- Article
Magnetically Separable and Synergistic CMC–Cu@Fe3O4 Nanocomposites for Efficient, Reusable, and High-Performance Laccase Biocatalysis
- Yousif Algamal,
- Rawan Altalhi and
- Yaaser Q. Almulaiky
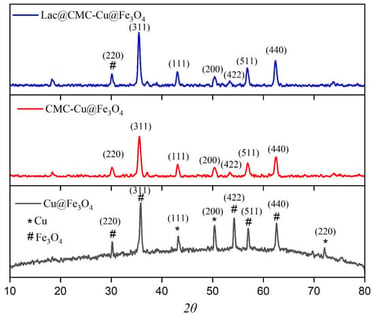
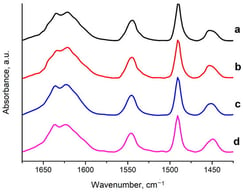
This study presents a novel multifunctional Lac@CMC-Cu@Fe3O4 nanocomposite for the efficient immobilization of laccase designed to overcome limitations in enzyme stability, reusability, and catalytic performance. The nanocomposite integrates magnetite (Fe3O4) for rapid magnetic separation, carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) as a biocompatible matrix for covalent enzyme attachment, and copper nanoparticles to enhance catalytic activity. The immobilization achieved an impressive yield of 87%, with comprehensive characterization by XRD, FT-IR, FESEM, EDX, BET, and VSM confirming successful synthesis and enzyme attachment. Kinetic analysis revealed a remarkable 37% increase in maximum reaction velocity (Vmax = 111 µmol/min) compared to free laccase (81.3 µmol/min), despite a moderate increase in Km from 1.54 to 3.22 mM. The immobilized biocatalyst demonstrated superior thermal stability, retaining 53% activity at 60 °C versus 17% for the free enzyme, and exhibited a broader pH tolerance, maintaining 41% activity at pH 8.0. Notably, the biocatalyst showed enhanced performance in organic solvents, with 153% activation in acetone. Operational reusability was exceptional, retaining 84% activity after 15 cycles, and storage stability was significantly improved, maintaining 68% activity after 90 days compared to only 11% for free laccase. This magnetically separable nanobiocatalyst represents a promising, scalable platform for sustainable industrial and environmental applications.
11 February 2026