- Article
Preliminary Toxicological Evaluation of Spherical Nanoparticles Containing an Imidazole Derivative (BzIm-DEA) Using the CAM Chicken Model
- Damian Duda,
- Agnieszka K. Grzegorzewska and
- Vigen Topuzyan
- + 5 authors
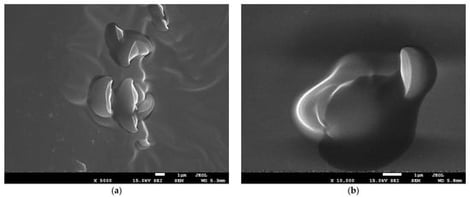
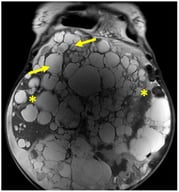
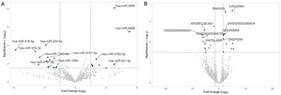
Due to the increasing antibiotic resistance of microorganisms, chronic diseases, and cancer, new-generation drugs such as imidazole derivatives are being sought. Recent advances in nanotechnology enable the potential use of nanomaterials, especially nanoparticles, as drug carriers for such compounds, but also systems capable of crossing biological barriers. This study aimed to perform a preliminary toxicological assessment of nanoparticles containing BzIm-DEA ((Z)-5-benzylidene-3-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-2-phenyl-3,5-dihydro-4H-imidazol-4-one) embedded in chitosan films, using chicken chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) as an alternative in vivo test. Fertilized chicken eggs were treated with this therapeutic agent at various concentrations of BzIm-DEA and incubated until the 11th day of embryogenesis. No morphological abnormalities, angiogenesis-related disorders, or increased mortality were observed in any of the experimental groups. A significant increase in Apaf-1 mRNA expression was detected in CAM tissue at a dose of D3 BzIm-DEA, while no significant changes were observed for caspase-3 and catalase compared to the control group. Moreover, no changes in gene expression were observed in the liver. Immunohistochemical localization and analysis of PCNA and b-catenin expression in chicken embryonic liver did not reveal any dose-dependent changes. Within the scope of this preliminary assessment, chitosan nanoparticles loaded with BzIm-DEA did not produce gross acute embryotoxicity or major disruptions to angiogenic development under the tested conditions, providing preliminary evidence of biocompatibility as a nanoparticle carrier system.
9 February 2026