The Feasibility of the Arabic Version of Ages and Stages Questionnaire 3 to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk of Developmental Delays in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Arabic Ages and Stages-3 Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
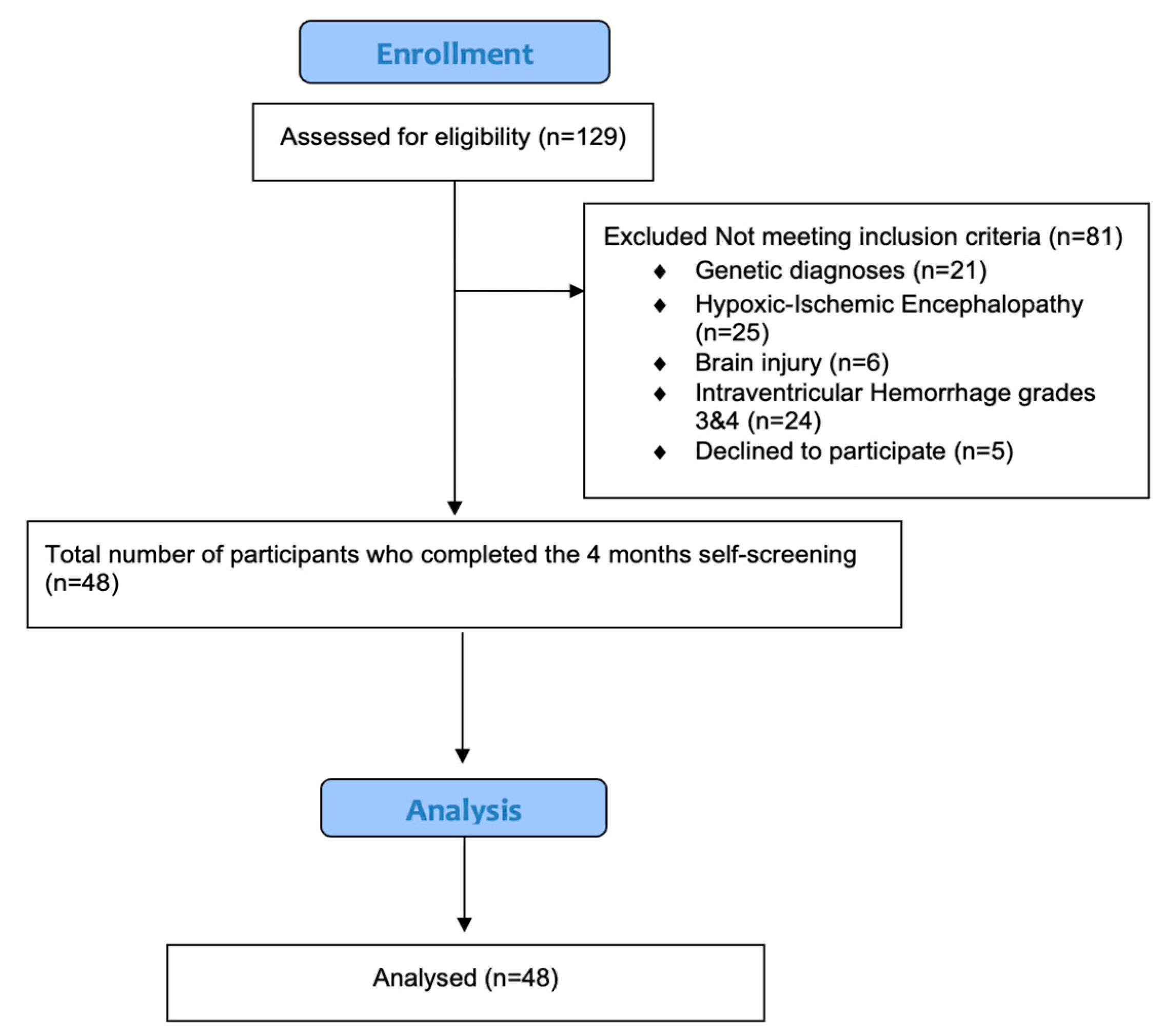
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. A-ASQ-3 Scores and Risk of Developmental Delays
3.3. Risk Factors Associated with Developmental Delays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DD | developmental delays |
| ASQ | Ages and Stages Questionnaire |
| CA | corrected age |
| GA | gestational age |
| IVH | intraventricular hemorrhage |
| RDS | respiratory distress syndrome |
| CLD | Chronic Lung Disease |
| PVL | periventricular leukomalacia |
References
- Walani, S.R. Global burden of preterm birth. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 150, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blencowe, H.; Cousens, S.; Oestergaard, M.Z.; Chou, D.; Moller, A.B.; Narwal, R.; Adler, A.; Vera Garcia, C.; Rohde, S.; Say, L.; et al. National, regional, and worldwide estimates of preterm birth rates in the year 2010 with time trends since 1990 for selected countries: A systematic analysis and implications. Lancet 2012, 379, 2162–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayed, A.; Wahabi, H.A.; Esmaeil, S.; Elmorshedy, H.; AlAniezy, H. Preterm, early term, and post-term infants from Riyadh mother and baby multicenter cohort study: The cohort profile. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 928037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahabi, H.; Fayed, A.; Esmaeil, S.; Alzeidan, R.; Elawad, M.; Tabassum, R.; Hansoti, S.; Magzoup, M.E.; Al-Kadri, H.; Elsherif, E.; et al. Riyadh Mother and Baby Multicenter Cohort Study: The Cohort Profile. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems: Alphabetical Index; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, J.A.; Munoz, F.M.; Gonik, B.; Frau, L.; Cutland, C.; Mallett-Moore, T.; Kissou, A.; Wittke, F.; Das, M.; Nunes, T.; et al. Preterm birth: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunisation safety data. Vaccine 2016, 34, 6047–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spong, C.Y. Defining “Term” Pregnancy: Recommendations From the Defining “Term” Pregnancy Workgroup. JAMA 2013, 309, 2445–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, T.; King, C.; Muhit, M.; Islam, M.K.; Jahan, I.; Baset, K.u.; Badawi, N.; Khandaker, G. Screening tools for early identification of children with developmental delay in low- and middle-income countries: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmmash, A.; Aljuhani, T.; Albesher, R.A. Early Detection and Intervention Practices Provided by Physical and Occupational Therapists in Saudi Arabia for Children with or at Risk for Cerebral Palsy. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2025, 18, 4045–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmmash, A.S.; Faquih, N.O. Perceptions of Healthcare Providers and Caregivers Regarding Procedures for Early Detection of Developmental Delays in Infants and Toddlers in Saudi Arabia. Children 2022, 9, 1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, J.L.; Doyle, L.W.; Burnett, A.C.; Lee, K.J.; Walsh, J.M.; Potter, C.R.; Treyvaud, K.; Thompson, D.K.; Olsen, J.E.; Anderson, P.J.; et al. Association Between Moderate and Late Preterm Birth and Neurodevelopment and Social-Emotional Development at Age 2 Years. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, e164805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.A.; Murray, D.M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Mathieson, S.R.; Livingstone, V.; Boylan, G.B. Neurodevelopmental outcome of low-risk moderate to late preterm infants at 18 months. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1256872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xiong, C.; Liu, H.; Duan, J.; Kang, C.; Yao, C.; Chen, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Impact of early term and late preterm birth on infants’ neurodevelopment: Evidence from a cohort study in Wuhan, China. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeschler, J.B.; Shevell, M. Comprehensive evaluation of the child with intellectual disability or global developmental delays. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e903–e918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatla, M.M.; Goweda, R.A. Prevalence and Factors Associated with Developmental Delays among Preschool Children in Saudi Arabia. J. High Inst. Public Health 2020, 50, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, P.H.; Macias, M.M. Promoting Optimal Development: Identifying Infants and Young Children With Developmental Disorders Through Developmental Surveillance and Screening. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20193449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, G.; Deavenport-Saman, A.; Stavros, S.; Farboodi, N.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.; Garcia, J.; Yin, L.; Gera, M.P. Standardizing and Improving Primary Care-Based Electronic Developmental Screening for Young Children in Federally Qualified Health Center Clinics. Matern. Child. Health J. 2024, 28, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troude, P.; Squires, J.; L’Hélias, L.F.; Bouyer, J.; de La Rochebrochard, E. Ages and Stages Questionnaires: Feasibility of postal surveys for child follow-up. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hindi, M.Y.; Almahdi, B.H.; Alasmari, D.A.; Alwagdani, R.K.; Hunjur, W.M.; Khalel, A.F.; AlQurashi, M.A. Screening for Neurodevelopmental Delay for Preterm Very Low Birth Weight Infants at Tertiary Care Center in Saudi Arabia. Cureus 2021, 13, e20092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Patel, P.; Pandya, N.; Dave, D.; Deshpande, T. Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Preterm Babies: A 12-Month Observational Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e47775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.N.; Luu, T.M.; Gosselin, J. Concurrent validity of ages and stages questionnaires in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e108–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonhaut, L.; Pérez, M.; Armijo, I.; Maturana, A. Comparison between Ages & Stages Questionnaire and Bayley Scales, to predict cognitive delay in school age. Early Hum. Dev. 2020, 141, 104933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: An algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 405–420. [CrossRef]
- Vitrikas, K.; Savard, D.; Bucaj, M. Developmental Delay: When and How to Screen. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, R.A.; Boyd, R.N.; Cioni, G.; Ware, R.S.; Doherty, J.; Jackson, M.P.; Salthouse, K.L.; Colditz, P.B.; PREMTiME Study Group. Early detection of developmental delay in infants born very preterm or with very low birthweight. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 65, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.S.; Magalhães, L.C.; Alves, C.R.L. Effect of preterm birth on motor development, behavior, and school performance of school-age children: A systematic review. J. De Pediatr. (Versão Em Port.) 2014, 90, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tanrıverdi, M.; Yılmaz, G.G. Early neuromotor and sensory development in premature infants: An 18-month longitudinal follow-up study. Infant Behav. Dev. 2025, 80, 102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonhaut, L.; Armijo, I.; Schönstedt, M.; Alvarez, J.; Cordero, M. Validity of the ages and stages questionnaires in term and preterm infants. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1468–e1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charafeddine, L.; Sinno, D.; Ammous, F.; Yassin, W.; Al-Shaar, L.; Mikati, M.A. Ages and stages questionnaires: Adaptation to an Arabic speaking population and cultural sensitivity. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2013, 17, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charafeddine, L.; Dani, A.; Badr, L.K.; Sinno, D.; Tamim, H.; Khoury, J.; Nasser, F.; Makki, M. The psychometric properties of the Ages and Stages Questionnaires-3 in Arabic: Cross-sectional observational study. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 136, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboktakin, L. Developmental delay in preterm infants during the first twelve months after birth and its risk factors. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2024, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.K.; Shi, L.; Daniel, L.M.; Yang, P.H.; Khoo, P.C.; Quek, B.H.; Zheng, Q.; Rajadurai, V.S. Prospective evaluation of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire 3rd Edition in very-low-birthweight infants. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2017, 59, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, H.; Albradie, R.; Bashir, S. Identifying pattern in global developmental delay children: A retrospective study at King Fahad specialist hospital, Dammam (Saudi Arabia). Pediatr. Rep. 2019, 11, 8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valla, L.; Wentzel-Larsen, T.; Hofoss, D.; Slinning, K. Prevalence of suspected developmental delays in early infancy: Results from a regional population-based longitudinal study. BMC Pediatr. 2015, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmari, P. Editorial: The Importance of Screening for Developmental Disorders and Demonstrating Improved Health Outcomes. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 62, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, R.A.; Boss, R.D.; Burton, V.J.; Raja, K.; Lemmon, M.E. Parent preferences for neurodevelopmental screening in the neonatal intensive care unit. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, N.S.; Arrushaid, O.M.; Farah Bakhiet, S.; Alkathiri, S. Examining the current practices of the individualized family services plan with young children with disabilities in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2023, 69, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, C.; Irvine, A.D.; Hourihane, J.O.; Kiely, M.E.; Murray, D.M. ASQ-3 and BSID-III’s concurrent validity and predictive ability of cognitive outcome at 5 years. Pediatr. Res. 2023, 94, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Nguyen, P.H.; Tran, L.M.; Khuong, L.Q.; Nguyen, S.V.; Young, M.F.; Ramakrishnan, U. Growth patterns of preterm and small for gestational age children during the first 10 years of life. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1348225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinger, K.J.; Copper, C.; Boyle, E.; Blower, S.; Hewitt, C.; Fraser, L. Risk of Developmental Disorders in Children Born at 32 to 38 Weeks’ Gestation: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatrics 2023, 152, e2023061878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.G. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm infants. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2023, 66, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughon, M.; O’Shea, M.T.; Allred, E.N.; Bose, C.; Kuban, K.; Van Marter, L.J.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Leviton, A. Chronic lung disease and developmental delay at 2 years of age in children born before 28 weeks’ gestation. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMauro, S.B. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 3509–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Neonatal Characteristics | All Infants (N = 48) | Infants with No Risk of DDs (N = 11) | Infants with High Risk of DDs (N = 37) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corrected age at assessment | 12 weeks | 34 (70.1) | 8 (23.5) | 26 (76.5) | |
| 13 weeks | 14 (29.1) | 3 (21.4) | 11 (78.6) | 0.9 | |
| Gender | Male | 22 (45.8) | 6 (27.3) | 16 (72.7) | |
| Female | 26 (54.2) | 5 (19.2) | 21 (80.8) | 0.4 | |
| Weight (g) | ELBW | 7 (14.6) | 4 (57.1) | 3 (42.9) | |
| VLBW | 27 (56.2) | 4 (14.8) | 23 (85.2) | 0.06 | |
| LBW | 14 (29.2) | 3 (21.4) | 11 (78.6) | ||
| Gestational age (weeks) | Extremely preterm | 8 (16.7) | 3 (37.5) | 5 (62.5) | |
| Very preterm | 32 (66.6) | 7 (21.9) | 25 (78.1) | 0.5 | |
| Moderate to late preterm | 8 (16.7) | 1 (12.5) | 7 (87.5) | ||
| Length of stay (days) | 42.1 (23.4) † | 52.3 (20.4) † | 39.5 (24.0) † | 0.13 | |
| Respiratory distress syndrome | No | 4 (8.3) | 0 | 4 (100) | |
| Yes | 1 (2.1) | 0 | 1 (100) | 0.7 | |
| Resolved | 43 (89.6) | 11 (25.6) | 32 (74.4) | ||
| Bronchopulmonary distress | No | 44 (91.6) | 10 (22.7) | 34 (77.3) | 0.9 |
| Yes | 4 (8.3) | 1 (25) | 3 (75) | ||
| Periventricular leukomalacia | No | 43 (89.6) | 10 (23.3) | 33 (76.3) | 0.8 |
| Yes | 5 (10.4) | 1 (20) | 4 (80) | ||
| Intraventricular hemorrhage (grade I and II) | No | 30 (62.5) | 5 (16.7) | 25 (83.3) | |
| Yes | 18 (37.5) | 6 (33.3) | 12 (66.7) | 0.2 | |
| A-ASQ-3 Domain | Infants with No Risk of DDs N (%) | Infants with High Risk of DDs N (%) | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication | 41 (85.4) | 7 (14.6) | 0.18 |
| Gross motor | 31(64.6) | 17 (35.4) | 0.004 * |
| Fine motor | 24 (50) | 24 (50) | <0.001 * |
| Problem-solving | 28 (58.3) | 20 (41.6) | <0.001 * |
| Personal–social | 17 (35.4) | 31 (64.6) | <0.001 * |
| Risk of DDs | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOS | 0.98 | 0.94–1.03 | 0.6 |
| RDS | 0.00 | 0.0–0.1 | 0.9 |
| Weight at birth | 1.0 | 0.99–1.03 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljuhani, T.; Aljurayyad, W.; Almudayfir, I.F.; Alhassan, R.M.; Alharran, M.I.; Aloushan, R.A.; Alsaleem, R.S.; Althunayyan, N.M.; Albesher, R.A. The Feasibility of the Arabic Version of Ages and Stages Questionnaire 3 to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk of Developmental Delays in Saudi Arabia. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050105
Aljuhani T, Aljurayyad W, Almudayfir IF, Alhassan RM, Alharran MI, Aloushan RA, Alsaleem RS, Althunayyan NM, Albesher RA. The Feasibility of the Arabic Version of Ages and Stages Questionnaire 3 to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk of Developmental Delays in Saudi Arabia. Pediatric Reports. 2025; 17(5):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050105
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljuhani, Turki, Waad Aljurayyad, Ibrahim F. Almudayfir, Ruyuf M. Alhassan, Monerah I. Alharran, Razan A. Aloushan, Reem S. Alsaleem, Nassar M. Althunayyan, and Reem A. Albesher. 2025. "The Feasibility of the Arabic Version of Ages and Stages Questionnaire 3 to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk of Developmental Delays in Saudi Arabia" Pediatric Reports 17, no. 5: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050105
APA StyleAljuhani, T., Aljurayyad, W., Almudayfir, I. F., Alhassan, R. M., Alharran, M. I., Aloushan, R. A., Alsaleem, R. S., Althunayyan, N. M., & Albesher, R. A. (2025). The Feasibility of the Arabic Version of Ages and Stages Questionnaire 3 to Identify Preterm Infants at Risk of Developmental Delays in Saudi Arabia. Pediatric Reports, 17(5), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric17050105






