Electric Vehicles Energy Management
Topic Information
Dear Colleagues,
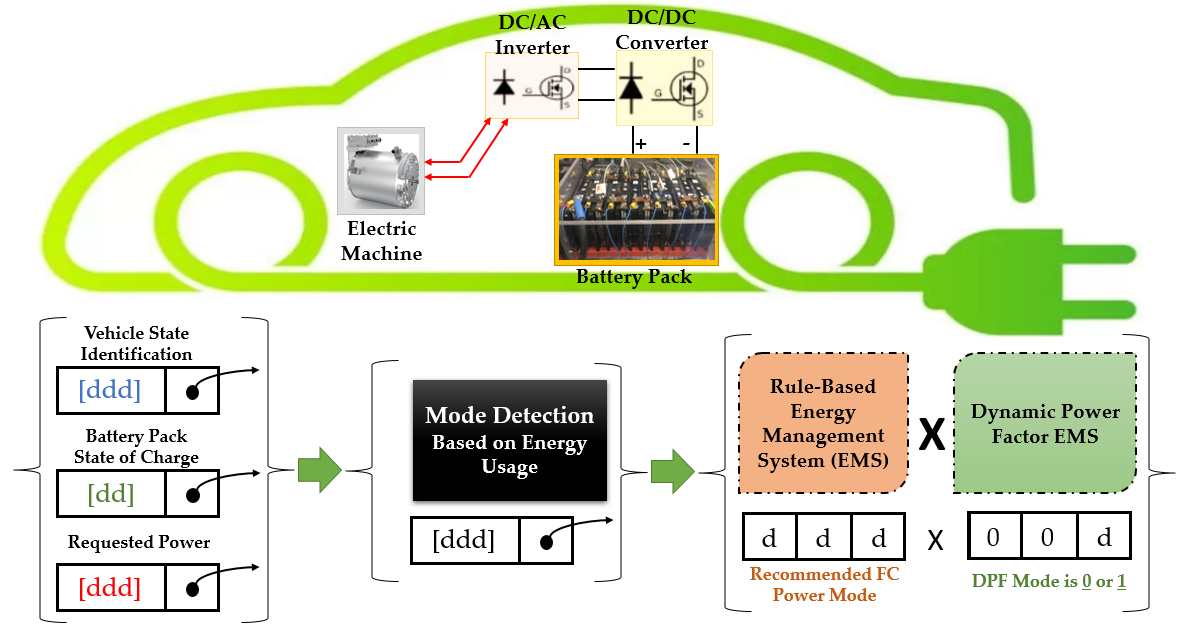
Energy management strategies (EMS) play a decisive role in electric vehicles (EV) to maximize the fuel economy (energy optimization control), prolong the battery lifetime, and extend the EV range. To this end, various strategies should be adopted to propose a nested bi-level design framework to enhance the fuel economy, and to minimize the size and cost of the powertrain. In this context, the EV components and corresponding EMSs should be designed and developed to build the full vehicle platform. The next step is to propose the nested bi-level optimization framework and to couple it into the developed model to iteratively work in tandem with the optimization algorithms. The mentioned online and offline strategies and optimization algorithms can be rule-based (RB), fuzzy logic control (FLC), genetic algorithm (GA), artificial neural network (ANN), particle swarm optimization (PSO), krill herd (KH), ant lion optimizer (ALO), ant colony optimization (ACO). The framework of this section explores such co-design optimization objectives and constraints as:
- Minimized fuel economy;
- Minimized powertrain costs;
- Enhanced battery state of charge (SoC);
- Extended battery lifetime;
- Battery charging limitations satisfaction;
- Extended EV range.
The main aim of the section is to critically benchmark the outcomes from various perspectives, including fuel economy, powertrain and driveline components, charge and discharge capabilities, computational costs, and experimental robustness validation, for the real-time design and modeling to provide insights for the integrated design of EVs from different aspects.
Dr. Danial Karimi
Dr. Amin Hajizadeh
Topic Editors
Keywords
- energy management
- electric vehicles
- extended range
- energy storage
- batteries
- fuel economy
- powertrain
- power electronics
- electrical machines and drives
- modeling and design