- Article
YouTube as an Educational Source for Pediatric Orthodontic Treatments: A Comparative Study of Clear Aligners, Fixed Braces, and Lingual Braces
- Sezai Erginbas,
- Andrea Boggio and
- Nur Ozel Erginbas
- + 3 authors
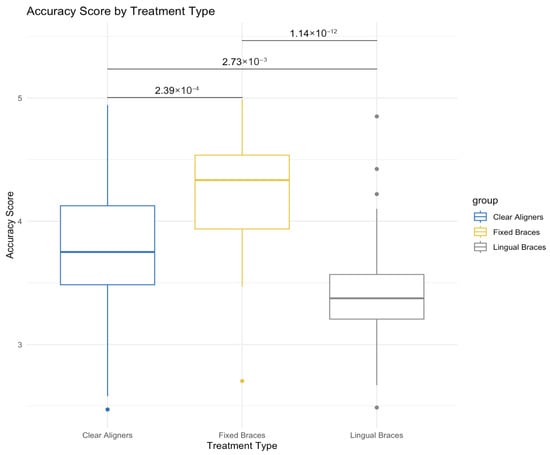
Introduction: This study aimed to evaluate the educational value of YouTube videos presenting information on pediatric orthodontic treatments, specifically clear aligners, fixed braces, and lingual braces. Methods: A cross-sectional analysis was conducted on 150 of the most-viewed English-language YouTube videos (50 per treatment type). Videos were assessed for accuracy, depth of explanation, source type (expert, commercial, or general user), and viewer engagement metrics. Statistical comparisons were made using the Kruskal–Wallis test and Dunn’s post hoc tests with Bonferroni correction. Results: Fixed brace videos demonstrated more accuracy (average score 4.2/5), than both clear aligners (p = 0.03) and lingual braces (p < 0.001), with 60% originating from expert sources. Clear aligner and lingual brace videos had lower accuracy scores (3.8 and 3.5, respectively), reflecting higher proportions of commercial influence (50% and 55%). The findings highlighted the predominance of promotional content in clear aligner and lingual brace videos, raising concerns about potential misinformation. Conclusions: YouTube provides accessible but variable-quality information on pediatric orthodontics. Fixed brace videos offer more reliable educational content, while clear aligner and lingual brace videos are more susceptible to commercial bias. Efforts to promote expert-driven content and implement content verification systems are needed to improve the quality of online orthodontic information for parents and caregivers.
24 December 2025