- Article
Investigation of Lignin-Based Catalysts’ Effectiveness and Constraints in Selective Hydrogenation
- Mahendra Kothottil Mohan,
- Nadiia Shevchenko and
- Yevgen Karpichev
- + 4 authors
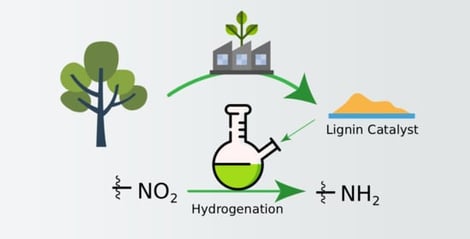
Lignin’s complex structure makes it a valuable resource for producing aromatic chemicals, but selectively converting it into specific products remains challenging. This study explores the use of technical hydrolysis lignin as a renewable support for palladium (Pd) and copper (Cu) catalysts in hydrogenation reactions. The materials were characterized using NMR, FTIR, XRF, AAS, XPS, and TEM. The reduction of nitrobenzene to aniline was tested with various Pd/Cu catalysts with different metal contents. The hydrogenation results showed that the Pd-only catalyst (catalyst-1) performed best on most substrates. In contrast, catalysts with only Cu or with Pd-Cu bimetallic showed no catalytic activity. The study discusses the effects of Pd incorporation and the Pd-Cu synergistic effect on catalyst stability, highlighting potential limitations in active-site stability and suggesting ways to enhance catalyst longevity. Overall, this research reveals that lignin is a promising, renewable support for catalysts, offering alternatives to traditional supports. These findings provide valuable insights into improving lignin modification and developing eco-friendly catalytic processes aligned with green chemistry principles.
6 February 2026