- Article
Systematic Assessment of Modeling Techniques to Support the Conceptual Design of Digital Ecosystems
- Karina Villela,
- Matthias Koch and
- Nedo Bartels
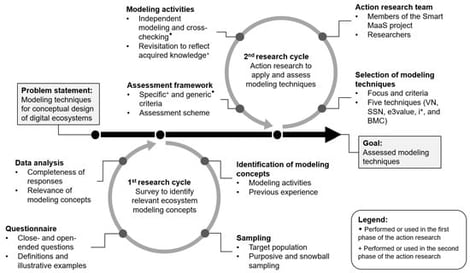
Digital ecosystems are sociotechnical systems that connect various business actors via digital platforms. While they drive digital transformation across domains, their conceptual design remains challenging due to the need to address legal, technical, and business aspects simultaneously. Our research investigates which modeling concepts are relevant for this purpose and to what extent existing modeling techniques support their representation. A survey with 32 experienced practitioners and researchers revealed a diverse set of relevant views, elements, cross-cutting concerns, and principles. Some concepts—such as ecosystem overview and value exchanges—were broadly accepted, whereas others—including legal aspects and cooperation mechanisms—raised controversy. Based on the survey results, we developed an assessment framework and applied it in an action research study to evaluate five established modeling techniques. Despite their strengths, none of the techniques supporting all concepts were deemed highly relevant. The findings underline the need for a unified modeling technique grounded in shared concepts and multi-view representations. The proposed framework defines requirements for modeling techniques to support digital ecosystem design and enables their systematic assessment.
27 February 2026