- Article
Research on Scheduling of Metal Structural Part Blanking Workshop with Feeding Constraints
- Yaping Wang,
- Xuebing Wei and
- Zihui Zhao
- + 2 authors
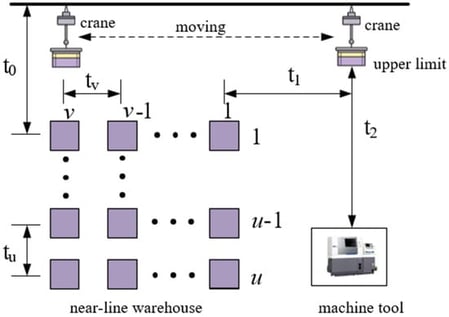
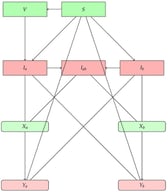
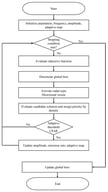
Taking a metal structural part blanking workshop as the application background, this study addresses the challenges of high material variety, long crane feeding travel caused by heterogeneous line-side storage layouts, and frequent machine stoppages due to the limited feeding capacity of a single overhead crane. To this end, an integrated machine–crane dual-resource scheduling model is developed by explicitly considering line-side storage locations. The objective is to minimize the maximum waiting time among all machine tools. Under constraints of material assignment, processing sequence, and the crane’s single-task execution and travel requirements, the storage positions of materials in line-side buffers are jointly optimized. To solve the problem, a genetic algorithm with fitness-value-based crossover is proposed, and a simulated-annealing acceptance criterion is embedded to suppress premature convergence and enhance the ability to escape local optima. Comparative experiments on randomly generated instances show that the proposed algorithm can significantly reduce the maximum waiting time and yield more stable results for medium- and large-scale cases. Furthermore, a simulation based on real production data from an industrial enterprise verifies that, under limited feeding capacity, the proposed method effectively shortens material-waiting time, improves equipment utilization, and enhances production efficiency, demonstrating its effectiveness.
6 February 2026




![Map of Yaoundé city according to the “Système d’Information Géographique”, Yaoundé City Council, Cameroon, (2011) [6].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/mca/mca-31-00018/article_deploy/html/images/mca-31-00018-g001-550.jpg)

