Abstract
Thaw consolidation of degrading permafrost is a serious hazard to the safety and operation of infrastructure. Monitoring thermal changes in the active layer (AL), the proportion of the soil above permafrost that thaws and freezes periodically, is critical to understanding the conditions of the top layer above the permafrost and regulating the construction, operation, and maintenance of facilities. However, this is a very challenging task using ground-based methods such as ground-penetrating radar (GPR) or temperature sensors. This study explores the integration of interferometric measurements from high-resolution X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images and volumetric water content (VWC) data from SoilGrids to quantify detailed spatial variations in active layer thickness (ALT) in Iqaluit, the territorial capital of Nunavut in Canada. A total of 21 SAR images from COSMO Sky-Med (CSK) were first analyzed using the freely connected network interferometric synthetic aperture radar (FCNInSAR) method to map spatial and temporal variations in ground surface subsidence in the study area. Subsequently, we built an ALT retrieval model by introducing the thaw settlement coefficient, which takes soil properties and saturation state into account. The subsidence measurements from InSAR were then integrated with VWC extracted from the SoilGrids database to estimate changes in ALT. For validation, we conducted a comparison between estimated ALTs and in situ measurements in the airport sector. The InSAR survey identifies several sites of ground deformation at Iqaluit, subsiding at rates exceeding 80 mm/year. The subsidence rate changes along the runway coincide with frost cracks and ice-wedge furrows. The obtained ALTs, ranging from 0 to 5 m, vary significantly in different sediments. Maximum ALTs are found for rock areas, while shallow ALTs are distributed in the till blanket (Tb), the intertidal (Mi) sediments, and the alluvial flood plain (Afp) sediment units. The intersection of taxiway and runway has an AL thicker than other parts in the glaciomarine deltaic (GMd) sediments. Our study suggests that combining high-resolution SAR imagery with VWC data can provide more comprehensive ALT knowledge for hazard prevention and infrastructure operation in the permafrost zone.
1. Introduction
Permafrost regions are defined as grounds that remain continuously frozen for two or more consecutive years. They underlie about 20% of the land surface of the Earth and are located mainly in the Arctic, Antarctic, and high mountainous regions [1]. The seasonal thawing and freezing of the active layer (AL), the surface layer atop permafrost, results in ground motion, making infrastructure in such regions vulnerable to varying degrees of damage. Therefore, accurate monitoring of active layer thickness (ALT) and related ground surface change is vital to characterize permafrost degradation and regulate the construction, operation, and maintenance of facilities [2,3,4,5,6,7].
Commonly used in situ investigation methods for ALT include point measurements obtained by recording soil temperatures of probes on the ground at different sparse locations [8] and profile exploration of the underground geophysical status using ground-penetrating radar (GPR) [9,10,11]. These methods are reliably accurate for estimating ALT at a single point or local area, but are extremely limited in space and are costly and inefficient for large-scale mapping in severe cold environments in the permafrost areas. Another method of acquiring ALT information is using analytical models, which evaluate permafrost thermal dynamics using air temperature, vegetation, snow, and soil properties [12,13,14]. However, the results of such models are inadequate, especially in data-poor areas. Remote-sensing-based assessment of ALT fulfills the urgent need to extend point observations to a broader spatial domain in permafrost areas. Similarly to GPR, the dielectric contrast between the thawed and frozen soils results in a strong scattering of electromagnetic waves, providing a signature in backscattering measurements for freeze/thaw boundary detection in radar remote sensing imagery. However, due to the lack of proper satellite sensors, few studies have explored the potential of such imagery for monitoring the processes operating in permafrost [15].
The retrieval of ALT from surface displacement measurements detected by the InSAR has been promising due to the technique’s capability for accurately mapping ground displacements on the scale of millimeters to centimeters [16,17,18,19,20]. There are two main types of ALT retrieval methods from InSAR-derived subsidence maps. The first works based on soil’s one-dimensional heat transfer process [16]. The basic idea is that ALT could be determined if the time intervals in which the maximal temperature diffuses from the ground surface downward to the bottom of the active layer are known. Considering the difficulty in measuring the time intervals directly, the model replaces them with the lag time between the periodic feature of InSAR-observed surface deformation over permafrost and the meteorologically recorded temperatures. The second method is based on the idea that the volume change from ice to the water of the AL leads to surface subsidence [17,18,19,20,21,22]. It can be represented by the Stefan formula or the Berggren model. In these models, soil moisture, as the most sensitive factor, is quantified as volumetric water content (VWC), defined as the volume of water divided by the total soil volume. It determines the soil heat capacity and thermal conductivity, influencing the flow of energy into and out of the soil, thus, ALT and ground temperature [23]. The more accurate the soil moisture data (i.e., VWC) as an input, the more accurate the predictions of ALT are to be expected.
Several studies used the second retrieval approach discussed above to monitor ALT with the subsidence derived from InSAR. According to the stratification of soil profiles, Liu et al. proposed a vertical distribution model containing organic, mineral, pure water, or mixed layers to estimate ALT over Alaska using uniform soil moisture values [17]. However, soil moisture is highly variable in both space and time [23]. Wang et al. built a multilayered groundwater model for different land cover types using field data, then integrated it into the Stefan formula to retrieve ALT over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau [20]. Anne et al. estimated ALT using the modified Berggren solution over Barrow Peninsula at a resolution of 30 × 30 m [24]. Both studies required detailed in situ measurements, e.g., surface meteorological variables and soil thermal parameters, which are not available everywhere. Zhang et al. used soil moisture data from ERA-Interim reanalysis and SMAP L4 for ALT estimation. The spatial resolutions of ERA-Interim reanalysis and SMAP are 0.1° (9 km) and 0.125° (13 km), respectively [24]. The data are too coarse to be used for integration with submeter level SAR images.
However, the active layer freezes, sometimes with no uplift of the surface and at other times with an uplift of even 100 percent of the depth of freezing [25,26,27,28]. The soil is an open system in that the frost heaving can be much greater than the volume change of pore water due to the available water supply [25]. In a summer season, the magnitude of the subsidence resulting from the soil thawing downward from the surface is mainly related to the soil thermal properties and ice content formed in the last winter. As Yanagiya commented in [29], the retrieval models based on the volume change of pore water are inadequate for obtaining more realistic results in most cases.
The objective of this study was to use a realistic model to quantify the meter-level resolution ALT in Iqaluit based on the accurate thaw subsidence and explicit knowledge of soil moisture from a global product. Here, we demonstrate the ALT retrieval solution combining both the six-layer VWC dataset from the SoilGrids database at 250 m spatial resolution and the subsidence field derived from FCNInSAR [30,31]. First, we explored 21 SAR images from COSMOSky-Med (SLC) using the FCNInSAR method to quantify and map spatial and temporal variations in ground surface subsidence in the study area. Secondly, the thaw-settlement coefficient was introduced to establish the relationship between the thaw settlement and ALT. Soil properties and saturation state are considered in the model. Then, ALT over the study area was obtained by integrating the high-resolution subsidence rates measurements from InSAR with VWC. The results are then interpreted against maps of surface geology to analyze the spatial distribution of ALT and find possible reasons for the differences in ALTs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Iqaluit is the territorial capital of Nunavut, Canada, as shown in Figure 1. In the far north latitude of 63, the city at the northern shore of Frobisher Bay is located in the permafrost zone, extending in the subarctic from a few meters to 1500 m into the ground, and is therefore extremely sensitive to climate change [32]. This area is under the subarctic-tundra climate and has a series of typical climate characteristics, e.g., short growing seasons, extremely low temperatures, strong winds, and variable sunlight periods. The summers here are very short and humid. The period that air temperatures drop below 0 centigrade is at least eight months per year. The active layer thaws during hot summers (usually in June to September) but heaves in winter when the air temperature slides dramatically to negative 30–40 centigrade. According to the temperature recordings in July and August, the highest temperature reached 21 centigrade in 2016, and it has been generally warmer than before in recent years.
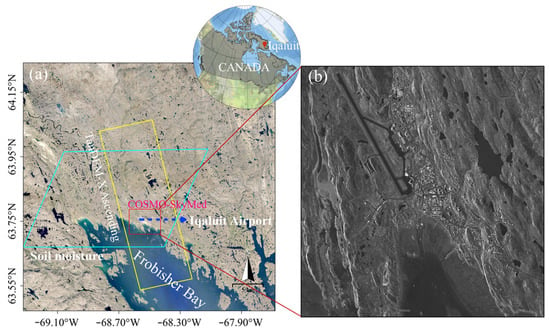
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the study area and coverage of SAR images and soil moisture; (b) a CSK amplitude image.
The subsurface sediments under the city are mainly composed of lacustrine (Lv) sediments, fluvial (coarse-grained) and glaciomarine deltaic (GMd) deposits, bedrock (R), and rock with till cover (Tv) [33]. Except for the bedrocks that are relatively stable, all subsurface sediments are considered to have an ice-rich content. As a result, in response to seasonal alternation, the ground surface in frozen soil areas undergoes dramatic freezing uplift and thawing settlement, as much as 10 cm [34], so the ALTs increase in thickness.
The elevation difference over the study area is about 70 m. Iqaluit airport was built on a flat basin surrounded by hills and rock plateaus. It serves as the transport hub for the eastern Canadian Arctic due to the lack of highway or railway there. The available alternative forms of transportation are mainly ships in summer to connect the city to other northern communities or the rest of Canada. The airport has been expanded with the increasing mining and tourism in addition to serving nearly 8000 residents of the city. Influenced by climate change in recent years, the airport and the houses built in this area are becoming more vulnerable to the freeze–thaw cycle. The taxiway and runway of the airport sustain continuous cracking due to the ground deformation. It is vital to monitor uneven subsidence at the airport to guarantee safe operation.
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. SAR Data
For the InSAR analysis, 21 COSMO-SkyMed images in Spotlight mode acquired from June to September 2014 with an incidence angle of 25.4° and “HH” polarization were used. The pixel spacing of the single-look complex image in the slant range and azimuth direction is 0.312 and 0.702 m, respectively. The coverage and the amplitude of the SAR images are shown in Figure 1. The acquisition dates of all images can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Iqaluit COSMO-SkyMed acquisition dates.
Two TanDEM-X images in bistatic mode acquired in July 2012 were used to produce a DEM with 5 m spatial resolution and 2 m relative height accuracy for acquiring more precise differential interferograms.
2.2.2. Soil Moisture Data
Publicly available soil profile data from SoilGridsTM [35] provide global predictions for standard numeric soil properties including pH, soil organic carbon content, bulk density, coarse fragment content, sand content, silt content, clay content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), total nitrogen soil organic carbon density, and soil organic carbon stock, as well as volumetric water content (VWC) at six standard depths (0–5, 5–15, 15–30, 30–60, 60–100, and 100–200 cm) with the highest scale of 250 m resolution. In this study, we used the VWC in 1500 kPa predictions with the prediction uncertainty at 95th percentiles. Figure 2a–f shows the spatial distribution of soil moisture over Iqaluit and the vicinity. Figure 3 gives examples of the vertical profile of random points located in different sediments.
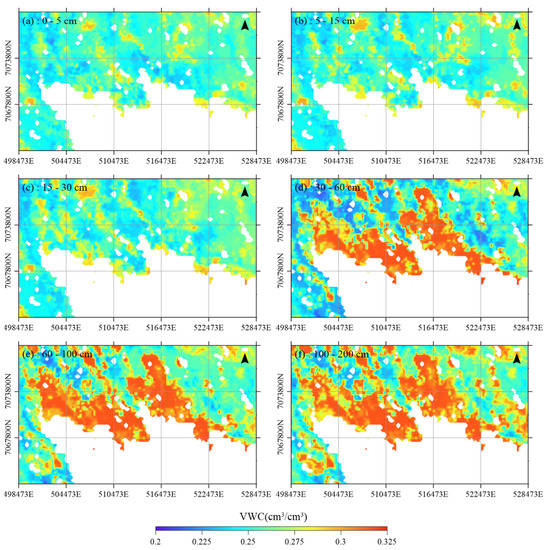
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of soil moisture over Iqaluit at six standard layers under UTM projection.
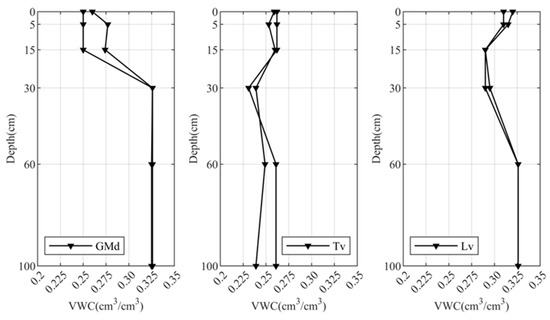
Figure 3.
Profiles of soil moisture at points in GMd, Tv, and Lv sediments.
2.3. Methodology
The aim of this study was to acquire high spatial resolution subsidence maps of Iqaluit using InSAR and estimate ALTs on the basis of seasonal thaw subsidence. The main two steps were (1) subsidence observation and (2) ALT retrieval.
2.3.1. Subsidence Observation from CSK Spotlight SAR Images
We applied the FCNInSAR algorithm to CSK images to map the subsidence in Iqaluit. This is a robust method taking advantage of both PSInSAR [36] and SBAS [37] methods. The main processing steps in FCNInSAR are similar to PSInSAR. The main differences are as follows: (1) Forming interferograms following the SBAS method to increase the measurements by connecting all possible images instead of using only one single master image. This is useful especially when the number of available images is limited. (2) More observations of arcs improve the stability of deformation acquisition. (3) The best estimation of linear deformation rates and DEM errors can be found by searching in a predefined value space rather than phase unwrapping. (4) SVD must be adopted to reconstruct the time series of nonlinear deformation due to the SBAS method of forming interferograms.
We used a linear deformation model to estimate velocities since all selected images were acquired in summer. However, the solution of FCNInSAR fully considers the extraction of the nonlinear deformation component. In order to select a sufficient number of persistent scatters (PSs) and obtain reliable subsidence, this study only processed SAR images spanning the thawing season without snow cover. In Iqaluit, as mentioned above, the average temperature from June to September is greater than 0 °C, so the thawing settlement of frozen soil mainly occurs throughout these four months. Therefore, 21 images in June and September (see Table 1) were selected to map the subsidence. The image acquired on 21 August was chosen to be the reference image for co-registration. All images were resampled into the reference image space. Then, the mean and the standard deviation (SD) of amplitudes were calculated based on the co-registered amplitude images. A total of 1,000,561 PSs were selected in the study area, of which the amplitude dispersion index is less than 0.25.
We also set the perpendicular baseline and temporal thresholds of 500 m and 90 days to generate 167 interferograms. We visually inspected the quality of all interferograms and removed those with temporal baselines longer than 30 days due to their low coherence. A total of 72 interferograms remained for deformation analysis (see Figure 4). The phase at each pixel consists of many components, such as topography, flat-earth trend, deformation, atmosphere, and decorrelation noise. We removed the topographic effects and the flat-earth trend from interferograms using the newly made DEM and the orbital data and then acquired 72 differential interferograms. The differential phase at each pixel of differential interferograms can be modeled as:
where denotes the th interferogram, and , , and are the differential phase of linear deformation, elevation error, and residual phase along the radar line of sight (LOS), respectively. The residue phase includes nonlinear deformation phase, atmospheric phase, and noise.
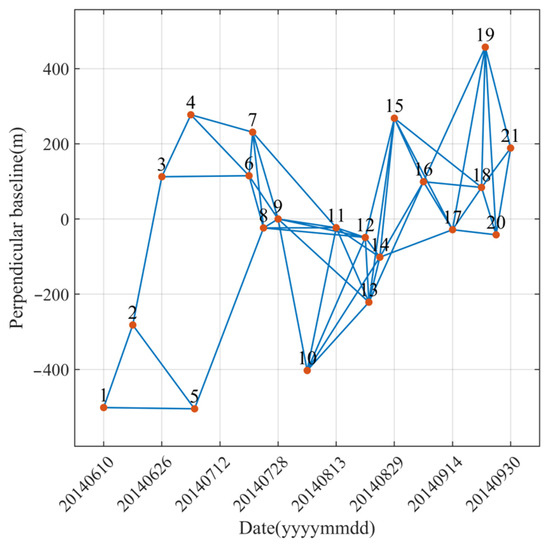
Figure 4.
Spatiotemporal baselines of interferograms.
We freely linked the neighborhood PSs (e.g., within 1 km distance) to form a strong network. By differencing the phase between two adjacent PSs, the residue phase can be largely subtracted due to spatial autocorrelation [38]. Therefore, the differential phase between two adjacent PSs (A and B) for the th interferogram can be illustrated as:
where denotes the residue phase on the arc AB, and , , and are the nonlinear deformation and the atmospheric and noisy differential phase between AB, respectively. and denote the DEM errors and linear displacement velocities at pixels, and ∆ε and ∆v are the increment of elevation errors and the increment of linear displacement velocities between two connected PSs (e.g., A and B), respectively. B⊥i and Ti are the perpendicular (spatial) and temporal baseline of the th interferogram, respectively; λ, R, and θ are the radar wavelength, sensor-to-target distance, and radar incident angle, respectively.
Due to the phase ambiguity in the differential interferograms, the two unknowns and of each pair of PS points can be determined by maximum likelihood estimation, i.e., by searching and in a pre-defined solution space (e.g., (−5, 5) m, (−200, 50) mm/year in this study) to maximize the following equation:
where is the model coherence, and denotes the difference between measured and estimated phase values. After the increments of velocities and DEM errors are calculated, we interpolated linear deformation rates and DEM errors at the regular grid points based on the irregular PS samples. The residual phases of every pixel were obtained by subtracting the gridded phase from each of the differential interferograms. As the interferograms were freely generated, the SVD was applied to reconstruct the time series of residual phases corresponding to the SAR acquisitions. We further isolated the nonlinear and atmospheric phase by using the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) method [38] on the unwrapped residue phase as the two terms have different frequencies in space and time. The deformation of each PS is the sum of the linear and the nonlinear deformation. A bedrock area close to the airport was chosen as the reference point for the velocity calculation. The velocities of all PSs can be calculated by spatial integration in the freely connected network with respect to the given reference point. InSAR measurements were along the direction of the line of sight (LOS). We converted all results from LOS to vertical displacement using the following equation:
2.3.2. ALT Estimation
The maximal thawing settlement throughout the year should be used as input for inversion of ALT from subsidence data. Considering Iqaluit, the monthly average temperatures from January to May or from October to December are all below 0 degrees Celsius. The daily temperature was almost negative in those months by 2015, and therefore, the frozen soil rarely thaws. In addition, the temperature decreases so rapidly in October that while the soil close to the permafrost table remains in a continuous thawing state, the surface starts freezing downward when the ground surface temperature becomes negative. Therefore, in this study, we assumed that the thawing settlement from June to the end of September equals the yearly thawing settlement, and the water totally changes to ice in winter.
The total settlement is mainly affected by three terms: one from thawing settlement and two volume-compressibility terms due to a surcharge load and the self-weight [39]. The volume compressibility can be ignored since consolidation comprises only a fraction of the surface settlement that occurs as a result of drainage from the lower boundary [25]. Thus, the total thawing settlement can be simplified as:
where H is the thaw-induced settlement of the frozen soil, is the thaw settlement coefficient, and Z is the depth to thaw front from the original surface. The maximum thawing depth corresponding to the largest settlement is the ALT. Thus, the relationship between ALT and the maximal thaw subsidence is:
The main factors that affect the thawing settlement coefficient are soil types, ice content, and the dry density of frozen soil [40,41]. With the same moisture content, sandy soil has a smaller thaw coefficient than clay. The thawing settlement coefficient increases with the decrease in the dry density when the soil is saturated. If the ice content is large, the thawing settlement coefficient and settlement of frozen soil are both significant because the settlement results not only from the volume shrink from the ice-water phase change but also the drainage of saturated or oversaturated soil thawing. Owing to extremely low temperatures in winter at Iqaluit (around −40 °C), we simply assumed that the ice content is equated to the water content in this study. Based on the aforementioned ideas, the thaw settlement coefficient can be calculated separately in the following conditions:
- Soil in an unsaturated state
It is generally assumed that when unsaturated soil freezes and thaws in situ, the volume expansion cannot fill the pores fully. As a result, there is no heave uplift or settlement. Experiments indicated that there is still observable uplifting upon freezing which results from the volume expansion of bound water [40,41]. The combining rate is introduced to denote the ratio of water attending the freezing expansion:
where is the water content of soil by mass and is the water content of saturated soil by mass. refers to the water density, while is the dry density of the soil, and is the specific gravity of soil particle. The thaw settlement coefficient of unsaturated soil is:
- Soil in a saturated state
For a saturated soil, = 1. The thaw settlement coefficient is:
- Soil in an oversaturated state
When the oversaturated soil freezes in winter, some water is pulled through the soil to build up layers of segregated ice. When the AL thaws in summer, part of the water becomes free water and discharges under good drainage conditions [25,26,27,28,29,39]. This part of the water contributes its whole volume to the subsidence. Therefore, the difference in volume between the frozen and thawed state is equated to the change in volume associated with melting the ice plus the volume of water expelled from the soil. The void ratio of oversaturated soil can be solved by:
The relationship of the height of the free water in unit area and the height of the thawing soil is:
where is the void ratio under the liquid limit, is the total height of the thawing soil, and is the height of the free water in unit area. The height of pore water that approaches the liquid limit in unit area is:
The thaw settlement coefficient can be expressed as:
It also can be described as:
Thawing settlement coefficients for all soil types can be determined given values of soil properties and VWC. In this study, the values of parameters [42] we used in the ALT estimation are listed in Table 2. The VWC at 1500 kPa is transferred to the absolute VWC in the soil by multiplying the ratio of VWC from remote sensing and the mean of VWC at 1500 kPa over the study site.

Table 2.
Values for thaw settlement coefficient calculation.
3. Results
3.1. Deformation Results
Figure 5a illustrates mean displacement velocities in summer 2014. The results, superimposed on Google Earth over the entire region, show that the city undergoes thaw subsidence in summer. Ground subsidence varies significantly in size and shape over the study area. It is larger at the airport and surrounding infrastructure than the natural ground. Five subsidence funnels can be seen in Figure 5a. The most conspicuous settlement (labeled as blue circle A) is centered the intersection of taxiway alpha and runway 17/35 of the airport, with a diameter of approximately 450 m. The vertical displacement rate is up to 163 mm/year which is so detrimental to the airport’s performance that the taxiway stopped working for some time. Another elliptical subsidence area (the ellipse where GPS station IQAC [43] is located) with a major axis of about 420 m elongated along the NW–ES direction was observed at the immediate south side of the runway. The mean velocity around this area is 80–88 mm/year. In the vicinity of oil depots and the city landfill (the ellipse where thaw tube T2 [44] is located), there is a significant settlement region of approximately 1 km2 with a 110 mm/year subsidence rate. Another settlement region appears in the south of the city (labeled as B), with a similar rate to the oil depot area. In the northern end of the runway (labeled as E) and the residential area, the subsidence rates are between 44 and 88 mm/year.
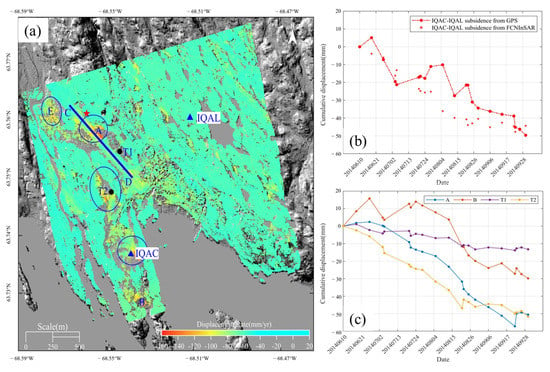
Figure 5.
(a) Displacement velocities over the study area. The red star is the reference point for velocity calculation; blue triangles denote GPS stations; black dots denote two thaw tubes; black polygons represent infrastructure and facilities; the blue line labeled as CD is the profile site along runway 17/35 for further discussion; (b) cumulative subsidence between IQAL and IQAC from GPS measurement and FCNInSAR time series; (c) time series subsidence of four points labeled in (a).
For further analysis of the dynamic evolution of the active layer, time series displacements at four points are plotted in Figure 5c. The points are selected from the different areas as presented in Figure 5a. A similar subsidence trend, albeit at different rates, is observed for all points. The ground surface subsides relatively slowly in June and in September, even with random uplifts, but much faster in July and August. Across four months, the settlement of point A on the runway of the airport amounted to 57 mm. The total subsidence of the thaw tube T2 installed in a marshy area [44] with seasonally ponded water is 51.5 mm. It has higher rates compared to B and T1. The thaw tube T1 has little sign of displacement of approximately 13 mm.
3.2. Estimated ALT Results
Figure 6 shows the ALT distribution over the entire study area. The magnitudes of estimated ALTs are between 0 and 5 m and exhibit considerable regional heterogeneity. ALTs in bedrock areas are generally larger than other sediments. The maximal ALTs are located at the southern part of the study area. The 1–2 m ALTs are widely spread in the Lv, GMd, and Mn sediments, while ALTs are smaller than 1 m in the Afp and the Tb sediments. Stable areas without subsidence also have shallow ALTs in rock area. A deeper AL of 1.2 to 2.5 m dominates the intersection of the runway and taxiway alpha.
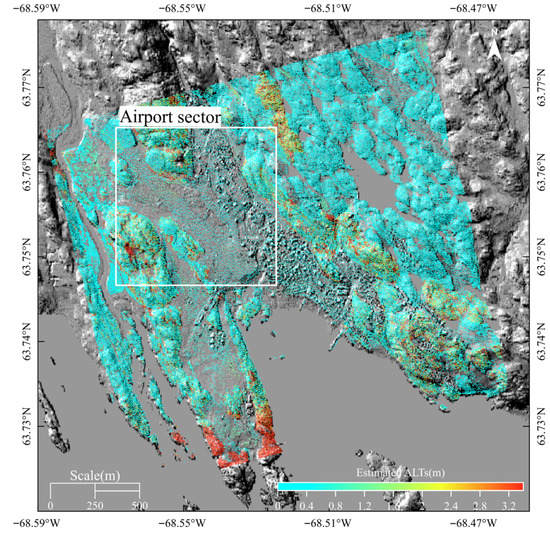
Figure 6.
Estimated ALTs.
Closer inspection of the airport sector (Figure 7) shows that the AL ranges between 0 and 2.5 m with a paved surface. The natural ground in the airport section shows a slightly smaller ALT trend with most part of it having an AL of less than 1 m. Only the bare surface between the taxiway and the runway has an AL similar to the paved ground which is even deeper than 2.5 m.
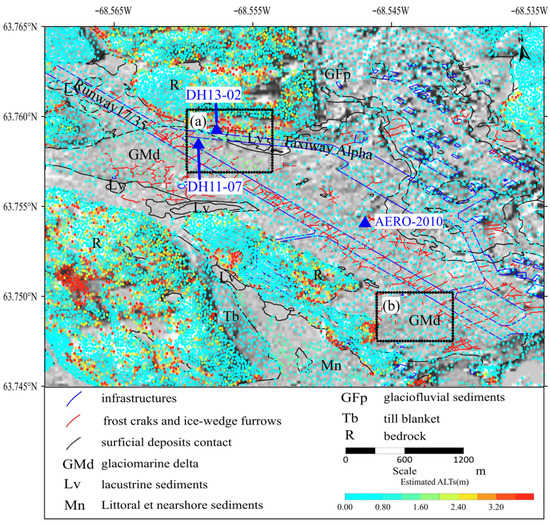
Figure 7.
The ALT distribution in the airport sector. Blue triangles denote boreholes.
4. Analysis and Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Subsidence with GPS Data and Thaw Tubes
In order to assess the accuracy of subsidence detection, GPS data and thaw-tube recordings were used for validation. We downloaded observations from the Nevada Geodetic Lab for two GPS stations that were contemporaneous with the SAR data used in this study [43]. The locations of GPS stations are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
GPS stations used for comparison.
Figure 5b presents the temporal evolution of displacements relevant to the points labeled as IQAC and IQAL. GPS station IQAL was set close to Geraldine Lake, and it is underlain by till veneer sediments. The other GPS station IQAC was installed in Sylvia Grinnell Park. Cumulative thawing settlements between IQAC and IQAL from FCNInSAR and GPS measurements are 4.5 and 5 cm, respectively. The discrepancies’ mean value and standard deviation are 7.06 and 8.76 mm. The FCNInSAR subsidence trend generally agrees well with GPS displacement, but there is a significant difference in July and August, up to 2.7 cm.
We also compared our subsidence to the results measured on site. Two thaw tubes located in well-drained glaciomarine deposits (T1) and poorly drained marine sediments (T2) were available [44,45]. As plotted in Figure 5c, the subsidence of T1 in the whole summer from FCNInSAR is 1.32 cm, while that recorded from the thaw tube is 0.8 cm. Due to the construction work, T1 was removed in July 2014. Therefore, only part of the subsidence was observed. Our InSAR result is somewhat consistent with that observed at T2, in which we see a difference of 0.15 cm in 2014 (see Table 4). Compared to the report published by Short in 2017 which stacked the DInSAR results for deformation analysis, as shown in Figure 8, the FCNInSAR deformation trend better matches the deformation from the measurement of the thaw tube [46].

Table 4.
Subsidence at the location of thaw tubes.
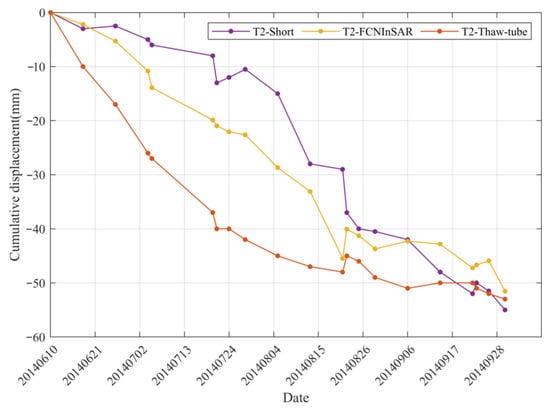
Figure 8.
Ground displacement at T2 from Short et al. (2017), in situ measurement and FCNInSAR.
4.2. ALT Validation with Thermistor Cable Measurements
Mathon et al. studied the ALTs over Iqaluit by installing thermistor cables in boreholes and recording schematic stratigraphy from boreholes [47]. The results show that the thickness of the active layer varies between 90 cm for sectors covered with vegetation and more than 2 m below paved surfaces [47]. In our study, the AL in the natural ground of the airport sector within GMd sediments ranges between 0 and 2 m, and it is up to 2.504 m under the paved taxiway, which shows good consistency with previous studies.
We averaged the ALTs of all PSs within the distance of 5 m to each thermistor cable for point-to-point validation. The ALT of 1.5 m was observed in the field in 2012 at thermistor cable AERO-2010 (with the same location as T1) [48], while it was 1.01 m in our results. The ALT of DH13-02 under the paved taxiway is 2.7 m, and the result of this study is 2.5 m. The ALT of thermistor DH11-07 installed on the taxiway shoulder increased from 1.5 m in 1992 to 2.2 m in 2012 [45,47,48]. The retrieved ALT in 2014 of this study is 1.8 m. All three datasets are generally consistent with each other. The slight difference could be partially attributable to the uncertainties in soil moisture data. Especially during the summertime, the soil is observed to be saturated or flooded in shallow layers [45], but the soil moisture data used to retrieve ALTs generally had values under 0.35. Subsidence detection errors and the different acquisition times of results for comparison are also possible reasons for the discrepancy.
4.3. Uneven Trend of Subsidence and ALT along the Runway
Both subsidence velocity and ALT profile along CD were plotted to assess the heterogeneous changes of the ground along runway 17/35. As shown in Figure 9, the subsidence velocity and ALT fluctuate considerably. The section from 230 to 800 m is recognized as the part close to the runway entrance that exhibits more subsidence and a thicker active layer than other parts of the airport. There were dense cracks on the asphaltic surface which can be easily seen on optical images. Allard [33] mapped them in 2012, as shown by red lines in Figure 7. Locations of cracks designated by dashed lines as shown in Figure 9 are consistent with sudden changes of displacement velocity and ALT along the runway. With the temperature rise, different soil characteristics of changing sediments introduce variable subsidence, which results in ground surface cracking. Due to the high resolution of SAR images, we obtained detailed subsidence fields and ALTs, showing many turning points on the profile CD. The geophysical results proved that ice wedges appeared along the runway [44]. Ice wedges are another possible reason for cracks. The v-shaped ice wedges that vertically taper down into the permafrost grow as ground cracks occur in response to thermal contraction of the ground during winter and that water entering the open cracks freezes [49]. As the temperature rises, vein ice and ice wedges melt. Surrounding rocks and upper soil collapse afterwards.
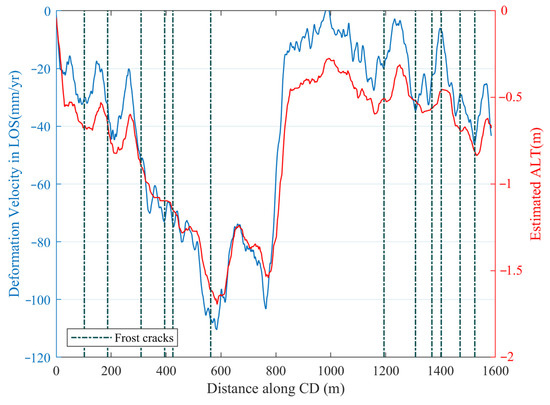
Figure 9.
Deformation and ALT profile along CD.
4.4. ALTs under Infrastructure and Natural Ground
The histograms of ALT (Figure 10) display the difference between the AL under infrastructure and the natural ground within the airport sector. This shows that the AL under the paved surface (the runway, aprons, and the taxiway) ranges from 0 to 2.504 m. As shown in Figure 10a, a part of taxiway alpha experienced significant subsidence, which led to several resurfacings and diversions. In total, 96% of the natural ground has an AL of less than 1.5 m. Only the tiny part mainly located at the shoulder of the runway has an AL of thicker than 2 m. The surface paving and the construction work probably increase the ground temperature, leading to the thicker ALs. According to previous field tests, the intersection part of the runway and taxiway alpha is wetter than neighboring parts [44,45]. Although the previous lake (where the Lv sediments on taxiway alpha are located) and drainage channels were modified and covered by the airport’s construction, a water-rich region extended from taxiway alpha across the runway remaining there. This indicates that there are errors in VWC data. We found that the subsidence is the dominant factor of the ALT in the paved area due to the subtle difference in VWC.
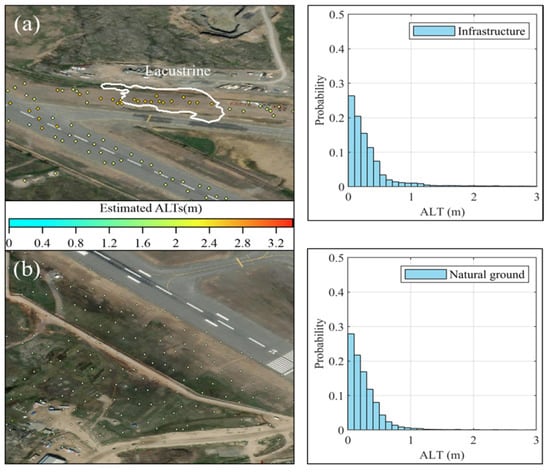
Figure 10.
(a) Enlarged view and the statistic histogram of ALTs under infrastructure; (b) enlarged view and the statistic histogram of ALTs under natural ground.
4.5. Relation between ALT and Geology
An ALT–geology combined analysis over the entire study area was conducted for a further ALT interpretation. The surface geology map [29] over Iqaluit (Figure 11) shows that the area mainly consists of glaciomarine deltaic (GMd) sediments, alluvial flood plain (Afp) sediments, alluvial terraced (At) sediments, lacustrine (Lv), Littoral and nearshore (marked as Mn) sediments, intertidal (marked as Mi) sediments, till blanket (Tb), till veneer (Tv), and bedrock (R).
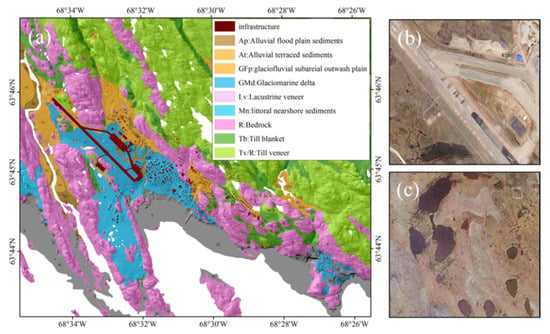
Figure 11.
(a) Surficial geology map over Iqaluit; (b) optical image of the intersection of the runway and taxiway alpha; (c) optical image of landscape in Mn sediments.
The solid and tightly bound bedrock is considered stable, as reflected by the slightly upward ground and patches without subsidence shown in Figure 5a. ALTs of almost 0 or small values exist in these patches resulting from their positively proportional relationship with the subsidence. Thick ALs up to 5 m shown at the southern tip of the study area agree well with the large settlement and the small thaw settlement coefficient of bedrock. Bedrocks are usually dry and prone to thaw deeper and quicker due to their high thermal conductivity. The considerable settlement was observed in the Tb unit which is composed of ice-rich coarse sediment. The ALTs in this area are generally less than 0.5 m (Figure 12). The underlying deposits on which large downward movements occur at the airport and nearby infrastructure (Figure 11b,c) are mainly related to the GMd and Mn shown in dark and light blue in Figure 11a, which agrees with previous studies [44,45]. The GMd was deposited in shallow water and formed adjacent to the grounded margin of a tidewater glacier since it formed when marine submergence occurred [49]. Therefore, it is dominantly filled with silt composition and salinity. Thus, the AL likely subsides more in summer. Subsequently, the ALT estimated from the thawing subsidence is larger (Figure 12), and thick estimated ALTs around 2 m are aligned well with the maximal subsidence in GMd sediments. They may be overestimated, however, in well-drained parts with low water content since ice-wedge melting is considered as soil thawing. Field campaign results [48,50,51] show that the sediments are composed of 10 cm organic and 90 cm ice-boned medium brown sand with grey silty sand layers. The higher the ground ice content, the larger the seasonal subsidence or shallower corresponding ALT.
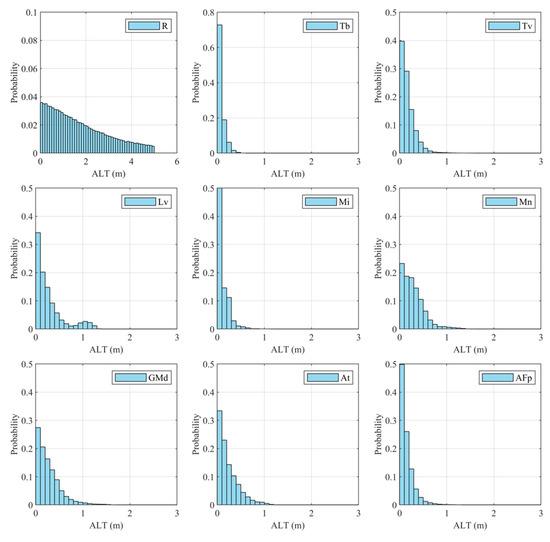
Figure 12.
Statistic histograms of ALT in different sediments.
ALT values reaching up to 2.504 m appear in the Lv, with a mean thickness of 0.5 m, and 20% of these kinds of sediments have an AL of more than 1 m (Figure 12). We can see several patches of Lv distributed at the northwest end of the runway and the immediate south side of the runway. In Figure 10, a notable patch of Lv could be the reason for the malfunction of taxiway alpha. The taxiway and marshy regions at the west side of Sylvia Grinnell Road have significant subsidence since the Lv sediment is generally fine-grained material with high moisture content [50,51].
Afp and At units exhibit an ALT less than 1 m (Figure 12). This is reasonable for sediments with grain size ranging from boulders to silt particles [52,53]. The saturated water content of this deposit is higher than other sediments. Therefore, to thaw or freeze fully, more heat is required in the same height layer of soil. This is why subsidence and ALTs are both subtle in this region.
4.6. Limitations
Even though the comparison of estimated ALTs and in situ measured results from other studies shows differences of less than 0.5 m, some limitations should be noted. The ice content is critical for ALT retrieval other than soil properties. The soil moisture data used in this study reveal changes in water content across space but do not include ice-wedge information. The data may introduce substantial errors when the water content and the ice content are considered the same thing. Furthermore, the VWC from SoilGrids at 1500 kPa is not identical to the VWC in the soil throughout the summer. The ratio between them should be appropriately examined before estimating the ALT. In SoilGrids, the explained soil property variance ranges between 30% and 70% [35]. As a result, the uncertainties of ALT estimation are possibly up to meter-level. In addition, the thaw settlement coefficient can properly indicate the thawing conditions of frozen soil. However, more in situ data are necessary for the precise determination of soil moisture and other parameters needed in this retrieval model.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we retrieved high-resolution ALTs at Iqaluit airport by integrating the subsidence derived from X-band interferometric measurements and volumetric water content (VWC) datasets with a resolution of 250 m. The InSAR survey using 21 CSK images in Spotlight mode identified several sites of ground deformation at Iqaluit, subsiding at rates exceeding 80 mm/year. The largest settlement occurs at the intersection of runway 17/35 and taxiway alpha, which is up to 163 mm/year. We determined the saturation state and the corresponding thaw settlement coefficient for all measurement points in different sediments using the VWC data from SoilGrids and soil dry density. Our results suggest ALTs that range from 0 to 5 m. Combined analysis of the ALT and surface geology indicates that the retrieved ALT distribution is highly related to the subsurface geological conditions. Maximal ALTs are distributed in bedrock areas. In the airport sector, thicker ALTs are found in large settlement sites due to the thaw settlement coefficient being positively proportional to the soil moisture where the soil is in an unsaturated state according to the VWC data.
We should emphasize that the detailed ALT map is valuable not only for supporting infrastructure design and maintenance over the permafrost zone but also for comprehensive understanding of the AL conditions with global warming. The proposed ALT solution can provide denser observations over large areas than traditional point-based methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M., G.L., X.W., R.Z., and M.M.; methodology, D.M., X.W., G.L., and M.M.; validation, D.M., R.Z., and B.Z.; data curation, B.Z. and W.X.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M.; writing—review and editing, R.Z., M.M., G.L., B.Z., and X.W.; funding acquisition, G.L., R.Z., B.Y., and X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42171355, 51774250, 41804009, 41801399, 42071410); the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (Grant No. 2019ZDZX0042, 2020JDTD0003, 2020YJ0322); and the Open fund of State Key Laboratory of Geodesy and Geodynamics(Grant No. SKLGED2020-5-1-E).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to compliance with commercial data confidentiality requirements.
Acknowledgments
We thank ASI (Italian Space Agency) and DLR (German Aerospace Center) for providing SAR images.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Obu, J. How Much of the Earth’s Surface Is Underlain by Permafrost? J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2021, 126, e2021JF006123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletskiy, D.A.; Suter, L.J.; Shiklomanov, N.I.; Porfiriev, B.N.; Eliseev, D.O. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Buildings, Structures and Infrastructure in the Russian Regions on Permafrost. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletskiy, D.; Anisimov, O.; Vasiliev, A. Permafrost Degradation. In Snow and Ice-Related Hazards, Risks and Disasters; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 303–344. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider von Deimling, T.; Lee, H.; Ingeman-Nielsen, T.; Westermann, S.; Romanovsky, V.; Lamoureux, S.; Walker, D.A.; Chadburn, S.; Trochim, E.; Cai, L.; et al. Consequences of Permafrost Degradation for Arctic Infrastructure–Bridging the Model Gap between Regional and Engineering Scales. Cryosphere 2021, 15, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, O.; Aalto, J.; Luoto, M.; Westermann, S.; Romanovsky, V.E.; Nelson, F.E.; Etzelmüller, B.; Hjort, J. Circumpolar Permafrost Maps and Geohazard Indices for Near-Future Infrastructure Risk Assessments. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, F.; Yin, G.; Luo, J.; Lin, Z.; Liu, M. Permafrost Distribution along the Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor, China Using High-Resolution Statistical Mapping and Modeling Integrated with Remote Sensing and GIS. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, J. Interaction between Permafrost and Infrastructure along the Qinghai–Tibet Railway Detected via Jointly Analysis of C- and L-Band Small Baseline SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, W.; Brown, J. The Performance of a Frost-Tube for the Determination of Soil Freezing and Thawing Depths. Soil Sci. 1972, 113, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasmueck, M.; Weger, R.; Horstmeyer, H. Full-Resolution 3D GPR Imaging. Geophysics 2005, 70, K12–K19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kang, M.-S.; An, Y.-K. Underground Object Classification for Urban Roads Using Instantaneous Phase Analysis of Ground-Penetrating Radar (GPR) Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonard, F.; Weihermüller, L.; Schwank, M.; Jadoon, K.Z.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. Estimation of Hydraulic Properties of a Sandy Soil Using Ground-Based Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3095–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, L.E. The Influence of Snow Cover on the Ground Thermal Regime. Can. Geotech. J. 1982, 19, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, P.; Oades, J. Organic Matter, Sodicity and Soil Structure. In Sodic Soils: Distribution, Properties, Management and Environmental Consequences; Topics in Sustainable Agronomy; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 51–75. [Google Scholar]
- Vuik, C. Some Historical Notes about the Stefan Problem; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.H.; Tabatabaeenejad, A.; Moghaddam, M. Retrieval of Permafrost Active Layer Properties Using Time-Series P-Band Radar Observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6037–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Wen, L.; Feng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. InSAR Analysis of Surface Deformation over Permafrost to Estimate Active Layer Thickness Based on One-Dimensional Heat Transfer Model of Soils. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Schaefer, K.; Zhang, T.; Wahr, J. Estimating 1992–2000 Average Active Layer Thickness on the Alaskan North Slope from Remotely Sensed Surface Subsidence. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Han, J.; Li, Z.; Wen, Y.; Hao, T.; Lu, P.; Li, R. Active Layer Thickness Retrieval Over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 2000 TO 2020 Based on Insar-Measured Subsidence and Multi-Layer Soil Moisture. ISPRS-Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouyet, L.; Liu, L.; Strand, S.M.; Christiansen, H.H.; Lauknes, T.R.; Larsen, Y. Seasonal InSAR Displacements Documenting the Active Layer Freeze and Thaw Progression in Central-Western Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Q. Active Layer Thickness Retrieval of Qinghai–Tibet Permafrost Using the TerraSAR-X InSAR Technique. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4403–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, L.K.; Schaefer, K.; Battaglia, M.J.; Bourgeau-Chavez, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, R.H.; Chen, A.; Bakian-Dogaheh, K.; Grelik, S.; Jafarov, E. Active Layer Thickness as a Function of Soil Water Content. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Active Layer Thickness Retrieval Over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Using Sentinel-1 Multitemporal InSAR Monitored Permafrost Subsidence and Temporal-Spatial Multilayer Soil Moisture Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 84336–84351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Jin, H.; Wu, Q.; Bense, V.F.; He, R.; Ma, Q.; Gao, S.; Jin, X.; Lü, L. Thermal Regime of Warm-Dry Permafrost in Relation to Ground Surface Temperature in the Source Areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, SW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klene, A.E.; Nelson, F.E. Urban Geocryology: Mapping Urban–Rural Contrasts in Active-Layer Thickness, Barrow Peninsula, Northern Alaska. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2019, 109, 1394–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, S. The Mechanics of Frost Heaving. J. Geol. 1930, 38, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskow, G. Soil Freezing and Frost Heaving with Special Application to Roads and Railroads; Osterberg, J.O., Translator; The Swedish Geological Society, C, no. 375, Year Book no. 3; Technological Institute, Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Black, P.B.; Hardenberg, M.J. Historical Perspectives in Frost Heave Research: The Early Works of S. Taber and G. Beskow; Special Report (Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory (U.S.)); Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1991; pp. 23–91. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, J.G.; Rempel, A.W.; Wettlaufer, J.S. The Physics of Premelted Ice and Its Geophysical Consequences. Rev. Modern Phys. 2006, 78, 695–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanagiya, K.; Furuya, M. Post-wildfire surface deformation near Batagay, Eastern Siberia, detected by l-band and c-band InSAR. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surface. 2020, 125, e2019JF005473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.X.; Buckley, S.M.; Ding, X.L.; Chen, Q.; Luo, X.J. Estimating Spatiotemporal Ground Deformation With Improved Persistent-Scatterer Radar Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jia, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Jia, H.; Yu, B.; Sang, M. Exploration of Subsidence Estimation by Persistent Scatterer InSAR on Time Series of High Resolution TerraSAR-X Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murton, J.B. Permafrost and Climate Change. In Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 281–326. [Google Scholar]
- Allard, M.; Doyon, J.; Oldenborger, G.A.; Sladen, W.; LeBlanc, A.-M.; Mathon-Dufour, V.; L’Hérault, E.; Mate, D. Surficial Geology, Iqaluit, Nunavut; Geological Survey of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012.
- International Permafrost Association. Frozen Ground-The News Bulletin of the International Permafrost Association, No. 25. Frozen Ground 2001, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T.; Mendes de Jesus, J.; Heuvelink, G.B.; Ruiperez Gonzalez, M.; Kilibarda, M.; Blagotić, A.; Shangguan, W.; Wright, M.N.; Geng, X.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; et al. SoilGrids250m: Global Gridded Soil Information Based on Machine Learning. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0169748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Nonlinear and Non-Stationary Time Series Analysis. Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, G.; Slusarchuk, W.; Rowley, R. Determination of Some Frozen and Thawed Properties of Permafrost Soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1973, 10, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, H.; Guodong, C.; Chengsong, Y. The Evaluation of Thawing-Settlement Coefficient of Frozen Soils. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2003, 25, 608–613. [Google Scholar]
- Xifa, Z.; Ji, C.; Dongqing, Z. Application of Thawing Settlement Coefficient to the Research on the Roadbed Frost Damage of Freeway in Seasonal Frost Region. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2002, 24, 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, H.; Doré, G.; Lemieux, C. Quantitative Risk Assessment of the Iqaluit International Airport, Iqaluit, Nu-navut.; Prepared for The Northern Transportation Adaptation Initiative from Transport Canada; Université Laval: Québec, QC, Canada, 2017; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Blewitt, G.; Hammond, W.C.; Kreemer, C. Harnessing the GPS data explosion for interdisciplinary science. Eos 2018, 99, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.M.; Short, N.; Oldenborger, G.A.; Mathon-Dufour, V.; Allard, M. Geophysical Investigation and InSAR Mapping of Permafrost and Ground Movement at the Iqaluit Airport. In Cold Regions Engineering 2012: Sustainable Infrastructure Development in a Changing Cold Environment; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; pp. 644–654. [Google Scholar]
- Short, N.; LeBlanc, A.M.; Sladen, W.; Oldenborger, G.; Mathon-Dufour, V.; Brisco, B. RADARSAT-2 D-InSAR for ground displacement in permafrost terrain, validation from Iqaluit Airport, Baffin Island, Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N. RADARSAT Constellation Mission DInSAR Potential in Permafrost Terrain; Natural Resources Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mathon-Dufour, V.; Allard, M.; Leblanc, A.; L’Hérault, E.; Oldenborger, G.; Sladen, W. Mapping Surficial Geology and Assessment of Permafrost Conditions under the Iqaluit Airport, Nunavut, Canada. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, A.M.; Mathon-Dufour, V.; Allard, M.; Oldenborger, G.A.; Short, N.; L’Hérault, E.; Sladen, W.E. Permafrost characterization at the Iqaluit International Airport, Nunavut, in support of decision-making and planning. Summ. Act. 2012, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Rémillard, A.M.; Hétu, B.; Bernatchez, P.; Buylaert, J.-P.; Murray, A.S.; St-Onge, G.; Geach, M. Chronology and Palaeoenvironmental Implications of the Ice-Wedge Pseudomorphs and Composite-Wedge Casts on the Magdalen Islands (Eastern Canada). Boreas 2015, 44, 658–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathon-Dufour, V. Caractérisation Du Pergélisol En Vue de La Réfection et de l’adaptation Aux Changements Climatiques de L’aéroport D’Iqaluit; Université Laval: Québec, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc, A.M.; Short, N.; Mathon-Dufour, V.; Allard, M.; Tremblay, T.; Oldenborger, G.A.; Chartrand, J. DInSAR seasonal surface displacement in built and natural permafrost environments, Iqaluit, Nunavut, Canada. In Proceedings of the GEO, Québec, QC, Canada, 25–28 February 2015; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Martini, I.P. Deglaciation Stages of the Laurentide Ice Sheet in Canada and Related Glaciomarine and Glaciolacustrine Deposits. Rev. Sel. Features 2007. Available online: https://minerva.usc.es/xmlui/handle/10347/3757 (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Hillier, S. Erosion, Sedimentation and Sedimentary Origin of Clays. In Origin and mineralogy of clays. In Origin and Mineralogy of Clays; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 162–219. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).