- Article
Hub Location and Truck Platoon Routing Optimization for Courier Line-Haul Networks with Carbon Benefits Under Undirected Symmetry
- Yinan Zhao and
- Hanwen Jiang
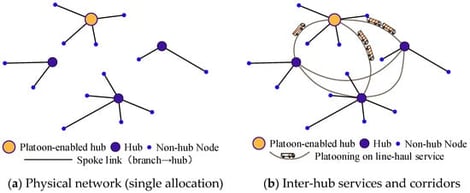
Truck platooning enabled by V2X and cooperative driving can reduce aerodynamic drag and consequently decrease fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. Meanwhile, hub-and-spoke courier networks require strategic decisions on hub locations, allocation, and line-haul routing. This paper introduces an integrated Hub Location-Platoon Routing Problem (HLPRP) that jointly optimizes (i) hub selection and single allocation of spokes; (ii) the departure hubs where platoons are formed; (iii) line-haul (inter-hub) service design and route selection; and (iv) demand routing, while internalizing monetized carbon benefits from platooning. A variable neighborhood search-based simulated annealing solution framework is developed to eliminate duplicated hub pair representations induced by network symmetry. Computational experiments on benchmark and large-scale North China instances demonstrate that the proposed approach consistently produces high-quality solutions within practical runtimes. The results indicate that the optimal network structure is primarily driven by transportation cost trade-offs and is further shaped by platoon-enabling investment and the associated carbon benefit, which concentrates on a subset of high-volume inter-hub corridors. Overall, the proposed framework provides a decision support approach for designing low-carbon courier line-haul networks.
16 February 2026