Emerging Agricultural Engineering Sciences, Technologies, and Applications
Topic Information
Dear Colleagues,
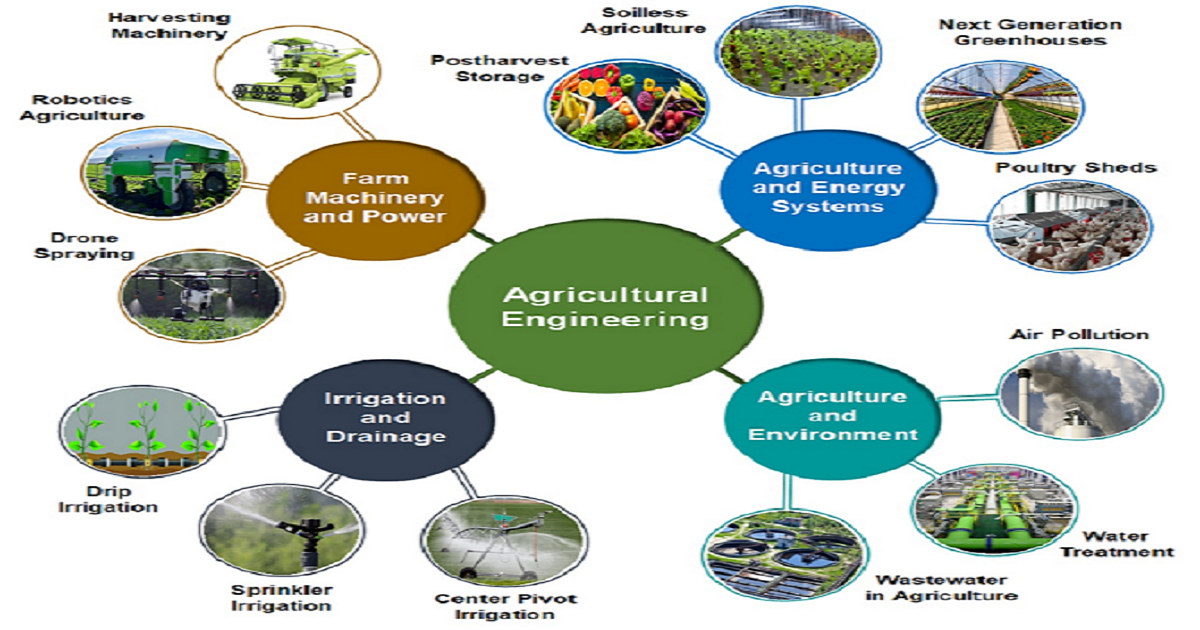
Modern agricultural engineering technologies and applications are directly linked with the 2030 United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN-SDGs). Technological advancement is essential to next-generation agriculture in order to ensure food security, poverty alleviation, and sustainability. Worldwide, it is directly associated with farm mechanization; automation and robotics; intelligent agriculture; high-efficiency irrigation systems; indoor farming and soilless agriculture; precision/conservation agriculture; farm energy systems; post-harvest storage/processing and value addition; tillage and cultivation; spraying and harvesting machinery; livestock and poultry sheds; safe utilization of coal and bioenergy; remote sensing and geographical studies; wastewater management; societal aspects in agriculture; and the associated bioenvironment. Consequently, this topic aims to explore the interdisciplinary nature of research on such agricultural engineering sciences, technologies, and applications from the viewpoint of the agricultural water–energy–food-security nexus. Increasing agriculture modernization mitigates conventional energy reserves, which also escalates greenhouse-gas emissions and climate change. Carbon-neutral development and clean-energy utilization are also associated with the UN-SDGs. Thus, it is important to develop energy-efficient and environmentally friendly solutions to ensure the agriculture sector achieves the UN-SDGs.
This topic invites a wide range of emerging concepts on the agricultural engineering technologies and applications by which sustainable agriculture and associated UN-SDGs can be ensured. We look forward to receiving cutting-edge original research, review, case studies, and/or recent progress/scenarios.
Dr. Muhammad Sultan
Dr. Yuguang Zhou
Dr. Redmond R. Shamshiri
Dr. Muhammad Imran
Topic Editors
Keywords
- biomass, bioenergy, and clean fuel
- farm mechanization and robotics
- food science and processing
- high-efficiency irrigation systems
- hydroponic and aeroponic agriculture
- irrigation systems and applications
- modern control sheds and livestock barns
- next-generation greenhouses
- precision farming and food security
- renewable energy for agriculture
- smart and sustainable agriculture
- solar dryers and solar pumping
- sustainable bioenvironment
- temperature/humidity control in agriculture
- water and wastewater treatment