Journal Description
Computation
Computation
is a peer-reviewed journal of computational science and engineering published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), CAPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, dblp, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Mathematics, Interdisciplinary Applications) / CiteScore - Q1 (Applied Mathematics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Mathematics and Its Applications: AppliedMath, Axioms, Computation, Fractal and Fractional, Geometry, International Journal of Topology, Logics, Mathematics and Symmetry.
Impact Factor:
1.9 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.9 (2024)
Latest Articles
Enhanced Chimp Algorithm and Its Application in Optimizing Real-World Data and Engineering Design Problems
Computation 2026, 14(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation14010001 (registering DOI) - 20 Dec 2025
Abstract
This work proposes an Enhanced Chimp Optimization Algorithm (EChOA) for solving continuous and constrained data science and engineering optimization problems. The EChOA integrates a self-adaptive DE/current-to-pbest/1 (with jDE-style parameter control) variation stage with the canonical four-leader ChOA guidance and augments the search with
[...] Read more.
This work proposes an Enhanced Chimp Optimization Algorithm (EChOA) for solving continuous and constrained data science and engineering optimization problems. The EChOA integrates a self-adaptive DE/current-to-pbest/1 (with jDE-style parameter control) variation stage with the canonical four-leader ChOA guidance and augments the search with three lightweight modules: (i) L’evy flight refinement around the incumbent best, (ii) periodic elite opposition-based learning, and (iii) stagnation-aware partial restarts. The EChOA is compared with more than 35 optimizers on the CEC2022 single-objective suite (12 functions). The results shows that the EChOA attains state-of-the-art results at both
Open AccessArticle
A Generalizable Agentic AI Pipeline for Developing Chatbots Using Small Language Models: A Case Study on Thai Student Loan Fund Services
by
Jakkaphong Inpun, Watcharaporn Cholamjiak, Piyada Phrueksawatnon and Kanokwatt Shiangjen
Computation 2025, 13(12), 297; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120297 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
The rising deployment of artificial intelligence in public services is constrained by computational costs and limited domain-specific data, particularly in multilingual contexts. This study proposes a generalizable Agentic AI pipeline for developing question–answer chatbot systems using small language models (SLMs), demonstrated through a
[...] Read more.
The rising deployment of artificial intelligence in public services is constrained by computational costs and limited domain-specific data, particularly in multilingual contexts. This study proposes a generalizable Agentic AI pipeline for developing question–answer chatbot systems using small language models (SLMs), demonstrated through a case study on the Thai Student Loan Fund (TSLF). The pipeline integrates four stages: OCR-based document digitization using Typhoon2-3B, agentic question–answer dataset construction via a clean–check–plan–generate (CCPG) workflow, parameter-efficient fine-tuning with QLoRA on Typhoon2-1B and Typhoon2-3B models, and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for source-grounded responses. Evaluation using BERTScore and CondBERT confirmed high semantic consistency (FBERT = 0.9807) and stylistic reliability (FBERT = 0.9839) of the generated QA corpus. Fine-tuning improved the 1B model’s domain alignment (FBERT: 0.8593 → 0.8641), while RAG integration further enhanced factual grounding (FBERT = 0.8707) and citation transparency. Cross-validation with GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5 Pro demonstrated dataset transferability and reliability. The results establish that Agentic AI combined with SLMs offers a cost-effective, interpretable, and scalable framework for automating bilingual advisory services in resource-constrained government and educational institutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Generative AI in Action: Trends, Applications, and Implications)
Open AccessArticle
Ship Model Identification Using Interpretable 4-DOF Maneuverability Models for River Combat Boat
by
Juan Contreras Montes, Aldo Lovo Ayala, Daniela Ospino-Balcázar, Kevin Velasquez Gutierrez, Carlos Soto Montaño, Roosvel Soto-Diaz, Javier Jiménez-Cabas, José Oñate López and José Escorcia-Gutierrez
Computation 2025, 13(12), 296; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120296 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Ship maneuverability models are typically defined by three degrees of freedom: surge, sway, and yaw. However, patrol vessels operating in riverine environments often exhibit significant roll motion during course changes, necessitating the inclusion of this dynamic. This study develops interpretable machine learning models
[...] Read more.
Ship maneuverability models are typically defined by three degrees of freedom: surge, sway, and yaw. However, patrol vessels operating in riverine environments often exhibit significant roll motion during course changes, necessitating the inclusion of this dynamic. This study develops interpretable machine learning models capable of predicting vessel behavior in four degrees of freedom (4-DoF): surge, sway, yaw, and roll. A dataset of 125 h of simulated maneuvers was employed, including 29 h of out-of-distribution (OOD) conditions to test model generalization. Four models were implemented and compared over a 15-step prediction horizon: linear regression, third-order polynomial regression, a state-space model obtained via the N4SID algorithm, and an AutoRegressive model with eXogenous inputs (ARX). Results demonstrate that all models captured the essential vessel dynamics, with the state-space model achieving the best overall performance (e.g., NMSE = 0.0246 for surge velocity on test data and 0.0499 under OOD conditions). Variable-wise, surge and sway showed the lowest errors, roll rate remained stable, and yaw rate was the most sensitive to distribution shifts. Model-wise, the ARX model achieved the lowest NMSE for surge prediction (0.0149), while regression-based models provided interpretable yet less accurate alternatives. Multi-horizon evaluation (1-, 5-, 15-, and 30-step) under OOD conditions confirmed a consistent monotonic degradation across models. These findings validate the feasibility of using interpretable machine learning models for predictive control, autonomous navigation, and combat scenario simulation in riverine operations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
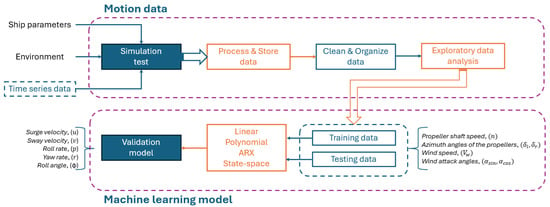
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Shared Nodes of Overlapping Communities in Complex Networks
by
Vesa Kuikka, Kosti Koistinen and Kimmo K. Kaski
Computation 2025, 13(12), 295; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120295 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
Overlapping communities are key characteristics of the structure and function analysis of complex networks. Shared or overlapping nodes within overlapping communities can either form subcommunities or act as intersections between larger communities. Nodes at the intersections that do not form subcommunities can be
[...] Read more.
Overlapping communities are key characteristics of the structure and function analysis of complex networks. Shared or overlapping nodes within overlapping communities can either form subcommunities or act as intersections between larger communities. Nodes at the intersections that do not form subcommunities can be identified as overlapping nodes or as part of an internal structure of nested communities. To identify overlapping nodes, we apply a threshold rule based on the number of nodes in the nested structure. As the threshold value increases, the number of selected overlapping nodes decreases. This approach allows us to analyse the roles of nodes considered overlapping according to selection criteria, for example, to reduce the effect of noise. We illustrate our method by using three small and two larger real-world network structures. In larger networks, minor disturbances can produce a multitude of slightly different solutions, but the core communities remain robust, allowing other variations to be treated as noise. While this study employs our own method for community detection, other approaches can also be applied. Exploring the properties of shared nodes in overlapping communities of complex networks is a novel area of research with diverse applications in social network analysis, cybersecurity, and other fields in network science.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computational Social Science and Complex Systems—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Fast Distributed Algorithm for Uniform Price Auction with Bidding Information Protection
by
John Sum, Chi-Sing Leung and Janet C. C. Chang
Computation 2025, 13(12), 294; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120294 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
In this paper, a fast distributed algorithm is proposed for solving the winners and price determination problems in a uniform price auction in which each bidder bids for multiple units out of a lot of k identical items with a per-unit price. In
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a fast distributed algorithm is proposed for solving the winners and price determination problems in a uniform price auction in which each bidder bids for multiple units out of a lot of k identical items with a per-unit price. In a conventional setting, all bidders disclose their bidding information to an auctioneer and let the auctioneer allocate the items and determine the uniform price, i.e., the least winning price. In our setting, all bidders do not need to disclose their bidding information to the auctioneer. The bidders and the auctioneer collaboratively compute by the distributed algorithm to determine in a small number of steps the units allocated and the uniform price. The number of steps is independent of the number of bidders. At the end of the computing process, each bidder can only know the units allocated to him/her and the uniform price. The auctioneer can only know the units being allocated to the bidders and the uniform price. Therefore, neither the bidders nor the auctioneer are able to know the per-unit bidding prices of the bidders except the uniform price. Moreover, the auctioneer is not able to know the bidding units of the losing bidders. Bidders’ per-unit bidding prices are protected, and the bidding units of the losing bidders are protected. Bidding information privacy is preserved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Social Science)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
DPCA-GCN: Dual-Path Cross-Attention Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition
by
Khadija Lasri, Khalid El Fazazy, Adnane Mohamed Mahraz, Hamid Tairi and Jamal Riffi
Computation 2025, 13(12), 293; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120293 - 15 Dec 2025
Abstract
Skeleton-based action recognition has achieved remarkable advances with graph convolutional networks (GCNs). However, most existing models process spatial and temporal information within a single coupled stream, which often obscures the distinct patterns of joint configuration and motion dynamics. This paper introduces the Dual-Path
[...] Read more.
Skeleton-based action recognition has achieved remarkable advances with graph convolutional networks (GCNs). However, most existing models process spatial and temporal information within a single coupled stream, which often obscures the distinct patterns of joint configuration and motion dynamics. This paper introduces the Dual-Path Cross-Attention Graph Convolutional Network (DPCA-GCN), an architecture that explicitly separates spatial and temporal modeling into two specialized pathways while maintaining rich bidirectional interaction between them. The spatial branch integrates graph convolution and spatial transformers to capture intra-frame joint relationships, whereas the temporal branch combines temporal convolution and temporal transformers to model inter-frame dependencies. A bidirectional cross-attention mechanism facilitates explicit information exchange between both paths, and an adaptive gating module balances their respective contributions according to the action context. Unlike traditional approaches that process spatial–temporal information sequentially, our dual-path design enables specialized processing while maintaining cross-modal coherence through memory-efficient chunked attention mechanisms. Extensive experiments on the NTU RGB+D 60 and NTU RGB+D 120 datasets demonstrate that DPCA-GCN achieves competitive joint-only accuracies of 88.72%/94.31% and 82.85%/83.65%, respectively, with exceptional top-5 scores of 96.97%/99.14% and 95.59%/95.96%, while maintaining significantly lower computational complexity compared to multi-modal approaches.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
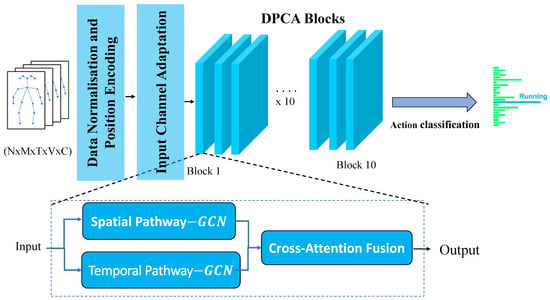
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
mDA: Evolutionary Machine Learning Algorithm for Feature Selection in Medical Domain
by
Ibrahim Aljarah, Abdullah Alzaqebah, Nailah Al-Madi, Ala’ M. Al-Zoubi and Amro Saleh
Computation 2025, 13(12), 292; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120292 - 13 Dec 2025
Abstract
The rapid expansion of medical data, characterized by its complex high-dimensional attributes, presents numerous promising opportunities and substantial challenges in healthcare analytics. Adopting effective feature selection techniques is essential to take advantage of the potential of such data. This research presents a modified
[...] Read more.
The rapid expansion of medical data, characterized by its complex high-dimensional attributes, presents numerous promising opportunities and substantial challenges in healthcare analytics. Adopting effective feature selection techniques is essential to take advantage of the potential of such data. This research presents a modified algorithm called (mDA), which is the hybrid algorithm between the Evolutionary Population Dynamics and the Dragonfly Algorithm. This method combines Evolutionary Population Dynamics’s strength with the Dragonfly Algorithm’s flexible capabilities, offering a robust evolutionary machine learning approach specifically designed for medical data analysis. By integrating the dynamic population modeling of Evolutionary Population Dynamics with the adaptive search techniques of Dragonfly Algorithm, the proposed mDA significantly improves accuracy, reduces the number of features, and obtains the minimum average of the fitness scores. Comparative experiments conducted on seven diverse medical datasets against other established algorithms confirm the superior performance of the proposed mDA, establishing it as a valuable approach in examining complex medical data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Intelligent Optimization Algorithm: Theory and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
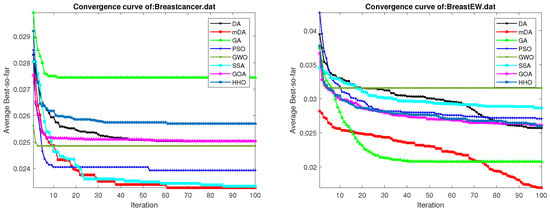
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Top-Down Optimization of a Multi-Physics TBS Model via Design-Change Propagation Network for Acoustic Levitation Devices
by
Yuchao Liu, Yi Gan, Fujia Sun and Yuping Long
Computation 2025, 13(12), 291; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120291 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
To address the challenges of interdependent design parameters and reliance on empirical trial-and-error in ultrasonic cell levitation culture devices, this study proposes a top-down design framework integrating multi-physics modeling with complex network analysis. First, acoustic field simulations optimize transducer arrangement and define the
[...] Read more.
To address the challenges of interdependent design parameters and reliance on empirical trial-and-error in ultrasonic cell levitation culture devices, this study proposes a top-down design framework integrating multi-physics modeling with complex network analysis. First, acoustic field simulations optimize transducer arrangement and define the cell manipulation field, establishing the Top-level Basic Structure (TBS). A skeleton model of the acoustofluidic coupled field is constructed based on the TBS. Core parameters are then determined by refining the TBS through multi-physics analysis. Second, a 24-node design change propagation network is constructed. Leveraging the TBS model coupled with multi-physics fields, a directed network model analyzes parameter interactions. The HITS algorithm is applied to prioritize the design sequence based on authority and hub scores, resolving parameter conflicts. Experimental validation demonstrates a device acoustic pressure of 1.3 × 104 Pa, stable cell levitation within the focused acoustic field, and a 40% reduction in design cycle time compared to traditional methods. This framework systematically sequences parameters, effectively determines the design order, enhances design efficiency, and significantly reduces dependence on empirical trial-and-error. It provides a novel approach for developing high-throughput organoid culture equipment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
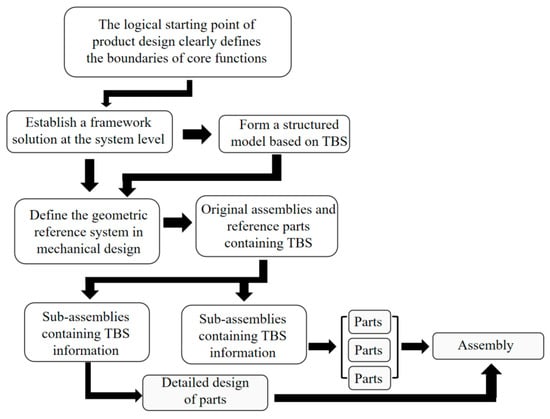
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Objective over Architecture: Fraud Detection Under Extreme Imbalance in Bank Account Opening
by
Wenxi Sun, Qiannan Shen, Yijun Gao, Qinkai Mao, Tongsong Qi and Shuo Xu
Computation 2025, 13(12), 290; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120290 - 9 Dec 2025
Abstract
Fraud in financial services—especially account opening fraud—poses major operational and reputational risks. Static rules struggle to adapt to evolving tactics, missing novel patterns and generating excessive false positives. Machine learning promises adaptive detection, but deployment faces severe class imbalance: in the NeurIPS 2022
[...] Read more.
Fraud in financial services—especially account opening fraud—poses major operational and reputational risks. Static rules struggle to adapt to evolving tactics, missing novel patterns and generating excessive false positives. Machine learning promises adaptive detection, but deployment faces severe class imbalance: in the NeurIPS 2022 BAF Base benchmark used here, fraud prevalence is 1.10%. Standard metrics (accuracy, f1_weighted) can look strong while doing little for the minority class. We compare Logistic Regression, SVM (RBF), Random Forest, LightGBM, and a GRU model on N = 1,000,000 accounts under a unified preprocessing pipeline. All models are trained to minimize their loss function, while configurations are selected on a stratified development set using validation-weighted F1-score f1_weighted. For the four classical models, class weighting in the loss (class_weight
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Machine Learning and Data Science Methods in Social Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Parametric Study of Shock/Boundary-Layer Interaction and Swirl Metrics in Bleed-Enabled External Compression Intakes
by
Muhammed Enes Ozcan and Nilay Sezer Uzol
Computation 2025, 13(12), 289; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120289 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
Flow quality at the engine face, especially total pressure recovery and swirl, is central to the performance and stability of external compression supersonic inlets. Steady-state RANS-based numerical computations are performed to quantify bleed/swirl trade-offs in a single-ramp intake. The CFD simulations were performed
[...] Read more.
Flow quality at the engine face, especially total pressure recovery and swirl, is central to the performance and stability of external compression supersonic inlets. Steady-state RANS-based numerical computations are performed to quantify bleed/swirl trade-offs in a single-ramp intake. The CFD simulations were performed first without a bleed system over M∞ = 1.4–1.9 to locate the practical onset of a bleed requirement. The deterioration in pressure recovery and swirl beyond M∞ ≈ 1.6, which is consistent with a pre-shock strength near the turbulent separation threshold, motivated the use of a bleed system. The comparisons with and without the bleed system were performed next at M∞ = 1.6, 1.8, and 1.9 across the operation map parameterized by the flow ratio. The CFD simulations were performed using ANSYS Fluent, with a pressure-based coupled solver with a realizable k-ε turbulence model and enhanced wall treatment. The results provide engine-face distortion metrics using a standardized ring to sector swirl ratio alongside pressure recovery. The results show that bleed removes low-momentum near-wall fluid and stabilizes the terminal–shock interaction, raising pressure recovery and lowering peak swirl and swirl intensity across the map, while extending the stable operating range to a lower flow ratio at a fixed M∞. The analysis delivers a design-oriented linkage between shock/boundary-layer interaction control and swirl: when bleed is applied at and above M∞ = 1.6, the separation footprints shrink and the organized swirl sectors weaken, yielding improved operability with modest bleed fractions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computational Heat and Mass Transfer (ICCHMT 2025))
►▼
Show Figures
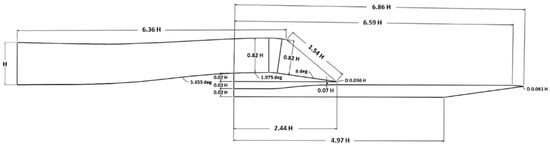
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Direct Cooling of Microsystems Using a Two-Phase Microfluidic Droplet
by
Wenpei Lu, Abdel Illah El Abed, Rachid Bennacer and Xiaoyan Ma
Computation 2025, 13(12), 288; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120288 - 6 Dec 2025
Abstract
Droplet-based microfluidics offers a promising approach for enhancing heat transfer in microchannels, which is critical for the thermal management of microsystems. This study presents a two-dimensional numerical investigation of flow and heat transfer characteristics of liquid–liquid two-phase droplet flow in a rectangular flow-focusing
[...] Read more.
Droplet-based microfluidics offers a promising approach for enhancing heat transfer in microchannels, which is critical for the thermal management of microsystems. This study presents a two-dimensional numerical investigation of flow and heat transfer characteristics of liquid–liquid two-phase droplet flow in a rectangular flow-focusing microchannel. The phase-field method was employed to capture the interface dynamics between the dispersed (water) and continuous (oil) phases. The effects of total velocity and droplet size on pressure drop and heat transfer performance are systematically analyzed. The results indicate that the heat transfer of two-phase droplet flow was significantly enhanced compared to single-phase oil flow, with its maximum heat transfer coefficient being approximately three times that of single-phase oil flow. The average heat transfer coefficient increases with total velocity and exhibits a non-monotonic dependence on droplet size. These findings provide valuable insights into the design and optimization of rectangular flow-focusing droplet-based microfluidic cooling systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Computational Heat and Mass Transfer (ICCHMT 2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Brain–Computer Interface for Control of a Virtual Prosthetic Hand
by
Ángel del Rosario Zárate-Ruiz, Manuel Arias-Montiel and Christian Eduardo Millán-Hernández
Computation 2025, 13(12), 287; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120287 - 6 Dec 2025
Abstract
Brain–computer interfaces (BCIs) have emerged as an option that allows better communication between humans and some technological devices. This article presents a BCI based on the steady-state visual evoked potentials (SSVEP) paradigm and low-cost hardware to control a virtual prototype of a robotic
[...] Read more.
Brain–computer interfaces (BCIs) have emerged as an option that allows better communication between humans and some technological devices. This article presents a BCI based on the steady-state visual evoked potentials (SSVEP) paradigm and low-cost hardware to control a virtual prototype of a robotic hand. A LED-based device is proposed as a visual stimulator, and the Open BCI Ultracortex Biosensing Headset is used to acquire the electroencephalographic (EEG) signals for the BCI. The processing and classification of the obtained signals are described. Classifiers based on artificial neural networks (ANNs) and support vector machines (SVMs) are compared, demonstrating that the classifiers based on SVM have superior performance to those based on ANN. The classified EEG signals are used to implement different movements in a virtual prosthetic hand using a co-simulation approach, showing the feasibility of BCI being implemented in the control of robotic hands.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Kinematics, Dynamics and Control for Rehabilitation Robotics and Prostheses)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Towards 6G: A Review of Optical Transport Challenges for Intelligent and Autonomous Communications
by
Evelio Astaiza Hoyos, Héctor Fabio Bermúdez-Orozco and Jorge Alejandro Aldana-Gutierrez
Computation 2025, 13(12), 286; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120286 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
The advent of sixth-generation (6G) communications envisions a paradigm of ubiquitous intelligence and seamless physical–digital fusion, demanding unprecedented performance from the optical transport infrastructure. Achieving terabit-per-second capacities, microsecond latency, and nanosecond synchronisation precision requires a convergent, flexible, open, and AI-native x-Haul architecture that
[...] Read more.
The advent of sixth-generation (6G) communications envisions a paradigm of ubiquitous intelligence and seamless physical–digital fusion, demanding unprecedented performance from the optical transport infrastructure. Achieving terabit-per-second capacities, microsecond latency, and nanosecond synchronisation precision requires a convergent, flexible, open, and AI-native x-Haul architecture that integrates communication with distributed edge computing. This study conducts a systematic literature review of recent advances, challenges, and enabling optical technologies for intelligent and autonomous 6G networks. Using the PRISMA methodology, it analyses sources from IEEE, ACM, and major international conferences, complemented by standards from ITU-T, 3GPP, and O-RAN. The review examines key optical domains including Coherent PON (CPON), Spatial Division Multiplexing (SDM), Hollow-Core Fibre (HCF), Free-Space Optics (FSO), Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs), and reconfigurable optical switching, together with intelligent management driven by SDN, NFV, and Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML). The findings reveal that achieving 6G transport targets will require synergistic integration of multiple optical technologies, AI-based orchestration, and nanosecond-level synchronisation through Precision Time Protocol (PTP) over fibre. However, challenges persist regarding scalability, cost, energy efficiency, and global standardisation. Overcoming these barriers will demand strategic R&D investment, open and programmable architectures, early AI-native integration, and sustainability-oriented network design to make optical fibre a key enabler of the intelligent and autonomous 6G ecosystem.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Computational Complex Networks)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Theoretical Insight into Non-Covalent Complexes of Closo-Borate Anions [BnHn−1X]y− with Glycine
by
Ilya N. Klyukin, Anastasia V. Kolbunova, Alexander S. Novikov, Alexandra A. Klyukina, Konstantin Y. Zhizhin and Nikolay T. Kuznetsov
Computation 2025, 13(12), 285; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120285 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Non-covalent contacts play a significant role in binding between fragments in supramolecular assemblies. Understanding the non-covalent binding capabilities of closo-borate anions and their derivatives is a significant research challenge, due to their ability to interact with biomolecules. The present work was focused
[...] Read more.
Non-covalent contacts play a significant role in binding between fragments in supramolecular assemblies. Understanding the non-covalent binding capabilities of closo-borate anions and their derivatives is a significant research challenge, due to their ability to interact with biomolecules. The present work was focused on the theoretical study of non-covalent complexes between glycine and closo-borate anions [BnHn−1X]y− (X = H, NH3, OH, SH, F; n = 10, 12; y = 1, 2). The main binding patterns between glycine and cluster systems were defined, and the effect of the exo-polyhedral substituent on the stability of non-covalent complexes was analysed. Complexes based on ammonium and hydroxy derivatives of closo-borate anions [BnHn−1X]y− (X = NH3, OH; n = 10, 12; y = 1, 2) were the most stable among all the derivatives considered. The findings of this work can be applied to the design of non-covalent complexes of closo-borate systems with biomolecules.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Computational Chemistry—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
A Visual Representation–Based Computational Approach for Student Dropout Analysis: A Case Study in Colombia
by
Juan-Carlos Briñez-De-León, Alejandra-Estefanía Patiño-Hoyos, Farley-Albeiro Restrepo-Loaiza and Gabriel-Jaime Cardona-Osorio
Computation 2025, 13(12), 284; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120284 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
Academic dropout is a persistent challenge in higher education, particularly in contexts with socio-economic disparities and diverse learning conditions. Traditional predictive models often fail to capture the complex, non-linear interactions underlying student trajectories due to their reliance on low-dimensional and linear representations. This
[...] Read more.
Academic dropout is a persistent challenge in higher education, particularly in contexts with socio-economic disparities and diverse learning conditions. Traditional predictive models often fail to capture the complex, non-linear interactions underlying student trajectories due to their reliance on low-dimensional and linear representations. This study introduces a visual representation–based computational approach for a student dropout analysis, applied to a real institutional dataset from Colombia. The methodology transforms structured student records into enriched visual encodings that map variable magnitudes, correlations, and latent relationships into spatial and textural patterns. These image-based representations allow convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to exploit hierarchical feature extraction, uncovering hidden dependencies not accessible through conventional classifiers. Experimental results demonstrate that a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) trained from scratch outperforms both baseline machine learning models and transfer learning architectures across all evaluation metrics. Beyond predictive accuracy, the approach enhances data expressiveness, interpretability, and generalization, offering a visual-analytical perspective for understanding dropout dynamics. The Colombian case study confirms the feasibility and potential of this strategy in real educational settings, supporting early identification of at-risk students and contributing to the development of robust, explainable models in educational data mining and learning analytics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
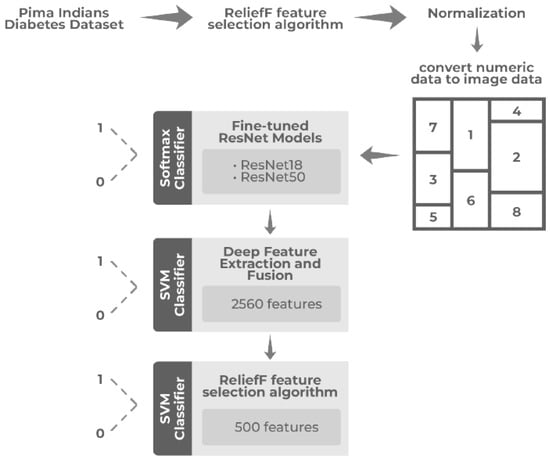
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Convergence Analysis and Optimisation of Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning for Hierarchical Graph Neural Networks in Distributed Cloud Anomaly Detection
by
Comfort Lawal, Olatayo M. Olaniyan, Kennedy Okokpujie and Emmanuel Adetiba
Computation 2025, 13(12), 283; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120283 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
Distributed cloud networks spanning multiple jurisdictions face significant challenges in anomaly detection due to privacy constraints, regulatory requirements, and communication limitations. This paper presents a mathematically rigorous framework for privacy-preserving federated learning on hierarchical graph neural networks, providing theoretical convergence guarantees and optimisation
[...] Read more.
Distributed cloud networks spanning multiple jurisdictions face significant challenges in anomaly detection due to privacy constraints, regulatory requirements, and communication limitations. This paper presents a mathematically rigorous framework for privacy-preserving federated learning on hierarchical graph neural networks, providing theoretical convergence guarantees and optimisation bounds for distributed anomaly detection. A novel layer-wise federated aggregation mechanism is introduced, featuring a proven convergence rate
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Deep Learning-Driven Integration of Multimodal Data for Material Property Predictions
by
Vítor Costa, José Manuel Oliveira and Patrícia Ramos
Computation 2025, 13(12), 282; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120282 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Advancements in deep learning have revolutionized materials discovery by enabling predictive modeling of complex material properties. However, single-modal approaches often fail to capture the intricate interplay of compositional, structural, and morphological characteristics. This study introduces a novel multimodal deep learning framework for enhanced
[...] Read more.
Advancements in deep learning have revolutionized materials discovery by enabling predictive modeling of complex material properties. However, single-modal approaches often fail to capture the intricate interplay of compositional, structural, and morphological characteristics. This study introduces a novel multimodal deep learning framework for enhanced material property prediction, integrating textual (chemical compositions), tabular (structural descriptors), and image-based (2D crystal structure visualizations) modalities. Utilizing the Alexandriadatabase, we construct a comprehensive multimodal dataset of 10,000 materials with symmetry-resolved crystallographic data. Specialized neural architectures, such as FT-Transformer for tabular data, Hugging Face Electra-based model for text, and TIMM-based MetaFormer for images, generate modality-specific embeddings, fused through a hybrid strategy into a unified latent space. The framework predicts seven critical material properties, including electronic (band gap, density of states), thermodynamic (formation energy, energy above hull, total energy), magnetic (magnetic moment per volume), and volumetric (volume per atom) features, many governed by crystallographic symmetry. Experimental results demonstrated that multimodal fusion significantly outperforms unimodal baselines. Notably, the bimodal integration of image and text data showed significant gains, reducing the Mean Absolute Error for band gap by approximately 22.7% and for volume per atom by 22.4% compared to the average unimodal models. This combination also achieved a 28.4% reduction in Root Mean Squared Error for formation energy. The full trimodal model (tabular + images + text) yielded competitive, and in several cases the lowest, error metrics, particularly for band gap, magnetic moment per volume and density of states per atom, confirming the value of integrating all three modalities. This scalable, modular framework advances materials informatics, offering a powerful tool for data-driven materials discovery and design.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Computational Tools for Analysing the Observability and Accessibility of Nonlinear Models
by
Mahmoud Shams Falavarjani, Adriana González Vázquez and Alejandro F. Villaverde
Computation 2025, 13(12), 281; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120281 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Accessibility and observability are two properties of dynamic models that provide insights into the structural relationships between their input, output, and state variables. They are closely related to controllability and structural local identifiability, respectively. Observability and identifiability determine, respectively, the possibility of inferring
[...] Read more.
Accessibility and observability are two properties of dynamic models that provide insights into the structural relationships between their input, output, and state variables. They are closely related to controllability and structural local identifiability, respectively. Observability and identifiability determine, respectively, the possibility of inferring the unmeasured state variables and parameters of a model from output measurements; accessibility and controllability describe the possibility of driving its state by changing its input. Analysing these structural properties in nonlinear models of ordinary differential equations can be challenging, particularly when dealing with large systems. Two main approaches are currently used for their study: one based on differential geometry, which uses symbolic computation, and another one based on sensitivity calculations that uses numerical integration. These approaches are implemented in two MATLAB (R2024b) software tools: the differential geometry approach in STRIKE-GOLDD, and the sensitivity-based method in StrucID. These toolboxes differ significantly in their features and capabilities. Until now, their performance had not been thoroughly compared. In this paper we present a comprehensive comparative study of them, elucidating their differences in applicability, computational efficiency, and robustness against computational issues. Our core finding is that StrucID has a substantially lower computational cost than STRIKE-GOLDD; however, it may occasionally yield inconsistent results due to numerical issues.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nonlinear System Modelling and Control)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Investigations of Water-Lubricated Core Annular Flow (CAF) for Heavy Oil Transportation
by
Salim Al Jadidi, Dadapeer Doddamani, Yahya Ubaid Al Shamsi, Ibrahim Nasser Al Siyabi and Siva Subramanian
Computation 2025, 13(12), 280; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120280 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study examines the flow behavior of water-lubricated heavy oil transport utilizing the core annular flow (CAF) technique. The goal is to enhance efficiency and minimize risks in pipeline operations. The flow was numerically simulated in a horizontal pipe using a Large Eddy
[...] Read more.
This study examines the flow behavior of water-lubricated heavy oil transport utilizing the core annular flow (CAF) technique. The goal is to enhance efficiency and minimize risks in pipeline operations. The flow was numerically simulated in a horizontal pipe using a Large Eddy Simulation (LES) model within a commercial Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) framework. The Geo Reconstruct scheme is employed to accurately capture the oil–water interface, and both oil and water initialization methods were assessed against experimental data. Results show that the LES model accurately reproduces the main flow features observed experimentally, particularly for low-viscosity oil–water systems. This suggests that the model can be a reliable tool for predicting flow behaviour in similar fluid systems. Further validation with varying parameters could enhance its applicability across a broader range of conditions. In cases of heavy oil, the velocity profile remains nearly constant within the oil core, indicating rigid body-like motion surrounded by a turbulent water annulus. Turbulence intensity and oil volume fraction distributions were closely related, with higher turbulence in water and lower in oil. Although wall adhesion modelling limited fouling prediction, simulations confirmed that fouling can significantly increase pressure losses. This illustrates the value of considering both fluid dynamics and material interactions in such systems. Future studies could explore the impact of varying temperature and pressure conditions on fouling behaviour to further refine predictive models. Overall, the LES approach proved suitable for analysing turbulent CAF, offering insights for optimizing viscosity ratios, flow rates, and design parameters for safer and more efficient heavy oil transport.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Computational Methods for Fluid Flow)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Elasticity Coefficients as Effects Measures in Model Formulations
by
Tarald O. Kvålseth
Computation 2025, 13(12), 279; https://doi.org/10.3390/computation13120279 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
When dealing with mathematical or statistical models involving one or more explanatory (independent) variables, one often wants to determine the effects of such variables on a response (independent) variable. In the case of linear regression models, one such effects measure is the so-called
[...] Read more.
When dealing with mathematical or statistical models involving one or more explanatory (independent) variables, one often wants to determine the effects of such variables on a response (independent) variable. In the case of linear regression models, one such effects measure is the so-called standardized regression coefficients used in various statistical software packages and discussed in regression textbooks. However, since strong reservations have been expressed against the use of standardized regression coefficients because of various limitations, the objective or initial working hypothesis behind the present research was that some alternative measure without such limitations ought to be explored. Consequently, elasticity coefficients are formulated and proposed as both relative and absolute such measures. While the standardized regression coefficients lack any convenient interpretation, the proposed elasticity coefficients have the particularly desirable property of having a logical and intuitively appealing interpretation in terms of the relative change in the value of the response variable as a consequence of a relative change (of 1 percent) in the value of one or more of the explanatory variables. Those elasticity measures have the flexibility of being applicable to individual or to all explanatory variables and to individual or to all observations or data sets. A numerical example is used to illustrate the use of these new measures. Comparison between values of the standardized regression coefficients and those of the corresponding elasticity coefficients based on reported data from various sources is provided. Also, the form of the elasticity coefficients for a variety of different types of models is presented. Statistical inferences are also discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Computational Social Science)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
AppliedMath, Axioms, Computation, Mathematics, Symmetry
A Real-World Application of Chaos Theory
Topic Editors: Adil Jhangeer, Mudassar ImranDeadline: 28 February 2026
Topic in
Axioms, Computation, Fractal Fract, Mathematics, Symmetry
Fractional Calculus: Theory and Applications, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: António Lopes, Liping Chen, Sergio Adriani David, Alireza AlfiDeadline: 30 May 2026
Topic in
Brain Sciences, NeuroSci, Applied Sciences, Mathematics, Computation
The Computational Brain
Topic Editors: William Winlow, Andrew JohnsonDeadline: 31 July 2026
Topic in
Sustainability, Remote Sensing, Forests, Applied Sciences, Computation
Artificial Intelligence, Remote Sensing and Digital Twin Driving Innovation in Sustainable Natural Resources and Ecology
Topic Editors: Huaiqing Zhang, Ting YunDeadline: 31 January 2027

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Computation
Integrative Computational Methods for Second-and Third-Generation Sequencing Data
Guest Editors: Hao Lin, Guojun Liu, Alexey SarapultsevDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Computation
Object Detection Models for Transportation Systems
Guest Editors: Taqwa AlHadidi, Shadi Jaradat, Ahmed JaberDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Computation
Advances in Computational Methods for Fluid Flow
Guest Editors: Ali Cemal Benim, Jeffrey S. Marshall, Sergey Karabasov, Dimitris DrikakisDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Computation
Smart Analytics for Future Energy Systems
Guest Editors: Marina Budanko, Martina Odeljan, Zvonimir GuzovićDeadline: 31 December 2025









