Effects of Sorghum Grain and Wort Composition on Dry Grind Fermentation Performance: A Model for Baijiu Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grain Samples
2.2. Analysis of Sorghum Grains
2.3. Dry Grind Fermentation
2.4. Analysis of Fermented Samples
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Major Grain Composition
3.2. Fermentation
3.2.1. Production of Ethanol
3.2.2. Consumption of Glucose
3.2.3. Fermentability
3.2.4. Consumption of Yeast Assimilable Nitrogen (YAN)
3.2.5. Other Changes during Fermentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.L.; Sun, B.G. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Shi, J.L.; Zhu, J.; Lv, H.L.; Du, S.K. Enzymes Extracted from Apple Peels Have Activity in Reducing Higher Alcohols in Chinese Liquors. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9529–9538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Zhao, J.R.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhao, Z.G.; Li, X.T.; Sun, B.G. Flavor mystery of Chinese traditional fermented baijiu: The great contribution of ester compounds. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grand View Research, Report ID: GVR-4-68039-925-3. Alcoholic Drinks Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Type (beer, Spirits, Wine, Cider, Perry & Rice Wine, Hard Seltzer), by Distribution Channel, by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2022–2028. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/alcoholic-drinks-market-report (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Brand Finance, Spirits 50—The Annual Report on the Most Valuable and Strongest Spirits Brands; Brand Finance: London, UK, 2020.
- Anglani, C. Sorghum for human food—A review. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 1998, 52, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoddami, A.; Messina, V.; Venkata, K.V.; Farahnaky, A.; Blanchard, C.L.; Roberts, T.H. Sorghum in foods: Functionality and potential in innovative products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoddami, A.; Tan, D.; Bishop, T.; Roberts, T.H. Physico-Chemical Properties of Australian Sorghum Grain. Interim Report for GRDC Project UCS00025: Expanding Options for Sorghum: Food and Distilling; University of Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Khoddami, A.; Truong, H.H.; Liu, S.Y.; Roberts, T.H.; Selle, P.H. Concentrations of specific phenolic compounds in six red sorghums influence nutrient utilisation in broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2015, 210, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, R.; Bean, S.R.; Seib, P.A.; McLaren, J.S.; Madl, R.L.; Tuinstra, M.; Lenz, M.C.; Wang, D. Factors impacting ethanol production from grain sorghum in the dry-grind process. Cereal. Chem. 2007, 84, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathgate, G.N. The Determination of Fermentable Extract in Brewing Worts. J. Inst. Brew. 1981, 87, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSW Department of Primary Industries. Grain Sorghum: Summary of Statewide Best Management Practices for Grain Sorghum; Department of Primary Industries: Dubbo, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, H.; Lee, L.S.; Henry, R.J. Variation in sorghum starch synthesis genes associated with differences in starch phenotype. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.B.; Ferrari, M.D.; Lareo, C. Fuel ethanol production from commercial grain sorghum cultivars with different tannin content. J. Cereal. Sci. 2016, 69, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja, Y.S. Popping and Flaking Quality of Sorghum Cultivars in Relation to Physicochemical Characteristics and In Vitro Starch and Protein Digestibility; Andhra Pradesh Agricultural University: Hyderabad, India, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Yin, Y.; Ali, B.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.N.; Xu, X.M. Isolation of yeast strains from Chinese liquor Daqu and its use in the wheat sourdough bread making. Food Biosci. 2019, 31, 100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamma, D.; Christakopoulos, P.; Koullas, D.; Kekos, D.; Macris, B.J.; Koukios, E. An Alternative Approach to the Bioconversion of Sweet Sorghum Carbohydrates to Ethanol. Biomass Bioenerg. 1995, 8, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacking, A.J.; Taylor, I.W.F.; Hanas, C.M. Selection of Yeast Able to Produce Ethanol from Glucose at 40-Degrees-C. Appl. Microbiol Biot. 1984, 19, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bvochora, J.M.; Read, J.S.; Zvauya, R. Application of very high gravity technology to the cofermentation of sweet stem sorghum juice and sorghum grain. Ind. Crop Prod. 2000, 11, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collura, M.A.; Luyben, W.L. Energy-Saving Distillation Designs in Ethanol-Production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1988, 27, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.L.; Du, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Sun, B.G. Sichuan Univ Sci & Engn: Applications, challenges, and prospects. Foods 2021, 10, 680. [Google Scholar]
- Dupreez, J.C.; Dejong, F.; Botes, P.J.; Lategan, P.M. Fermentation Alcohol from Grain-Sorghum Starch. Biomass 1985, 8, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuanpeng, S.; Thanonkeo, S.; Klanrit, P.; Thanonkeo, P. Ethanol production from sweet sorghum by Saccharomyces cerevisiae DBKKUY-53 immobilized on alginate-loofah matrices. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaker, B.R.; Mohamed, A.A.; Habben, J.E.; Huang, C.P.; Larkins, B.A. Efficient Procedure for Extracting Maize and Sorghum Kernel Proteins Reveals Higher Prolamin Contents Than the Conventional Method. Cereal Chem. 1995, 72, 583–588. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.H.; Lau, T.; Cai, N.; Singh, J.; Pedersen, J.F.; Vensel, W.H.; Hurkman, W.J.; Wilson, J.D.; Lemaux, P.G.; Buchanan, B.B. Digestibility of protein and starch from sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) is linked to biochemical and structural features of grain endosperm. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnavathi, C.V. Study on genotypic variation for ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice. Biomass Bioenerg. 2010, 34, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredor, D.Y.; Bean, S.R.; Schober, T.; Wang, D. Effect of decorticating sorghum on ethanol production and composition of DDGS. Cereal Chem. 2006, 83, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor-Cox, E.S.C.; Paik, J.; Ingledew, W.M. Improved Ethanol Yields through Supplementation with Excess Assimilable Nitrogen. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1991, 8, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coote, N.; Kirsop, B.H. Factors responsible for the decrease in pH during beer fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 1976, 82, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).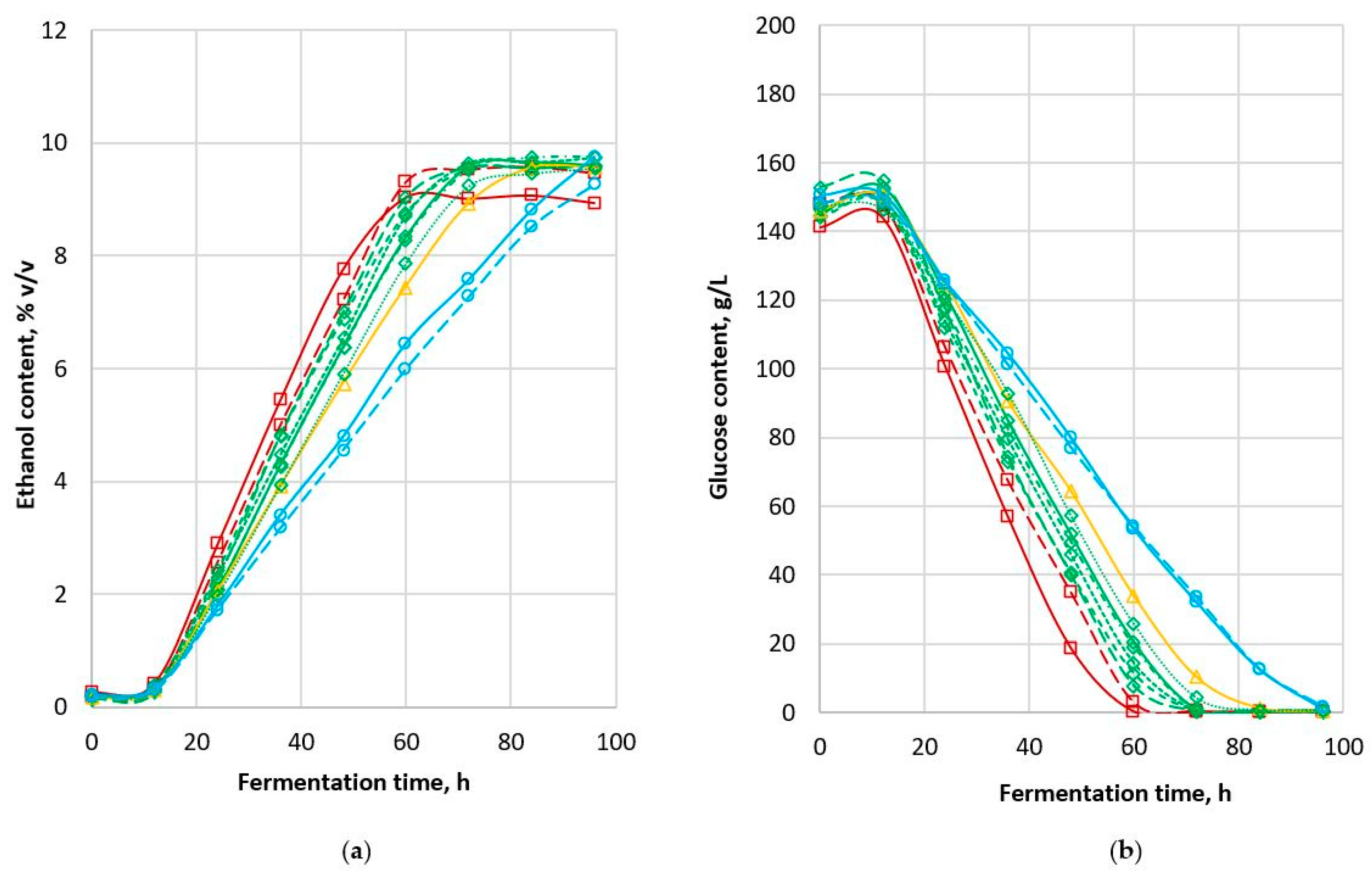
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).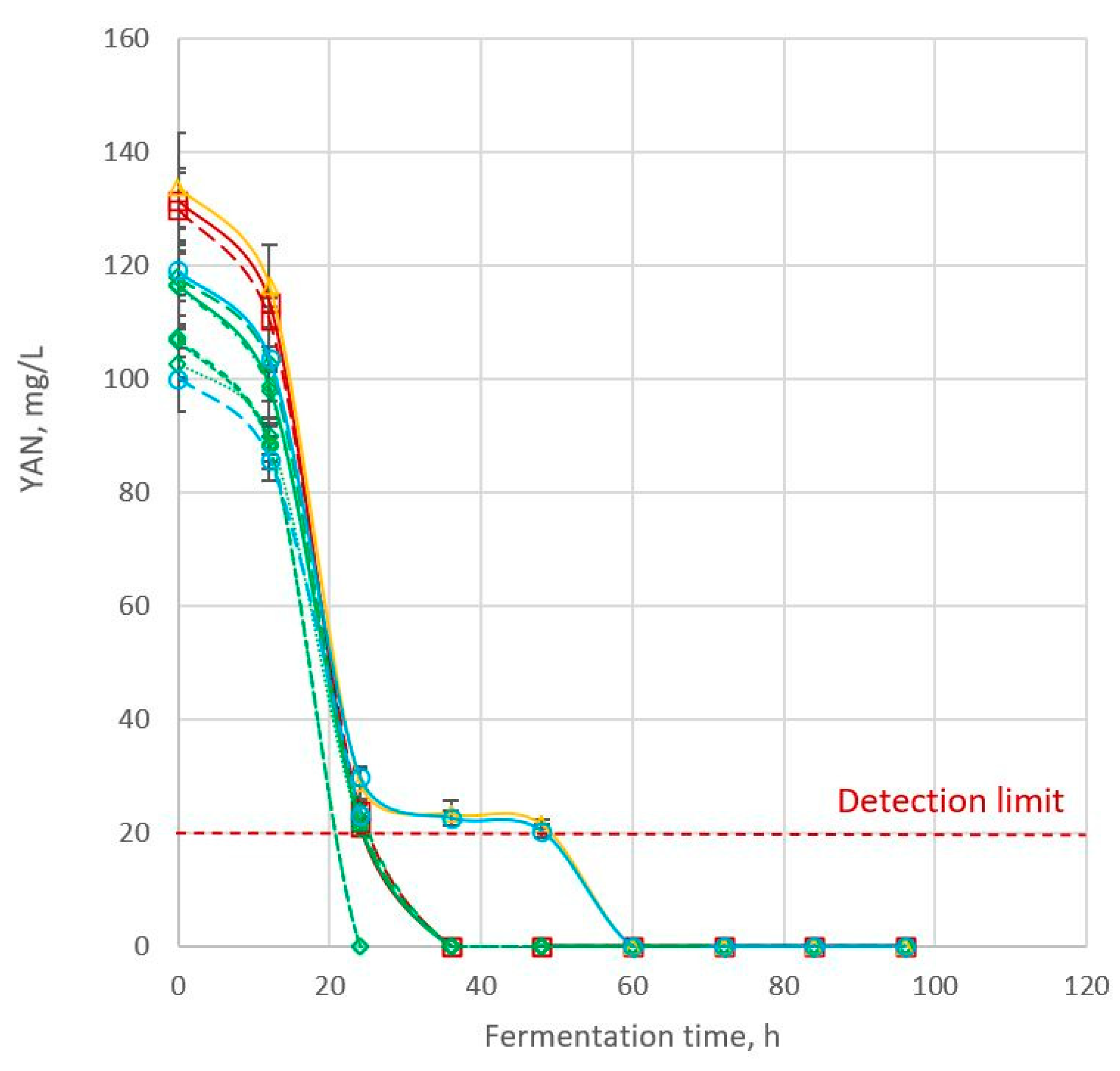
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).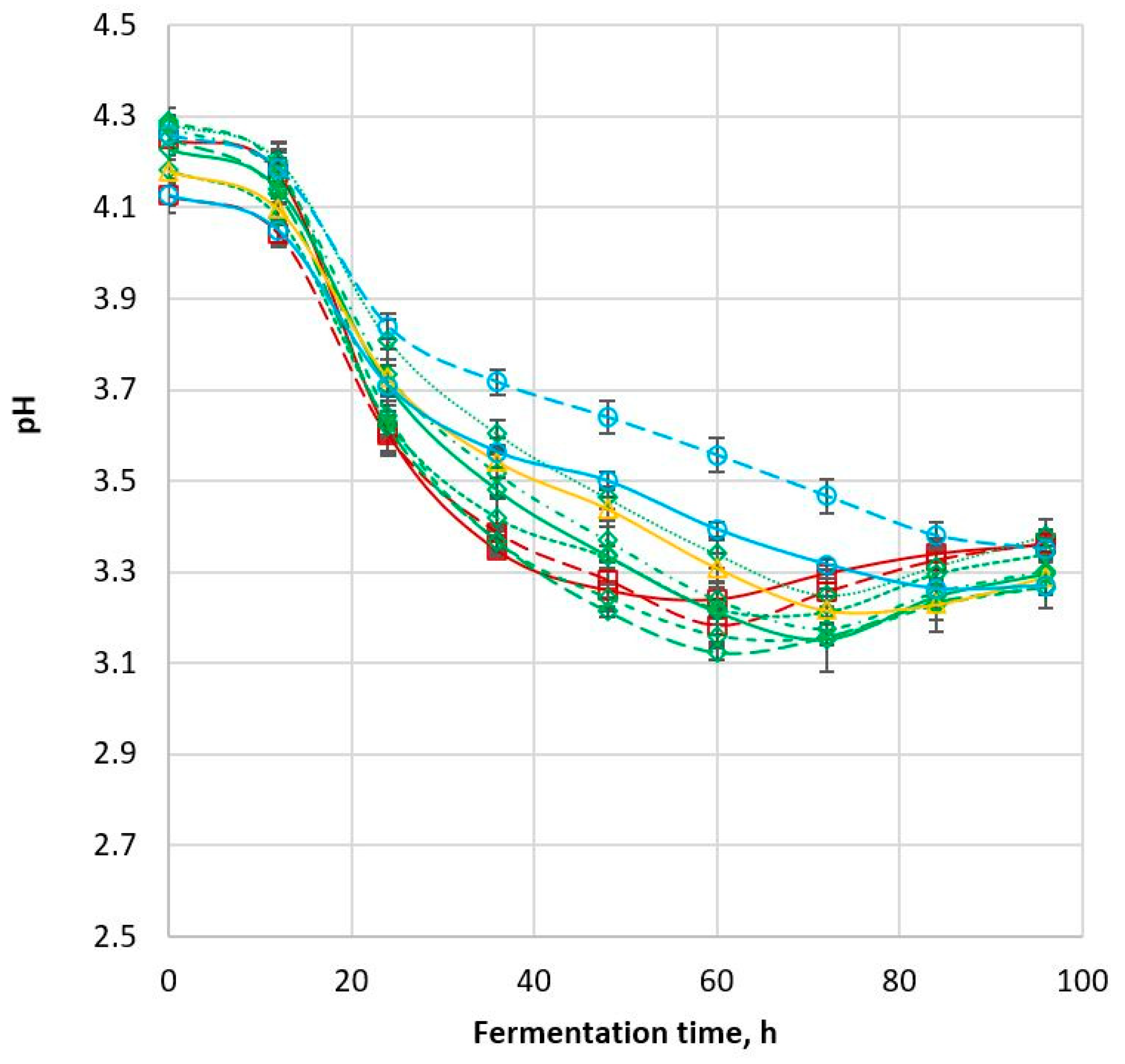
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).
 MR-Apollo,
MR-Apollo,  Rippa,
Rippa,  MR-Bazley,
MR-Bazley,  MR-Buster,
MR-Buster,  84G22,
84G22,  85G33,
85G33,  Liberty,
Liberty,  MR-Taurus,
MR-Taurus,  Cracka,
Cracka,  85G44,
85G44,  Tiger).
Tiger).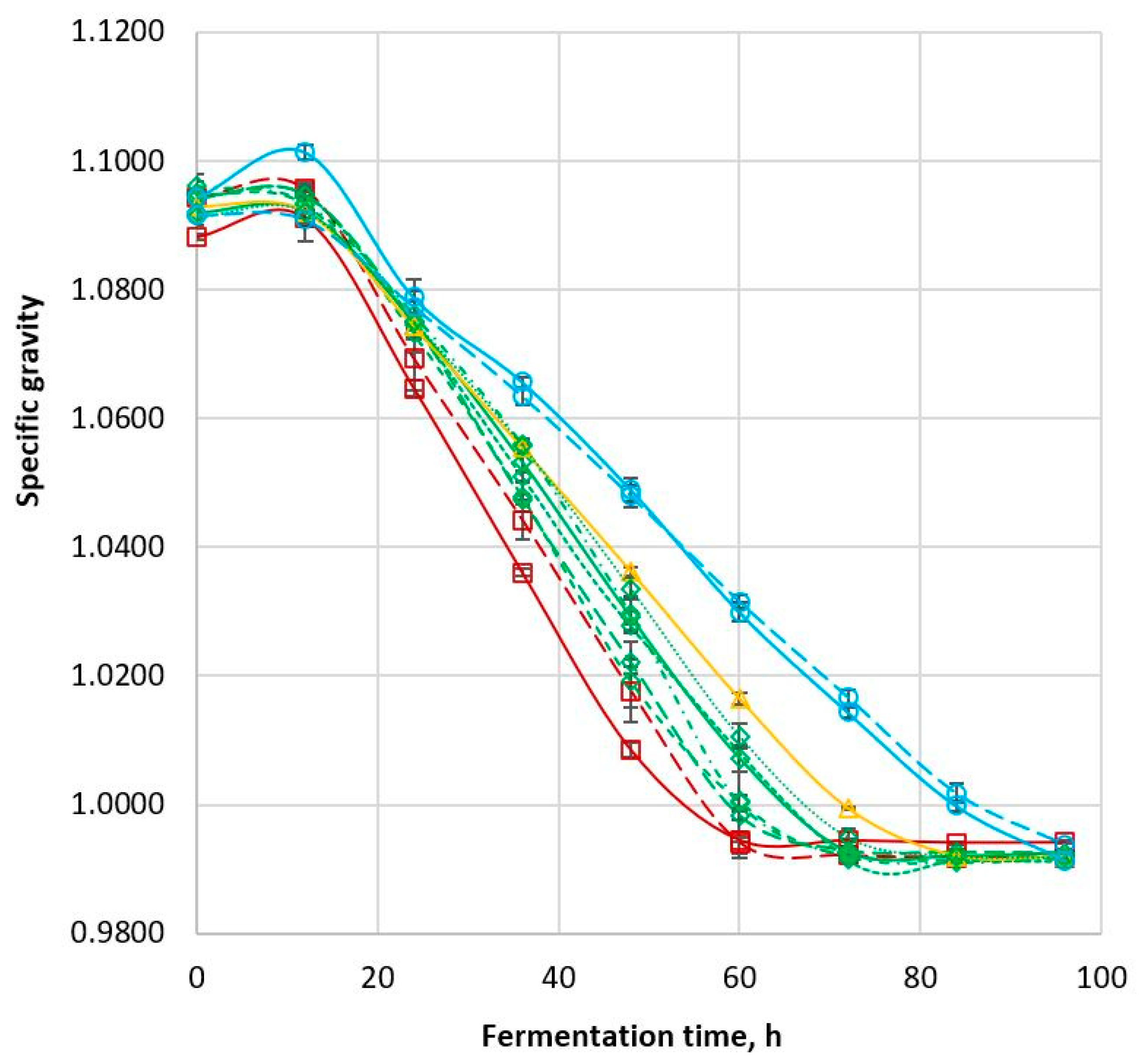
| Cultivar | Grain Moisture Content (%) | Starch (%) | Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MR-Apollo | 11.89 ± 0.42a | 58.26 ± 0.76d | 12.90 ± 0.09a |
| Rippa | 11.80 ± 0.25ab | 59.48 ± 1.04bd | 12.40 ± 0.29ab |
| MR-Bazley | 11.73 ± 0.27ab | 60.46 ± 2.28bcd | 11.68 ± 0.31cd |
| MR-Buster | 11.71 ± 0.19ab | 60.78 ± 0.44abcd | 11.74 ± 0.31cd |
| 84G22 | 11.85 ± 0.34ab | 61.03 ± 1.46abcd | 11.52 ± 0.35c |
| 85G33 | 11.92 ± 0.26a | 62.31 ± 1.99abc | 11.53 ± 0.23c |
| Liberty | 11.26 ± 0.16b | 63.63 ± 2.18ac | 11.43 ± 0.26ce |
| MR-Taurus | 11.90 ± 0.41a | 59.04 ± 1.90bd | 12.25 ± 0.17bd |
| Cracka | 11.90 ± 0.18a | 60.39 ± 0.98bcd | 11.71 ± 0.28cd |
| 85G44 | 11.83 ± 0.28ab | 63.99 ± 0.15a | 10.88 ± 0.23e |
| Tiger | 11.43 ± 0.15ab | 59.59 ± 1.45bd | 12.62 ± 0.45ab |
| Cultivar | Fermentation Endpoint (h) | Ethanol Content (% v/v) | Ethanol Production Rate (ml/L h) | Glucose Content (g/L) | Glucose Consumption Rate (g/L h) | Fermentability (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation Time (h): | 0 | 96 | 24–48 | 0 | 96 | 24–48 | 96 | |
| MR-Apollo | 62.4 ± 0.8a | 0.26 ± 0.06a | 8.94 ± 0.00f | 2.03 ± 0.06a | 141.32 ± 3.38i | 0.42 ± 0.13ab | 3.41 ± 0.06a | 87.33 ± 0.20h |
| Rippa | 66.8 ± 5.8a | 0.17 ± 0.01bc | 9.47 ± 0.01d | 1.93 ± 0.03ac | 148.35 ± 2.61ac | 0.43 ± 0.10ab | 3.08 ± 0.01bc | 89.05 ± 0.67bcd |
| MR-Bazley | 75.8 ± 1.4b | 0.18 ± 0.06bd | 9.60 ± 0.05bd | 1.79 ± 0.02bd | 144.65 ± 0.49ci | 0.33 ± 0.10ab | 2.91 ± 0.06de | 88.60 ± 0.42b |
| MR-Buster | 73.6 ± 0.7b | 0.16 ± 0.01bd | 9.59 ± 0.02ed | 1.98 ± 0.01a | 152.85 ± 0.96ad | 0.53 ± 0.05ab | 3.22 ± 0.11b | 88.42 ± 0.26bd |
| 84G22 | 78.9 ± 5.5b | 0.13 ± 0.08b | 9.76 ± 0.19ab | 1.79 ± 0.07bf | 144.38 ± 3.00ci | 0.36 ± 0.16a | 2.83 ± 0.06dg | 89.07 ± 0.15be |
| 85G33 | 74.5 ± 0.6b | 0.17 ± 0.01bd | 9.59 ± 0.09dg | 1.87 ± 0.03cdf | 144.06 ± 2.48ei | 0.42 ± 0.22ab | 2.96 ± 0.10cegh | 89.03 ± 0.21bf |
| Liberty | 74.9 ± 2.1b | 0.18 ± 0.01bd | 9.73 ± 0.07beg | 1.76 ± 0.10b | 146.22 ± 1.87cef | 0.74 ± 0.49ab | 2.83 ± 0.07dh | 89.48 ± 0.64cdefg |
| MR-Taurus | 79.0 ± 5.6b | 0.21 ± 0.01acd | 9.55 ± 0.03d | 1.63 ± 0.04e | 147.42 ± 3.11ceh | 1.02 ± 0.84ab | 2.66 ± 0.17f | 89.24 ± 0.11bd |
| Cracka | 86.2 ± 0.5c | 0.16 ± 0.04bd | 9.56 ± 0.11d | 1.54 ± 0.04e | 146.01 ± 1.83ceg | 0.50 ± 0.23ab | 2.52 ± 0.11f | 89.02 ± 0.28abg |
| 85G44 | ≥96d | 0.22 ± 0.04acd | 9.75 ± 0.03be | 1.25 ± 0.03g | 150.50 ± 1.64abfgh | 0.74 ± 0.00b | 1.98 ± 0.01i | 89.68 ± 0.19acdef |
| Tiger | ≥96d | 0.18 ± 0.01bc | 9.26 ± 0.06c | 1.18 ± 0.05g | 148.19 ± 0.94bcde | 1.32 ± 0.12c | 1.99 ± 0.05i | 87.50 ± 0.60h |
| YAN (mg/L) | pH | pH Decrease Rate (pH/h) | Specific Gravity | |||||
| Fermentation Time (h): | 0 | 96 | 0 | 96 | 24–48 | 0 | 96 | |
| MR-Apollo | 131.51 ± 4.79ac | <DL | 4.25 ± 0.04ad | 3.36 ± 0.03a | 0.0144 ± 0.0037acde | 1.0881 ± 0.0005j | 0.9942 ± 0.0002a | |
| Rippa | 123.24 ± 1.53cd | <DL | 4.13 ± 0.02f | 3.36 ± 0.03a | 0.0132 ± 0.0034cde | 1.0944 ± 0.0035bd | 0.9918 ± 0.0005bc | |
| MR-Bazley | 116.68 ± 5.54bdf | <DL | 4.23 ± 0.06d | 3.30 ± 0.08bdf | 0.0156 ± 0.0006acd | 1.0920 ± 0.0003bc | 0.9925 ± 0.0005b | |
| MR-Buster | 117.97 ± 8.60d | <DL | 4.25 ± 0.02de | 3.27 ± 0.02f | 0.0169 ± 0.0005a | 1.0943 ± 0.0010bef | 0.9925 ± 0.0003b | |
| 84G22 | 116.28 ± 7.38dg | <DL | 4.28 ± 0.02db | 3.30 ± 0.02ef | 0.0151 ± 0.0005acf | 1.0961 ± 0.0020deg | 0.9917 ± 0.0001bd | |
| 85G33 | 107.30 ± 7.44efgh | <DL | 4.29 ± 0.03abe | 3.27 ± 0.02f | 0.0167 ± 0.0008ac | 1.0950 ± 0.0010bg | 0.9917 ± 0.0003be | |
| Liberty | 106.79 ± 2.94fgi | <DL | 4.18 ± 0.03cg | 3.34 ± 0.02acde | 0.0124 ± 0.0034dfg | 1.0943 ± 0.0025bgh | 0.9913 ± 0.0009cdef | |
| MR-Taurus | 102.78 ± 2.58hi | <DL | 4.28 ± 0.02abe | 3.38 ± 0.04a | 0.0144 ± 0.0010acgh | 1.0913 ± 0.0014acfhi | 0.9918 ± 0.0002bfh | |
| Cracka | 133.80 ± 9.64a | <DL | 4.18 ± 0.03bg | 3.29 ± 0.04cf | 0.0119 ± 0.0009befh | 1.0931 ± 0.0022bgi | 0.9919 ± 0.0002bfg | |
| 85G44 | 119.10 ± 5.36d | <DL | 4.13 ± 0.04f | 3.27 ± 0.02f | 0.0088 ± 0.0026bi | 1.0943 ± 0.0007abg | 0.9913 ± 0.0005cdegh | |
| Tiger | 100.24 ± 5.96hi | <DL | 4.26 ± 0.02de | 3.35 ± 0.02ade | 0.0083 ± 0.0004i | 1.0916 ± 0.0008ab | 0.9937 ± 0.0007a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, S.H.; Blanchard, C.L.; Roberts, T.H.; Waters, D.L.E.; Mawson, A.J. Effects of Sorghum Grain and Wort Composition on Dry Grind Fermentation Performance: A Model for Baijiu Production. Beverages 2023, 9, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020029
Tan SH, Blanchard CL, Roberts TH, Waters DLE, Mawson AJ. Effects of Sorghum Grain and Wort Composition on Dry Grind Fermentation Performance: A Model for Baijiu Production. Beverages. 2023; 9(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Siong H., Christopher L. Blanchard, Thomas H. Roberts, Daniel L. E. Waters, and A. John Mawson. 2023. "Effects of Sorghum Grain and Wort Composition on Dry Grind Fermentation Performance: A Model for Baijiu Production" Beverages 9, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020029
APA StyleTan, S. H., Blanchard, C. L., Roberts, T. H., Waters, D. L. E., & Mawson, A. J. (2023). Effects of Sorghum Grain and Wort Composition on Dry Grind Fermentation Performance: A Model for Baijiu Production. Beverages, 9(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9020029









