technological characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Turkish dry-fermented sausage (sucuk). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Sagdic, O.; Yetim, H. Effects of autochthonous yeast cultures on some quality characteristics of traditional Turkish fermented sausage “Sucuk”. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaban, G.; Sallan, S.; Çinar Topçu, K.; Sayın Börekçi, B.; Kaya, M. Assessment of technological attributes of autochthonous starter cultures in Turkish dry fermented sausage (sucuk). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 4392–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akköse, A.; Oğraş, Ş.Ş.; Kaya, M.; Kaban, G. Microbiological, physicochemical and sensorial changes during the Rripening of sucuk, a traditional Turkish dry-fermented sausage: Effects of autochthonous strains, sheep tail fat and ripening rate. Fermentation 2023, 9, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-S.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, B.-C. Enhancement of fermented sausage quality driven by mixed starter cultures: Elucidating the perspective of flavor profile and microbial communities. Food Res. Int. 2024, 178, 113951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Xu, N.; Sun, J.; Xu, X. Effects of different mixed starter cultures on microbial communities, taste and aroma compounds of traditional Chinese fermented sausages. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ning, J.; Wang, S.; Nie, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ji, L. Effect of fermentation by Pediococcus pentosaceus and Staphylococcus carnosus on the metabolite profile of sausages. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.; Sayın, B.; Çinar Topçu, K.; Karadayı, M.; Kamiloğlu, A.; Güllüce, M.; Kaban, G. Genotypic and technological characterization of lactic acid bacteria and coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from sucuk: A Preliminary Screening of Potential Starter Cultures. Foods 2025, 14, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, J.; Eigener, V.; Firnhaber, J.; Hildebrant, G.; Reenen Hoekstra, E.S.; Samson, R.A.; Spicher, G.; Timm, F.; Yarrow, D.; Zschaler, R. Mikrobiologische Untersuchung von Lebensmitteln; Behr’s GmbH &Co.: Hamburg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Lemon, D.W. An Improved TBA Test for Rancidity; Fisheries and Marine Service: Halifax, NS, Canada, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- ChiPlot. Available online: https://www.chiplot.online/ (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Lücke, F.K. Mikrobiologische Vorgänge bei der Herstellung von Rohwurst und Rohschinken. In Mikrobiologie und Qualität von Rohwurst und Rohschinken; Bundesanstalt für Fleischforschung: Kulmbach, Germany, 1985; pp. 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Agüero, N.d.L.; Frizzo, L.S.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Aleu, G.; Rosmini, M.R. Technological characterisation of probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria as Starter Cultures for Dry Fermented Sausages. Foods 2020, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Effects of Staphylococcus carnosus on quality characteristics of sucuk (Turkish dry-fermented sausage) during ripening. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Cheng, H.; Ma, J.-K.; Li, Z.-J.; Wang, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-L. Effect of starter culture on microbiological, physiochemical and nutrition quality of Xiangxi sausage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbiere Morot-Bizot, S.; Leroy, S.; Talon, R. Monitoring of staphylococcal starters in two French processing plants manufacturing dry fermented sausages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.; Díez, V. The effect of nitrite and starter culture on microbiological quality of “chorizo”—A Spanish dry cured sausage. Meat Sci. 2002, 60, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquete, R.; Benito, M.J.; Martín, A.; Ruiz-Moyano, S.; Aranda, E.; Córdoba, M.G. Microbiological quality of salchichón and chorizo, traditional Iberian dry-fermented sausages from two different industries, inoculated with autochthonous starter cultures. Food Control 2012, 24, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Cavella, S.; Di Monaco, R.; Ercolini, D.; Toldrá, F.; Villani, F. Biochemical and sensory characteristics of traditional fermented sausages of Vallo di Diano (Southern Italy) as affected by the use of starter cultures. Meat Sci. 2007, 76, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Munekata, P.E.; Agregán, R.; Lorenzo, J.M. Effect of commercial starter cultures on free amino acid, biogenic amine and free fatty acid contents in dry-cured foal sausage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palavecino Prpich, N.Z.; Castro, M.P.; Cayré, M.E.; Garro, O.A.; Vignolo, G.M. Indigenous starter cultures to improve quality of artisanal dry fermented sausages from chaco (Argentina). Int. J. Food Sci. 2015, 2015, 931970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jin, Y.; Ma, C.; Song, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, S. Physico-chemical characteristics and free fatty acid composition of dry fermented mutton sausages as affected by the use of various combinations of starter cultures and spices. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Gómez, M.; Purriños, L.; Fonseca, S. Effect of commercial starter cultures on volatile compound profile and sensory characteristics of dry-cured foal sausage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-González, M.; Fonseca, S.; Centeno, J.A.; Carballo, J. Biochemical changes during the manufacture of Galician Chorizo sausage as affected by the addition of autochthonous starter cultures. Foods 2020, 9, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pragalaki, T.; Bloukas, J.G.; Kotzekidou, P. Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in liquid broth medium and during processing of fermented sausage using autochthonous starter cultures. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Du, B.; Zhao, L.; Jin, Y.; Su, L.; Tian, J.; Wu, J. The effect of different starter cultures on biogenic amines and quality of fermented mutton sausages stored at 4 and 20°C temperatures. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4472–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Fang, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhong, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, F. Rethinking salt in dry-cured meats: Innovations for a healthier and flavorful future. Food Rev. Int. 2025, 41, 2437–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škaljac, S.; Jokanović, M.; Tomović, V.; Šojić, B.; Ikonić, P.; Peulić, T.; Ivić, M.; Vranešević, J.; Kartalović, B. Color characteristics and content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of traditional dry fermented sausages throughout processing in controlled conditions. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2022, 42, 3124–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ba, H.; Seo, H.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ham, J.-S.; Park, B.-Y.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, T.-B.; Seong, P.-N. The effects of starter culture types on the technological quality, lipid oxidation and biogenic amines in fermented sausages. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez, J.A.; Hierro, E.M.; Bruna, J.M.; de la Hoz, L. Changes in the components of dry-fermented sausages during ripening. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1999, 39, 329–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.A.; Saldaña, E.; da Silva Pinto, J.S.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J.; Sentandreu, M.A.; Fadda, S.G. A peptidomic approach of meat protein degradation in a low-sodium fermented sausage model using autochthonous starter cultures. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 368–379, Erratum in Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viallon, C.; Berdagué, J.L.; Montel, M.C.; Talon, R.; Martin, J.F.; Kondjoyan, N.; Denoyer, C. The effect of stage of ripening and packaging on volatile content and flavour of dry sausage. Food Res. Int. 1996, 29, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdagué, J.L.; Monteil, P.; Montel, M.C.; Talon, R. Effects of starter cultures on the formation of flavour compounds in dry sausage. Meat Sci. 1993, 35, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierro, E.; de la Hoz, L.; Ordóñez, J.A. Contribution of the microbial and meat endogenous enzymes to the free amino acid and amine contents of dry fermented sausages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.J.; Rodríguez, M.; Martín, A.; Aranda, E.; Córdoba, J.J. Effect of the fungal protease EPg222 on the sensory characteristics of dry fermented sausage “salchichón” ripened with commercial starter cultures. Meat Sci. 2004, 67, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.C.; Kerry, J.P.; Arendt, E.K.; Kenneally, P.M.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Neill, E.E. Characterization of proteolysis during the ripening of semi-dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, K. Effect of inoculating mixed starter cultures of Lactobacillus and Staphylococcus on bacterial communities and volatile flavor in fermented sausages. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, A.; Ertaş, A.H.; Üzümcüoğlu, Ü. Effect of processing conditions on the quality of naturally fermented Turkish sausages (sucuks). Meat Sci. 2005, 69, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorrin, R.J. The significance of volatile sulfur compounds in food flavors. In Volatile Sulfur Compounds in Food; Qian, M.C., Fan, X., Mahattanatawee, K., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aziz, T.; Bai, R.; Zhang, X.; Shahzad, M.; Sameeh, M.Y.; Khan, A.A.; Dablool, A.S.; Zhu, Y. Dynamic change of bacterial diversity, metabolic pathways, and flavor during ripening of the Chinese fermented sausage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 990606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Yue, X. Microbial succession in representative fermented sausages: Driving flavor development and variations across Eastern and Western products. Food Sci. Anim. Prod. 2025, 3, 9240128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, K.A.; Tran, T.B.T.; Vogel, R.F. Production of volatile compounds by Lactobacillus sakei from branched chain α-keto acids. Food Microbiol. 2012, 29, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, M. Understanding the implications of current health trends on the aroma of wet and dry cured meat products. Meat Sci. 2018, 144, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.; Kaban, G. Volatile compounds of sucuk, a dry fermented sausage: The effects of ripening rate, autochthonous starter cultures and fat type. Foods 2024, 13, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Pan, D.; Guo, T.; Ren, H.; Wang, L. Role of Lactobacillus plantarum with antioxidation properties on Chinese sausages. LWT 2022, 162, 113427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).