- Article
Integrating Mathematics into Prenatal Diagnosis—Different Phenotypes of Complex Ventral Wall Malformations Determined by Hierarchical Clustering
- Julia Bijok,
- Anna Kucińska-Chahwan and
- Tomasz Roszkowski
- + 2 authors
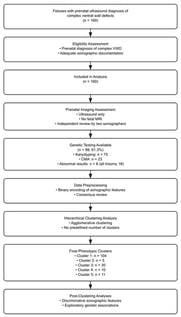
Background/Objectives: To identify distinct sonographic phenotypes of complex malformations of the fetal ventral wall. Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of ultrasound reports from 160 fetuses diagnosed with complex ventral wall defects at a single tertiary referral center between 1997 and 2021. Agglomerative hierarchical clustering was applied to identify distinct sonographic phenotypes based on the level of the ventral wall defect and associated anomalies. Results: Ventral wall defects involved the abdominal wall in 150 cases, the thoracic wall in 42 cases, and the pelvic wall in 28 cases, either in isolation or in combination. Open neural tube defects were present in 58 fetuses (36.3%), spinal defects in 110 fetuses (68.8%), and limb anomalies in 45 fetuses (28.1%). Additional anomalies were identified in 38 fetuses (23.8%), including cardiac anomalies in 18 cases (11.3%). Amniotic bands were observed in seven cases (4.4%). Using agglomerative hierarchical clustering, five groups of fetuses with differing numbers of observations were identified (cluster 1, n = 104; cluster 2, n = 5; cluster 3, n = 30; cluster 4, n = 10; cluster 5, n = 11). The silhouette score of the clustering model was 0.3285. The most discriminative features for each cluster, expressed as feature importance values, were as follows: kyphoscoliosis for cluster 1 (0.924), pelvic wall defect for cluster 2 (0.852), ectopia cordis for cluster 3 (0.662), limb anomalies for cluster 4 (0.767), and spina bifida for cluster 5 (0.691). Conclusions: Complex malformations of the fetal ventral wall are associated with a wide spectrum of additional anomalies. Hierarchical clustering identified five distinct sonographic phenotypes of complex ventral wall defects, highlighting the heterogeneity of these conditions.
8 February 2026