Journal Description
Knowledge
Knowledge
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on knowledge and knowledge-related technologies published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 48.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
subject
Imprint Information
Open Access
ISSN: 2673-9585
Latest Articles
Can the JUSTICE Framework Help Assess the Ethics of Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040028 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Artificial Intelligence, now commonly called AI, is having an increasingly big impact on society. There are fears that may be negatives or downsides, especially when Artificial Intelligence is used unethically. But how are humans guiding these machines to know whether the choice, the
[...] Read more.
Artificial Intelligence, now commonly called AI, is having an increasingly big impact on society. There are fears that may be negatives or downsides, especially when Artificial Intelligence is used unethically. But how are humans guiding these machines to know whether the choice, the decision, is ethical? Since 2007, one way to check the ethicality of any choice has been to apply the JUSTICE model. This framework helps practitioners decide whether a specific action is or is not ethical by looking through one or more of the seven JUSTICE lenses: Justice, Utilitarian, Spiritual Values, TV rule or Transparency, Influence, Core, and Emergency. Now, in this era of increasing prevalence of Artificial Intelligence, with humans making decisions often together with machines, can the JUSTICE framework still be useful? Yes, it can. We look at each of those seven components. Each may give guidance in some situations. Of the seven, it seems that T or the TV test is most likely to give guidance in this new era.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Intersection of Knowledge Management and Digital Transformation in SMEs: Success Factors, Barriers, and a Research Framework
by
Bonginkosi A. Thango, Ralebitso K. Letshaba and Lerato Matshaka
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040027 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly embracing digital transformation (DT) to remain competitive; however, the enabling role of knowledge management (KM) remains underexplored. This systematic literature review investigates how KM supports DT in SMEs, focusing on strategic processes, tools, barriers, and policy
[...] Read more.
Small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly embracing digital transformation (DT) to remain competitive; however, the enabling role of knowledge management (KM) remains underexplored. This systematic literature review investigates how KM supports DT in SMEs, focusing on strategic processes, tools, barriers, and policy contexts. A structured search was conducted in Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science using the string: (“knowledge management” OR “KM”) AND (“digital transformation” OR “DT”) AND (“small and medium enterprises” OR “SME”). The search yielded 32,547 results, from which 19 studies met the eligibility criteria (English, 2020–2025, KM–DT focus, clear methodology). Results indicate that KM supports DT primarily through change management (31.58%), innovation enablement (21.05%), as well as improved decision-making and agility (15.79%). The most cited tools include KM systems, AI/analytics, and collaborative platforms. Major barriers include limited resources, lack of digital skills, and poor KM culture. Critical success factors identified are leadership commitment (26.32%) and strategic alignment (21.05%). Theoretical foundations are dominated by the Resource-Based View and Dynamic Capabilities Theory. While KM is proven to be a strategic driver of DT in SMEs, more empirical and policy-grounded studies are needed. This review provides a framework to guide future research and inform SME practitioners and policymakers.
Full article
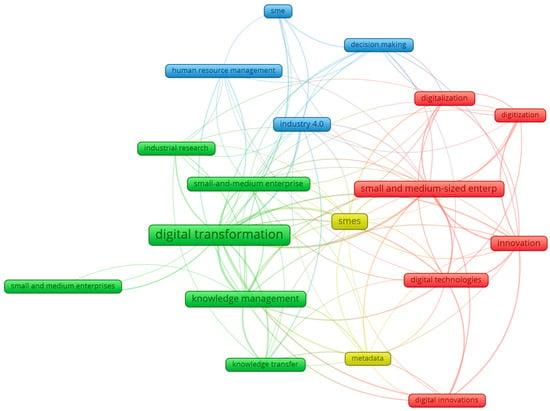
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Online Collaborative Approach to Developing Ontologies to Study Questions About Behaviour
by
Suvodeep Mazumdar, Fatima Maikore, Vitaveska Lanfranchi, Harriet Baird, Fabio Ciravegna, Vyv Huddy, Paul Norman, Richard Rowe, Alexander J. Scott and Thomas L. Webb
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040026 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Almost all societal grand challenges, whether concerning the environment, health, well-being, or the development of sustainable economic models, have at their heart a need to understand people’s behaviour. However, uniting data and insights across disparate fields requires an explicit and shared understanding of
[...] Read more.
Almost all societal grand challenges, whether concerning the environment, health, well-being, or the development of sustainable economic models, have at their heart a need to understand people’s behaviour. However, uniting data and insights across disparate fields requires an explicit and shared understanding of concepts, variables, and ideas (e.g., how to characterise and differentiate behaviours). Ontologies provide a mechanism for creating this explicit and shared understanding and are starting to be developed and used in the social and behavioural sciences. This paper proposes an online co-design approach to use and develop ontologies of behaviour to specify the characteristics of behaviour (e.g., habitual, changeable, effortless) and studies that investigate behaviour as part of a project designed to understand how behaviours are related. We report on our experience of collaborative co-development of ontologies using real-time interactive tools and reflect on the benefits and challenges of our approach. We also offer a set of recommendations for researchers interested in applying such methods to co-develop ontologies. The work contributes to efforts to understand the characteristics of behaviour and enable these to be used to understand questions about behaviour (e.g., is poor sleep associated with greater engagement in habitual behaviours?).
Full article
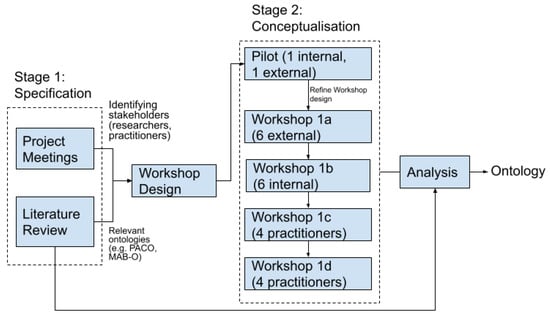
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhancing Chatbot Performance in a SaaS Platform Through Retrieval-Augmented Generation and Prompt Engineering: A Case Study in Behavioral Safety Analysis
by
Jorge Rivera, Scarlett Zapata, Ricardo Pizarro and Brian Keith
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040025 - 5 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article presents a case study showing the development of a chatbot, named Selene, in a Software-as-a-Service platform for behavioral analysis using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) integrating domain-specific knowledge and enforcing adherence to organizational rules to improve response quality. Selene is designed to provide
[...] Read more.
This article presents a case study showing the development of a chatbot, named Selene, in a Software-as-a-Service platform for behavioral analysis using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) integrating domain-specific knowledge and enforcing adherence to organizational rules to improve response quality. Selene is designed to provide deep analyses and practical recommendations that help users optimize organizational behavioral development. To ensure that the RAG pipeline had updated information, we implemented an Extract, Transform, and Load process that updated the knowledge base of the pipeline daily and applied prompt engineering to ensure compliance with organizational rules and directives, using GPT-4 as the underlying language model of the chatbot, which was the state-of-the-art model at the time of deployment. We followed the Generative AI Project Life Cycle Frameworkas the basic methodology to develop this system. To evaluate Selene, we used the DeepEval library, showing that it provides appropriate responses and aligning with organizational rules. Our results show that the system achieves high answer relevancy in 78% of the test cases achieved and a complete absence of bias and toxicity issues. This work provides practical insights for organizations deploying similar knowledge-based chatbot systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Automating Lexical Graph Construction with Large Language Models: A Scalable Approach to Japanese Multi-Relation Lexical Networks
by
Benedikt Perak and Dragana Špica
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040024 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
In recent advancements within natural language processing (NLP), lexical networks play a crucial role in representing semantic relationships between words, enhancing applications from word sense disambiguation to educational tools. Traditional methods for constructing lexical networks, however, are resource-intensive, relying heavily on expert lexicographers.
[...] Read more.
In recent advancements within natural language processing (NLP), lexical networks play a crucial role in representing semantic relationships between words, enhancing applications from word sense disambiguation to educational tools. Traditional methods for constructing lexical networks, however, are resource-intensive, relying heavily on expert lexicographers. Leveraging GPT-4o, a large language model (LLM), our study presents an automated, scalable approach to creating multi-relational Japanese lexical networks for the general Japanese language. This study builds on previous methods of integrating synonyms but extends to other relations such as hyponymy, hypernymy, meronymy, and holonomy. Using a combination of structured prompts and graph-based data storage, the model extracts detailed lexical relationships, which are then systematically validated and encoded. Results reveal a substantial expansion in network size, with over 155,000 nodes and 700,000 edges, enriching Japanese lexical associations with nuanced hierarchical and associative layers. Comparisons with WordNet show substantial alignment in relation types, particularly with soft matching, underscoring the model’s efficacy in reflecting the multifaceted nature of lexical semantics. This work contributes a versatile framework for constructing expansive lexical resources that hold promises for enhancing NLP tasks and educational applications across various languages and domains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Navigating Emotional Barriers and Cognitive Drivers in Mobile Learning Adoption Among Greek University Students
by
Stefanos Balaskas, Vassilios Tsiantos, Sevaste Chatzifotiou, Dionysia Filiopoulou, Kyriakos Komis and George Androulakis
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040023 - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
Mobile learning (m-learning) technologies are gaining popularity in universities but not uniformly across institutions because of cognitive, affective, and behavior obstacles. This research tested and applied an expansion of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) with technostress (TECH) and resistance to change (RTC) as
[...] Read more.
Mobile learning (m-learning) technologies are gaining popularity in universities but not uniformly across institutions because of cognitive, affective, and behavior obstacles. This research tested and applied an expansion of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) with technostress (TECH) and resistance to change (RTC) as affective obstacles, as well as the core predictors of perceived usefulness (PU), perceived ease of use (PE), and perceived risk (PR). By employing a cross-sectional survey of Greek university students (N = 608) and partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM), we tested direct and indirect impacts on behavioral intention (BI) to apply m-learning applications. The results affirm that PU and PE are direct predictors of BI, while PR has no direct impact on BI but acts indirectly through TECH and RTC. Mediation is partial in terms of PE and PU and indirect-only (complete) in terms of PR with respect to the impact of affective states on adoption. Multi-group comparisons found differences in terms of gender, age, confidence, and years of use but not frequency of use, implying that psychological and experiential characteristics have a greater impact on intention than habitual patterns. These results offer theory-driven and segment-specific guidelines for psychologically aware, user-focused m-learning adoption in higher education.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The New Normal and the Era of Misknowledge—Understanding Generative AI and Its Impacts on Knowledge Work
by
Zhiguo Yang, Xiang Guo and Peng Zhang
Knowledge 2025, 5(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5040022 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The revealed capability of generative AI tools can significantly transform the way knowledge work is conducted. With more tools being built and implemented, generative AI-aided knowledge work starts to emerge as a new normal, where knowledge workers shift a significant portion of their
[...] Read more.
The revealed capability of generative AI tools can significantly transform the way knowledge work is conducted. With more tools being built and implemented, generative AI-aided knowledge work starts to emerge as a new normal, where knowledge workers shift a significant portion of their workloads to the tools. This new normal can lead to many concerns and issues including workers’ mental health, employees’ confusion in production, and potential spreading misknowledge. Considering the substantial portion of knowledge work in the US economy, this paper calls for more research to be conducted on this important area. This paper synthesizes relevant economic and behavioral research findings in the AI automation field and opinions of field experts, and presents a comprehensive framework, “generative AI-aided knowledge work”. This framework theoretically addresses concerns such as job replacement and organizational and behavioral factors in using generative AI and provides directions for future research and guidelines for practitioners in incorporating generative AI tools. This is one of the early attempts to provide a comprehensive overview of generative AI’s impacts on knowledge workers and production. It has the potential to seed future research in many areas such as countering misknowledge and employees’ mental health.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Ethical Challenges in AI for Emergency Management
by
Xiaojun (Jenny) Yuan, Qingyue Guo, Yvonne Appiah Dadson, Mahsa Goodarzi, Jeesoo Jung, Yanjun Dong, Nisa Albert, DeeDee Bennett Gayle, Prabin Sharma, Oyeronke Toyin Ogunbayo and Jahnavi Cherukuru
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030021 - 21 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are increasingly integrated into emergency management, ethical considerations demand greater attention. Essential components of comprehensive emergency management include mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery, which should serve as the foundation for integrating AI-driven science and technologies to effectively safeguard
[...] Read more.
As artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are increasingly integrated into emergency management, ethical considerations demand greater attention. Essential components of comprehensive emergency management include mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery, which should serve as the foundation for integrating AI-driven science and technologies to effectively safeguard populations and infrastructure in times of crisis. This paper reviewed the ethical challenges of AI in emergency management in terms of critical issues, best practices, applications, emerging ethical considerations, and strategies addressing ethical challenges. Three core ethical themes are identified: algorithmic bias; privacy, transparency and accountability; and human–AI collaboration. This paper thoroughly analyzed the associated ethical challenges, reviewed the theoretical frameworks and proposed strategies to mitigate ethical challenges by strengthening the audits of algorithms, enhancing transparency in AI decision-making, and incorporating stakeholder engagement. Finally, the importance of creating policies to govern AI ethics was discussed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEssay
Generative Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Public Knowledge
by
Dirk H. R. Spennemann
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030020 - 17 Sep 2025
Abstract
Generative artificial intelligence (AI), in particular large language models such as ChatGPT, have reached public consciousness with a wide-ranging discussion of their capabilities and suitability for use in various professions. Following the printing press and the internet, generative AI language models are the
[...] Read more.
Generative artificial intelligence (AI), in particular large language models such as ChatGPT, have reached public consciousness with a wide-ranging discussion of their capabilities and suitability for use in various professions. Following the printing press and the internet, generative AI language models are the third transformative technological invention, with truly cross-sectoral impact on knowledge transmission and knowledge generation. While the printing press allowed for the transmission of knowledge that is independent of the physical presence of the knowledge holder, with publishers emerging as gatekeepers, the internet added levels of democratization, allowing anyone to publish, along with global immediacy. The development of social media resulted in an increased fragmentation and tribalization in online communities regarding their ways of knowing, resulting in the propagation of alternative truths that resonate in echo chambers. It is against this background that generative AI language models have entered public consciousness. Using the strategic foresight methodology, this paper will examine the proposition that the age of generative AI will emerge as an age of public ignorance.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
A Mathematical Model on Brain’s Ability of Learning
by
Eleftherios Protopapas
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030019 - 17 Sep 2025
Abstract
The human brain is one of the most complex parts of the human body. Its function has been studied extensively in biology and medicine. Along this line, applied mathematics plays a crucial role through the formulation and analysis of mathematical models. A student’s
[...] Read more.
The human brain is one of the most complex parts of the human body. Its function has been studied extensively in biology and medicine. Along this line, applied mathematics plays a crucial role through the formulation and analysis of mathematical models. A student’s ability to learn is an important aspect of these studies. In this paper, a theoretical mathematical model is presented to study the brain’s ability to learn, with parameters such as human intelligence, the expected amount of knowledge a student seeks to acquire, and the tendency to forget. A parametric study of the obtained model is conducted, and by taking into account actual data from the literature, the values of the parameters that fit these data are derived, demonstrating the validity of the model. The findings of this study indicate that the proposed model accurately embodies the core principles of mastery learning and offers a practical framework that educators can employ to improve instructional planning, thereby optimizing students’ readiness for examinations scheduled on fixed dates.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures
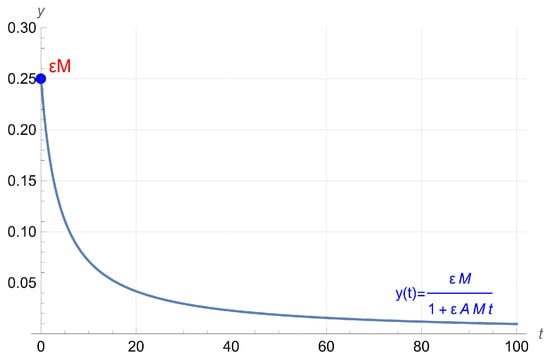
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Generative AI as a Sociotechnical Challenge: Inclusive Teaching Strategies at a Hispanic-Serving Institution
by
Víctor D. Carmona-Galindo, Hou Ung, Manhao Zeng, Christine Broussard, Elizaveta Taranenko, Yousef Daneshbod, David Chappell and Todd Lorenz
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030018 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is reshaping science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education by offering new strategies to address persistent challenges in equity, access, and instructional capacity—particularly within Hispanic-Serving Institutions (HSIs). This review documents a faculty-led, interdisciplinary initiative at the University of La
[...] Read more.
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is reshaping science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education by offering new strategies to address persistent challenges in equity, access, and instructional capacity—particularly within Hispanic-Serving Institutions (HSIs). This review documents a faculty-led, interdisciplinary initiative at the University of La Verne (ULV), an HSI in Southern California, to explore GenAI’s integration across biology, chemistry, mathematics, and physics. Adopting an exploratory qualitative design, this study synthesizes faculty-authored vignettes with peer-reviewed literature to examine how GenAI is being piloted as a scaffold for inclusive pedagogy. Across disciplines, faculty-reported benefits such as simplifying complex content, enhancing multilingual comprehension, and expanding access to early-stage research and technical writing. At the same time, limitations—including factual inaccuracies, algorithmic bias, and student over-reliance—underscore the importance of embedding critical AI literacy and ethical reflection into instruction. The findings highlight equity-driven strategies that position GenAI as a complement, not a substitute, for disciplinary expertise and culturally responsive pedagogy. By documenting diverse, practice-based applications, this review provides a flexible framework for integrating GenAI ethically and inclusively into undergraduate STEM instruction. The insights extend beyond HSIs, offering actionable pathways for other minority-serving and resource-constrained institutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Gen2Gen: Efficiently Training Artificial Neural Networks Using a Series of Genetic Algorithms
by
Ioannis G. Tsoulos and Vasileios Charilogis
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030017 - 22 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Artificial neural networks have been used in a multitude of applications in various research areas in recent decades, providing excellent results in both data classification and data fitting. Their success is based on the effective identification (training) of their parameters using optimization techniques,
[...] Read more.
Artificial neural networks have been used in a multitude of applications in various research areas in recent decades, providing excellent results in both data classification and data fitting. Their success is based on the effective identification (training) of their parameters using optimization techniques, and hence a series of programming methods have been developed for training these models. However, many times these techniques either can identity only some local minima of the error function with poor overall results or present overfitting problems in which the performance of the artificial neural network is significantly reduced when it is applied to different data from the training set. This manuscript introduces a method for the efficient training of artificial neural networks, where a series of genetic algorithms is applied to the network parameters in several stages. In the first stage, an initial identification of the network value interval is performed; in the second stage, the initial estimate of the value interval is improved; and in the third stage, the final adjustment of the network parameters within the previously identified value interval takes place. The new method was tested on some classification and regression problems found in the relevant literature, and the experimental results were compared against the results obtained by the application of other well-known methods used for neural network training.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
FEA-Assisted Test Bench to Enhance the Comprehension of Vibration Monitoring in Electrical Machines—A Practical Experiential Learning Case Study
by
Jose E. Ruiz-Sarrio, Carlos Madariaga-Cifuentes and Jose A. Antonino-Daviu
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030016 - 12 Aug 2025
Abstract
Rotating electrical machine maintenance is a core component of engineering education curricula worldwide. Within this context, vibration monitoring represents a widespread methodology for electrical rotating machinery monitoring. However, the multi-physical nature of vibration monitoring presents a complex learning scenario, including concepts from both
[...] Read more.
Rotating electrical machine maintenance is a core component of engineering education curricula worldwide. Within this context, vibration monitoring represents a widespread methodology for electrical rotating machinery monitoring. However, the multi-physical nature of vibration monitoring presents a complex learning scenario, including concepts from both mechanical and electrical engineering domains. This article proposes a novel knowledge-based educational experience design leveraging an integrated FEA-assisted test bench aimed at comprehensively addressing the electromechanical link between stator current and frame vibration. To this aim, a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) model is utilized to link excitation electrical signals with airgap radial forces acting in the stator. The subsequent correlation of these FEA predictions with measured frame vibrations on a physical test bench provides students with the theoretical concepts and practical tools to adequately comprehend this complex multi-physical phenomenon of wide application in real industrial scenarios. The pedagogical potential of the method also includes the development of critical thinking and problem-solving soft skills, and foundational understanding for digital twin concepts. A Delphi-style expert survey conducted with 25 specialists yielded strong support for the pedagogical robustness and relevance of the method, with mean ratings between 4.32 and 4.64 out of 5 across key dimensions. These results confirm the potential to enhance deep understanding and practical skills in vibration-based electrical machine diagnosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Structural Causal Model Ontology Approach for Knowledge Discovery in Educational Admission Databases
by
Bern Igoche Igoche, Olumuyiwa Matthew and Daniel Olabanji
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030015 - 4 Aug 2025
Abstract
Educational admission systems, particularly in developing countries, often suffer from opaque decision processes, unstructured data, and limited analytic insight. This study proposes a novel methodology that integrates structural causal models (SCMs), ontological modeling, and machine learning to uncover and apply interpretable knowledge from
[...] Read more.
Educational admission systems, particularly in developing countries, often suffer from opaque decision processes, unstructured data, and limited analytic insight. This study proposes a novel methodology that integrates structural causal models (SCMs), ontological modeling, and machine learning to uncover and apply interpretable knowledge from an admission database. Using a dataset of 12,043 records from Benue State Polytechnic, Nigeria, we demonstrate this approach as a proof of concept by constructing a domain-specific SCM ontology, validate it using conditional independence testing (CIT), and extract features for predictive modeling. Five classifiers, Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), and Support Vector Machine (SVM) were evaluated using stratified 10-fold cross-validation. SVM and KNN achieved the highest classification accuracy (92%), with precision and recall scores exceeding 95% and 100%, respectively. Feature importance analysis revealed ‘mode of entry’ and ‘current qualification’ as key causal factors influencing admission decisions. This framework provides a reproducible pipeline that combines semantic representation and empirical validation, offering actionable insights for institutional decision-makers. Comparative benchmarking, ethical considerations, and model calibration are integrated to enhance methodological transparency. Limitations, including reliance on single-institution data, are acknowledged, and directions for generalizability and explainable AI are proposed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Artificial Intelligence in Curriculum Design: A Data-Driven Approach to Higher Education Innovation
by
Thai Son Chu and Mahfuz Ashraf
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030014 - 29 Jul 2025
Cited by 3
Abstract
This paper shows that artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming college curricula by enabling data-driven personalization, which enhances student outcomes and better aligns educational programs with evolving workforce demands. Specifically, predictive analytics, machine learning algorithms, and natural language processing were applied here, grounded in
[...] Read more.
This paper shows that artificial intelligence is fundamentally transforming college curricula by enabling data-driven personalization, which enhances student outcomes and better aligns educational programs with evolving workforce demands. Specifically, predictive analytics, machine learning algorithms, and natural language processing were applied here, grounded in constructivist learning theory and Human–Computer Interaction principles, to evaluate student performance and identify at-risk students to propose personalized learning pathways. Results indicated that the AI-based curriculum achieved much higher course completion rates (89.72%) as well as retention (91.44%) and dropout rates (4.98%) compared to the traditional model. Sentiment analysis of learner feedback showed a more positive learning experience, while regression and ANOVA analyses proved the impact of AI on enhancing academic performance to be real. Therefore, the learning content delivery for each student was continuously improved based on individual learner characteristics and industry trends by AI-enabled recommender systems and adaptive learning models. Its advantages notwithstanding, the study emphasizes the need to address ethical concerns, ensure data privacy safeguards, and mitigate algorithmic bias before an equitable outcome can be claimed. These findings can inform institutions aspiring to adopt AI-driven models for curriculum innovation to build a more dynamic, responsive, and learner-centered educational ecosystem.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Competency Mapping as a Knowledge Driver in Modern Organisations
by
Farshad Badie and Anna Rostomyan
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030013 - 11 Jul 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper explores the concept of ‘competency’ in modern organisations. It emphasises the strategic importance of aligning organisational values, strategic goals, and employee competencies. It introduces competency mapping as a framework for ensuring such an alignment, as well as for developing a culture
[...] Read more.
This paper explores the concept of ‘competency’ in modern organisations. It emphasises the strategic importance of aligning organisational values, strategic goals, and employee competencies. It introduces competency mapping as a framework for ensuring such an alignment, as well as for developing a culture of continuous learning and development, where the emotions and feelings of the interactants are also taken into account based on intrapersonal and interpersonal aspects of human behaviour. The article also elucidates the interconnection among diverse human ‘intelligences’ that are of paramount importance in shaping human knowledge and guiding us in navigating through life more smoothly and efficiently. Thus, through an interdisciplinary scope, we have attempted to analyse the intrinsic value of competency mapping as a knowledge driver in modern organisational and educational settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transformative Potential of Digital Manufacturing Laboratories: Insights from Mexico and Spain
by
Carmen Bueno Castellanos and Álvaro Fernández-Baldor
Knowledge 2025, 5(3), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5030012 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This article presents a comparative analysis of digital manufacturing laboratories (DMLs) in Mexico and Spain. It is argued that DMLs, also known as makerspaces or FabLabs, play a key role in innovation and experimentation, but that their success depends on the relationships they
[...] Read more.
This article presents a comparative analysis of digital manufacturing laboratories (DMLs) in Mexico and Spain. It is argued that DMLs, also known as makerspaces or FabLabs, play a key role in innovation and experimentation, but that their success depends on the relationships they establish with social actors, such as local governments, universities, and firms. Key concepts of the transformative innovation approach such as “protective space” and “embeddedness” are introduced, which allow us to understand how DMLs operate within a complex system. The comparative analysis of a DML in Mexico City (Mexico) and a DML in Valencia (Spain) allows us to identify similarities and differences in their operational contexts. While the Mexican DML faces a lack of government support and dependence on the private sector, the Spanish one benefits from strong institutional support and public policies that facilitate its development. This results in greater stability and capacity for action for the Valencian FabLab VLC compared to the Mexican FabLab Finally, we reflect on how the embeddedness received from different social actors affects the autonomy and transformative capacity of DMLs, suggesting that while both labs have the potential to innovate, their contexts and relationships determine their effectiveness and sustainability in the digital sociotechnical system.
Full article
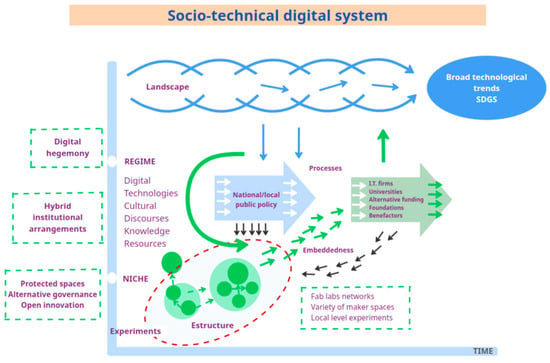
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Ayatutu as a Framework for Mathematics Education: Integrating Indigenous Philosophy with Cooperative Learning Approaches
by
Terungwa James Age
Knowledge 2025, 5(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5020011 - 9 Jun 2025
Abstract
This article explores the integration of “Ayatutu”, a communal philosophy from Nigeria’s Tiv people, into mathematics education frameworks. Ayatutu—embodying collective responsibility and mutual assistance—aligns with contemporary cooperative learning approaches while offering unique cultural dimensions. Through analysis of the ethnomathematics literature, indigenous knowledge systems,
[...] Read more.
This article explores the integration of “Ayatutu”, a communal philosophy from Nigeria’s Tiv people, into mathematics education frameworks. Ayatutu—embodying collective responsibility and mutual assistance—aligns with contemporary cooperative learning approaches while offering unique cultural dimensions. Through analysis of the ethnomathematics literature, indigenous knowledge systems, and cooperative learning theories this article develops a theoretical framework for Ayatutu-based mathematics instruction built on the following five core elements: collective problem-solving, resource sharing, complementary expertise, process orientation, and intergenerational knowledge transfer. The framework demonstrates significant alignment with sociocultural learning theory, communities of practice, and critical pedagogy while also offering potential benefits including enhanced mathematical engagement, positive identity development, stronger learning communities, and cultural sustainability. Implementation challenges involving teacher preparation, structural constraints, cultural translation, and balancing individual with collective learning are examined. This research contributes to decolonizing mathematics education by positioning indigenous philosophical systems as valuable resources for creating culturally responsive and mathematically powerful learning environments that serve diverse student populations while honoring cultural wisdom.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Interpretable Ensemble Learning Approach for Predicting Student Adaptability in Online Education Environments
by
Shakib Sadat Shanto and Akinul Islam Jony
Knowledge 2025, 5(2), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5020010 - 3 Jun 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards online education, making it a critical focus for educational institutions. Understanding students’ adaptability to this new learning environment is crucial for ensuring their academic success. This study aims to predict students’ adaptability levels in online
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the shift towards online education, making it a critical focus for educational institutions. Understanding students’ adaptability to this new learning environment is crucial for ensuring their academic success. This study aims to predict students’ adaptability levels in online education using a dataset of 1205 observations that incorporates sociodemographic factors and information collected across different educational levels (school, college, and university). Various machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) models, including decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), K-nearest neighbors (KNN), XGBoost, and artificial neural networks (ANNs), are applied for adaptability prediction. The proposed ensemble model achieves superior performance with 95.73% accuracy, significantly outperforming traditional ML and DL models. Furthermore, explainable AI (XAI) techniques, such as LIME and SHAP, were employed to uncover the specific features that significantly impact the adaptability level predictions, with financial condition, class duration, and network type emerging as key factors. By combining robust predictive modeling and interpretable AI, this study contributes to the ongoing efforts to enhance the effectiveness of online education and foster student success in the digital age.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures
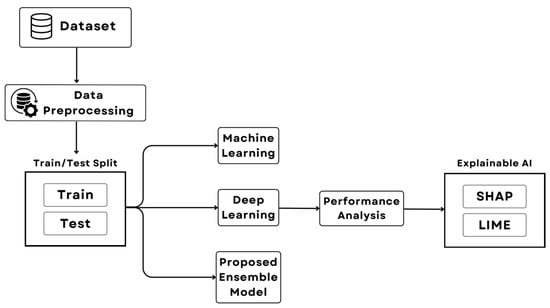
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CORE: Cultivation of Collaboration Skills via Educational Robotics
by
Emmanouil A. Demetroulis, Ilias Papadogiannis, Manolis Wallace, Vassilis Poulopoulos and Angeliki Antoniou
Knowledge 2025, 5(2), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/knowledge5020009 - 6 May 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Collaboration skills are an important component of 21st century skills and a critical skill for citizens of the future. In this work, we propose collaboration-oriented robotics education (CORE), a methodology aimed at fostering the development of collaboration skills in primary school students aged
[...] Read more.
Collaboration skills are an important component of 21st century skills and a critical skill for citizens of the future. In this work, we propose collaboration-oriented robotics education (CORE), a methodology aimed at fostering the development of collaboration skills in primary school students aged 11–12 via an adjusted approach to the teaching of educational robotics. In order to assess the existence and level of collaboration skills in a student, a suitable tool is also proposed. Using a collaboration-oriented performance evaluation test (COPE) for both a pre- and post-intervention measurement and applying both the conventional and CORE approaches to teaching educational robotics to 32 students, split into control and intervention groups, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Specifically, the experimental implementation shows that CORE statistically significantly increases the performance of the experimental group compared to the conventional way of teaching educational robotics. These results, in addition to validating CORE itself, demonstrate that the conventional approach to STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, Mathematics) education is not necessarily already optimized, thus facilitating an overall re-evaluation of the field.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Knowledge Management in Learning and Education)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Education Sciences, Knowledge, Sustainability, Social Sciences, World
Formal and Non-Formal Learning Contexts: Interdisciplinary Perspectives in Educational Sciences
Topic Editors: Davide Di Palma, Domenico Tafuri, Antonio AscioneDeadline: 31 May 2027

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Knowledge
Knowledge Management in Learning and Education
Guest Editors: Dan-Alexandru Szabo, Carmen Pârvu, George MocanuDeadline: 5 February 2026






