- Article
Research on Characterization and Detection Methods of Photovoltaic Cell Thermal Defects Based on Temperature Derivatives
- Zhizhen Du,
- Kai Liu and
- Guangning Wu
- + 2 authors
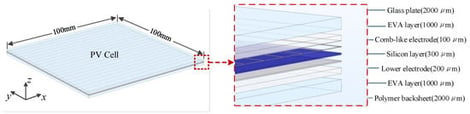
Photovoltaic (PV) cells play an important role in the development of green energy. However, in practical photovoltaic systems, shunting-related defects and hotspot phenomena may originate not only from manufacturing imperfections, but also from mechanical stress and environmental factors during transportation, installation, and long-term field operation. Such hotspots not only reduce the power-generation efficiency and service life of PV cells but may also pose safety risks to grid-connected photovoltaic power stations. To address this problem, a squared even-order derivative (SEOD) method based on surface temperature analysis is introduced to enable the quantitative detection of thermal defects in PV cells. In this study, typical faults in PV cells, including low-resistance defects and silicon-based deep scratches, are analyzed. A simulation model is established to correlate typical faults with their equivalent volumetric heat sources, followed by experimental validation for low-resistance defects. Based on this framework, the SEOD algorithm is developed and applied to achieve high-precision localization and quantitative characterization of thermal defects in both simulation models and experimental samples.
4 February 2026