-
 A Decade of Transformation in the Management of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: From Conventional Chemotherapy to Precision Medicine
A Decade of Transformation in the Management of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: From Conventional Chemotherapy to Precision Medicine -
 Sociodemographic Factors, Intent-Uptake Disparities, and Nirsevimab Availability in Infant RSV Immunoprophylaxis
Sociodemographic Factors, Intent-Uptake Disparities, and Nirsevimab Availability in Infant RSV Immunoprophylaxis -
 Use of Technological Devices in Children Aged 3–11 Years: Possible Effects on Sleep and Behavioral Difficulties
Use of Technological Devices in Children Aged 3–11 Years: Possible Effects on Sleep and Behavioral Difficulties
Journal Description
Pediatric Reports
Pediatric Reports
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of pediatrics, and is published bimonthly online by MDPI (since Volume 12, Issue 3 - 2020). The Italian Society of Pediatric Psychology (SIPPed) is affiliated with Pediatric Reports and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 31.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
1.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Clinical Practice and Diagnostic Confidence Regarding Pediatric Oral Mucosal Lesions Among Dentists, Pediatricians, and General Practitioners: A Cross-Sectional Study
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18020033 (registering DOI) - 2 Mar 2026
Abstract
Background: Pediatric oral mucosal lesions are common and may indicate local or systemic disease, yet their recognition in primary healthcare often depends on non-dental professionals. Aim: To assess the preparedness of dentists, pediatricians, and family/general practitioners for pediatric oral mucosal conditions based on
[...] Read more.
Background: Pediatric oral mucosal lesions are common and may indicate local or systemic disease, yet their recognition in primary healthcare often depends on non-dental professionals. Aim: To assess the preparedness of dentists, pediatricians, and family/general practitioners for pediatric oral mucosal conditions based on self-assessed diagnostic confidence, clinical management, and referral behavior. Methods: An online cross-sectional survey was conducted among 632 primary healthcare professionals (dentists: n = 262; family/general practitioners: n = 278; pediatricians: n = 92). The questionnaire assessed clinical exposure, self-assessed knowledge, diagnostic confidence, management practices, and referral patterns. Data were analyzed using chi-square or Fisher’s exact test and the Kruskal–Wallis test (p < 0.05). Results: Dentists reported significantly higher self-assessed knowledge and diagnostic confidence than pediatricians and family/general practitioners (p < 0.001). Good self-assessed knowledge of pediatric oral health was reported by 26.3% of dentists, compared with 7.9% of family/general practitioners and 6.5% of pediatricians. While most pediatricians (80.4%) and family/general practitioners (77.0%) reported routinely examining the oral cavity in children, independent treatment of oral mucosal lesions was more frequently reported by dentists (75.2%) than by pediatricians (52.2%) or family/general practitioners (70.9%) (p < 0.001). Referral patterns differed between groups, and willingness to attend future pediatric oral health education was high across all professionals (75.0–84.2%). Conclusions: Dentists demonstrated higher diagnostic confidence in pediatric oral mucosal lesions than pediatricians and family/general practitioners, who more often relied on referral. These findings support the value of targeted education and strengthened interdisciplinary collaboration in primary pediatric healthcare.
Full article
Open AccessCommunication
Preservation vs. Resection? Pediatric and Non-Pediatric Management Patterns in Ovarian Torsion
by
Xiaoyan Feng, Peter Zimmermann, Nicolas Pardey, Richard Gnatzy, Stefan Bassler, Jona T. Stahmeyer, Martin Lacher and Jan Zeidler
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(2), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18020032 (registering DOI) - 2 Mar 2026
Abstract
Background: Ovarian torsion (OT) is a rare but urgent surgical condition in children and adolescents. Evidence on how management differs between pediatric (PD) and non-pediatric (Non-PD) departments in Germany remains limited. Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using anonymized claims data from
[...] Read more.
Background: Ovarian torsion (OT) is a rare but urgent surgical condition in children and adolescents. Evidence on how management differs between pediatric (PD) and non-pediatric (Non-PD) departments in Germany remains limited. Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using anonymized claims data from two major German statutory health insurance funds (2010–2019), covering 6.3 million insured individuals (≈1 million children). Patients ≤18 years with an inpatient diagnosis of OT (ICD-10-GM N83.5) were analyzed with respect to demographics, department type (PD vs. Non-PD), hospital type (university/maximum care [UM] vs. non-university/maximum care [Non-UM]), surgical procedures, and outcomes. Results: A total of 293 patients (mean age 12.4 ± 4.5 years) were included; 71% were adolescents (12–18 years). Adolescents were predominantly treated in Non-PD (89%), whereas younger children were more often managed in PD (50%; p < 0.0001). Most cases were treated in Non-UM (82%). Laparoscopy was more commonly used in Non-PD departments (85%), while open surgery and oophorectomy occurred more frequently in PD and university hospitals (UM). Ovary-sparing procedures accounted for 77% of all cases, whereas 23% underwent oophorectomy. Mean hospital stay was longer in PD (6.7 ± 9.0 days) than in Non-PD (4.9 ± 2.2 days; p = 0.0167). Readmission rates were comparable across groups. Conclusions: Management of OT in Germany varies markedly by department and hospital type. PD and UM treat more younger patients but perform oophorectomy more frequently, whereas Non-PD and Non-UM favor laparoscopic, ovary-sparing strategies. These differences highlight the urgent need for standardized, evidence-based protocols prioritizing ovarian preservation and optimizing long-term outcomes in affected children and adolescents.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Complications of Paediatric Flexible Bronchoscopy with Six-Lobe Bronchoalveolar Lavage Performed Under General Anaesthesia
by
Maria van Veelen, Kelly Bakewell, Christopher W. A. Jolley, Sheng-Ang Ho, James Chapman, Lauren Edwards, Rahul Kumar and Francis J. Gilchrist
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(2), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18020031 - 26 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aim: To undertake a prospective review to identify the intra-procedure complications in children undergoing flexible bronchoscopy with six-lobe lavage and a retrospective review to identify the rates of delayed discharge and readmission. Methods: The prospective review analysed consecutive procedures from August 2023 to
[...] Read more.
Aim: To undertake a prospective review to identify the intra-procedure complications in children undergoing flexible bronchoscopy with six-lobe lavage and a retrospective review to identify the rates of delayed discharge and readmission. Methods: The prospective review analysed consecutive procedures from August 2023 to August 2024 and collected data on intra-procedure and immediate post-procedure desaturations, laryngospasm, bronchospasm/wheeze, tachypnoea, pyrexia, hypothermia, and vomiting. The retrospective review analysed consecutive paediatric flexible bronchoscopies from October 2014 to August 2023 identifying discharge delays and readmissions. All children underwent flexible bronchoscopy at a single tertiary paediatric centre under general anaesthesia (GA) with a single aliquot BAL obtained from all six lobes. When cytology was required, the BAL from the right middle or most affected lobe was changed to triple aliquot. Results: Six hundred and twenty-two procedures performed on 540 children were analysed. This included 502 in the retrospective review and 120 in the prospective review. In the prospective group 4/120 (3.3%) children experienced a significant (<90%) desaturation requiring anaesthetic intervention; 11/120 (9.2%) experienced an immediate post-procedure complication such as desaturation, pyrexia, tachypnoea, wheeze, or vomiting; 53/622 (8.5%) had their discharge delayed overnight; and 13/120 (11%) children in the prospective group experienced hypothermia. A further 18/622 (3%) children re-attended hospital within 48 h of discharge. Conclusions: Flexible bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage in all six lobes under GA in children is a safe procedure with low incidence of major complications when performed by expert clinicians. Parents should be advised of a 9% risk of delayed overnight discharge.
Full article
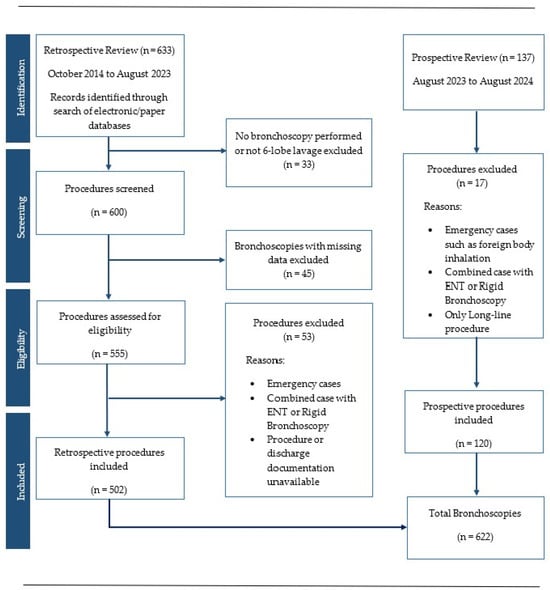
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Critical Intestinal Perforations in Pediatric Immunocompromised Patients: A Case-Based Review
by
William Hunt Stafford, Jennifer McArthur and Saad Ghafoor
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010030 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As survival rates for children with cancer and immune disorders have improved, clinical focus has shifted toward managing serious treatment-related complications. Intestinal perforation remains life-threatening and is typically diagnosed by signs of peritonitis and inflammation. This report presents three high-risk pediatric patients who
[...] Read more.
As survival rates for children with cancer and immune disorders have improved, clinical focus has shifted toward managing serious treatment-related complications. Intestinal perforation remains life-threatening and is typically diagnosed by signs of peritonitis and inflammation. This report presents three high-risk pediatric patients who developed severe intestinal perforation without the usual clinical symptoms. Each patient was receiving high-dose corticosteroids and/or targeted biologic immunomodulators (ruxolitinib, anakinra, tocilizumab, eculizumab). Classic indicators such as fever, leukocytosis, hemodynamic instability, and abdominal pain were absent, despite surgical findings of fecal contamination and bowel necrosis. All three patients survived to hospital discharge. These cases demonstrate that potent immunomodulatory therapies can mask the physiological response to perforation. Relying solely on traditional clinical signs may delay diagnosis. In this population, subtle findings such as persistent gastrointestinal bleeding, feeding intolerance, or minor imaging abnormalities should prompt consideration of perforation. Early imaging and multidisciplinary review are essential for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mediation and Moderation Effect of Psychosocial Factors on the Relationship Between Health Literacy and Well-Being in Adolescents
by
Tania Gaspar, Marina Carvalho, Miguel Arriaga, Barbara Sousa and Margarida Gaspar-Matos
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010029 - 12 Feb 2026
Abstract
Purpose: Higher health literacy is associated with better health behaviors and better overall well-being; however, the contribution of relational and socio-economic factors to this association remains insufficiently explored. The present study aimed to examine the relationships between health literacy, well-being, social support, and
[...] Read more.
Purpose: Higher health literacy is associated with better health behaviors and better overall well-being; however, the contribution of relational and socio-economic factors to this association remains insufficiently explored. The present study aimed to examine the relationships between health literacy, well-being, social support, and stress among adolescents. In particular, the mediating roles of social support (family, peers, and teachers) and stress in the association between health literacy and well-being were analyzed. Participants and Methods: Data were drawn from the 2022 wave of the Health Behaviour in School-aged Children (HBSC) study, an international survey conducted every four years in collaboration with the World Health Organization (WHO) and implemented according to a standardized protocol. The sample comprised 7643 students from the 6th, 8th, 10th, and 12th grades of Portuguese public schools. Of the participants, 53.9% were female, and the mean age was 15.05 years (SD = 2.36). Gender-based comparisons indicated statistically significant differences for all study variables, with the exception of health literacy. Results: Mediation analysis reveals an effect of health literacy on well-being. After the inclusion of the mediating variables, the direct effect of health literacy on lack of well-being remained negative. All four mediators showed statistically significant indirect effects, accounting for the difference between the total and direct effects. These findings indicate that the association between health literacy and lack of well-being was partially mediated by family support, peer support, relationships with teachers, and stress. Health literacy influenced lack of well-being both directly and indirectly through these mediating pathways, with stress emerging as the strongest indirect contributor. Conclusions: The findings support an ecological interpretation of health literacy and well-being, as these constructs are embedded within multiple interacting systems. Individual adolescent characteristics, such as gender, age, and stress management, are interconnected with interpersonal contexts, including relationships with family members, peers, and teachers. In addition, adolescents’ socio-economic circumstances appear to play a relevant role in shaping both health literacy and perceptions of well-being.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pediatric Psychology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Descriptive Case Series of Childhood Lymphomas Treated at the Children’s Hospital of Mexico
by
Miguel A. Palomo-Colli, Daniela Vega-Ruiz, Argelia Escobar-Sánchez, Matilde Galicia-Esquivel, Luis E. Juárez-Villegas and Abigail Morales-Sánchez
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010028 - 10 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Pediatric lymphomas comprise a heterogeneous group of malignancies with substantial variation in their clinical presentation. In Mexico, detailed case-based characterization remains limited. This study summarizes the demographic and clinical characteristics of pediatric lymphomas diagnosed at a national referral center over an
[...] Read more.
Background: Pediatric lymphomas comprise a heterogeneous group of malignancies with substantial variation in their clinical presentation. In Mexico, detailed case-based characterization remains limited. This study summarizes the demographic and clinical characteristics of pediatric lymphomas diagnosed at a national referral center over an 11-year period. Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of lymphoma cases in children aged 0–17 years diagnosed at the Children’s Hospital of Mexico between 2004 and 2014. Cases were classified according to the ICCC-3 system and further described by histopathological subtype, age group, sex, and clinical outcomes. Results: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) was the most frequent diagnosis, followed by non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Among HL cases, nodular sclerosis and mixed cellularity predominated, particularly in school-age children and adolescents. Within NHL, precursor T-cell lymphoma represented the largest subgroup, whereas mature B-cell lymphomas, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, were less common than typically reported in high-income settings. Burkitt lymphoma occurred mainly among younger children. HL showed high survival, while some NHL subtypes exhibited poorer outcomes. Conclusions: This large hospital-based case series provides characterization of pediatric lymphomas in a major Mexican referral center. While HL subtype patterns resembled global trends, the predominance of precursor T-cell lymphomas within NHL contrasts with observations from high-income regions. These findings highlight the value of institutional case registries and the need for more comprehensive outcome reporting in future studies.
Full article
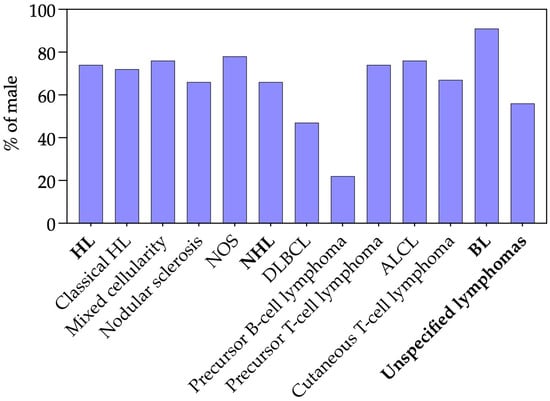
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
How Healthcare Professionals Perceive Emergency Pediatric Care Provision in Two Public Hospitals in Greece: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Eleni Vathi, Konstantinos Petsios, Evangelos Dousis, Ioannis Koutelekos, Despoina Koumpagioti, Eirini Anastasopoulou, Anastasia Ntikoudi, Eugenia Vlachou and Eleni Evangelou
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010027 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: High-quality pediatric emergency care requires timely access, effective communication, privacy, pain management, comfort, and child- and family-centered practices; however, implementation may be constrained by several barriers. The aim of the study was to evaluate the quality of pediatric emergency care as
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: High-quality pediatric emergency care requires timely access, effective communication, privacy, pain management, comfort, and child- and family-centered practices; however, implementation may be constrained by several barriers. The aim of the study was to evaluate the quality of pediatric emergency care as perceived by healthcare professionals, with emphasis on child-centered care and variations based on workplace and professional characteristics. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was performed in the emergency departments in two tertiary public pediatric hospitals in Athens, Greece. A study-developed 14-item Quality of Care Assessment Scale with paired ratings of agreement with quality principles and implementation in practice was completed by 162 professionals (122 doctors, 24 nurses, 16 assistant nurses). Independent items evaluated perceived barriers, overall assessments (0–100), and information provided to parents/children (5-point Likert scale). Inferential tests and descriptive statistics were also used (p < 0.05). Results: There was a significant degree of agreement with quality principles, but there was a constant lack of implementation (principle–practice gap). The primary perceived weakness was waiting times; child-friendly settings and privacy during examinations and information-giving were also lacking. Internal consistency ranged from good to acceptable (implementation α = 0.800; agreement α = 0.711). Children were most frequently rated as “moderately informed” (48.1%), while parents were most frequently rated as “quite informed” (50.0%). Compared to the organization of care (mean 60.85), perceived safety was higher (mean 73.27). Perceptions varied by age, educational level, profession, department, shift rotations, and hospital. The main barriers were workload (30.2%), poor coordination (34.0%), and lack of resources (46.9%). Conclusions: Health professionals seem to perceive that consistent delivery of child-centered care is impaired by organizational and structural limitations. Reducing the standards-to-practice gap requires targeted system-level interventions that focus on staffing, care organization, environment, and professional support.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adolescents’ Knowledge and Attitudes Toward Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Greek Secondary Schools
by
Angeliki Giannakea, Vicky Nanousi and Voula Chris Georgopoulos
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010026 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Adolescence is a critical developmental period during which peer attitudes and school experiences play an important role in social inclusion and academic adjustment. Although attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is common in secondary school populations, adolescents’ own knowledge and attitudes toward ADHD remain underexplored,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Adolescence is a critical developmental period during which peer attitudes and school experiences play an important role in social inclusion and academic adjustment. Although attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is common in secondary school populations, adolescents’ own knowledge and attitudes toward ADHD remain underexplored, particularly in non-Anglophone contexts. This study aimed to assess knowledge and attitudes toward ADHD among Greek secondary school students, focusing on awareness of the disorder, perceptions of ADHD-related classroom behaviors, and views on educational support and intervention. Methods: A cross-sectional survey was conducted among 154 adolescents aged 12–18 years attending Gymnasium (Grades 7–9) and Lyceum (Grades 10–12) in Greece. Data were collected using an anonymous online questionnaire assessing prior awareness of ADHD, perceptions of classroom behaviors associated with ADHD, attitudes toward inclusion and teacher support, and views on educational and therapeutic interventions. Adolescents with and without a self-reported ADHD diagnosis completed different questionnaire sections according to study design. Descriptive statistics and chi-square tests were used for data analysis. Results: Approximately two thirds of participants (66.9%) reported prior awareness of ADHD. Among typically developing adolescents (n = 134), 83.0% recognized distractibility due to external noise, 70.4% noted off-topic interruptions, and 60.0% reported peers getting up without permission. While 75.5% believed students with ADHD can participate in the classroom, 65.9% also reported academic challenges such as incomplete homework or lower performance. Overall, 79.2% of participants stated that school success depends on teacher and specialist support; however, among adolescents with ADHD (n = 20), only 60.0% endorsed this, with 40.0% emphasizing personal effort. Speech-language therapy was viewed as helpful by 55.6% of typically developing adolescents, though 76.9% of adolescents with ADHD reported not receiving such services. Conclusions: Greek adolescents demonstrate moderate awareness of ADHD and generally supportive attitudes toward peers with ADHD, alongside some uncertainty regarding available educational supports. Schools may represent an important context for improving adolescents’ mental health literacy and understanding of ADHD-related support options.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Mechanisms and Severity of Injuries in Infants and Children <2 Years: A Retrospective Analysis over 30 Years in a European Urban Level 1 Trauma Center
by
Vanessa Groß, Anna Theresa Schauß, Lara Marie Bogensperger, Antonia Schwarz, Bikash Parajuli, Sanika Rapole, Janina M. Patsch, Notburga Payr, Kurt Payr and Stephan Payr
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010025 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Injuries remain a major cause of childhood morbidity and mortality in Europe, despite improved prevention. Infants under one year are particularly vulnerable because of limited motor control and complete dependence on caregivers. Existing studies are often small or cover broad age ranges,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Injuries remain a major cause of childhood morbidity and mortality in Europe, despite improved prevention. Infants under one year are particularly vulnerable because of limited motor control and complete dependence on caregivers. Existing studies are often small or cover broad age ranges, limiting infant-specific insights. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of injury types, mechanisms, and treatments, focusing exclusively on infants aged zero to one year. Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 29,574 infants and children (<2 years) treated at a level 1 trauma department from 1993 to 2022. Primary data included main diagnosis, injury mechanism, and treatment. Injuries were classified by diagnosis and mechanism. Surgeries were categorized by procedure type. Results: Injury frequency increased with age. A total of 31.1% of cases occurred in infants (<12 months) and 68.9% in children (12–24 months). Head injuries were the most common trauma type (44%), particularly among infants (69.9%; children: 32.2%), while wounds (infants: 10.2%; children: 31.5%) and fractures (infants: 4.2%; children: 8.4%) were more frequent in children. Falls were the predominant mechanism (77.9%) across both groups. Most injuries were treated conservatively. A total of 228 surgical interventions were performed (0.8%), mainly for wounds (54.8%) and fractures (30.3%). Conclusions: This study shows that, even within the first two years of life, child development shapes both injury frequency and type. As mobility and independence increase, injuries rise, from predominantly head trauma among infants to a higher incidence of wounds and fractures in children. The majority of injuries were minor and managed conservatively.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Understanding Motivating Factors for COVID-19 Vaccination in Families Defaulting from Childhood Immunization: A Mixed-Methods Study in Pakistan
by
Kifayat Ullah, Chukwuma Mbaeyi, Javeria Saleem, Muhammad Ishaq, Muhammad Rana Safdar, Aslam Pervaiz, Tamkeen Ghafoor, Mumtaz Ali Laghari, Sumbal Hameed, Fatima Majeed, Usman Javed Iqbal and Amjad Mehmood
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010024 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted health systems, including the delivery of childhood immunizations. This study assessed COVID-19 vaccination coverage in families of children with incomplete routine immunization and explored why adults accepted COVID-19 vaccines despite skipping routine vaccination for their children in
[...] Read more.
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted health systems, including the delivery of childhood immunizations. This study assessed COVID-19 vaccination coverage in families of children with incomplete routine immunization and explored why adults accepted COVID-19 vaccines despite skipping routine vaccination for their children in the district of Swat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Methods: A mixed-methods study was conducted in Swat District during March 2022–April 2023. A cross-sectional survey assessed COVID-19 vaccination in household members of children under 2 years of age for whom vaccination registries showed missed routine vaccinations. In-depth interviews with 18 household members explored motivations for vaccine acceptance through thematic analysis. Results: Among 249 families of children with incomplete immunization found through vaccination records, 237 families (88% response) were interviewed. Among 382 children below 2 years of age in these families, 29.5% (n = 113) were fully vaccinated, 67.5% (n = 258) were incompletely vaccinated according to age, and 2.9% (n = 11) had not received any vaccine. Data from 237 of the defaulter children—one per household—was included in further analysis. Among household members above 12 years of age, 87% (964/1103) of males and 82% (n = 901/1093) of females were vaccinated against COVID-19. Households with at least one fully vaccinated child were significantly more likely to have vaccinated family members. Multivariable analysis showed maternal COVID-19 vaccination (AOR 2.08, 95% CI: 1.15–3.76) and urban residence (AOR 2.08, 95% CI: 1.14–3.79) were associated with full childhood vaccination. In-depth interviews revealed that key motivators for COVID-19 vaccination included the perception that it was mandatory, house-to-house vaccination, and fear of hospitalization or death. Conclusions: Vaccine requirements and ease of access to vaccination services enhanced coverage with COVID-19 vaccines among families of children with incomplete routine immunization. Ethical use of vaccine requirements and community education to enhance levels of risk perception of vaccine-preventable diseases could potentially improve childhood immunization.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Estimation of Antioxidant Consumption in an Adolescent Population from a School in Pachuca de Soto, Mexico: A Cross-Sectional Study by Convenience Sample
by
Eli Mireya Sandoval-Gallegos, Alejandra López-García, Karen Rubí Escamilla-Gutiérrez, José Arias-Rico, Quinatzin Yadira Zafra-Rojas, Esther Ramírez-Moreno, Araceli Monter-Arciniega, Nelly del Socorro Cruz-Cansino, Alma Delia Román-Gutiérrez and Zacnicté Olguín-Hernández
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010023 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Adolescence is a critical stage for establishing lifelong dietary habits and preventing non-communicable diseases through adequate intake of bioactive compounds. Numerous studies have thoroughly examined the antioxidant profile of traditional diets such as the Mediterranean diet. In contrast, current research provides limited
[...] Read more.
Background: Adolescence is a critical stage for establishing lifelong dietary habits and preventing non-communicable diseases through adequate intake of bioactive compounds. Numerous studies have thoroughly examined the antioxidant profile of traditional diets such as the Mediterranean diet. In contrast, current research provides limited insights into the antioxidant properties of foods typically consumed by Mexican adolescents. Objective: So, this study aimed to quantify the total phenolic compound (TPC) content and antioxidant capacity (AC) of frequently consumed foods and to estimate dietary intake in Mexican adolescents. Methodology: The selected food groups were identified based on their frequency of consumption by 15% or more of the adolescent population, considering those that have demonstrated a sufficient quantity of antioxidants. It was analyzed TPC and ABTS•+ and DPPH• to determine the antiradical activity of the analyzed samples. Results: The estimated daily intake of TPC was 1484.01 mg GAE/person, while AC intake was 345.67 mg AAE/person (ABTS•+) and 5399.14 µmol TE/person (DPPH•). Cereals and fruits were the major contributors to total antioxidant intake, while the contribution of leafy vegetables and nuts was relatively low. The statistical analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between TPC and AC. The results of the study indicate the antioxidant potential of the adolescent diet. Conclusions: Despite certain limitations, the values obtained from the study are comparable to those of other studies that employed similar methodologies. Consequently, promoting the early consumption of fresh plant-based foods rich in antioxidants, such as polyphenols, which can enhance the dietary profile and contribute to adolescents’ long-term health, constitutes a significant area of research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Personalized and Sustainable Nutrition for Children and Adolescents: An Important Step for the 2030 Agenda)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCase Report
Kawasaki Disease-Associated Pancreatitis in an Adolescent: A Case Report and Literature Review
by
Akihiro Ichiki, Keisuke Takata and Tadashi Moriwake
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010022 - 4 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic involvement in Kawasaki disease (KD) is rare. Case presentation: A 13-year-old adolescent presented with severe epigastric pain, elevated pancreatic enzyme levels, and conjunctival injection, but he lacked a fever and the other classic features of KD. The patient was initially diagnosed
[...] Read more.
Background: Pancreatic involvement in Kawasaki disease (KD) is rare. Case presentation: A 13-year-old adolescent presented with severe epigastric pain, elevated pancreatic enzyme levels, and conjunctival injection, but he lacked a fever and the other classic features of KD. The patient was initially diagnosed with acute pancreatitis and treated conservatively. As his abdominal pain improved, mucocutaneous findings emerged, leading to a diagnosis of complete KD. A literature review was conducted to summarize reported cases of KD-associated pancreatitis. This review highlights the older age of affected patients, the variability in the timing of pancreatitis onset, and a tendency toward delayed diagnosis. Conclusions: Pancreatic involvement, including pancreatitis, can occur before typical mucocutaneous features and should be considered in older children and adolescents presenting with unexplained abdominal pain and pancreatic enzyme elevation. Increased awareness of this atypical presentation may help reduce diagnostic delay and support timely management.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Local Diagnostic Reference Levels for Common Nuclear Medicine Procedures for Pediatric in Dubai Health
by
Entesar Z. Dalah, Najlaa K. Al Mazrouei and Zahra A. Al Ali
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010021 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study aims to establish diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) for common pediatric nuclear medicine (NM) procedures performed within the Dubai Health sector. The established DRLs will serve as a benchmark for pediatric NM practice, supporting standardized healthcare delivery and guiding ongoing quality improvement
[...] Read more.
This study aims to establish diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) for common pediatric nuclear medicine (NM) procedures performed within the Dubai Health sector. The established DRLs will serve as a benchmark for pediatric NM practice, supporting standardized healthcare delivery and guiding ongoing quality improvement and internal audit activities. Patient dose survey data were collected from the solo NM center within the Dubai Health sector. The study included common scintigraphy procedures using gamma cameras and the hybrid positron emission tomography with computed tomography (PET/CT) procedures. Scintigraphy procedures include the dynamic and static renal scans, and ocular eye scans. The hybrid PET/CT procedures entail tumor/infection and neuroendocrine scans. Patient demographics, administered activities, CT doses, and study description were recorded. Both weight bands of <5, 5–<15, 15–<30, 30–<50, and 50–<80 kg, and age bands of <1, 1–<5, 5–<10, and 10–<15 years were considered. Statistical analysis was performed to determine the 25th percentile, median and 75th percentile of the dose distribution. The median value was used to establish the DRLs for the Dubai Health sector. The analyses revealed significant variation in the administered activities across the different pediatric NM procedures. The proposed DRLs for various pediatric NM procedures for the weight band 15–<30 kg are as follows: renal dynamic 98.4 MBq, renal static 96.2 MBq, ocular eyes 18.5 MBq, tumor/infection 155 MBq, and neuroendocrine 80 MBq. This work provides the first pediatric NM DRLs for the Dubai Health sector, offering a key reference for developing the local DRLs for the Emirate of Dubai. The findings indicate that achieving meaningful dose optimization will require systematic revision of existing imaging protocols, with targeted parameter adjustments informed by continuous dose monitoring and benchmarking to enhance patient safety and overall diagnostic quality.
Full article
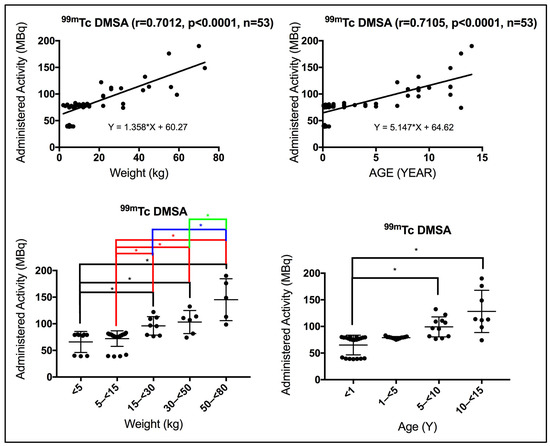
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Severe Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Otherwise Healthy Children: A Three-Case Series and Narrative Review
by
Olivia-Oana Stanciu, Andreea Moga, Laura Balanescu, Mircea Andriescu, Ruxandra Caragata and Radu Balanescu
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010020 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Severe lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) in neurologically and anatomically normal children is uncommon and frequently underdiagnosed. When severe, functional voiding disorders may closely mimic obstructive or reflux pathology, leading to diagnostic errors, unnecessary invasive procedures, and potential risk to the upper
[...] Read more.
Background: Severe lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) in neurologically and anatomically normal children is uncommon and frequently underdiagnosed. When severe, functional voiding disorders may closely mimic obstructive or reflux pathology, leading to diagnostic errors, unnecessary invasive procedures, and potential risk to the upper urinary tract. Case presentation: We present three pediatric cases (aged 3–10 years) referred for recurrent febrile urinary tract infections, incontinence, or acute urinary retention in the absence of neurological or structural abnormalities. Urodynamic evaluation identified three distinct severe functional phenotypes: detrusor overactivity with reduced bladder capacity, poor compliance with detrusor–sphincter dyssynergia and secondary high-grade vesicoureteral reflux (Hinman syndrome), and detrusor underactivity with significant post-void residual volumes. All patients demonstrated marked bladder wall remodeling on cystoscopy, including trabeculation and pseudopolypoid mucosal changes. Case discussion: Despite similar clinical severity, the cases illustrated substantial functional heterogeneity and differing risks of upper urinary tract involvement. Urodynamic phenotyping proved central to diagnosis, differentiation from structural disease, and treatment planning. Multimodal conservative management—including urotherapy, pelvic floor biofeedback, targeted pharmacologic therapy, and, when indicated, clean intermittent catheterization or antibiotic prophylaxis—led to resolution of recurrent infections and meaningful improvement in bladder function during medium-term follow-up, although symptom recurrence occurred in one patient after treatment withdrawal. Conclusions: These cases highlight the heterogeneity and potential reversibility of severe functional LUTD in otherwise healthy children. Early functional recognition based on urodynamic assessment is essential to avoid misdiagnosis, prevent unnecessary surgical intervention, and protect renal function. Conservative, function-oriented management remains the cornerstone of effective treatment. The findings are discussed in the context of the existing literature on severe non-neurogenic LUTD and Hinman syndrome.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pediatric Cholestatic Diseases in the Era of Ileal Bile Acid Transporter (IBAT) Inhibitors
by
Marco Sciveres, Silvio Veraldi, Francesco Cirillo and Giuseppe Maggiore
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010019 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cholestatic diseases in children represent a heterogeneous group of disorders that, with few exceptions, have no cure. For decades, off-label drugs and/or drugs with little evidence of efficacy have been used to treat pruritus or as supportive therapy. In recent years, a family
[...] Read more.
Cholestatic diseases in children represent a heterogeneous group of disorders that, with few exceptions, have no cure. For decades, off-label drugs and/or drugs with little evidence of efficacy have been used to treat pruritus or as supportive therapy. In recent years, a family of molecules known as bile acid transporter inhibitors (IBATis) has been developed, with two of these being approved for treating pruritus in progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) and Alagille syndrome (ALGS). Blocking the ileal reabsorption of bile acids (BAs) lowers serum levels. This contributes to reducing cholestatic pruritus. Such a mechanism of action may also have a potential benefit in other cholestatic diseases and even in the consequences of chronic cholestasis. This is a narrative review of the literature, including the most recent communications, to summarize data on the efficacy and safety of IBATis in the treatment of pruritus in PFIC and ALGS in children, including a description of the latest results from their use in a real-world setting. Reports on off-label use and experiences in adults are also discussed. This review aims to help physicians understand the potential and limitations of these new drugs in the treatment of cholestatic pruritus.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
The Role of Serial Fetal Echocardiography in Postnatal Surgical Decision-Making for Borderline Left Ventricle: A Case Report
by
Andreea Cerghit-Paler, Dorottya Gabor-Miklosi, Iolanda Muntean, George-Andrei Crauciuc, Daniela Toma, Laura Beligan and Liliana Gozar
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010018 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Borderline left ventricle represents a heterogeneous spectrum of congenital heart disease for which accurate prediction of suitability for biventricular versus univentricular circulation is often difficult. Serial fetal echocardiography may provide dynamic information to support postnatal decision-making. Case Presentation: We report
[...] Read more.
Background: Borderline left ventricle represents a heterogeneous spectrum of congenital heart disease for which accurate prediction of suitability for biventricular versus univentricular circulation is often difficult. Serial fetal echocardiography may provide dynamic information to support postnatal decision-making. Case Presentation: We report the case of a fetus diagnosed at 32 weeks’ gestation with a borderline left ventricle, ventricular disproportion, hypoplastic left-sided structures, ductal-dependent systemic circulation, and a non-restrictive ostium secundum atrial septal defect. Serial fetal echocardiographic evaluations demonstrated stable left ventricular dimensions, preserved systolic function, impaired diastolic relaxation, and absence of endomyocardial fibroelastosis. Postnatal echocardiography confirmed hypoplastic aortic arch and coarctation. Following multidisciplinary evaluation, a biventricular repair strategy was selected. At 14 days of life, the patient underwent aortic arch reconstruction and partial atrial septal defect closure with preservation of a small therapeutic interatrial communication. Postoperative evolution was favorable, with progressive left ventricular growth and preserved function. At 2-year follow-up, echocardiography showed normalized mitral and aortic valve z-scores, good left ventricular systolic performance, and no evidence of myocardial fibrosis. Conclusions: This case highlights the value of serial fetal echocardiography in guiding individualized management of borderline left ventricle. Careful assessment of ventricular function and atrial septal physiology may support selection of a biventricular strategy in selected patients and contribute to favorable mid-term outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Copycat Behavior and Somatic Symptoms in Italian Children Exposed to a Violent TV Series: An Observational Study of Squid Game Viewers
by
Martina Gnazzo, Giuditta Bargiacchi, Luigi Vetri, Lucia Parisi, Davide Testa, Daniela Smirni, Agata Maltese, Valentina Baldini, Giulia Pisanò, Eva Germanò, Beatrice Gallai, Antonella Gagliano, Carola Costanza, Michele Roccella and Marco Carotenuto
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010017 - 30 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Violent TV series and streaming content are increasingly accessible to children, raising concerns about behavioral imitation and psychological effects. This study examined copycat behaviors and associated emotional and somatic symptoms among children who reported watching the age-restricted series Squid Game. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: Violent TV series and streaming content are increasingly accessible to children, raising concerns about behavioral imitation and psychological effects. This study examined copycat behaviors and associated emotional and somatic symptoms among children who reported watching the age-restricted series Squid Game. Methods: In this observational study of 228 Italian primary school children (aged 8–11), 128 who had watched Squid Game formed the analytic sample. They were categorized into a Copycat Behavior (CB) group or a Non-Copycat Behavior (NCB) group based on self-reported imitation of scenes or games from the series. Parents completed the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL). Group differences were assessed using Mann–Whitney U tests, and gender distribution was compared with Chi-square tests (α = 0.05). Results: Among viewers, 42 children (32%) engaged in imitation behaviors, typically reenacting game-based violent scenes with friends (52%), siblings (28%), or classmates (20%). Age and gender distributions did not differ between groups. The CB group scored slightly higher on the CBCL Somatic Complaints scale compared with the NCB group (M = 54.12 vs. 52.92; U = 1414.5, p = 0.033), although this difference was small. No significant differences emerged on other CBCL syndrome or broadband scales. Conclusions: Among children engaging in copycat behaviors exhibited a small, subclinical increase in somatic complaints. While causality cannot be inferred, the findings highlight the need to protect vulnerable children—particularly those prone to somatic distress—from unsupervised access to violent, age-inappropriate content. Media literacy for parents and educators, and longitudinal studies including non-viewers are recommended.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Customized Mouthguard Design for a Child with Orofacial Myofunctional Disorder: A Case Report
by
Masatoshi Otsugu, Fumikazu Tojo, Rena Okawa and Kazuhiko Nakano
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010016 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
When fabricating custom-made mouthguards for children, tooth replacement is an important factor for dentists to consider. In addition, orofacial myofunctional disorders and deleterious oral habits—such as incompetent lip seal and tongue thrusting—are relatively common among children and are associated with an increased risk
[...] Read more.
When fabricating custom-made mouthguards for children, tooth replacement is an important factor for dentists to consider. In addition, orofacial myofunctional disorders and deleterious oral habits—such as incompetent lip seal and tongue thrusting—are relatively common among children and are associated with an increased risk of oral and dental trauma. Therefore, individual oral functional characteristics should be taken into account when designing custom-made mouthguards for pediatric patients. This report presents a case involving the design, fabrication, and appliance management of a custom-made mouthguard for a Japanese boy exhibiting incompetent lip seal and tongue thrusting. In this case, the anterior palate region of the mouthguard was left uncut, and multiple holes were created using a carbide bur to permit tongue–palate contact and provide sensory feedback related to tongue elevation. Over a 20-month follow-up period, no oral or dental trauma was observed. During appliance use, the patient demonstrated improved tongue elevation and an increased frequency of lip seal at rest. This case illustrates a custom mouthguard design that incorporates individual oral functional characteristics in a pediatric patient.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
A Pediatric Supracondylar Fracture with Bilateral (Medial and Lateral) Pillar Comminution–A Recommendation for a New Stable Pin Configuration for a Highly Unstable Fracture
by
Lara Marie Bogensperger, Sandeep Patwardhan and Stephan Payr
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010015 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The management of supracondylar fractures in children remains a challenging area of orthopedic practice. Medial comminution is a recognized complication that can result in unstable fracture patterns, which can pose challenges in diagnosis and management. However, when anticipated surgical treatment with an additional
[...] Read more.
The management of supracondylar fractures in children remains a challenging area of orthopedic practice. Medial comminution is a recognized complication that can result in unstable fracture patterns, which can pose challenges in diagnosis and management. However, when anticipated surgical treatment with an additional medial K-wire is administered, stable fixation is typically ensured. However, an additional radial comminution poses several challenges for reduction, alignment assessment, and pin configuration for stable fixation, as presented in this case. This case report presents a fracture pattern of a Gartland type 3 fracture with medial and lateral comminution that has not been sufficiently described previously and illustrates an effective pin configuration that has yet to be theoretically described.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Integrating the Genomic Revolution into Newborn Screening: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
by
Albina Tummolo, Emanuela Ponzi, Simonetta Simonetti and Mattia Gentile
Pediatr. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric18010014 - 19 Jan 2026
Abstract
In recent years, the development of new diagnostic technologies, such as tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), has caused a veritable revolution in the diagnosis of genetic diseases, reducing time, cost, and invasiveness associated with prior diagnostic techniques. While MS/MS laid
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the development of new diagnostic technologies, such as tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and next-generation sequencing (NGS), has caused a veritable revolution in the diagnosis of genetic diseases, reducing time, cost, and invasiveness associated with prior diagnostic techniques. While MS/MS laid the foundation for the development of numerous, usually institutionally based, neonatal screening programs, NGS has gained traction in newborn screening (NBS), primarily through pilot projects and private funding across different countries. As a result, the traditional Wilson and Jungner criteria have been supplemented by additional criteria, including considerations of equity and access, in response to emerging technologies. This review aims to provide an up-to-date overview of the global landscape of metabolic screening panels, highlight the major ongoing genomic screening projects, and outline the current models for integrating these two screening systems. Substantial differences exist across countries in the numbers and types of diseases included in national NBS programmes. In this context, Italy represents a prominent case, as its neonatal screening framework has seen significant expansion and development in recent years, reaching a particularly comprehensive metabolic screening panel. Nonetheless, a number of initiatives to incorporate genomic technologies into the NBS pathway are currently underway, primarily involving high-income countries. Nonetheless, unlike metabolomic-based NBS programs, no country has a government-mandated NGS program as first-tier testing for newborns. New evidence is emerging from ongoing models of integration of multi-omics approaches into NBS, including the use of AI and machine learning. Identifying the most appropriate system for this integration to reduce the false-positive and false-negative rates associated with both screening types, ensure more equitable access to screening, and facilitate faster access to treatment may represent a useful and foresightful way to conceptualize NBS in the future. This transitional phase should promote rigorous improvements before full-scale adoption.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Global Neonatal Screening: Expanding Horizons in Diagnostic Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Pediatric Reports Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Feature Papers on Child Developmental Disorders and Neurology Research
Guest Editors: Giovanni Battista Dell’Isola, Alberto Verrotti di PianellaDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Diagnosis and Treatment of the Maxillofacial Region in Pediatric Patients
Guest Editors: Maciej Chęciński, Maciej SikoraDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Infectious Diseases in Children and Adolescents
Guest Editors: Désirée Caselli, Melodie Olivia Loredana Rosa AricòDeadline: 15 August 2026
Special Issue in
Pediatric Reports
Advanced Diagnostic and Treatment Approach in Pediatric Hepatology
Guest Editor: Tudor PopDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Pediatric Reports
Recent Advances and Critical Issues in Pediatrics: a Collection of Feature Papers
Collection Editors: Maurizio Aricò, Claudia Mandato, Pietro Vajro







