Journal Description
Epidemiologia
Epidemiologia
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on epidemiologic research published bimonthly online by MDPI. The Italian Society of Environmental Medicine (SIMA) is affiliated with Epidemiologia, and its members receive discounts on article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus, PMC, PubMed, FSTA, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 21.9 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Public, Environmental and Occupational Health) / CiteScore - Q2 (Medicine (miscellaneous))
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Epidemiologia is a companion journal of JCM.
Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.9 (2024)
Latest Articles
Systematic Review of Health Literacy and Health Behavior in Adolescents Research
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010029 - 18 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Despite the publication of several systematic reviews on adolescent health literacy, comprehensive evaluations of the relationship between health literacy and health-related behaviors are still limited. This systematic review sought to synthesize and critically appraise the available evidence on associations between health literacy
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Despite the publication of several systematic reviews on adolescent health literacy, comprehensive evaluations of the relationship between health literacy and health-related behaviors are still limited. This systematic review sought to synthesize and critically appraise the available evidence on associations between health literacy and health behaviors among adolescents. Methods. A systematic search of three databases (Scopus, PubMed, and PsycINFO) was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. Thirty-seven eligible cross-sectional studies were selected for qualitative synthesis. Methodological quality was evaluated using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale adapted for cross-sectional studies. Results: The 37 included studies encompassed 71,558 adolescents (mean age range 11.0–17.0 years) and were conducted primarily in Europe (n = 22), with additional studies from the USA (n = 5), Asia (n = 8), and cross-cultural settings (n = 2). Across studies, 11 HL instruments were used (including two eHealth literacy measures), most commonly the Health Literacy for School-aged Children scale (n = 14). Physical activity (n = 22), nutrition-related indicators (n = 26), and smoking/alcohol/drug outcomes (n = 16) were assessed using heterogeneous operationalisations. Overall, higher HL was more often associated with healthier behavioral profiles, with more consistent patterns for nutrition-related outcomes. Findings for physical activity and substance use were more heterogeneous and, in some cases, varied depending on the HL measurement approach (subjective vs. objective) and the behavioral reference period. Conclusions: Current evidence indicates that higher health literacy in adolescents is generally associated with more favorable health behaviors, particularly regarding nutrition-related indicators. However, study heterogeneity and the predominance of cross-sectional designs limit comparability and causal inference. Future research should prioritize standardized measurement tools and longitudinal designs to clarify directionality and underlying mechanisms.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Climatic Factors on the Incidence of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Essaouira, Morocco: A Decadal Analysis (2014–2023)
by
Said Benkhira, Najma Boudebouch and Bouchra Benazzouz
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010028 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) remains a major public health and economic challenge in Morocco, where its transmission dynamics are increasingly influenced by climatic variability. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of meteorological factors on CL incidence in the province of Essaouira,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) remains a major public health and economic challenge in Morocco, where its transmission dynamics are increasingly influenced by climatic variability. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of meteorological factors on CL incidence in the province of Essaouira, a high-incidence region, to identify the environmental drivers behind recent epidemic trends. Methods: Epidemiological data (N = 834 cases) were collected from the Hygiene and Health Laboratory of Essaouira for the period between January 2014 and December 2023. Climatic variables were obtained from the Moroccan Directorate of National Meteorology. Data were analyzed at annual, seasonal, and monthly scales using the Spearman rank correlation in R 4.5.0 software to account for non-normal distributions and non-linear associations. Results: CL incidence remained stable from 2014 to 2021 before an unprecedented surge in cases during 2022–2023. Annual analysis indicated that warm and dry years pose a higher risk, with incidence positively correlated with temperatures and negatively associated with humidity and precipitation. Monthly results identified a biphasic regulatory mechanism: a winter hydric constraint phase with strong negative correlations with January rainfall and humidity (p < 0.05), followed by a summer thermal promotion phase where minimum temperature (Tmin) emerged as the dominant driver (rho = 0.53), peaking in September (rho = 0.59). Conclusions: Our findings confirm the significant influence of climatic factors on CL incidence through complex seasonal dynamics. These results highlight the necessity of integrating high-resolution meteorological monitoring and predictive modeling into public health surveillance to anticipate future outbreaks in the context of increasing Mediterranean aridification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Environmental Epidemiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluating the Feasibility of Using Historical Placebo Control in Osteoarthritis Trials
by
Justine Monseur, Emma Barbeau, Anne-Françoise Donneau and Olivier Bruyère
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010027 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are the gold standard for evaluating treatment efficacy, yet recruitment and retention remain challenging, particularly when placebo arms are required. Using historical placebo data may reduce the need for contemporaneous placebo groups, but comparability between historical and real-time
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are the gold standard for evaluating treatment efficacy, yet recruitment and retention remain challenging, particularly when placebo arms are required. Using historical placebo data may reduce the need for contemporaneous placebo groups, but comparability between historical and real-time placebo responses is uncertain. This study assessed the feasibility of replacing a placebo control group with a historical placebo arm in osteoarthritis (OA) RCTs using several matching approaches. Methods: Data from three published knee OA RCTs (2009, 2013, 2017) were analyzed. The study followed three steps: (1) development of matching techniques using the 2009 and 2013 trials, (2) validation in the 2017 trial, and (3) post hoc analyses comparing placebo responses across trials. Methods included direct covariate adjustment, exact and nearest-neighbor matching, and propensity score matching based on baseline characteristics (age, sex, BMI, OA duration, baseline pain). The main outcome was change in 100 mm visual analogue scale (VAS) pain. Results: Initial attempts showed moderate to good success in adjusting historical placebo response on the VAS using various adjustment methods. However, in the validation process, a significant discrepancy was observed between real placebo VAS changes data and historical placebo VAS changes data, and various matching techniques failed to sufficiently reduce this discrepancy. In the post hoc analysis, despite the application of advanced matching techniques, substantial variability in VAS placebo responses persisted across trials. Even among placebo patients with highly similar baseline characteristics, the VAS changes over time differed significantly between studies. Conclusions: The findings indicate that replacing a real placebo group with a historical placebo in osteoarthritis RCTs is hardly feasible. These results underscore the complexity of placebo effects in osteoarthritis trials and the limitations of historical control data in this context.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vaccine-Preventable Diseases in Mexico: A Time Series Analysis (2014–2024)
by
María Fernanda Hernández-Batres, Sofía Bernal-Silva, Georgina Cristina Delgado-Juárez and Andreu Comas-Garcia
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010026 - 11 Feb 2026
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted public health in Mexico. Background/Objectives: This study evaluated its impact on the frequency of vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs) from 2020 to 2024. Methods: The analyzed information was extracted from the weekly epidemiological bulletins, which compile the suspected, probable,
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted public health in Mexico. Background/Objectives: This study evaluated its impact on the frequency of vaccine-preventable diseases (VPDs) from 2020 to 2024. Methods: The analyzed information was extracted from the weekly epidemiological bulletins, which compile the suspected, probable, and confirmed cases reported to the Ministry of Health. The epidemiological behavior of VPDs was analyzed with endemic channels based on 2014–2019 data. An endemic channel is a graphical tool that is used to plot a central tendency and its limits; with this tool we can detect the presence of an epidemic and quantify it. Between 2020 and 2024, VPDs presented variable patterns due to the pandemic. Results: Rotavirus cases exhibited an 81% negative deviation in 2020 and a final 47% negative deviation in comparison with the expected values from 2014–2019. Chickenpox declined by 91% in 2020, with a partial recovery in reports afterward. Hepatitis A and B declined initially, but hepatitis B surpassed pre-pandemic levels later. Mumps declined by 45% in 2020, with a partial recovery, remaining 35% below expected reports. Meningeal and pulmonary tuberculosis increased by 125% and 33%, respectively. Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection and mild cervical dysplasia showed negative deviations, with partial increases later. However, severe dysplasia and in situ cervical cancer reports exceeded expected levels. Conclusions: Overall, several VPDs showed negative deviations, which could increase the size of the susceptible population. In contrast, increases in tuberculosis and HPV infection present a major challenge for health systems, given their chronic and high treatment costs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Surveillance Systems and Predictive Analytics for Epidemics)
►▼
Show Figures
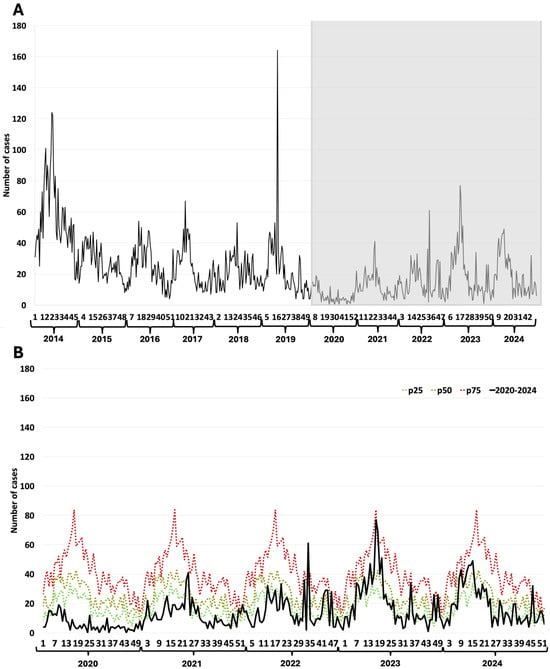
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Regional Inequities in Mammography Access and Utilization in Latin America: Ethnic, Rural, and Structural Barriers Identified Through a Narrative Review
by
Nina Méndez-Domínguez, Mariana Jaqueline Arce Medina, Maricela Balam Gomez, Marco Esteban Morales Rojas and Esmeralda Novelo Moreno
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010025 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Breast cancer remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among women in Latin America. Mammography is the most effective population-based tool for early detection; however, its impact is limited by persistent social, geographic, and structural inequities. Evidence from the region indicates
[...] Read more.
Background: Breast cancer remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality among women in Latin America. Mammography is the most effective population-based tool for early detection; however, its impact is limited by persistent social, geographic, and structural inequities. Evidence from the region indicates that ethnicity, rural residence, and health system organization play a central role in shaping unequal access to screening services. Methods: We conducted a narrative review informed by a systematic search strategy, following PRISMA 2020 recommendations. Searches were performed in 17 international and regional databases in English and Spanish, covering publications from 2015 to 2025. Eligible studies included non-interventional quantitative designs reporting mammography access, utilization, or coverage among women residing in Latin American countries. Three reviewers independently screened records, extracted data, and classified determinants of inequality into sociodemographic, geographic, and health-system domains. Results: Of 532 records identified, 12 studies met the inclusion criteria, primarily from Mexico, Brazil, Peru, and Chile. Most analyses were based on nationally representative surveys. Mammography coverage ranged from approximately 20% to 60%, with consistently lower uptake among Indigenous women, rural populations, and women without health insurance. Reduced screening was associated with low educational attainment, socioeconomic disadvantages, rural residence, ethnic self-identification, and fragmented health system affiliation. Structural barriers, including concentration of diagnostic infrastructure in urban areas, reliance on opportunistic screening models, and limited capacity for systematic follow-up, were recurrent across countries. Conclusions: Inequities in mammography access and utilization in Latin America reflect deeply rooted social and structural determinants rather than a lack of screening technology alone. Reducing preventable breast cancer mortality requires strengthening organized, population-based screening programs, decentralizing diagnostic services, improving continuity of care, and implementing culturally appropriate strategies tailored to Indigenous, rural, and uninsured populations.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Limitations of Daily Step Count for Assessing Health in Older Adults: The Need to Consider Walking Intensity
by
Pedro Ángel Latorre-Román, Ana de la Casa-Pérez, Juan Antonio Párraga-Montilla, Jesús Salas-Sánchez, Manuel Lucena-Zurita and José Carlos Cabrera-Linares
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010024 - 5 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: This study explored the association between daily step count (DSC) and health outcomes in older adults in Spain. A total of 668 individuals aged 60–100 years (mean = 71.33 ± 8.11 years) participated. Methods: Participants wore a Xiaomi Mi Band 4 accelerometer
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study explored the association between daily step count (DSC) and health outcomes in older adults in Spain. A total of 668 individuals aged 60–100 years (mean = 71.33 ± 8.11 years) participated. Methods: Participants wore a Xiaomi Mi Band 4 accelerometer continuously for seven days. Physical and cognitive tests were conducted, along with questionnaires on depression, quality of life, and physical activity. Results: On average, men walked 8919.08 ± 4455.65 steps/day, significantly more than women (7855.46 ± 7855.46 steps/day, p = 0.002). A moderate negative correlation was found between age and DSC (r = −0.460, p < 0.001). The coefficient of variation in DSC increased across age groups, indicating growing heterogeneity with advancing age. Individuals in the high International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) category walked 1517 more steps/day than those in the low activity group (p < 0.001), confirming IPAQ level as a strong determinant of physical activity. Participation in organized physical activity was associated with an additional 909 steps/day (p = 0.004). Meeting age-specific step recommendations is associated with better anthropometric, psychosocial, and cardiometabolic markers, but many of these differences disappear after adjusting for age and sex. Conclusions: DSC in older adults is strongly influenced by age, sex, and physical activity level. DSC may not adequately assess health in older adults. Walking intensity should be considered for accurate evaluation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Syndromic Surveillance—Review on Different Practices’ Performance and Added Value for Public Health
by
Zhivka Getsova and Vanya Rangelova
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010023 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Timely identification of infectious disease threats is essential for public health readiness. Conventional indicator-based surveillance systems, while dependable for tracking established pathogens, frequently lack the agility and sensitivity to detect new infections promptly. Syndromic surveillance, which examines pre-diagnostic and non-specific health indicators from
[...] Read more.
Timely identification of infectious disease threats is essential for public health readiness. Conventional indicator-based surveillance systems, while dependable for tracking established pathogens, frequently lack the agility and sensitivity to detect new infections promptly. Syndromic surveillance, which examines pre-diagnostic and non-specific health indicators from many data sources in near real time, serves as a significant complementary method that improves early warning and situational awareness. This narrative study analysed selected experiences with syndromic surveillance, utilising peer-reviewed literature and institutional records. Four primary data streams were examined: emergency department and hospital records, pharmacy and over the counter (OTC) sales, participative citizen-generated data, and hybrid multi-source systems. Syndromic indicators were reported to identify outbreaks two to fourteen days before standard laboratory reporting across many trials. Data from the emergency department exhibited the highest sensitivity and specificity (47.34% and 91.95%, respectively), whereas pharmacy and participative data offered early indicators at the community level. Integrated systems like ESSENCE (Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Laurel, MD, USA) and SurSaUD® (Saint-Maurice cedex, Paris, France) attained enhanced accuracy yet necessitated significant data integration and governance capabilities. Syndromic surveillance enhances epidemic preparation by detecting atypical health-seeking behaviours and variations from baseline patterns prior to formal diagnosis. Nonetheless, its efficacy is contingent upon data quality, interoperability, and contextual adaptation. Countries like Bulgaria could improve national early-warning capabilities and overall health security through the gradual adoption of pilot projects and integration with existing surveillance networks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Association Between Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior and Breast Cancer Risk Among Moroccan Women: A Multicenter Case–Control Study
by
Siham Mrah, Najoua Lamchabbek, Mounia Amzerin, Najia Mane, Nawfel Mellas, Karima Bendahou, Chaimaa Elattabi, Saber Boutayeb, Lahcen Belyamani, Elodie Faure, Inge Huybrechts, Adil Najdi, Fatima Zahra El M’rabet and Mohamed Khalis
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010022 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer (BC) incidence has been increasing rapidly in North Africa, including Morocco, yet evidence regarding modifiable lifestyle factors remains limited. This study aimed to assess the associations between physical activity, sedentary behavior, daily work habits, and BC risk among Moroccan women,
[...] Read more.
Purpose: Breast cancer (BC) incidence has been increasing rapidly in North Africa, including Morocco, yet evidence regarding modifiable lifestyle factors remains limited. This study aimed to assess the associations between physical activity, sedentary behavior, daily work habits, and BC risk among Moroccan women, addressing an important gap in regional data. Methods: We conducted a case–control study between 2019 and 2023, including 1400 histologically confirmed incident BC cases and 1400 matched controls. Physical activity was assessed across the lifespan, considering type, intensity, and duration. Associations with BC risk were estimated using adjusted odds ratios (aORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: Moderate physical activity was inversely associated with BC risk, showing a clear dose–response relationship. Compared with the lowest physical activity level, the highest quartile showed significantly lower odds of BC (aOR = 0.37 (95% CI: 0.29–0.47). Vigorous physical activity during young adulthood and mid-adulthood was similarly linked to reduced risk. Active daily habits, such as walking and regular stair climbing, were associated with lower odds, whereas frequent occupational fatigue and sweating were linked to increased risk. Conclusions: Our findings highlight a significant inverse association between physical activity and BC risk among Moroccan women. Notably, moderate PA and active daily habits like brisk walking are linked to lower odds of the disease. While these findings support the role of physical activity as an important factor associated with breast cancer prevention, the retrospective design of the study limits causal inference.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Environmental Epidemiology, Health and Lifestyle)
Open AccessArticle
Unfolding Success Factors and Barriers in Adapting Slovenia’s Health Promotion Centre Model to Bergamo Province: A PIET-T Feasibility Assessment with Time-Dependent Care Implications
by
Giacomo Crotti, Antonio Antonelli, Federica Bonomi, Giulio Borghi, Giulia Parisi, Isabella Trezzi, Nicola Rizzardi, Radivoje Pribakovic Brinovec, Maja Zupanc, Alberto Zucchi and Nicoletta Castelli
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010021 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Health Promotion Centres (HPCs) in Slovenia represent a European best practice for integrated prevention and health promotion. This study explores the feasibility of adapting the Slovenian HPC model to Bergamo Province, Lombardy, considering local population needs and health system characteristics. Methods: We
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Health Promotion Centres (HPCs) in Slovenia represent a European best practice for integrated prevention and health promotion. This study explores the feasibility of adapting the Slovenian HPC model to Bergamo Province, Lombardy, considering local population needs and health system characteristics. Methods: We conducted a qualitative feasibility and policy analysis based primarily on documentary review, complemented by a webinar, a study visit to Slovenia, and expert consultations (conducted in two group discussions) with professionals from ATS (Agenzia Tutela della Salute) Bergamo and local ASST (Azienda Socio-Sanitaria Territoriale) providers. Data were analysed using the PIET-T framework (Population–Intervention–Environment–Transfer). Results: Eight key elements define the Slovenian model: (1) governance and stewardship; (2) structural financing; (3) standardized service portfolio; (4) systematic preventive referrals; (5) integration with primary care and screening; (6) multidisciplinary teams with codified training; (7) community outreach and equity orientation; and (8) information systems and reporting. While Bergamo shares similar demographic and epidemiological profiles, differences in behavioral risk factors, project-based financing, fragmented initiatives, and limited digital integration necessitate adaptation. The comparative assessment highlighted key areas requiring contextual adaptation, including financing mechanisms, organisational coordination, workforce capacity, digital interoperability, and approaches to equity. Conclusions: The Slovenian HPC experience demonstrates the potential of integrated, community-based health promotion. Its adaptation to Lombardy appears feasible if core components are preserved and tailored to local governance, population, and health system conditions. These organisational features may be particularly relevant for time-dependent conditions, such as acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, by potentially supporting more timely risk-factor management and coordination across diagnostic and emergency pathways. Rather than a blueprint for reform, this experience offers useful insights to reinforce prevention and health promotion within the ongoing territorial care reform in Lombardy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Acute Diseases and Epidemiological Studies)
Open AccessReview
The Global Impact of Sepsis: Epidemiology, Recognition, Management, and Health System Challenges
by
Luigi La Via, Salvatore Ferlito, Maria Stella Di Modica, Andrea Marino, Giuseppe Nunnari, Bruno Cacopardo, Jerome Rene Lechien, Mario Lentini, Salvatore Lavalle, Giancarlo Carmelo Botto, Paolo Buscema, Loris Gruppuso and Antonino Maniaci
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010020 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Sepsis constitutes a major healthcare burden worldwide, with an estimated 48.9 million incident cases and 11.0 million deaths in 2017, accounting for nearly one-fifth of all global deaths. Even with advances in definitions and guidelines, significant inequalities persist in awareness, early treatment,
[...] Read more.
Background: Sepsis constitutes a major healthcare burden worldwide, with an estimated 48.9 million incident cases and 11.0 million deaths in 2017, accounting for nearly one-fifth of all global deaths. Even with advances in definitions and guidelines, significant inequalities persist in awareness, early treatment, and health system readiness. Methods: We performed a structured narrative review of epidemiology studies, clinical case definitions, diagnostic approaches, stewardship interventions, and health system reports. Both electronic sources (PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Scopus) and grey literature (World Health Organization [WHO], National Institute for Health and Care Excellence [NICE], Society Critical Care [SSC]) were explored. Evidence incorporated themes were organized across recognition, diagnostics, antimicrobial therapy, organ support, guidelines, and health system determinants. Results: Measurement tools, including quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (qSOFA) and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA), exhibited suboptimal sensitivity and utility in varied clinical environments. Biomarkers (procalcitonin, presepsin, CD64) and rapid molecular diagnostics, including metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) and AI-based devices, enhance detection but are limited by cost and infrastructure constraints. Each hour of delay in antibiotic therapy is associated with a 6–10% increased risk of mortality, underscoring the importance of stewardship, including the incorporation of empiric regimens with rapid de-escalation. Health system bottlenecks—human resources, funding, infrastructure—continue to be a significant determinant of outcomes, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Conclusions: Attaining the 2030 WHO targets for sepsis involves precision diagnostics, adaptable guidelines, stewardship frameworks, and resilient health systems. Fair application and resource allocation are crucial to lower the incidence and mortality worldwide.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Prevention as a Pillar of Communicable Disease Control: Strategies for Equity, Surveillance, and One Health Integration
by
Giovanni Genovese, Caterina Elisabetta Rizzo, Linda Bartucciotto, Serena Maria Calderone, Francesco Loddo, Francesco Leonforte, Antonio Mistretta, Raffaele Squeri and Cristina Genovese
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010019 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Global health faces unprecedented challenges driven by communicable diseases, which are increasingly amplified by persistent health inequities, the impact of climate change, and the speed of emerging crises. Prevention is not merely a component but the foundational strategy for an effective, sustainable, and
[...] Read more.
Global health faces unprecedented challenges driven by communicable diseases, which are increasingly amplified by persistent health inequities, the impact of climate change, and the speed of emerging crises. Prevention is not merely a component but the foundational strategy for an effective, sustainable, and fiscally responsible public health response. This paper delves into the pivotal role of core prevention levers: robust vaccination programs, stringent hygiene standards, advanced epidemiological surveillance, and targeted health education. We detail how contemporary technological advancements, including Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and genomics, are fundamentally reshaping infectious disease management, enabling superior predictive capabilities, faster early warning systems, and personalized prevention models. Furthermore, we thoroughly examine the imperative of integrating the One Health approach, which formally recognizes the close, interdependent links between human, animal, and environmental health as critical for combating complex threats like zoonoses and Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). Despite significant scientific progress, persistent socio-economic disparities, the pervasive influence of health-related misinformation (infodemics), and structural weaknesses in global preparedness underscore the urgent need for decisive international cooperation and equitable financing models. We conclude that only through integrated, multidisciplinary, and resource-equitable strategies can the global community ensure effective prevention, mitigate severe socio-economic disruption, and successfully build resilient healthcare systems capable of withstanding future global health threats.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Local Healthcare Preparedness and Alert Systems—How to Prevent Future Pandemics?)
Open AccessArticle
Interactions Between BMI and Age on Fall Risk in Older Adults
by
Filipe Rodrigues, Diogo Monteiro, António Miguel Monteiro and Pedro Forte
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010018 - 2 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The aging process is typically marked by a reduction in functional fitness, which heightens the likelihood of falling. Although obesity is established as a determinant of poor mobility, the interplay between excess weight and advanced age is still a topic of research
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The aging process is typically marked by a reduction in functional fitness, which heightens the likelihood of falling. Although obesity is established as a determinant of poor mobility, the interplay between excess weight and advanced age is still a topic of research interest. Therefore, this research investigated how age, sex, and Body Mass Index (BMI) interact to influence fall risk among older adults living in the community. Methods: This cross-sectional investigation involved 815 participants (Mage = 70.45 ± 6.10 years), stratified by age (sexagenarians, septuagenarians, octogenarians) and BMI (normal weight, overweight, obesity). Fall risk was assessed using the Timed Up and Go test. A Three-Way ANOVA examined the main and interaction effects. Results: No significant three-way interaction (p = 0.334) or main effect of sex (p = 0.079) was found. However, a significant age x BMI interaction was observed (p = 0.007). In sexagenarians and septuagenarians, obesity was associated with significantly slower fall risk performance compared to normal weight (p < 0.001). Conversely, in octogenarians, this difference was not significant (p = 1.000) with normal-weight individuals. Conclusions: Obesity may be a significant risk factor for falls, especially in adults aged 60 to 79 years. In octogenarians, the protective benefit of normal weight disappears, revealing a “weight paradox” likely driven by sarcopenia. Fall risk assessments and weight management strategies should be tailored to age, focusing on preserving muscle mass in octogenarians.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Erectile Dysfunction and Its Impact on Health-Related Quality of Life in Prostate Cancer Patients: A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study from Pakistan
by
Mateen Abbas, Márió Gajdács, Georgina Balogh, Sana Ahmed, Rabia Mahfooz and Abad Khan
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010017 - 27 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer (PC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed malignancies globally; depending on the treatment strategy used, erectile dysfunction (ED) is a frequently reported adverse outcome among PC patients. The current study evaluated ED prevalence among Pakistani PC patients and its
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer (PC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed malignancies globally; depending on the treatment strategy used, erectile dysfunction (ED) is a frequently reported adverse outcome among PC patients. The current study evaluated ED prevalence among Pakistani PC patients and its effects on physical, psychological, and social well-being, aiming to address critical gaps in survivorship care for this population. Methods: A cross-sectional, multicenter, observational, questionnaire-based study was conducted in Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan, from February to April 2025. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among PC patients was measured using the Short Form Health Survey 36 (SF-36), while ED prevalence and severity were assessed by the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) instrument. Results: Among N = 400 PC patients, surgical treatments predominated (radical prostatectomy: 61.0%; n = 244), while hormonal (androgen-deprivation therapy: 31.5%; n = 126) and chemotherapy (23.3%; n = 93) were also commonly utilized. ED experience was high among PC patients in the erectile function (40.8%; n = 163) and in the intercourse satisfaction (45.0%; n = 180) domains; these showed moderately strong and significant positive correlations across all SF-36 domains, particularly physical functioning (r = 0.52; p < 0.001) and social functioning (r = 0.49; p < 0.001). Regression analysis confirmed sexual function domains explained 60% of HRQoL variance (adjusted R2 = 0.60). Conclusions: This study reveals high rates of treatment-related ED—and its biopsychosocial impact–among Pakistani PC patients, with significant negative impacts on HRQoL. The findings underscore the urgent need to integrate sexual health management into standard oncological care practices to improve holistic patient outcomes.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Mortality and Economic Burden of Prostate Cancer in Bulgaria: Years of Life Lost, Working Years of Life Lost, and Indirect Costs (2008–2023)
by
Nadia Veleva, Konstantin Ivanov, Antonia Yaneva and Hristina Lebanova
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010016 - 22 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality among the male population worldwide. It is among the leading reasons for the increasing number of years of life lost, working years of life lost, and gross domestic product (GDP) loss
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Prostate cancer is the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality among the male population worldwide. It is among the leading reasons for the increasing number of years of life lost, working years of life lost, and gross domestic product (GDP) loss in Bulgaria. The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the burden of prostate cancer in Bulgaria, including calculating years of life lost (YLL), years of working life lost (YWLL), and the associated indirect costs. Methods: An observational time-series study was conducted using official national data from the National Statistical Institute (NSI), the INFOSTAT database, and the National Social Security Institute. The study covered the period 2008–2023 and included all registered male deaths attributed to malignant neoplasm of the prostate (ICD-10: C61). YLL, YWLL, and indirect costs were calculated using the human capital approach. Due to restricted access to age-specific mortality files, additional mortality records were obtained through formal data requests to NSI. Results: Prostate cancer led to 127,457 YLL and 6345 YWLL, with productivity losses reaching €88.2 million. Mortality showed an overall increasing trend up to 2020, while YWLL declined due to deaths shifting to older age groups. Conclusions: Despite the advancements in prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment, our findings demonstrate a negative trend regarding YLL, YWLL, and indirect costs associated with the disease, in contrast to other European countries. Strengthening early screening, reducing diagnostic delays, and improving national cancer registry capacity are critical to mitigating future health and economic losses.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Geographical Variation in SARS-CoV-2 Transmission Potential in Massachusetts
by
Ina Sze-Ting Lee, Xinyi Hua, Jing Xiong Kersey, Kayoko Shioda, Gerardo Chowell and Isaac Chun-Hai Fung
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010015 - 21 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: This ecological study aimed to investigate changes in the time-varying reproduction number (Rt) of SARS-CoV-2 across six regions of Massachusetts from 2020 to 2022 and to evaluate the impact of various nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) implemented in 2020 by examining associated changes in
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This ecological study aimed to investigate changes in the time-varying reproduction number (Rt) of SARS-CoV-2 across six regions of Massachusetts from 2020 to 2022 and to evaluate the impact of various nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) implemented in 2020 by examining associated changes in the Rt. Methods: COVID-19 incident case data from the Johns Hopkins University database were adjusted for reporting delays using deconvolution and for underreporting via a Poisson-distributed multiplier of 4. Negative and zero counts were corrected using imputation. Rt was estimated using R package EpiEstim (Version 2.2-4) with a 7-day sliding window from 2020 to 2022 and with non-overlapping time windows between policy changes in 2020. Results: From 2020 to 2022, Massachusetts experienced five COVID-19 surges, linked to the wild-type strain and emerging variants, with Rt exceeding 1 during each wave and stabilizing at or dropping below 1 during low-incidence phases. School closure and gathering restrictions, the first major intervention, were associated with a 14.7% statewide reduction in Rt (95% credible interval (CrI): −23.6%, −5.6%), with greater reductions in high-density areas such as Boston (−16.9%; 95% CrI: −26.9%, −7.5%). No statistically significant changes in Rt were found to be associated with other NPIs in 2020, including the mask mandate, reopening phases, travel restrictions and quarantine requirements, and curfews. Conclusions: Our findings highlight the different NPIs’ varying impacts on COVID-19 transmission dynamics across regions in Massachusetts in 2020 and underscore the importance of early interventions for future pandemic preparedness.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trends and Determinants of Dementia-Related Mortality in Mexico, 2017–2023
by
Dennis M. Lopez-Samayoa, Angel M. Campos-Sosa, Paola Asuncion Bojorquez-Chan, Sara E. Martinez-Medel, Jorge C. Guillermo-Herrera, Edgar Villarreal-Jimenez, Reinhard Janssen-Aguilar, Cristina Rodriguez Peres-Mitre and Nina Mendez-Dominguez
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010014 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Dementia is an increasing public health challenge in Mexico, yet recent national data on mortality patterns remain limited. This study examines temporal trends in dementia-related mortality and its sociodemographic and ecological characteristics among adults aged ≥65 years from 2017 to 2023. Methods:
[...] Read more.
Background: Dementia is an increasing public health challenge in Mexico, yet recent national data on mortality patterns remain limited. This study examines temporal trends in dementia-related mortality and its sociodemographic and ecological characteristics among adults aged ≥65 years from 2017 to 2023. Methods: National mortality records from the General Directorate of Health Information were analyzed. Annual dementia-related mortality rates were calculated based on mid-year population estimates from CONAPO. Trends were assessed with regression analysis, including population offsets, and individual- and state-level characteristics were evaluated. Results: Between 2017 and 2023, dementia-related deaths increased from 761 to 1425, corresponding to an observed rise from 7.9 to 14.6 deaths per 100,000 inhabitants aged ≥65 years. Period trend indicated an average annual expected increase of 18.6% in dementia related mortality. A transient decline occurred in 2020–2021, coinciding with the COVID-19 pandemic. At the individual level, higher education was associated with greater odds of dementia certification, whereas Indigenous ethnicity appeared protective, which may reflect patterns consistent with diagnostic and reporting disparities. Higher state-level life expectancy correlated with higher dementia mortality, while greater population aging was inversely associated. Conclusions: Dementia-related mortality in Mexico shows a sustained upward trend with regional heterogeneity and apparent inequities in diagnosis and reporting. Strengthening mortality surveillance, improving certification quality, and integrating dementia indicators into national non-communicable disease registries are essential to guide equitable policy responses.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Individual- and Community-Level Predictors of Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness: Multilevel Evidence from Southern Ethiopia
by
Amanuel Yoseph, Lakew Mussie, Mehretu Belayineh, Francisco Guillen-Grima and Ines Aguinaga-Ontoso
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010013 - 14 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Birth preparedness and complication readiness (BPCR) is a cornerstone of maternal health strategies designed to minimize the “three delays” in seeking, reaching, and receiving skilled care. In Ethiopia, uptake of BPCR remains insufficient, and little evidence exists on how individual- and
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Birth preparedness and complication readiness (BPCR) is a cornerstone of maternal health strategies designed to minimize the “three delays” in seeking, reaching, and receiving skilled care. In Ethiopia, uptake of BPCR remains insufficient, and little evidence exists on how individual- and community-level factors interact to shape preparedness. This study assessed the determinants of BPCR among women of reproductive age in Hawela Lida district, Sidama Region. Methods: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 3540 women using a multistage sampling technique. Data were analyzed with multilevel mixed-effect negative binomial regression to account for clustering at the community level. Adjusted prevalence ratios (APRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were reported to identify determinants of BPCR. Model fitness was assessed using Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC), the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), and log-likelihood statistics. Results: At the individual level, women employed in government positions had over three times higher expected BPCR scores compared with farmers (AIRR = 3.11; 95% CI: 1.89–5.77). Women with planned pregnancies demonstrated higher BPCR preparedness (AIRR = 1.66; 95% CI: 1.15–3.22), as did those who participated in model family training (AIRR = 2.53; 95% CI: 1.76–4.99) and women exercising decision-making autonomy (AIRR = 2.34; 95% CI: 1.97–5.93). At the community level, residing in urban areas (AIRR = 2.78; 95% CI: 1.81–4.77) and in communities with higher women’s literacy (AIRR = 4.92; 95% CI: 2.32–8.48) was associated with higher expected BPCR scores. These findings indicate that both personal empowerment and supportive community contexts play pivotal roles in enhancing maternal birth preparedness and readiness for potential complications. Random-effects analysis showed that 19.4% of the variance in BPCR was attributable to kebele-level clustering (ICC = 0.194). The final multilevel model demonstrated superior fit (AIC = 2915.15, BIC = 3003.33, log-likelihood = −1402.44). Conclusions: Both individual- and community-level factors strongly influence BPCR practice in southern Ethiopia. Interventions should prioritize women’s empowerment and pregnancy planning, scale-up of model family training, and address structural barriers such as rural access and community literacy gaps. Targeted, multilevel strategies are essential to accelerate progress toward improving maternal preparedness and reducing maternal morbidity and mortality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue High-Risk Pregnancy Management: From Prenatal Care to Postpartum Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Knowledge, Attitudes, Practice, and Hesitancy of Patients and HCWs Towards COVID-19 Vaccination and Factors Associated with Vaccination in the Republic of Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina
by
Biljana Mijović, Tihomir Dugandžija, Dragana Sokolović, Dragana Drakul, Jovan Kulić, Kristina Drašković Mališ, Anđela Bojanić, Nasta Manojlović, Milena Dubravac Tanasković, Marija Milić, Radmila Balaban-Đurević, Dajana Nogo-Živanović, Slađana Mihajlović and Bojan Joksimović
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010012 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The COVID-19 pandemic caused over seven million deaths globally as of July 2024. In an attempt to bring the pandemic under control, immunization was implemented as the main preventive strategy. This study aimed to investigate the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The COVID-19 pandemic caused over seven million deaths globally as of July 2024. In an attempt to bring the pandemic under control, immunization was implemented as the main preventive strategy. This study aimed to investigate the knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) of hospitalized patients and healthcare workers (HCWs) regarding COVID-19 vaccination, as well as the factors contributing to COVID-19 vaccination rates. Methods: This cross-sectional, survey-based KAP study was conducted between November 2024 and February 2025 in five hospitals across five cities of the Republic of Srpska, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Results: There were 571 respondents, 68% of whom were female, with an average age of 39.17 ± 14.74 years; one-third held a university degree. The study sample consisted of patients and healthcare workers (HCWs) (59% vs. 41%). During the pandemic period, 46.6% of respondents were diagnosed with COVID-19, with a higher prevalence among healthcare workers compared to patients (54.2% vs. 41.2%). Among the 55.2% of respondents who were vaccinated, HCWs were more often vaccinated than patients (70.9% vs. 44.2%) and more likely to know that vaccines protect against severe forms of disease and death (80.8% vs. 68.5%). Patients more often believed that vaccination against COVID-19 may lead to sterility in young patients (11.3% vs. 6%) and were more often afraid of vaccination compared to the occurrence of COVID-19 (35.6% vs. 24.8%). Regression analyses showed that independent predictors of COVID-19 vaccination were older age (p < 0.001), higher education level (p = 0.039), knowledge of vaccine production technology, and the belief that vaccinated individuals have milder symptoms of the disease (p = 0.002). Conversely, the belief that the COVID-19 situation was overblown was negatively associated with vaccination (p = 0.004). Conclusions: HCWs had better knowledge, more positive attitudes, and better vaccination practices against COVID-19 in comparison to patients. However, there are still certain dilemmas and hesitations among HCWs toward COVID-19 vaccination.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Insights into Clustering Patterns in Romania’s 2020–2024 Measles Cases
by
Valerian-Ionuț Stoian, Cătălin Pleșea-Condratovici, Mădălina Nicoleta Matei, Iulia Draghiev, Liliana Baroiu, Carmina Mușat, Mihaela Patriciu, Valerii Luțenco, Mariana Daniela Ignat and Mihaela Debita
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010011 - 7 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background and objectives: During an outbreak, measles cases tend to aggregate into increasingly bigger clusters that show specific characteristics, different from the non-cluster cases. As the measles threat continues throughout Europe in 2025 with a high notification rate in Romania as well,
[...] Read more.
Background and objectives: During an outbreak, measles cases tend to aggregate into increasingly bigger clusters that show specific characteristics, different from the non-cluster cases. As the measles threat continues throughout Europe in 2025 with a high notification rate in Romania as well, exploring how clustering affects the disease propagation can provide additional insights into how to improve measles surveillance and control. Methods: National measles cases from 2020 to 2024 have been split into cluster (at least three related cases) and non-cluster-related cases and analyzed comparatively based on vaccination status, disease-related data (hospitalization) and patient-related data (age, location). Large outbreaks with at least 150 cases, allowing for more comprehensive R0 analysis, have been described and the basic reproduction numbers computed for each of them. Results: There are statistically significant differences in vaccination status, age, and hospital stay between outbreak and non-outbreak cases. Large outbreaks (≥150 cases) show a high degree of variability, with R0 values varying from as low to 1 to as high as 3.92, indicating limited measles transmission control. Conclusions: The findings in this research highlight the critical impact of clustering on measles transmission dynamics during outbreaks. Significant differences in vaccination status, age, and hospitalization rates between cluster and non-cluster cases underscore the importance of targeted surveillance and intervention strategies while the wide range of R0 values observed in large outbreaks points to inconsistent control measures and emphasizes the need for strengthened vaccination campaigns and improved outbreak response protocols to better contain measles spread.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Cardiovascular Disease Burden in Rural Central Asia: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Trends and Mortality Patterns
by
Akerke Kassymkhan, Alma-Gul Ryskulova, Zhanara Buribayeva, Bakytgul Nurmukhambetova, Kenzhebek Bizhanov, Daria Nabok, Nargiza Nassyrova, Magripa Bapayeva and Erkin Mirrakhimov
Epidemiologia 2026, 7(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/epidemiologia7010010 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with a particularly high burden in Central Asian countries. Despite ongoing urbanization, rural populations constitute a significant demographic in this region, yet epidemiological data stratified by urban and rural residence are limited
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain a leading cause of mortality worldwide, with a particularly high burden in Central Asian countries. Despite ongoing urbanization, rural populations constitute a significant demographic in this region, yet epidemiological data stratified by urban and rural residence are limited and fragmented. This systematic review aimed to synthesize current evidence on the incidence, prevalence, mortality, and risk factor profiles of CVDs among urban and rural populations in Central Asia, identify disparities, and inform targeted prevention and control strategies. Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across the PubMed, Science Direct, Web of Science, and Google Scholar databases for studies published between 2015 and 2025. Included studies reported cardiovascular health indicators with urban–rural stratification in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan. Data extraction and qualitative synthesis were performed, with methodological quality assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. Results: Eight original studies met the inclusion criteria, encompassing national and regional datasets with diverse designs, including retrospective analyses, cross-sectional surveys, and registry data. Overall, CVD incidence and prevalence showed increasing trends in both urban and rural areas, with consistently higher mortality rates in urban populations. Key modifiable risk factors—hypertension, obesity, dyslipidemia, and smoking—were prevalent, particularly in rural settings. Variability in healthcare access and preventive program implementation contributed to the observed disparities. Limited data from some countries, particularly Tajikistan and Turkmenistan, highlight gaps in epidemiological surveillance. Conclusions: The cardiovascular disease burden in Central Asia demonstrates significant urban–rural disparities, underscoring the need for tailored public health interventions and enhanced healthcare resource allocation in rural regions. Strengthening epidemiological monitoring and implementing region-specific prevention programs targeting modifiable risk factors are imperative for reducing CVD morbidity and mortality. Further high-quality research is necessary to address existing data gaps and optimize cardiovascular health strategies across the region.
Full article

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Epidemiologia Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Diseases, Epidemiologia, Infectious Disease Reports, Medicina, TropicalMed
Surveillance Systems and Predictive Analytics for Epidemics
Topic Editors: Georgia Kourlaba, Elisavet StavropoulouDeadline: 31 January 2027
Topic in
AMH, Antibiotics, Epidemiologia, Microorganisms
Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Therapy
Topic Editors: Diamantis P. Kofteridis, Petros IoannouDeadline: 28 February 2027
Topic in
Children, Dietetics, Epidemiologia, Healthcare, Obesities, Medical Sciences, Diseases, Trends in Public Health
Dietary and Lifestyle Determinants of Non‑Communicable Diseases: Salt, Sugar, Alcohol and Physical Activity
Topic Editors: Kotsedi Daniel Monyeki, Machoene Derrick SekgalaDeadline: 30 April 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Epidemiologia
Psychiatric Comorbidities and Substance Use Among Individuals with Physical Health Issues and Chronic Diseases
Guest Editor: Jagdish KhubchandaniDeadline: 30 March 2026
Special Issue in
Epidemiologia
Local Healthcare Preparedness and Alert Systems—How to Prevent Future Pandemics?
Guest Editors: Giuseppe Stirparo, Alberto Arnedo-PenaDeadline: 15 April 2026
Special Issue in
Epidemiologia
Recent Advances in Acute Diseases and Epidemiological Studies
Guest Editors: Giuseppe Stirparo, Giuseppe RistagnoDeadline: 30 April 2026
Special Issue in
Epidemiologia
Advances in Environmental Epidemiology, Health and Lifestyle
Guest Editor: Rajendra Prasad ParajuliDeadline: 30 April 2026









