- Article
MoE Based Consistency and Complementarity Mining for Multi-View Clustering
- Xiaoping Wang,
- Yang Cao and
- Qiyue Yin
- + 2 authors
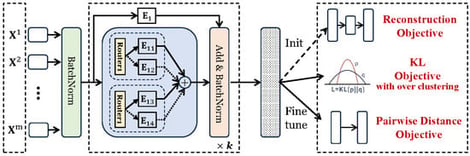
Multi-view clustering, which improves clustering performance by using the complementary and consistent information from multiple diverse feature sets, has been attracting increasing research attention owing to its broad applicability in real world scenarios. Conventional approaches typically leverage this complementarity by projecting different views into a common embedding space using view-specific or shared non-linear neural networks. This unified embedding is then fed into standard single-view clustering algorithms to obtain the final clustering results. However, a single common embedding may be insufficient to capture the distinct or even contradictory characteristics of multi-view data, due to the divergent representational capacities of different views. To address this issue, we propose a mixture of experts (MoE) based embedding learning method that adaptively models inter-view relationships. This architecture employs a typical MoE module as a projection layer across all views, which uses shared expert and several groups of experts for consistency and complementarity mining. Furthermore, a Kullback-Leibler divergence based objective with over clustering is designed for clustering-oriented embedding learning. Extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets confirm that our method achieves superior performance compared to a number of state-of-the-art approaches.
6 February 2026