- Article
Land Cover and Land Use Controls on Landslide Morphometry and Occurrence in a Heterogeneous Mountain Watershed
- Gumbert Maylda Pratama,
- Takashi Gomi and
- Wahyu Wilopo
- + 3 authors
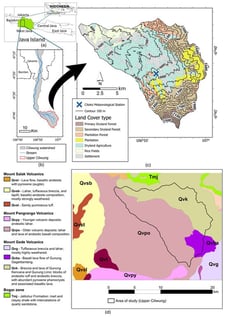
Tropical mountain watersheds contain heterogeneous land cover and land use (LCLU) mosaics, yet the relationship between these mosaics and landslide morphometry and occurrence at the watershed scale remains unclear. We compiled landslide inventory from 2002 to 2023 for the 152.3 km2 Upper Ciliwung Watershed, West Java, Indonesia. We mapped morphometry for a subset of 84 landslides, classified the events into seven LCLU classes, and compared landslide size–frequency distributions across vegetation groups. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed that LCLU type influences landslide size and mobility. Forested terrain produced narrower, longer-runout landslides on steeper slopes, whereas agricultural and other herbaceous-dominated terrain generated wider landslides on gentler slopes. Clarifying landslides by vegetation characteristics as either tree- or herbaceous-dominated areas (including urban areas) revealed distinct size–frequency patterns, especially for small landslides (tree-dominated: 133 m2, herbaceous-dominated and other: 97 m2; overall 112 m2), which are consistent with the contrasting vegetation structures and hydrological responses. PCA supported these patterns, with PC1 describing a morphometric axis and PC2 capturing gradients in event rainfall and antecedent wetness. Together, these results support the conclusion that vegetation structure and land-use conditions influence slope stability by affecting soil reinforcement and hydrological responses. This provides a foundation for land–use–specific geohazard mitigation and vegetation-based slope stability planning.
1 March 2026



![Map of the study area (purple dashed-line polygon) showing: earthquakes with magnitudes greater than M 6.0; seismic monitoring networks of southern California [16] and northwestern Mexico [17]; active faults from the GEM catalog [18]; regional geology [19]. The inset shows the study area, located in the interaction zone between the North American and Pacific tectonic plates, within the San Andreas–Gulf of California fault system.](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/geohazards/geohazards-07-00027/article_deploy/html/images/geohazards-07-00027-g001-550.jpg)