- Article
Trade Trends and Price Determination in Mexico’s Domestic Frozen Octopus Market: Challenges in Sustaining Its Supply
- José A. Duarte,
- Álvaro Hernández-Flores and
- Francisco Iván Hernández-Cuevas
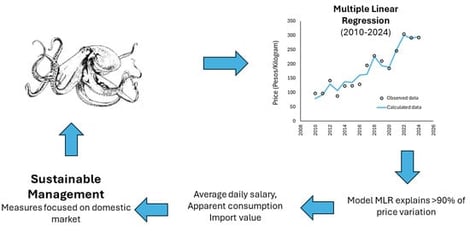
Mexican octopus fisheries play an important role in both domestic and international seafood markets, yet little is known about the determinants of retail price in the national frozen octopus sector. This study examines how trade flows and domestic demand interact to shape price dynamics, providing insights into sustainability challenges. Multiple linear regression was employed to test the influence of economic, production, and trade variables on retail prices, based on annual data from 2010 to 2024. The best-performing model identified average daily salary, apparent consumption and import value as significant determinants, explaining more than 90% of the observed variation. Results show that rising salaries and greater domestic consumption are exerting upward pressure on prices, while imports, although limited, contribute to price moderation. Export values have declined, signaling a weakening role of the international markets. These findings suggest that domestic demand is becoming increasingly important for sustaining value in the sector, but this shift could intensify fishing pressure on wild stocks. Strengthening compliance with management measures and aligning policies with domestic market realities are crucial to ensuring long-term sustainability of the Mexican octopus supply.
24 February 2026