- Article
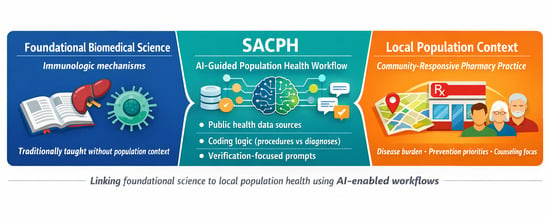
Foundational biomedical sciences are commonly taught without routine integration of local population health contexts, limiting students’ ability to connect mechanisms to community disease burden and practice responsibilities. In this method paper, we developed and piloted an AI-enabled “Sacramento County Public Health (SACPH)” AI workflow and app prototype, a structured, faculty-authored prompt sequence designed to guide population-to-practice reasoning using publicly available data. The workflow was implemented during a TBL session with first-year PharmD students in an immunology course. Using splenectomy and risk of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI) as an illustrative use case, students executed a standardized prompt sequence addressing data source identification, coding logic (diagnosis vs. procedure codes), population-level estimation with uncertainty framing, and translation to pharmacist-relevant prevention and counseling implications. Feasibility was defined by conceptual convergence. The validated reasoning workflow was subsequently translated into a prototype, app-style interface using generative design prompts. Across student teams, outputs converged on similar categories, consistent recognition of coding frameworks and verification steps, and directionally similar interpretations of local burden and pharmacist responsibilities. The prototype demonstrated successful externalization of the reasoning workflow into a modular, reproducible artifact. SACPH demonstrates a feasible, reproducible method for using generative AI to integrate foundational science instruction with local population health context and pharmacist practice reasoning, while supporting AI literacy competencies.
16 January 2026