Ethics of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Academia and Research: The Most Relevant Approaches, Challenges and Topics
Abstract
1. Introduction
- What are the ethical challenges of integrating artificial intelligence into teaching and research?
- What are the opportunities and risks arising from this integration in various academic disciplines and practices?
- What AI tools have been used and researched, and with what approach?
- What criteria and practical guidelines can be derived from this critical analysis?
2. State of the Art
2.1. Forging Responsibilities in the Face of Artificial Intelligence
2.2. Facing the Consequences of Artificial Intelligence
2.3. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Science Writing
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Appolloni, A.; Treiblmaier, H.; Iranmanesh, M. Exploring the impact of ChatGPT on education: A web mining and machine learning approach. Int. J. Manag. Educ. 2024, 22, 100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz Virlan, A.; Tomak, B. AI tools for writing: A Q-method study with Turkish instructors of English. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2025, 30, 16997–17021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, Z.; Kafipour, R.; Khojasteh, L.; Pakdel, F. Is artificial intelligence for everyone? Analyzing the role of ChatGPT as a writing assistant for medical students. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1457744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Kosonocky, C.W.; Wang, J.Z. How our authors are using AI tools in manuscript writing. Patterns 2024, 5, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Li, K.K.; Kwok, K.O.; Cao, L.; Luong, S.; Tam, W. The importance of transparency: Declaring the use of generative artificial intelligence (AI) in academic writing. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2024, 56, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrot, J.S. Leveraging Google Gemini as a Research Writing Tool in Higher Education. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2025, 30, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Sanaullah, M.; Fuzail, M.; Malik, T.S.; Shuhidan, S.M. Comparative analysis of text-based plagiarism detection techniques. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirjalili, F.; Neysani, M.; Nikbakht, A. Exploring the boundaries of authorship: A comparative analysis of AI-generated text and human academic writing in English literature. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1347421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Ibrahim, R.; Mahmood, J. Systematic analysis of generative AI tools integration in academic research and peer review. Online J. Commun. Media Technol. 2025, 15, e202502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombaers, P.; de Bruin, J.; van de Schoot, R. Reproducibility and Data Storage for Active Learning-Aided Systematic Reviews. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almegren, A.; Hassan Saleh, M.; Abduljalil Nasr, H.; Jamal Kaid, A.; Almegren, R.M. Evaluating the quality of AI feedback: A comparative study of AI and human essay grading. Innov. Educ. Teach. Int. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Tang, G.; Huang, R.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, X. Based on Medicine, The Now and Future of Large Language Models. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2024, 17, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattaru, A.; Yanamala, N.; Sengupta, P.P. Revolutionizing Cardiology With Words: Unveiling the Impact of Large Language Models in Medical Science Writing. Can. J. Cardiol. 2024, 40, 1950–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A. Comparison of generative AI performance on undergraduate and postgraduate written assessments in the biomedical sciences. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2024, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Journalists as individual users of artificial intelligence: Examining journalists’ “value-motivated use” of ChatGPT and other AI tools within and without the newsroom. Journalism 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekera, T.; Hosseini, Z.; Perera, U.; Bazhaw Hyscher, A. Generative artificial intelligence tools for diverse learning styles in design education. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2024, 23, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaichana, P.; Oo, M.Z.; Thorup, G.L.; Chansakaow, C.; Arworn, S.; Rerkasem, K. Integrating Artificial Intelligence in Medical Writing: Balancing Technological Innovation and Human Expertise, with Practical Applications in Lower Extremity Wounds Care. Int. J. Low. Extrem. Wounds 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengul, C.; Neykova, R.; Destefanis, G. Software engineering education in the era of conversational AI: Current trends and future directions. Front. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 1436350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llerena-Izquierdo, J.; Mendez-Reyes, J.; Ayala-Carabajo, R.; Andrade-Martinez, C. Innovations in Introductory Programming Education: The Role of AI with Google Colab and Gemini. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.R.; Walter, N.G.; Sevryugina, Y.V. Implementation and Evaluation of a ChatGPT-Assisted Special Topics Writing Assignment in Biochemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2024, 101, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, F.M.; Li, A.; Riffon, M.F.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Pearson, A.T. Characterizing the Increase in Artificial Intelligence Content Detection in Oncology Scientific Abstracts From 2021 to 2023. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2024, 8, e2400077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo-García, M.E.; Hernández-De la Cerda, H.; Benavides-García, I.G.; Caratozzolo, P.; Membrillo-Hernández, J. Who is solving the challenge? The use of ChatGPT in mathematics and biology courses using challenge-based learning. Front. Educ. 2025, 10, 1417642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eachempati, P.; Komattil, R.; Arakala, A. Should oral examination be reimagined in the era of AI? Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2025, 49, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clift, L.; Petrovska, O. Learning without Limits: Analysing the Usage of Generative AI in a Summative Assessment. In Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Computing Education Practice, Durham, UK, 7 January 2025; CEP ’25. pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segooa, M.A.; Modiba, F.S.; Motjolopane, I. Generative Artificial Intelligence Tools to Augment Teaching Scientific Research in Postgraduate Studies. S. Afr. J. High. Educ. 2025, 39, 300–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rujeedawa, M.I.H.; Pudaruth, S.; Malele, V. Unmasking AI-Generated Texts Using Linguistic and Stylistic Features. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2025, 16, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deanda, D.; Alsmadi, I.; Guerrero, J.; Liang, G. Defending mutation-based adversarial text perturbation: A black-box approach. Clust. Comput. 2025, 28, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, M.; Sheikh, S.; Minhas, A.M.K.; Vaughan, E.M.; Krittanawong, C.; Samad, Z.; Lavie, C.J.; Khoja, A.; D’Cruze, M.; Slipczuk, L.; et al. A review of top cardiology and cardiovascular medicine journal guidelines regarding the use of generative artificial intelligence tools in scientific writing. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oates, A.; Johnson, D. ChatGPT in the Classroom: Evaluating its Role in Fostering Critical Evaluation Skills. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Gero, K.I.; Chung, J.J.Y.; Shum, S.B.; Raheja, V.; Shen, H.; Venugopalan, S.; Wambsganss, T.; Zhou, D.; Alghamdi, E.A.; et al. A Design Space for Intelligent and Interactive Writing Assistants. In Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024. CHI ’24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Shah, S.; Haddad, A.; Raper, D.M.S. Introducing Our Custom GPT: An Example of the Potential Impact of Personalized GPT Builders on Scientific Writing. World Neurosurg. 2025, 193, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, S.H.; Stakhanova, N.; Branca, E. Learning AI Coding Style for Software Plagiarism Detection. In Proceedings of the Security and Privacy in Communication Networks, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 28–30 October 2024; Duan, H., Debbabi, M., de Carné de Carnavalet, X., Luo, X., Du, X., Au, M.H.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzeralnd, 2025; pp. 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysechko, A.; Lytvynenko, A.; Goian, A. Artificial Intelligence in Academic Media Environment: Challenges, Trends, Innovations. Media Lit. Acad. Res. 2024, 7, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Martínez, I.M.; Flores-Bueno, D.; Gómez-Puente, S.M.; Vite-León, V.O. AI in higher education: A systematic literature review. Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1391485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.; Husain, O.; Hamdan, M.; Abdelsalam, S.; Elshafie, H.; Motwakel, A. Transforming education with AI: A systematic review of ChatGPT’s role in learning, academic practices, and institutional adoption. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrot, J.S. Balancing Innovation and Integrity: An Emerging Technology Report on SciSpace in Academic Writing. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2025, 30, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, E.; Schlichktrull, M.; Vlachos, A. Automated focused feedback generation for scientific writing assistance. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.20477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaloul, K. Identifying AI-Written Text in Academia: A Machine Learning-Based Framework. In Proceedings of the 2024 1st International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Telecommunication and Energy Technologies (ECTE-Tech), Oum El Bouaghi, Algeria, 17–18 December 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obura, E.A.; Emoit, P.I. Artificial Intelligence in Academic Writing and Research Skills in Kenyan Universities: Opportunities and Challenges. Afr. Educ. Rev. 2024, 20, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramar, N.; Bedrych, Y.; Shelkovnikova, Z. Ukrainian Phd Students’ Attitudes Toward AI Language Processing Tools in the Context of English for Academic Purposes. Adv. Educ. 2024, 12, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tang, L.; Le, H.; Tan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, K.; Li, X.; Juelich, T.; Wang, Q.; Gašević, D.; et al. Aligning and comparing values of ChatGPT and human as learning facilitators: A value-sensitive design approach. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2025, 56, 1391–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, H.; Suherman; Hasruddin; Ridha, M. Between Shortcut and Ethics: Navigating the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Writing Among Indonesian Doctoral Students. Eur. J. Educ. 2025, 60, e70083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubaidi, K.; Jaafari, M.; Touzani, F.Z. Impact of ChatGPT on Academic Writing at Moroccan Universities. Arab World Engl. J. 2024, 1, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szandała, T. ChatGPT vs human expertise in the context of IT recruitment. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 264, 125868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshaei, S.P.; Rietsche, R.; Su, X.; Wambsganss, T. Enhancing Peer Review with AI-Powered Suggestion Generation Assistance: Investigating the Design Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Greenville, SC, USA, 18–21 March 2024; IUI ’24. pp. 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherheș, V.; Fărcașiu, M.A.; Cernicova-Buca, M.; Coman, C. AI vs. Human-Authored Headlines: Evaluating the Effectiveness, Trust, and Linguistic Features of ChatGPT-Generated Clickbait and Informative Headlines in Digital News. Information 2025, 16, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawlik-Kobylińska, M. Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Enhanced Scientific Collaboration: Insights from Students and Educational Implications. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.K.; Bansal, T.; Modi, S.; Singh, A. How Sensitive Are the Free AI-detector Tools in Detecting AI-generated Texts? A Comparison of Popular AI-detector Tools. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2024, 47, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, V.; Federico, S.; Jonathan, M.; Marco, C.; Bignami, E. Between human and AI: Assessing the reliability of AI text detection tools. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2024, 40, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Nacke, L.; Rogers, K. Introducing the INSPIRE Framework: Guidelines From Expert Librarians for Search and Selection in HCI Literature. Interact. Comput. 2025, iwaf001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirón-Mérida, V.A.; García-García, R.M. Developing written communication skills in engineers in Spanish: Is ChatGPT a tool or a hindrance? Front. Educ. 2024, 9, 1416152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Jain, A. Generative AI in Writing Research Papers: A New Type of Algorithmic Bias and Uncertainty in Scholarly Work. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems and Applications, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29–30 August 2024; Arai, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.J.; Hui, K.T.K.; Al Zoubi, F.; Zhou, Z.Z.X.; Samartzis, D.; Yu, C.C.H.; Chang, J.R.; Wong, A.Y.L. The great detectives: Humans versus AI detectors in catching large language model-generated medical writing. Int. J. Educ. Integr. 2024, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desaire, H.; Isom, M.; Hua, D. Almost Nobody Is Using ChatGPT to Write Academic Science Papers (Yet). Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Májovský, M.; Černý, M.; Netuka, D.; Mikolov, T. Perfect detection of computer-generated text faces fundamental challenges. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 101769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Li, F.; Luo, B. On the Detectability of ChatGPT Content: Benchmarking, Methodology, and Evaluation through the Lens of Academic Writing. In Proceedings of the 2024 on ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 14–18 October 2024; CCS ’24. pp. 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadán-Guerrero, J.; Acosta-Vargas, P.; Gutiérrez-De Gracia, N.E. Enhancing Scientific Research and Paper Writing Processes by Integrating Artificial Intelligence Tools. In Proceedings of the HCI International 2024 Posters, Washington, DC, USA, 29 June–4 July 2024; Stephanidis, C., Antona, M., Ntoa, S., Salvendy, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J. The use of generative AI in statistical data analysis and its impact on teaching statistics at universities of applied sciences. Teach. Stat. 2025, 47, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz Durak, H.; Eğin, F.; Onan, A. A Comparison of Human-Written Versus AI-Generated Text in Discussions at Educational Settings: Investigating Features for ChatGPT, Gemini and BingAI. Eur. J. Educ. 2025, 60, e70014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, A.; Shi, W.; Corriveau, J.P. AI-generated or AI touch-up? Identifying AI contribution in text data. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2024, 20, 3759–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










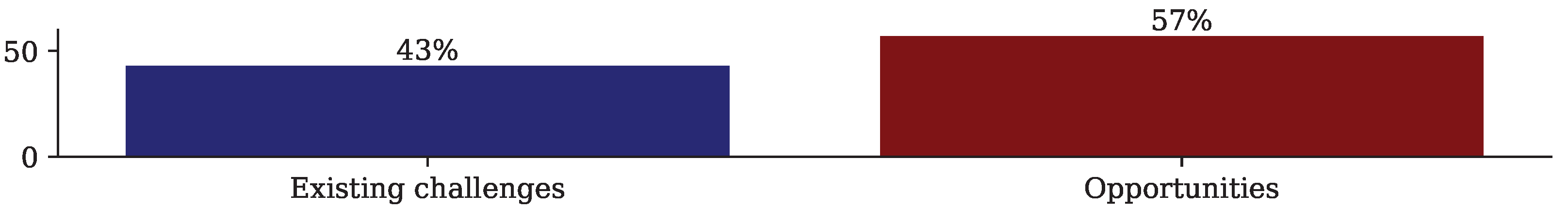
| Thematic Area of Research | Classification | Reference | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI in education and training | Applications in education. | [1,2,6,19,22,35,39,41,51] | 15.0% |
| Applications in medical education, clinical practice and nursing. | [12,13] | 3.3% | |
| Applications in the assessment process. | [11] | 1.7% | |
| AI in academic and research production | Applications in research processes. | [7,9,21,24,25,29,30,34,40,42,49,50,52,53,58] | 25.0% |
| Applications in article and poster writing. | [5,31,37,38,47,48,56,57] | 13.3% | |
| Applications in academic writing. | [3,8,28,43,59] | 8.3% | |
| Automated academic writing assistance. | [36,46] | 3.3% | |
| Applications in peer review. | [45] | 1.7% | |
| Applications in scientific work selection processes. | [10] | 1.7% | |
| AI in life and health sciences | Application in biomedical sciences. | [14,20] | 3.3% |
| Application in healthcare communication. | [17] | 1.7% | |
| AI in the media | Applications in the field of communication. | [15,33] | 3.3% |
| Applications in journalism, education, and law. | [26] | 1.7% | |
| AI in computer science and design | Applications in computer science. | [18,32] | 3.3% |
| Application in interior design. | [16] | 1.7% | |
| AI in cross-cutting and ethical aspects | Authenticity of the content. | [23,27,54,55,60] | 8.3% |
| Applications in immediate feedback. | [4] | 1.7% | |
| Applications in assisted decision making. | [44] | 1.7% |
| Categories | Classification |
|---|---|
| Topics and objectives | A1: AI application in education |
| A2: Use of AI in research | |
| A3: Ethics-focused guidelines for AI use | |
| A4: Detection and authenticity of AI-generated content | |
| A5: Evaluating AI tools for academia | |
| Problem formulation and data implications | B1: Impact of AI on learning and skills |
| B2: Challenges to academic integrity and ethics | |
| B3: Technical and reliability limitations of AI | |
| B4: Need for reference frameworks and guidelines for AI integration | |
| B5: Perceptions and reactions towards AI | |
| Limitations encountered | C1: Reliability and accuracy of AI-generated content |
| C2: Challenges in AI-generated text and information detection | |
| C3: Limitations in human understanding and interaction with AI | |
| C4: Impact on the development of human skills | |
| C5: Effectiveness of AI tools depending on factors such as context and language | |
| Proposals and applied methodology | D1: Empirical studies to assess the impact of AI, proposals, and methodologies applied |
| D2: Systematic literature reviews to synthesise knowledge | |
| D3: Evaluation of frameworks and models for AI integration and detection | |
| D4: Linguistic analysis to understand the content of the AI | |
| D5: Design approaches centred on user values and perspectives | |
| Solution found, outcomes, and challenges | E1: Understanding users’ perceptions and use of AI |
| E2: Evaluation of the effectiveness of AI tools in academic and professional tasks | |
| E3: Identification of factors influencing the adoption and impact of AI | |
| E4: Evaluation of methods and tools for AI content detection | |
| E5: Need for guidelines and perception of AI |
| Code | Approach | References |
|---|---|---|
| A | Comparative analysis of AI tools | [3,14,16,17,18,44,45,46,47,49,60] |
| B | Integration of AI in information search | [8,48,50,51] |
| C | Challenges to be addressed with the use of AI | [1,28,33,34,36,37] |
| D | Strategies of use with AI | [4,5,9,12,15,20,21,23,24,25,26,27,29,38] |
| E | Ethics and transparency in the use of AI | [7,13,22,32,41,42,52,53,54,55,59] |
| F | Innovative methodologies with the use of AI | [10,11,19,35,40,53,56,57] |
| G | Novelty with the use of AI | [2,6,30,31,39,43,58] |
| Approaches * | AI Tool | References |
|---|---|---|
| Comparative analysis of AI tools | ChatGPT, Bing, and Bard | [14] |
| ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and Mistral | [44] | |
| Hamta.ai | [45] | |
| GPTZero, ZeroGPT, Writer ACD, and Originality | [49] | |
| GPTZero, and AICIS-2S | [60] | |
| Integration of AI in information search | Sapling, Undetectable AI, Copyleaks, QuillBot, and Wordtune | [48] |
| Turnitin, Unicheck, GPTZero, and ChatGPT | [51] | |
| Challenges to be addressed with the use of AI | SciSpace | [36] |
| SWIF2T | [37] | |
| Strategies of use with AI | GPTZero, Originality.ai, and Sapling | [21] |
| ResearchBuddie artefact, ChatGPT, Elicit, and Research Rabbit | [25] | |
| Ethics and transparency in the use of AI | ChatGPT, and Bard | [32] |
| ChatGPT, Connected Papers, Zotero, Humata, Scite AI, and Deepl | [42] | |
| Turnitin, GPTZero, Originality.ai, Wordtune, ZeroGPT, GPT-2 Output Detector, and Content at Scale | [53] | |
| ChatGPT, Google Gemini, and BingAI | [59] | |
| Innovative methodologies with the use of AI | Google Gemini | [19] |
| Grammarly, QuillBot, and ChatGPT | [40] | |
| CheckGPT, and GPABench2 | [56] | |
| Novelty with the use of AI | Google Gemini | [6] |
| Medi Research Assistant, and Neurosurgical Research Paper Writer | [31] | |
| ChatGPT | [43] |
| Aspects * | Reference |
|---|---|
| Opportunities in the use of AI | [1,3,8,10,11,13,14,16,17,18,19,23,24,25,26,28,30,31,33,34,36,37,39,40,41,42,44,45,47,50,56,57,58,59] |
| Existing challenges in the use of AI | [2,4,5,6,7,9,12,15,20,21,22,27,29,32,35,38,43,46,48,49,51,52,53,54,55,60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Llerena-Izquierdo, J.; Ayala-Carabajo, R. Ethics of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Academia and Research: The Most Relevant Approaches, Challenges and Topics. Informatics 2025, 12, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040111
Llerena-Izquierdo J, Ayala-Carabajo R. Ethics of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Academia and Research: The Most Relevant Approaches, Challenges and Topics. Informatics. 2025; 12(4):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040111
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlerena-Izquierdo, Joe, and Raquel Ayala-Carabajo. 2025. "Ethics of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Academia and Research: The Most Relevant Approaches, Challenges and Topics" Informatics 12, no. 4: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040111
APA StyleLlerena-Izquierdo, J., & Ayala-Carabajo, R. (2025). Ethics of the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Academia and Research: The Most Relevant Approaches, Challenges and Topics. Informatics, 12(4), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics12040111







