- 3.0Impact Factor
- 6.0CiteScore
- 19 daysTime to First Decision
Agricultural Water Management—Coupling Hydrological and Crop Models
This special issue belongs to the section “Hydrology“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
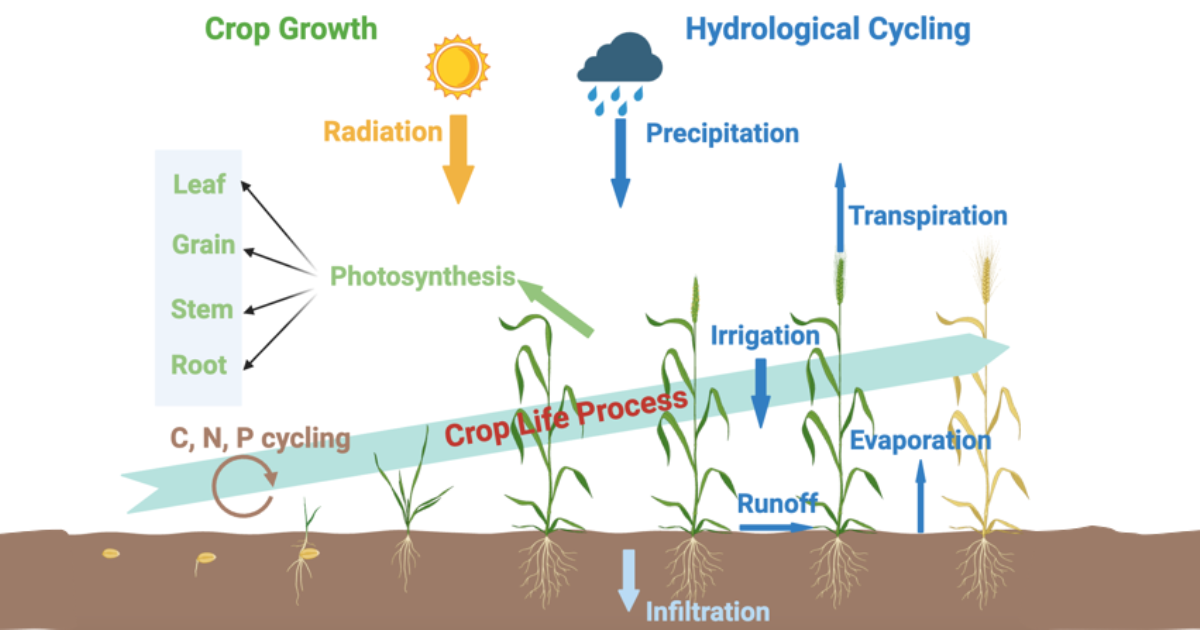
In the context of global climate change, increasing water scarcity, and rising demands for food production, efficient agricultural water management has become a pressing global concern. Traditional approaches often rely on either hydrological models to simulate water movement and availability or crop models to project plant growth and yield. However, these approaches often fail to capture the complex, dynamic interactions between soil moisture, plant processes, and atmospheric drivers.
To address these challenges, there is a growing interest in coupling hydrological and crop models as an integrated strategy for better simulating the soil–plant–atmosphere continuum. By linking the strengths of both model types, researchers can improve predictions of crop performance under variable water availability, optimize irrigation strategies, and assess the impacts of climate variability on agricultural productivity. Such integrated modeling frameworks offer significant potential to enhance water use efficiency and support decision-making in precision agriculture and sustainable land management.
In this Special Issue, original research articles and reviews are welcome. Research areas may include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Coupling frameworks and technical approaches between hydrological models and crop models;
- Coupled model calibration, validation, and uncertainty analysis;
- Improving yield prediction accuracy and water management efficiency through data assimilation and remote sensing integration;
- Applications of the models in water-saving irrigation and drought adaptation;
- Scenario analysis under future climate and land-use change based on process-based models.
We look forward to receiving your contributions.
Dr. Yunfei Wang
Dr. Danyang Yu
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Water is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- eco-hydrological modeling
- crop modeling
- model coupling
- soil–plant–atmosphere continuum
- agricultural water management
- root growth and water uptake
- soil moisture
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.


