Abstract
Hair dyes are widely used cosmetic products that can contain trace metals and metalloids, posing potential health risks through dermal exposure. This study aimed to assess and compare the concentrations of selected metals and metalloids in six brands of commercial hair dyes sold in Brazil and Paraguay and to evaluate their average daily dermal exposure doses, hazard quotients, hazard indices, and carcinogenic risk. Concentrations of Cr, Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, As, Al, Pb, Ba, Ag, and Zn in hair dye were quantified by standardized analytical methods. The Paraguayan brand showed the highest levels for several elements, including As (4.17 mg/kg), Al (130.276 mg/kg), and Fe (30.033 mg/kg). Estimated dermal exposure doses reached up to 3.35 × 10−6 mg/kg/day for arsenic, 1.68 × 10−3 mg/kg/day for aluminum, and 8.59 × 10−8 mg/kg/day for chromium. Although all hazard indices remained below 1, suggesting low non-carcinogenic risk, the calculated carcinogenic risk for arsenic in the Paraguayan product was 1.23 × 10−5, entering the medium-risk range. These findings highlight relevant differences in raw material control and potential cumulative health risks, especially for frequent users. Continuous quality control, harmonized regulatory standards, clear labeling, and further biomonitoring studies are strongly recommended to minimize long-term exposure to toxic elements in hair dye formulations and to ensure safer consumer products.
1. Introduction
Hair dyes are among the most widely used cosmetic products worldwide, with millions of people applying them regularly to alter or maintain their hair color. In recent years, advances in analytical instrumentation have enabled more sensitive detection of trace metals and metalloids in cosmetics, revealing contaminants that may originate from raw materials, manufacturing processes, or packaging [1,2,3]. However, most existing investigations have been concentrated in Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa [4,5], with a marked scarcity of systematic research in Brazil and neighboring Latin American countries, despite their high consumption rates. In addition, while the toxicological hazards of heavy metals are well known, there is limited data on their specific occurrence, concentrations, and potential dermal risks in hair dye formulations marketed in several countries.
Heavy metal toxicity has been associated with beauty products such as lipsticks and hair dyes, prompting international health agencies, including the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the World Health Organization (WHO), to establish maximum permissible exposure limits for heavy metals in various cosmetic products [6]. However, the presence and permissible concentrations of metal components in hair dyes remain subject to country-specific regulations, which can vary considerably in their strictness and enforcement [7]. According to Naqvi et al. (2022) [8], in developing countries, the monitoring system is very poor or even absent, which leads to the violation of international standards. To address these concerns, the European Commission has imposed strict regulations on hair dye ingredients, including Directive 2012/21/EU and Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009, which limit or prohibit the use of certain harmful substances [9]. Nevertheless, studies show that metals banned under Annex II of Directive 76/768/EEC—such as antimony (Sb), arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni)—can still be found in cosmetics due to contamination during manufacturing [10].
This regulatory disparity, combined with inadequate enforcement in certain countries, creates an environment where contaminated products can still reach consumers. Evidence from studies indicates that certain brands of hair dyes may contain measurable levels of toxic metals, even when not intentionally added in the form of pigments. For instance, in Iran, 36 hair dye samples from popular brands revealed lead (Pb) and Cd within legal limits, but Cr, Ni, and Co exceeded allergenic thresholds [3]. Similar results were reported in Nigeria and Pakistan [4,5]. In Brazil, electroanalytical techniques have detected Pb2+ in progressive hair dyes [11]. However, comparable multi-element assessments, particularly in the Brazilian–Paraguayan border context, are lacking, where a significant portion of hair dyes is imported from other countries through informal trade channels. Such products often bypass official sanitary inspections, increasing the likelihood of contamination with heavy metals and metalloids. Therefore, the hair dye market is highly globalized, with products circulating across multiple countries. Detecting contamination in Brazil may serve as an early-warning signal for batches distributed to other markets, supporting cross-border recall and risk mitigation strategies.
Exposure to heavy metals can cause a wide range of health issues because these elements can be absorbed through the skin, inhaled, or ingested, accumulating in organs and tissues [12]. Heavy metals like lead, cadmium, and chromium pose significant health risks due to their bioaccumulative nature—once absorbed, they are not easily eliminated [12,13]. Studies have found lead in lipsticks and other cosmetics, while cadmium and chromium have also been detected in lip products, posing risks for chronic exposure. Hair dyes are no exception; their complex formulations often contain oxidizing agents, as well as potentially harmful heavy metals such as As and Pb [3,14].
The excessive presence of metals in hair dyes can cause potential endocrine disruption and carcinogenic effects [15]. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), which is part of the World Health Organization, occupational exposure of hairdressers and barbers to hair dyes is classified as probably carcinogenic to humans, mainly due to certain chemicals historically used in some hair dye formulations [16].
Lead, for instance, can severely affect cardiovascular, respiratory, and reproductive health, especially among pregnant women and young children [17]. The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified cobalt and its compounds as possible human carcinogens, with high-level exposure linked to respiratory issues and allergic reactions [18]. Even barium (Ba), generally used safely in medical imaging, can be extremely toxic if misapplied, as highlighted by a tragic poisoning case in Brazil in 2003 that resulted in multiple deaths [19]. In addition, long-term cadmium exposure is also a concern, with evidence showing that it can remain in the kidneys for decades and cause kidney dysfunction, bone fragility, and severe respiratory problems [20].
Metal allergy is a distinct category of hypersensitivity conditions in which different metallic elements can trigger an immune response mediated by the adaptive immune system. Out of the 92 metals in the periodic table, about half have limited or no known role in allergic reactions, but approximately 45 are recognized as having the potential to provoke allergies. According to the Contact Dermatitis Institute, 35 metals are currently identified as contact allergens, while the World Allergy Organization lists 11 metals capable of causing respiratory allergies. Some metals are well-established sensitizers, whereas others are linked to allergic reactions only rarely. What makes metal allergies unique is that people are consistently exposed to metals through multiple pathways, including skin contact with everyday products like cosmetics, tools, and electronics, inhalation of airborne metal particles, ingestion through diet and drinking water, and medical or dental procedures. Because of this wide range of exposure routes, allergic responses to metals can affect different organs and tissues throughout the body [21].
Given the potential risks of chronic exposure to Pb (lead), Cu (copper), Fe (iron), Cd (cadmium), Cr (chromium), Mn (manganese), Mo (molybdenum), Sr (strontium), Mg (magnesium), As (arsenic), Al (aluminum), Ag (silver), Ba (barium), and Ni (nickel) through hair dye use, comprehensive monitoring and rigorous chemical testing are essential to ensure product safety and protect public health. These specific elements were selected because they are among the most frequently quantified in previous studies on hair dyes and cosmetics [3,10,22,23,24] and are recognized for their toxicological relevance, with several being subject to international regulatory limits. While international studies have reported the presence of these metals in hair dye formulations, creams, and other cosmetics, there remains a significant gap in data regarding products sold in Brazil and Latin America more broadly. This gap is even more pronounced in border towns, where imports from third countries may bypass formal safety checks. This is particularly relevant for hair dye products imported or circulated informally through porous dry borders, such as the well-known frontier between Ponta Porã in Brazil and Pedro Juan Caballero in Paraguay [25]. This region is characterized by intense cross-border trade, including the entry of cosmetics, household chemicals, and personal care products that often bypass formal regulatory controls, raising additional public health concerns due to the increased risk of contamination with potentially harmful substances, including heavy metals and metalloids [10].
Therefore, this study aims to quantify Pb, Cu, Fe, Cd, Cr, Mn, Mo, Sr, Mg, As, Al, Ag, Ba, and Ni in hair dye products produced and marketed by different brands in Brazil, as well as one brand commercially available in Paraguay. The quantification of these elements will be carried out using Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP OES) analysis, which allows for sensitive and precise multi-element detection. Additionally, the study seeks to assess the potential health risks associated with dermal exposure to these metals through risk characterization indicators such as the hazard quotient (HQ), hazard index (HI), and cancer risk (CR).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Selection
A total of 32 samples of medium blonde hair dyes were selected for this study. The samples were purchased in June 2021 from pharmacies located in the city of Campo Grande/MS, Brazil. It is worth noting that five of the brands included in the study (with five samples of each) are sold in Brazil. On the other hand, one international brand with seven samples from different batches was purchased in Pedro Juan Caballero, Paraguay, on the border between Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil (Table 1).

Table 1.
Description of the permanent hair dye samples analyzed, including brand, quantity, and shade.
In this study, the medium blonde shade was specifically chosen as a representative sample for the quantification of heavy metals in hair dyes for several technical and practical reasons. First, medium blond tones are among the most popular shades commercially available in Brazil and across Latin America, widely used by consumers who seek moderate lightening or subtle color adjustments [23,24]. Second, medium blonde dyes typically require more complex formulations compared to darker tones because they often contain base pigments and bleaching agents such as titanium dioxide and peroxide compounds, which can increase the likelihood of metallic residues [10,22].
Furthermore, the application of medium blonde dye typically involves extended skin contact time on the scalp and requires frequent touch-ups to maintain the color, factors that directly increase the potential for dermal absorption of any residual metal(loid)s present. This makes this shade relevant for dermal exposure risk assessment, especially for calculating the Hazard Quotient (HQ) and Hazard Index (HI) for non-carcinogenic risks and for estimating carcinogenic risks [26].
Finally, the choice of Medium Blonde allows direct comparability with existing international data, as similar shades have been included in prior studies assessing heavy metal contamination and consumer health risks associated with hair dye use [23,24]. Therefore, the selection of this shade supports both the practical and scientific goals of the present investigation.
2.2. Sample Preparation for Digestion
All Falcon DAp60 (Berghof Products + Instruments GmbH, Ehningen, Germany) tubes used for ICP-OES analysis were carefully prepared to prevent contamination. First, the tubes were rinsed with ultrapure water and then immersed in 10% nitric acid (HNO3) for 24 h to remove any residual metals. Following the acid treatment, each tube was rinsed three times with ultrapure water and dried in an oven at 60 °C (Model: CBL EC-695VF, Company C.B.L., São Paulo, Brazil). This sterilization process ensured that the tubes were free of contaminants prior to sample handling.
Once the Falcon tubes were prepared, hair dye samples were digested using an adapted method from Pehlić et al. (2019) [27]. For each sample, 0.50 g of hair dye was accurately weighed on an analytical balance and transferred to individual DAp60 tubes. To achieve complete digestion, 1 mL of 35% ultrapure H2O2 (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), 5 mL of 65% ultrapure HNO3 (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), and 2 mL of ultrapure water (18 MΩ·cm, Milli-Q Biocel Water Purification System, Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) were added. Subsequently, all tubes containing the hair dye samples were placed in the microwave digestion system (Berghof Products + Instruments GmbH—Speedwave4 Microwave Digestion System, Ehningen, Germany) and subjected to the digestion program, which consisted of two steps with specific temperatures and pressure variations as detailed in Table 2. The samples were then cooled according to the program. For quality control, an analytical blank was prepared using the same reagent volumes as the hair dye samples. All digestions were carried out in triplicate to ensure reproducibility and reliability of the results.

Table 2.
Heating program for microwave digestion of hair dye samples.
2.3. Quantification of Metal(loid)s by ICP OES
After digestion, the hair dye samples were analyzed for quantification of Pb, Cu, Fe, Cd, Cr, Mn, Mo, Sr, Mg, As, Al, Ag, Ba, and Ni by inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy (ICP OES, iCAP 6300, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) under the conditions shown in Table 3. The spectral lines (wavelength) used for the quantification of the elements were selected with the assistance of the iTEVA 2.0 software, based on criteria of minimal spectral overlap and maximum emission intensity, aiming to reduce interferences and enhance the reliability of the measurements performed by ICP OES.

Table 3.
Operational parameters used for ICP OES analysis and wavelengths for each element.
The calibration curves for quantification of the element concentrations were prepared from standard solutions of 100 mg/L (SpecSol, Quinlab, Jacareí, São Paulo, Brazil) using ultrapure water (18 MΩcm, Milli-Q Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). External calibration curves were built on seven different concentrations in the range of 0.001–2.0 mg/L. The fundamental parameters to ensure the acceptability of the performance of our analytical method validation were the accuracy (recovery test), limit of detection (LOD), and limit of quantification (LOQ). The limit of detection (LOD) itself was calculated considering the standard deviation of multiple blank measurements (10 replicates) and the sensitivity (slope) of the calibration curve according to the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) [28]. Using the factor 3 ensures that the LOQ corresponds to a concentration where the analyte signal can be quantified reliably above background noise, with adequate reproducibility [28]. Thus, the solution was prepared to add 1000 ppm (100 mg/L) of an analyte to a sample, and a 0.25 mg/L recovery test was conducted. The values of LOD, LOQ, correlation coefficients (R2), and spike concentration obtained by external calibration are shown in Table 4. The method had a recovery interval of 82–110%. Then, the range of all elements LOD was 0.00029–0.0045 mg/L, and the range of all elements LOQ was 0.00087–0.0135 mg/L. The range of the correlation coefficient (R2) was 0.9869–0.9998.

Table 4.
Values of limits of detection (LODs), limits of quantification (LOQs), correlation coefficients (R2), and Spike concentration obtained by external calibration.
2.4. Exposure Assessment and Risk Characterization
To assess the levels of exposure to heavy metals resulting from the use of hair dyes, Equation (1) was applied, in which dermal exposure to heavy metals due to the use of hair colorants is estimated according to the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) [29].
For the calculation of Dermal Dose (CDDdermal (mg/kg/day) (Equation (1)) resulting from skin exposure to hair dyes, the following values were considered for the estimation: C (mg/kg): average concentration of metals in hair dye, obtained by spectroscopic techniques according to ICP OES; SA: exposed skin area; in this study, 5700 cm2 for adults [29]; SL: skin adherence factor; in this study, 0.07 mg/cm2·h for adults [29], or, for daily value, 16.8 mg/cm2·day; ABS: dermal absorption factor (unitless); in this study, 0.001 for all elements except for As, for which the value is 0.03 [29,30]; EF: 200 days/year (out of 365 days, assuming a person dyes their hair monthly, they spend approximately 200 days per year with dyed hair, i.e., an exposure frequency of 200 days/year); ED: 40 years, refers to the number of years during which hair dyes are used; BW: 70 kg, body weight considered according to values commonly reported in the literature; AT: ED × 365 days/year = 40 years × 365 days/year = 14,600 days [29,30].
In this study, an exposed skin area (SA) of 5700 cm2 was adopted for adults to estimate dermal exposure to metal(loid)s from hair dye application. This value represents a conservative estimate based on the typical scalp and adjacent skin regions (forehead, ears, neck) that may come into direct contact with the product during dyeing procedures. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) Exposure Factors Handbook (2011) and related cosmetic exposure studies, the scalp area of an adult human ranges from approximately 500 to 700 cm2, but when accounting for possible spillage, dripping, and manual application, additional skin areas can be exposed [31]. Considering that many users apply dyes at home, the inclusion of surrounding skin and potential secondary contact points justifies the use of a larger surface area. Therefore, the use of 5700 cm2 provides a protective estimate for potential dermal absorption of metals during hair dyeing.
2.5. Risk Quotient (HQ) and Hazard Index (HI)
Considering the information previously available, the non-carcinogenic health risk quotient (HQ) was calculated using Equation (2) [26,32]:
where CDDdermal was determined according to Equation (1), and RfD (mg/kg/day) is the dermal reference dose. The HQ is dimensionless; when HQ > 1, it suggests that adverse health effects may occur, whereas HQ < 1 indicates a lower probability of such effects. To estimate the overall potential for non-carcinogenic health risks resulting from exposure to multiple elements, the Hazard Index (HI) was calculated as the sum of individual HQs, assuming additive effects [26]. Thus, the HI (chronic hazard index) is obtained using Equation (3), which considers the sum of HQs derived from different elements or exposure scenarios [32,33]:
The RfD values (reference dose for dermal exposure, mg/kg/day) used for each element were as follows: Al = 1.0, Fe = 0.7, Cr = 1.95 × 10−2, Mg = not determined, Cu = 0.04, As = 3.00 × 10−4 [34], Mn = 9.60 × 10−4, Ba = 14.0, Ni = 5.40 × 10−3, Cd = 1.25 × 10−5, Mo = 5.00 × 10−3, Pb = 0.04, Sr = 1.2 × 10−1 [35,36]. The carcinogenic risk (CR) reflects the probability that an individual may develop cancer due to exposure to carcinogenic metals. To estimate CR [37], the dose (CDDdermal) is multiplied by the corresponding cancer slope factor (SF) as shown below:
where SF is the cancer slope factor for each element. For this study, a dermal cancer slope factor for Pb was given as 1.5, 20 for Cr, and 3.66 for As [37]. According to international guidelines, acceptable risk levels are between 10−6 and <10−4 for individual and combined carcinogens. The classification for carcinogenic risk levels is as follows: Risk <10−6: very low; 10−6–10−5: low; 10−5–10−4: medium; 10−4–10−3: high; 10−3: very high [38].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The results are expressed as the mean of the triplicates ± standard deviation. Origin 9.0 was used to perform the statistics. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess the normality of the data. One-way ANOVA was performed to determine whether there were significant differences in the mean concentrations of metals and metalloids among the brands (p < 0.05). Post hoc comparisons using Tukey’s HSD test confirmed which brand pairs differed significantly. In addition, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was conducted to investigate the multivariate relationships among the concentrations of Pb, Cu, Fe, Cd, Cr, Mn, Mo, Sr, Mg, As, Al, Ag, Ba, and Ni detected in different hair dye brands.
3. Results
3.1. Metal and Metalloid Concentrations in Hair Dye Brands
The quantified concentrations of metals and metalloids detected in the six Brazilian and Paraguayan hair dye brands are presented in Table 5. The elemental concentrations for each brand can be arranged in descending order as follows:

Table 5.
Concentration of metal(loid)s (mg/kg) quantified in hair dye brands sold in Brazil and Paraguay.
Brand 1: Al > Fe > Cr > Mg > As > Mn > Cu > Ba > Ni > Sr > Cd > Mo > Pb.
Brand 2: Al > Fe > Mg > As > Cr > Ni > Mn > Cu > Ba > Cd > Ag > Mo > Sr > Pb.
Brand 3: Al > Fe > Cr > Mg > Ag > Ni > Ba > Sr > Cu > Cd > Pb > Mo.
Brand 4: Al > Fe > Cr > As > Mg > Ni > Mn > Cu > Ba > Pb > Sr > Cd > Mo > Ag.
Brand 5: Al > Fe > Mg > Cr > As > Cu > Ni > Mn > Ba > Sr > Pb > Ag > Cd > Mo.
Brand 6: Al > Fe > Mg > As > Cr > Ni > Mn > Sr > Cu > Ba > Pb > Mo > Cd > Ag.
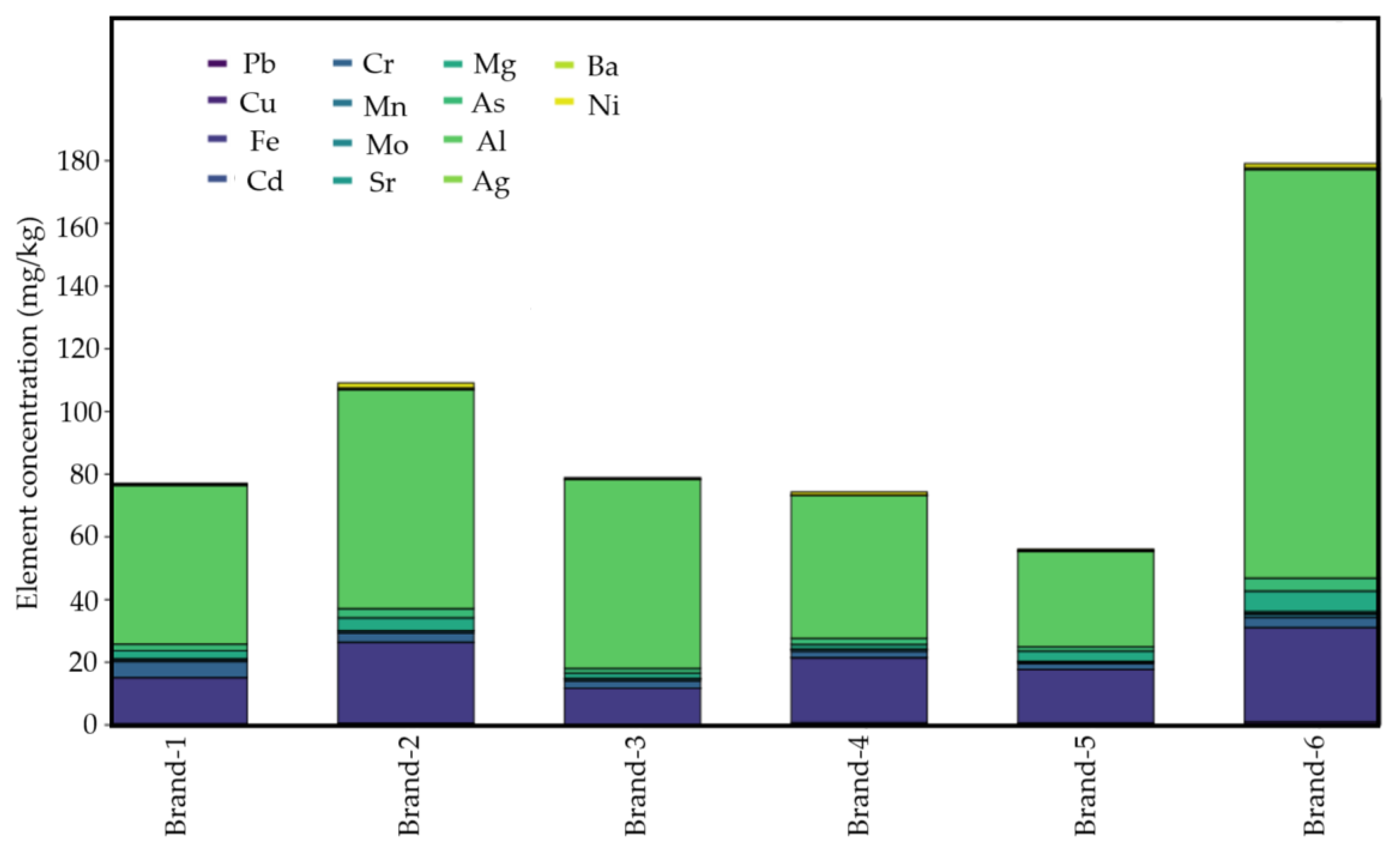
The results indicate that aluminum (Al) and iron (Fe) were consistently the most abundant elements across all brands, whereas elements such as cadmium (Cd) and silver (Ag) were generally present in the lowest concentrations. In addition, Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of element concentrations across the analyzed brands. Brand-6 exhibits the highest total concentration (≈180), followed by Brand-2 (≈110), while Brand-5 shows the lowest values (<60). The green group of elements (As, Al, Ag, Mg) accounts for the majority of the composition, whereas elements in blue/purple (Pb, Cu, Fe, Cd, Cr, Mn, Sr, Mo) are present in lower amounts. Ba and Ni (yellow) make only a minimal contribution.
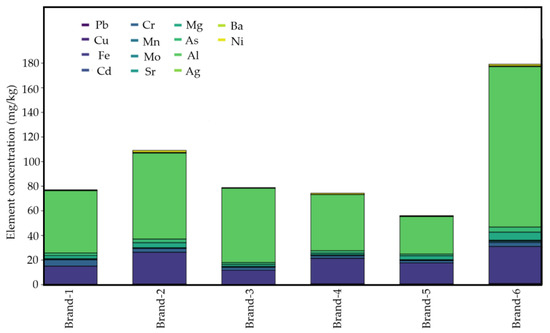
Figure 1.
Comparative element concentrations (mg/kg) across brands.
Statistical analysis of metal concentrations among the six studied hair dye brands revealed significant differences. The Shapiro–Wilk test indicated that there is normality. One-way ANOVA showed a highly significant difference in mean Pb concentrations between brands (F = 51.34; p < 0.001). Post hoc comparisons using Tukey’s HSD test confirmed that pairs of brands differed significantly. For example, Brand 1 showed significantly lower Pb levels compared to Brands 2, 4, and 6 (p < 0.01), while Brand 2 differed significantly from Brands 3 and 5 (p < 0.01). These results demonstrate that Pb concentrations vary significantly among commercial hair dye brands.
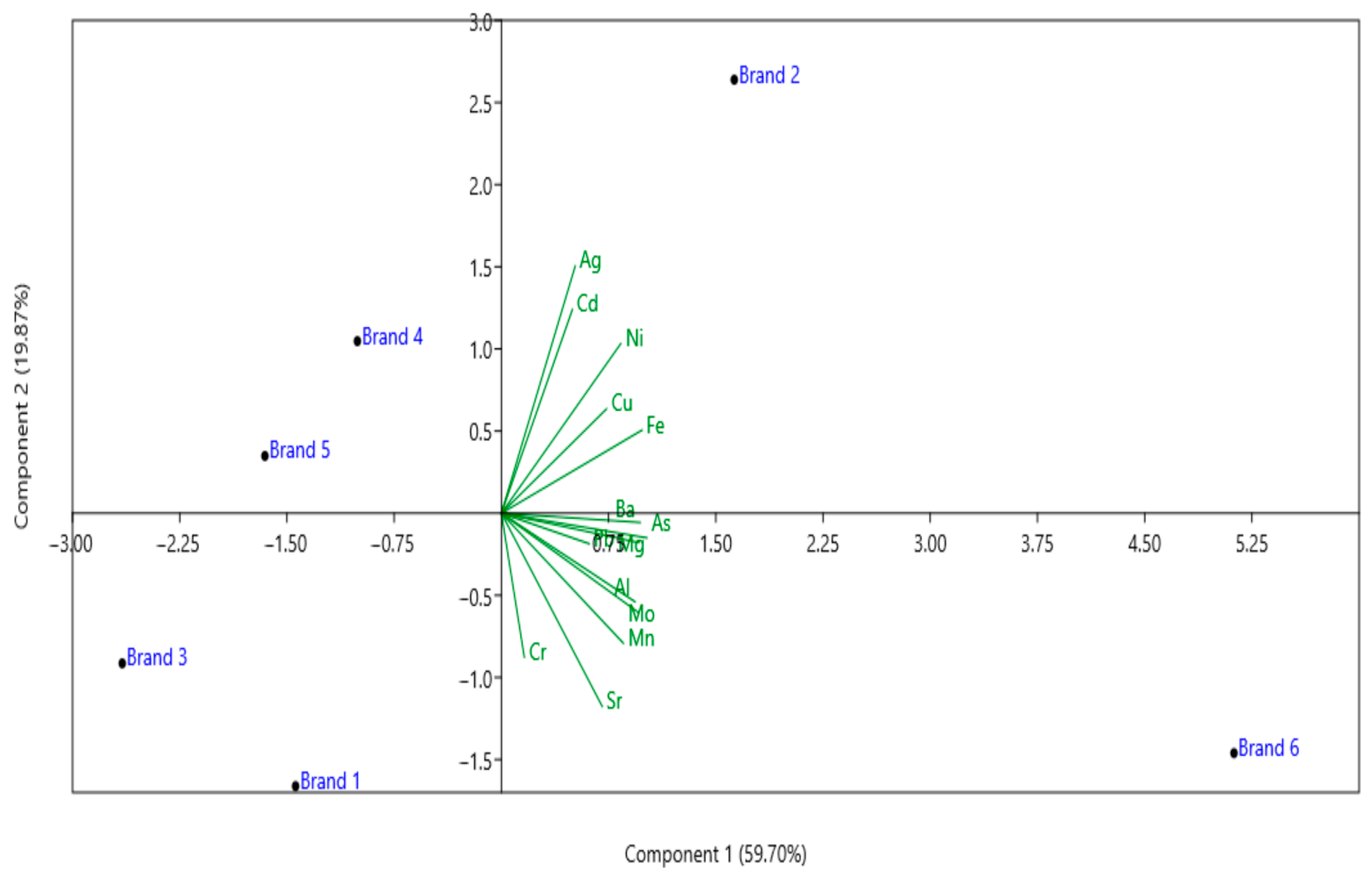
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used to explore the multivariate structure of metal and metalloid concentrations in hair dye samples (Figure 2). The first two principal components together explained approximately 79.57% of the total variance, evidencing clear clustering and dispersion patterns among the six brands analyzed. It is observed that brand 2 and brand 6 present more distinct chemical profiles, associated mainly with higher concentrations of Ag, Cd, Ni, Cu, Fe, Ba, and As, as indicated by the directed vectors. In contrast, brands 1 and 3 clustered in the same quadrant, suggesting similarity in composition, with a greater influence of Sr, Cr, Al, and Mo. Vectors pointing in the same direction indicate positive correlations between the elements, while opposite directions reflect inverse relationships. These results corroborate the findings of the univariate analyses, which already indicated significant differences (ANOVA/Tukey) in specific elements among some brands.
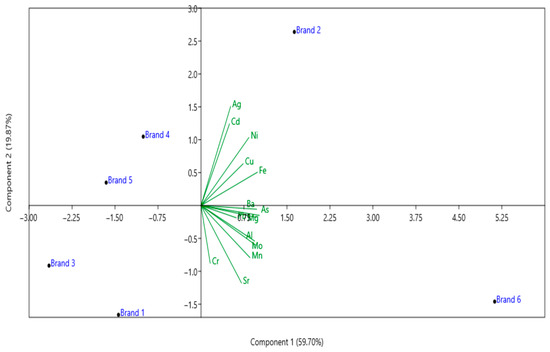
Figure 2.
Principal Component Diagram (PCA) representing the distribution of the six brands of hair dyes (Brand 1–5 (Brazil) and Brand 6 (Paraguay)) based on the metal and metalloid concentration profiles. The green arrows indicate the vectors of each chemical element analyzed, evidencing their contribution to the total variability. The distances between the brands reflect the similarity or dissimilarity in relation to the contents of the elements, while the direction of the vectors shows the relative influence of each metal/metalloid in the separation of the samples.
3.2. Assessment of Average Daily Dermal Exposure Dose (CDDdermal)
To assess the levels of exposure to heavy metals due to the use of hair dyes, Equation (1) was used, in which skin exposure to heavy metals and hair dyes is given by Ref. [29]. Table 6 presents the estimated average daily dermal dose (CDDdermal) for heavy metals quantified in six brands of hair dyes—five Brazilian and one Paraguayan. The calculated values, expressed in mg/kg/day, were obtained based on the measured concentrations and the standard parameters for dermal absorption (Equation (1)).

Table 6.
Average daily dermal exposure dose (CDDdermal) to heavy metals for adults (calculated using Equation (1)), based on dermal exposure to metals from five Brazilian hair dye brands and one Paraguayan brand.
A detailed ranking of the quantified elements for each hair dye brand underscores the varying potential for dermal exposure and absorption, which is particularly relevant for chronic users of hair coloring products. In Brand 1, the elements ranked in descending order of estimated dermal dose were: arsenic (As) > aluminum (Al) > iron (Fe) > chromium (Cr) > magnesium (Mg) > manganese (Mn) > nickel (Ni) > barium (Ba) > copper (Cu) > strontium (Sr) > lead (Pb) > molybdenum (Mo) > silver (Ag) > cadmium (Cd). In Brand 2, the order was: Al > As > Fe > Mg > Cr > Ni > Cu > Mn > Ba > Ag > Mo = Sr > Pb > Cd. Brand 3 showed the following pattern: Fe > Al > As > Mg > Cr > Ni > Mn > Cu > Sr > Ba > Ag > Pb > Mo > Cd. In Brand 4, the descending order was: Fe > As > Al > Mg > Cr > Ni > Mn > Cu > Ba > Sr > Ag > Mo > Pb > Cd. Brand 5 followed a similar trend: Fe > As > Al > Mg > Cr > Ni > Mn > Cu > Ba > Sr > Ag > Pb > Mo > Cd. Finally, the Paraguayan brand (Brand 6) revealed the highest overall potential for dermal intake, with the elements ranked as: Fe > As > Al > Mg > Cr > Ni > Mn > Cu > Sr > Ba > Pb > Mo > Ag > Cd.
3.3. Hazard Quotient (HQ), Hazard Index (HI), and Cancer Risk (CR)
Table 7 presents the hazard quotient (HQ) for individual heavy metals and the overall hazard index (HI) for dermal exposure in adults. The HQ is calculated as the ratio between the estimated dermal dose (CDDdermal) and the reference dose (RfD). An HQ value below 1 indicates that non-carcinogenic health risks are within acceptable limits, whereas HQ values above 1 suggest potential health concerns.

Table 7.
Hazard Quotient (HQ) and Hazard Index (HI) calculated for dermal exposure to heavy metals in adults from Brazilian and Paraguayan hair dye brands.
In this study, none of the metals individually exhibited HQ values greater than 1, indicating that the estimated levels of dermal exposure do not exceed international safety thresholds for non-carcinogenic effects. However, arsenic (As) showed the highest HQ values across all brands, with the highest found in Brand 6 (Paraguay) reaching an HQAs of 0.011. This highlights arsenic as the most critical element contributing to potential health risks.
Other elements, such as cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and nickel (Ni), also presented relatively higher HQs compared to the remaining metals analyzed. These elements are widely recognized for their cumulative toxicological relevance and their potential to cause adverse health effects through prolonged exposure.
The HI represents the sum of all HQs for each sample, thereby reflecting the cumulative non-carcinogenic risk associated with simultaneous exposure to multiple elements. In this study, HI values ranged from 3.74 × 10−3 (Brand 5) to 9.46 × 10−3 (Brand 2). Despite the fact that all HI values remained below 1, indicating an overall low combined risk under the estimated exposure scenario, they nevertheless reveal a non-negligible simultaneous exposure to several metals [26].
3.4. Carcinogenic Risk (CR) for Pb, Cr, and As
The results of the carcinogenic risk (CR) calculations for Pb, Cr, and As through dermal exposure in adults using Brazilian and Paraguayan hair dye brands are presented in Table 8. The estimates were based on an exposure frequency (EF) of 200 days per year (assuming the consumer dyes their hair monthly and therefore remains exposed for approximately 200 days each year) and an exposure duration (ED) of 40 years, representing a typical adult lifetime use of these products.

Table 8.
Carcinogenic Risk (CR) for Pb, Cr, and As through dermal exposure for adults (Brazilian and Paraguayan brands).
The results show that for all brands, the CR values for Pb remain in the very low category, while Cr and As reach the low risk range (10−6 to 10−5). This suggests that although the estimated dermal exposure does not pose a significant carcinogenic threat according to standard thresholds, continued monitoring and regulatory control are advisable, especially for arsenic and chromium.
The calculated CR values for lead (Pb) were all below 10−8, indicating a very low risk, far below the acceptable threshold for carcinogenic risk according to international guidelines (10−6–10−4). For chromium (Cr), the estimated risks ranged between 1.01 × 10−6 and 2.72 × 10−6, with all brands falling within the low-risk classification.
In contrast, the calculated CR values for arsenic (As) ranged from 3.99 × 10−6 to 1.23 × 10−5, showing that most brands fall within the low-risk range (10−6–10−5). However, the Paraguayan brand presented a CR for As slightly above 10−5, classifying it as a medium carcinogenic risk according to international benchmarks.
4. Discussion
In this section, the discussion of results will be presented in three parts. First, Section 4.1 Metal and Metalloid Concentrations in Different Brands of Hair Dyes and Brazilian and Paraguayan hair samples addresses the concentrations of metals and metalloids quantified in different brands of hair dyes sold in Brazil and Paraguay. This part discusses the concentrations found for the analyzed elements, highlighting relevant patterns and potential sources. Next, Section 4.2 Average Daily Dermal Exposure Dose (CCDdermal) examines the estimated daily dermal exposure doses, relating them to reference values and their potential implications for human health. Finally, Section 4.3 presents the results, providing an integrated overview of the non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks related to dermal exposure to these metals. The Hazard Quotient (HQ) and Hazard Index (HI) were calculated for all analyzed elements (Pb, Cd, Cu, Fe, Cr, Ni, Al, Ba, Ag, Mn, Mo, Sr, Mg, and As) to assess potential non-carcinogenic effects. In contrast, the Carcinogenic Risk (CR) was estimated only for lead (Pb), chromium (Cr), and arsenic (As), which are recognized as human carcinogens.
4.1. Metal and Metalloid Concentrations
Based on Table 5, the post hoc Tukey’s HSD test confirmed that the concentrations of metals and metalloids differed significantly between individual hair dye brands. The results showed clear variations in the levels of Pb, Cd, Cu, Fe, Cr, Ni, Al, Ba, Ag, Mn, Mo, Sr, Mg, and As among the six brands sold in Brazil and Paraguay, highlighting substantial differences in their elemental profiles and indicating that each brand presents a distinct contamination pattern. In addition, the PCA biplot (Figure 2) provides clear evidence of how the quantified heavy metals and metalloids contribute to the variance observed among the six hair dye brands analyzed. In this plot (Figure 2), the first principal component (PC1) explains 59.7% of the total variance, while the second principal component (PC2) accounts for an additional 19.87%, yielding a cumulative variance explanation of almost 79.57%. Therefore, these two components were considered sufficient to represent the multivariate structure of the data.
The Brazilian brands (1–5) are clustered predominantly on the left side of the PCA space, spread across the negative portion of PC1 and the vertical axis of PC2 (Figure 2). This indicates that these samples share a similar chemical profile, with relatively moderate or lower concentrations of the elements considered (Pb, Cd, Cr, Ni, Fe, Cu, As, etc.). The clustering of brand 1, brand 3, brand 4, and brand 5 in proximity confirms this shared profile, while brand 2 is slightly offset along PC2, reflecting subtle variation, possibly due to specific formulations or raw material differences.
In sharp contrast, in Figure 2, the Paraguayan brand (brand 6) is distinctly positioned far to the right along PC1, indicating a significantly higher combined contribution of multiple heavy metals and metalloids to its total variance. The clear separation of brand 6 from the cluster of Brazilian brands suggests that this product has a markedly different chemical signature, with higher loadings especially for elements like Al, Fe, Mg, Ni, and As, as indicated by the vector directions.
The strong projection of brand 6 along the same direction as the vectors for these elements confirms that this hair dye likely contains elevated concentrations of multiple target elements. This is consistent with the quantification results, which showed brand 6 leading for As (4.17 mg/kg), Al (130.276 mg/kg), and Fe (30.033 mg/kg), among others—all substantially higher than the average values for the Brazilian brands.
This pattern highlights potential regulatory and quality control disparities between domestic (Brazilian) and imported (Paraguayan) products. The chemical signature captured by PCA supports the inference that users of the Paraguayan dye may face a greater cumulative exposure risk, especially given the repeated nature of hair dye use. The positioning of brand 6 reinforces the need for harmonized standards for permissible levels of trace elements in cosmetic products across neighboring countries. In summary, the PCA clearly demonstrates that brand 1–brand 5 form a chemically consistent cluster typical of the Brazilian market, while brand 6 stands out with distinctly higher multi-element loadings, emphasizing the importance of cross-border surveillance and routine monitoring of imported cosmetic products to safeguard public health.
A critical comparison with recent international studies highlights important patterns, potential health risks, and regulatory gaps that warrant attention. In this study, the concentrations of various heavy metals and metalloids quantified in the six analyzed hair dye brands, as presented in Table 5, offer a solid basis for direct comparison with international data and previously published findings. Accordingly, our discussion examines the quantified elements in the sequence presented in Table 5, as detailed below.
As shown in Table 5, Pb levels in this study ranged from 0.011 to 0.318 mg/kg and Cd from 0.0204 to 0.0526 mg/kg. These values are up to 20 times higher for Pb and 15 times higher for Cd compared to Ahmed et al. (2019) [24], who reported 0.003–0.014 mg/kg Pb and 0.0015–0.0035 mg/kg Cd. They are also consistent with Mostafaii et al. (2022) [3], who found even higher concentrations in Iranian blond hair dyes (Pb: 1.45 mg/kg; Cd: 0.525 mg/kg), and with Khalili et al. (2019) [23], who detected Pb up to 0.228 mg/kg and Cd up to 0.00050 mg/kg in similar products. Although the Pb concentrations found here remain below the maximum limits for residual impurities set by Health Canada (10 mg/kg) [39] and Brazil (20 mg/kg) [40], cumulative exposure is still a concern, particularly with repeated use. For Cd, permissible limits are stricter—about 3 mg/kg in Health Canada and around 100 mg/kg in Brazilian regulations. While our Cd values did not exceed these thresholds, their presence indicates a toxic element capable of bioaccumulating through chronic dermal exposure. Such disparities between studies and regulatory frameworks point to inconsistencies in raw material control, manufacturing standards, and market oversight, underscoring the need for stricter quality monitoring and harmonized safety standards.
In this study (Table 5), copper (Cu) concentrations varied between 0.0314 and 0.688 mg/kg. When compared to values reported by Khalili et al. (2019) [23], who found a mean concentration of 0.06132 mg/kg for blond hair dyes, the lower bound of the present study is slightly below this mean value, whereas the upper bound is substantially higher. In contrast, Yashim et al. (2020) [4] reported considerably higher Cu levels, ranging from 3.50 to 65.10 mg/kg depending on the product type (pure dye, henna, black shampoo), which exceeds the concentrations observed in our study. This indicates that copper is frequently incorporated in hair dye formulations as a pigment or stabilizer, although its levels can vary significantly depending on the dye type and local production practices [4,23]. Health Canada has not defined regulatory limits for copper (Cu) concentrations in cosmetic products; conversely, Brazilian regulations stipulate a maximum allowable concentration of 100 mg/kg of Cu in cosmetics [40].
Iron (Fe) content ranged from 11.679 to 30.033 mg/kg, as reported in Table 5. Khalili et al. (2019) [23] found Fe at 1.19 mg/kg, which is notably lower than in the present samples. This difference may be due to formulation type or mineral additives used in some brands. In fact, the presence of iron (Fe) in cosmetic products, including hair dyes, is primarily due to its role as a pigment in the form of iron oxides. Yashim et al. (2020) did not quantify Fe [4], so direct comparison is limited. Furthermore, neither Health Canada nor Brazilian regulations establishes specific limits for Fe in cosmetics; however, for metals in general, Brazil sets a maximum allowable concentration of 100 mg/kg [40].
Table 5 shows chromium (Cr) concentrations spanning 2.026 to 5.073 mg/kg, which are higher than the levels reported by Amhimmid et al. (2022) [41] for light brown (0.70 mg/kg) and blond hair dyes (1.23 mg/kg). However, the concentrations found in Table 5 are lower than those observed for dark brown formulations (42.9 mg/kg) by the same authors. Similarly, Mostafaii et al. (2022) [3] and Yashim et al. (2020) [4] reported broader Cr ranges, with values reaching up to 32.9 mg/kg for blond hair dyes and 42.45 mg/kg for pure mineral dye, respectively. Compared to these, the Cr levels in the Brazilian and Paraguayan brands analyzed here are relatively low and below the 100 mg/kg maximum limit set by Brazilian regulations [40]. Notably, Health Canada has no established limit for Cr in cosmetics, highlighting regulatory discrepancies. These findings suggest variability in raw materials, formulation, and quality control across regions and manufacturers. The absence of harmonized global standards may result in inconsistent metal content in cosmetics, underlining the need for stricter regulation and enforcement to ensure product safety.
Nickel (Ni) levels were found to range from 0.266 to 1.611 mg/kg (Table 5). These values are considerably lower than those reported by Mostafaii et al. (2022) [3], who found Ni levels of 4.15 mg/kg in blond hair dyes, 2.35 mg/kg in light brown dyes, and 2.4 mg/kg in dark brown dyes. They are also significantly below the concentration of 7.40 mg/kg reported for pure mineral dyes by Yashim et al. (2020) [4]. Furthermore, the Ni concentrations detected in this study are far below the maximum allowable limit of 100 mg/kg for metals established by Brazilian regulations [40], indicating minimal regulatory concern for Ni levels in the analyzed hair dye samples. This reinforces that Ni is a recurring contaminant in hair dyes, primarily as an unintended impurity originating from pigments, metallic containers, or processing equipment.
The aluminum (Al) content in the samples varied between 30.473 and 130.276 mg/kg, as indicated in Table 5, which is substantially higher than the 0.41 mg/kg in blond hair dyes reported by Khalili et al. (2019) [23]. Moreover, the upper range of Al concentrations in our samples does not exceed the allowable limit for metals (100 mg/kg) established by Brazilian regulations [40]. On the other hand, these values are still considerably lower than the extremely high Al concentrations (142.10 mg/kg) found in henna (hair dye) products from markets in the West Bank, Palestine [42]. This discrepancy may be attributed to differences in pigment or extender additives, as well as possible contamination from processing equipment. Notably, neither Ahmed et al. (2019) [24] nor Yashim et al. (2020) [4] reported aluminum concentrations in their studies. It is also important to note that Health Canada has not established regulatory limits for aluminum in cosmetic products.
Barium (Ba) concentrations ranged from 0.201 to 0.584 mg/kg, according to Table 5. Khalili et al. (2019) [23] reported a slightly higher value of 0.86 mg/kg, which is still comparable. Amhimmid et al. (2022) found notably higher Ba concentrations in hair dye products, ranging from 1 mg/kg in light brown hair dye to 8.58 mg/kg in dark brown shades, showing that Ba content can vary significantly depending on product type and color [41]. However, few other studies detail Ba levels, which limits broader comparison. These findings suggest that Ba may be present in hair dyes either as an impurity or as an opacifying agent, consistent with its accepted use in cosmetics according to the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) [43]. Importantly, the Ba levels quantified here are significantly below the maximum allowable concentration of 100 mg/kg established by Brazilian regulations for metals in cosmetics [40]. Notably, Health Canada has not set specific regulatory limits for barium in cosmetic products.
Table 5 indicates silver (Ag) concentrations between 0.0157 and 0.0652 mg/kg, which is well below the maximum allowable limit of 100 mg/kg established by Brazilian regulations for metals in cosmetics [40]. While other authors occasionally discuss other metals [3,4,23,24,40,41,42], silver is not widely quantified in the other selected references, which limits broader comparisons. These differences likely reflect variations in formulations, raw materials, and manufacturing processes that may explain the trace levels of Ag found in the brands assessed in this study. It is important to note that Health Canada does not currently specify regulatory limits for silver in cosmetic products.
Few comparative studies have reported manganese (Mn), molybdenum (Mo), strontium (Sr), and magnesium (Mg) in hair dyes. Their small concentrations likely originate from mineral impurities in raw materials or pigments. In Table 5, values such as Mn (up to 1.068 mg/kg), Mo (0.194 mg/kg), Sr (0.679 mg/kg), and Mg (6.496 mg/kg) align with those in similar matrices, though robust benchmarks are scarce. Khalili et al. (2019) [23] found Mn below detection limits in several brands. Compared to Brazil’s regulatory threshold of 100 mg/kg for these metals [40], the detected levels are much lower, indicating compliance. The lack of reference data, however, limits assessment of long-term exposure and bioaccumulation, despite notable concentrations of these elements in human hair samples, including those from cancer patients [44].
Arsenic (As) levels varied from 1.360 to 4.170 mg/kg (Table 5), exceeding the maximum concentration established by Health Canada and Brazil of 3 mg/kg [39,40]. The levels found here are significant enough to warrant more detailed risk assessments, especially given that As bioaccumulates. These findings are consistent with the study by Amhimmi et al. (2022) [41], which reported As concentrations in hair dye brands from the Libyan market ranging from 1.27 mg/kg in light brown dyes to 5.14 mg/kg in dark brown dyes. This similarity suggests that elevated arsenic levels in hair dyes may be a widespread issue across different markets, underscoring the need for regulatory oversight and consumer awareness
4.2. Average Daily Dermal Exposure Dose (CDDdermal)
The average daily dermal exposure dose (CDDdermal) for each metal or metalloid varied across the analyzed hair dye brands, highlighting differences in potential dermal risk (Table 6). For Pb, for instance, dermal exposure ranged from 2.95 × 10−10 mg/kg/day (Brand 1) to 8.52 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). Lead is highly toxic, with no safe blood concentration, especially for pregnant women. It may accumulate even through low-dose dermal contact over time, building up in tissues or organs and activating pathways that lead to cell death through apoptosis and necrosis [45].
For copper (Cu), dermal exposure dose values varied between 9.49 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 1) and 1.76 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). Although copper is an essential micronutrient, prolonged dermal exposure can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals [46].
The dermal exposure dose values of Fe ranged from 3.13 × 10−7 mg/kg/day (Brand 3) to 8.13 × 10−7 mg/kg/day (Brand 6) (Table 6). Iron is not significantly absorbed through intact skin; however, iron particles may cause mild irritation or skin staining. In addition, iron toxicity is classified as either corrosive or cellular. At the cellular level, excess iron disrupts metabolic processes in the heart, liver, and central nervous system. Free iron enters cells and accumulates in mitochondria, where it interferes with oxidative phosphorylation, catalyzes lipid peroxidation, and promotes the formation of free radicals. These processes shift metabolism toward anaerobic pathways and ultimately result in cell death [47].
As Table 6 shows, the cadmium (Cd) dermal exposure dose ranges from 5.47 × 10−10 mg/kg/day (Brand 3) to 1.41 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). No studies were located regarding death in humans after dermal exposure to cadmium. Cadmium compounds, particularly their colored salts, have historically been used as cosmetic pigments. Although dermal absorption of cadmium through cosmetic use is generally minimal, it remains linked to various adverse health effects. Topical exposure may cause local irritant dermatitis in some individuals [48].
In Table 6, for chromium (Cr), dermal exposure presented doses from 5.04 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 5) to 8.59 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 6); hexavalent chromium is a potent skin sensitizer and a frequent cause of allergic contact dermatitis. Dermal exposure to chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)), may cause irritant and allergic contact dermatitis, as well as ulcerations known as ‘chrome ulcers’ that can penetrate deep into the skin and underlying tissues. These effects are frequently observed in workers handling chromium compounds in industries such as electroplating, tanning, and construction. While systemic absorption through intact skin is limited, damaged skin can allow greater penetration, contributing to the total body burden. No human deaths have been reported solely from dermal exposure to chromium; however, chronic skin contact remains an important occupational hazard due to its local and sensitizing effects [49].
The manganese (Mn) dermal exposure dose in Table 6 ranged from 1.22 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 5) to 2.86 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). Regarding dermal toxicity, manganese (Mn) presents a very low risk of significant absorption through intact human skin. According to the ATSDR Toxicological Profile for Manganese, cutaneous exposure to manganese compounds generally does not result in systemic toxicity, as percutaneous penetration is minimal. The main concern is localized irritation or mild contact dermatitis, which may occur with repeated or prolonged skin contact, particularly in occupational settings where manganese dust or solutions are handled without appropriate protection. Overall, manganese is not classified as a dermal carcinogen, and the primary preventive measure involves standard protective equipment and good hygiene practices [50].
In this study (Table 6), molybdenum (Mo) showed exposure ranging from 2.60 × 10−10 mg/kg/day (Brand 3) to 5.20 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). Molybdenum (Mo) is not commonly discussed in cosmetics but may appear as a trace contaminant. Available toxicological data indicate that molybdenum has minimal direct dermal toxicity. According to the ATSDR, no significant skin effects were observed in rats following 24 h dermal application of high doses of molybdenum compounds. Some animal studies reported alopecia and mild dermatosis, but these were associated with oral exposure and are likely related to copper deficiency induced by high molybdenum intake rather than a direct dermal effect. Overall, systemic toxicity through intact skin appears negligible, with local irritation risk being minimal under normal laboratory conditions [51]
The Sr dermal exposure in this study (Table 6) ranged from 4.13 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 4) to 1.82 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). Although Sr is not considered highly toxic at low levels, excessive exposure can affect bone metabolism due to its chemical similarity to calcium. Strontium, whether stable or radioactive, behaves similarly to calcium in the human body. Absorption depends on the exposure route and the compound’s solubility: soluble forms are rapidly absorbed through the lungs, while insoluble particles may persist for years. Gastrointestinal absorption averages about 20% in humans but can be higher in neonates. Dermal absorption is negligible through intact skin but increases with cuts or abrasions. Strontium does not undergo metabolic transformation but forms complexes with proteins, inorganic anions, and organic acids. Due to its storage in bone, the estimated terminal elimination half-life in humans is approximately 25 years, although faster clearance occurs from soft tissues and more exchangeable bone fractions [52]. Regulatory limits are not clearly established for Sr in cosmetics, reinforcing the need for monitoring.
As indicated in Table 6, the dermal daily exposure for Mg ranged from 6.66 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 1) to 1.74 × 10−7 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). Magnesium is used in many topical formulations with negligible toxicity and may cause only minor irritation in rare cases [9]. Magnesium (Mg) is an abundant element used as a filler or pigment in various cosmetic formulations. In addition to its role as a formulation component, magnesium has demonstrated beneficial effects on skin physiology, particularly in promoting dermal repair and regeneration. According to studies, topical application of magnesium significantly promotes the healing process in pre-clinical burn wounds by enhancing re-epithelialization, modulating inflammation, and stimulating fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis [53]. Magnesium ions are involved in various cellular activities within the dermis, including the regulation of cell migration and protein synthesis, which are critical for restoring the structural integrity of injured skin. Moreover, magnesium exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects that help mitigate tissue damage and accelerate wound closure. These findings highlight the dual relevance of magnesium: while it contributes to the physical properties of hair dye formulations, it may also offer a protective or reparative benefit to the scalp and surrounding skin [53,54].
According to Table 6, overall, arsenic (As) showed the highest dermal exposure doses among all evaluated elements. The Paraguayan Brand 6 recorded the highest As dose (3.35 × 10−6 mg/kg/day), exceeding the average values found in Brazilian brands (e.g., Brand 2 = 2.32 × 10−6 mg/kg/day). Arsenic is recognized as a well-established human carcinogen, classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as Group 1, with sufficient evidence linking chronic exposure to various cancers, including skin cancer (IARC, 2012) [55]. Although inhalation and ingestion are the primary routes of arsenic exposure, dermal absorption can also contribute significantly to systemic accumulation, especially under repeated or prolonged contact with contaminated water or soil. According to the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), inorganic arsenic compounds can penetrate the skin barrier, particularly when the skin is damaged, facilitating entry into the bloodstream and increasing the internal dose [56]. Dermal exposure to arsenic has been associated with local effects such as hyperkeratosis, melanosis, and skin lesions that may progress to malignancies over time [55,56]. Therefore, in the context of hair dye products, occupational and consumer exposure involving direct skin contact with arsenic-containing compounds should be considered a relevant route for both local and systemic toxicity.
As presented in Table 6, aluminum (Al) was another element of concern, with Brand 2 reaching the highest CDDdermal (1.68 × 10−3 mg/kg/day), significantly above other brands. In contrast, Brand 5 showed the lowest value (8.17 × 10−7 mg/kg/day). In the context of hair dye formulations, aluminum compounds may be present as pigments, opacifiers, or stabilizing agents. Although aluminum is not readily absorbed through intact skin, a small amount may enter the body through dermal contact [57]. According to the Toxicological Profile for Aluminum, there is limited evidence of significant dermal toxicity in humans, but some individuals may develop skin rashes or irritation after repeated application of certain aluminum compounds, such as aluminum chloride in ethanol or alum solutions. Experimental studies have reported skin damage in animals like mice, rabbits, and pigs following direct application of aluminum chloride or aluminum nitrate, whereas other forms—such as aluminum sulfate, aluminum hydroxide, aluminum acetate, or aluminum chlorhydrate—did not produce comparable effects. Importantly, no substantial histological skin changes were observed in rodents exposed to aluminum chlorhydrate by inhalation for prolonged periods. Therefore, in the case of hair dye use, aluminum-containing ingredients are unlikely to pose significant risks of dermal toxicity for users under normal cosmetic application, although sensitive individuals may experience minor skin irritation. Appropriate handling and formulation controls should be considered to minimize potential skin reactions among frequent users or professionals exposed to hair dyes containing aluminum compounds [57].
Table 6 reveals that silver (Ag) showed dermal exposure values ranging from 4.21 × 10−10 mg/kg/day (Brand 1) to 1.74 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 2); although dermal absorption is minimal, prolonged use can lead to localized argyria in extreme cases [54]. Silver (Ag) is widely used in consumer products, including cosmetics and topical antiseptics, due to its antimicrobial properties. According to the Toxicological Profile for Silver by the ATSDR (1990) [58], metallic silver and silver compounds can be absorbed through the skin, although dermal absorption is generally low under normal conditions. Repeated or prolonged skin contact with silver compounds, especially soluble forms such as silver nitrate, can lead to localized effects like skin irritation and discoloration [58]. One well-documented condition is localized argyria, which manifests as bluish-gray pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes due to the deposition of silver particles in dermal tissues [59]. While argyria is primarily a cosmetic concern and not associated with severe systemic health effects, chronic dermal exposure to high concentrations of silver-containing compounds can contribute to systemic accumulation. Experimental studies have also noted mild skin irritation and, in some cases, allergic contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals following topical application of silver preparations. In the context of cosmetic products like hair dyes, the risk of significant dermal toxicity from silver is considered low when good manufacturing practices and regulated limits for silver content are followed, but prolonged or excessive exposure should be avoided to prevent potential skin discoloration and sensitization [58].
Based on Table 6, barium (Ba) was detected with daily dermal doses ranging from 5.40 × 10−9 mg/kg/day (Brand 4) to 1.56 × 10−8 mg/kg/day (Brand 6). According to Johnson et al. (2018) [43], barium sulfate has a long history of safe medical and cosmetic use, with no significant systemic toxicity concerns and no evidence of sensitization risk based on extensive clinical experience and patch testing. Nonetheless, as salts of sulfuric acid can cause skin irritation, formulations containing barium sulfate should be designed to be non-irritating. No human studies have reported clear dermal toxicity related to barium contact under typical environmental or occupational conditions. Animal studies also provide minimal data, and available findings do not indicate marked skin absorption or dermal hazard from barium salts. However, certain soluble barium compounds could potentially cause skin or eye irritation upon direct and repeated contact. Therefore, while the risk of systemic toxicity from dermal exposure to barium in cosmetic products such as hair dyes is expected to be low, basic protective measures and formulation controls should be considered to prevent possible local irritation, especially when handling soluble barium salts [60].
In Table 6, nickel (Ni)—a common allergen with well-documented dermatological sensitization potential—showed its highest dermal doses in Brand 2 (4.32 × 10−8 mg/kg/day) and Brand 6 (3.62 × 10−8 mg/kg/day). Nickel is a well-known skin sensitizer and one of the most common causes of allergic contact dermatitis worldwide [61]. Direct skin contact with nickel or nickel-containing compounds can trigger local hypersensitivity reactions, particularly in sensitized individuals. Symptoms often include itching, erythema, and eczema at the site of contact. Chronic exposure to nickel through personal care products, jewelry, or occupational activities is a major contributor to the high prevalence of nickel-induced dermatitis. Moreover, systemic contact dermatitis can occur in nickel-sensitive individuals following dietary intake of nickel, demonstrating that both dermal and systemic exposure routes are relevant for nickel toxicity [62]. In the context of hair dye formulations, the presence of trace levels of nickel may pose a risk of allergic reactions, especially for users with pre-existing nickel sensitivity. Therefore, minimizing residual nickel content in cosmetic ingredients is important to reduce the potential for contact dermatitis and to comply with regulatory restrictions for nickel release in consumer products.
Comparatively, the Paraguayan Brand 6 generally displayed higher exposure doses for most metals, indicating potential differences in regulatory enforcement or raw material sourcing compared to the Brazilian brands.
This distribution pattern is critical because the skin can act as a direct pathway for toxic elements to enter the human body, especially when hair dyes are applied frequently and remain in contact with the scalp for prolonged periods. Elements such as arsenic (As), lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), and nickel (Ni) are of particular concern due to their well-documented potential for percutaneous absorption, bioaccumulation, and association with carcinogenic and allergenic effects. Notably, the Paraguayan sample (Brand 6) exhibited the highest dermal exposure estimates for key toxic elements (As, Fe, Al, and Mg), which supports the results of the principal component analysis (PCA) showing this brand as distinct in its risk profile.
Given that the dermal route can contribute significantly to total body burden for these metals—especially for frequent users—the results emphasize the need for regulatory oversight, clearer labeling, and risk communication regarding the cumulative impact of heavy metals absorbed through the skin. Moreover, these findings align with evidence from recent studies indicating that even trace levels, when absorbed dermally over time, may pose health risks, including irritation, sensitization, systemic toxicity, and carcinogenicity [23,24].
Overall, while the absolute dermal doses are low, the presence of multiple toxic or sensitizing elements in hair dye formulations justifies concern regarding cumulative and repeated exposure, especially for people who use hair dyes frequently or for occupationally exposed professionals.
4.3. Hazard Quotient (HQ), Hazard Index (HI), and Carcinogenic Risk (CR) for Pb, Cr, and As
According to Table 7, arsenic was the primary contributor to the total HI in all brands analyzed, followed by cadmium and nickel. Although other metals, such as lead (Pb), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and molybdenum (Mo), presented low HQ values individually, their contribution becomes relevant in the cumulative risk assessment.
These results underscore the need for rigorous quality control during production processes and regulatory oversight for cosmetic products such as hair dyes, especially to limit levels of elements like arsenic, cadmium, and nickel. It is important to note that these estimates assume standard conditions of use; variations in frequency, duration, or application practices may significantly affect actual exposure levels.
Finally, although the combined risk estimates remain below international thresholds for concern, the potential for long-term accumulation and chronic effects due to repeated dermal absorption cannot be disregarded. Therefore, continuous monitoring, stricter regulatory standards, and improved consumer awareness are strongly recommended to ensure safe use of these products and to minimize potential health impacts associated with chronic low-level exposure to heavy metals.
According to the USEPA and other international guidelines, the non-carcinogenic hazard quotient (HQ) should ideally remain below 1 to indicate negligible risk. For carcinogens like arsenic and chromium, the acceptable lifetime cancer risk is often set between 1 × 10−6 and 1 × 10−4, with values above 1 × 10−4 generally considered unacceptable for consumer products.
Therefore, despite the relatively low daily dermal exposure values found for each metal individually (Table 7), the cumulative exposure (HI) to multiple metals in frequent and prolonged use can pose a significant health risk. This is particularly relevant for products such as hair dyes, which are applied close to the scalp, increasing absorption potential due to thinner skin and possible microlesions.
These results reinforce the need for stricter quality control, continuous monitoring, and clearer labeling to limit consumer exposure to heavy metals in cosmetic products. Regulatory agencies should also align with international best practices to ensure consumer safety and reduce the health risks associated with chronic exposure to toxic and carcinogenic elements.
When comparing our findings (Table 7) with previously published studies, the magnitude of HQs for lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) is noteworthy. For example, Khalili et al. (2019) [23] reported HQs for Pb reaching 7.46 × 10−4 and an HI of 2.8 × 10−4 for domestic hair dyes sold in Iran, values that, although below 1, suggest relevant cumulative exposure through frequent use. Similarly, Mostafaii et al. (2022) demonstrated that the combined exposure to Pb, Cr, Ni, and Co in hair dye products sold in Kashan, Iran, resulted in measurable HQs and HIs [3], confirming the dermal route as an important pathway of concern. In our study, some individual HQs for Pb, Cr, and As approach or slightly exceed levels that require closer scrutiny, especially considering chronic exposure scenarios typical of regular hair dye use.
Moreover, the calculated HI values for some brands approach thresholds reported in the literature. For instance, Ahmed et al. (2019) highlighted that even low metal concentrations can contribute to cumulative risk detectable in users’ biological samples, demonstrating the bioavailability of metals like Pb and Cd from repeated dermal contact [24]. While our study focused exclusively on dermal exposure, the HQ and HI patterns reinforce that cumulative exposure through the scalp—where skin is thinner and often abraded by dyeing processes can facilitate significant metal absorption over time, especially for elements with low permissible exposure levels.
Overall, the comparison demonstrates that, while none of the calculated HI values in this study exceeds the critical value of 1—implying no immediate non-carcinogenic health effect—some individual HQs for priority elements (e.g., Pb, As, Cr) emphasize the importance of considering cumulative exposure, product labeling, and tighter regulation. These observations are consistent with the global literature, which repeatedly calls for monitoring toxic metals in cosmetic formulations due to the potential health impact of chronic dermal absorption [3,23,24].
According to results in Table 8, the calculated CR values for Pb were consistently low across all brands, remaining well below 10−8, which is classified as a very low risk according to other international studies [32,38,41]. This indicates that, under the evaluated conditions, the likelihood of carcinogenic outcomes specifically attributable to lead content in these hair dyes is negligible. For Cr, the CR values ranged from 1.01 × 10−6 to 2.72 × 10−6. Although still within the acceptable limit (10−6–10−4) [36], these values place Cr in the low-risk category, with the highest values found in Brand 1. Chromium is of particular concern because certain chemical forms, such as hexavalent chromium (Cr VI), are well-documented human carcinogens with proven dermal absorption potential [55,63]. The presence of Cr in this range reinforces the need for continuous surveillance of its concentrations in consumer products.
The most critical results were found for arsenic (Table 8), with CR values ranging from 3.99 × 10−6 (Brand 5) to 1.23 × 10−5 (Brand 6, Paraguayan origin). For most brands, CR values for As fell within the low-risk range (10−6–10−5); however, the estimate for the Paraguayan product marginally exceeded the lower threshold of the medium-risk category (>10−5). While this exceedance is minimal and within the range of potential analytical and model-related uncertainty, it still warrants attention, given arsenic’s classification by the IARC as a Group 1 human carcinogen and its high dermal absorption efficiency and cumulative toxicity even at trace levels [55]. This slight elevation above the threshold, despite uncertainty bounds, underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and rigorous quality control of such products.
Although the absolute CR values for hair dyes are within acceptable risk levels [32,38,41], the simultaneous presence of multiple carcinogenic elements increases the concern about cumulative risk and the potential for additive or synergistic effects, especially in individuals with prolonged and repeated exposure over decades. This aligns with regulatory frameworks such as the European Union Cosmetics Regulation (Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009) [9], which prohibits or restricts the use of hazardous substances in cosmetic products. In addition, it is important to highlight that these estimates are conservative because they do not account for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women, adolescents, or individuals with compromised skin barriers, which could significantly increase dermal absorption and overall susceptibility. Factors such as frequency of use, scalp microabrasions, and concurrent exposure to other products may also elevate actual exposure levels beyond modeled scenarios.
Taken together, the findings underline the importance of establishing continuous quality control measures, clear labeling of trace metals in personal care products, and harmonized regulatory monitoring across borders. The presence of higher CR values for arsenic in the Paraguayan brand compared to Brazilian products may also reflect differences in raw material sourcing, processing standards, or local regulatory enforcement, suggesting the need for stronger regional harmonization and market surveillance.
Finally, this study supports recommendations for further toxicological investigations, including biomonitoring studies and bioavailability tests, to better understand actual systemic absorption under real-life conditions. Such actions are essential to safeguard consumer health and to align domestic regulations with international best practices for cosmetic product safety.
Overall, these results highlight that while the estimated risks for individual elements generally remain within internationally acceptable ranges for carcinogenic exposure, continuous monitoring is recommended, especially for As in some brands, to ensure long-term consumer safety. These findings reinforce the importance of assessing metal contaminants in personal care products and aligning national regulations with international safety standards.
5. Conclusions
This study provides clear evidence that hair dyes sold in Brazil and Paraguay contain varying concentrations of metals and metalloids, with significant differences observed among brands. The principal component analysis (PCA) highlighted a distinct chemical profile for the Paraguayan product, which showed higher concentrations of several toxic elements, including arsenic, iron, and aluminum, compared to the Brazilian brands.
The estimated average daily dermal exposure doses (CDDdermal) for key elements, while generally low in absolute terms, reveal that cumulative exposure through frequent and repeated hair dye application can contribute meaningfully to total body burden. Particular concern is warranted for arsenic, lead, chromium, and nickel due to their known carcinogenic and allergenic properties and their capacity for dermal absorption.
The calculated hazard quotients (HQ) and hazard indices (HI) remained below international thresholds for non-carcinogenic risk, indicating no immediate health threat under standard use. However, the hazard quotients for some elements approach levels that justify continued scrutiny, especially considering the real-life scenario of repeated exposure over many years. Notably, the carcinogenic risk (CR) for arsenic in the Paraguayan brand exceeded the lower limit of the medium-risk range, underscoring the need for stricter control of raw materials and better harmonization of regulations across borders.
Overall, these findings emphasize the importance of strengthening quality control measures, routine monitoring of metal impurities in cosmetic products, and transparent labeling to inform consumers of potential cumulative risks. Regulatory agencies should align national standards with international best practices to protect public health, particularly for frequent users and vulnerable groups such as pregnant women and individuals with compromised skin barriers.
Finally, further research, including biomonitoring and real-life bioavailability studies, is recommended to better understand the long-term health implications of chronic dermal exposure to trace metals in hair dye products.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.M.d.S. and M.A.P.A.; methodology, G.M.d.S.; software, M.L.B.V.; validation, E.S.d.P.M. and O.D.L.; formal analysis, R.S.d.C.F.C., A.C.P.L., A.C.L.C. and A.L.F.d.O.; investigation, A.C.P.L. and M.L.B.V.; resources, V.A.d.N.; data curation, V.A.d.N.; writing—original draft preparation, V.A.d.N.; writing—review and editing, V.A.d.N.; visualization, D.A.Z.G., A.d.S.A.J. and O.D.L.; supervision, V.A.d.N.; project administration, V.A.d.N.; funding acquisition, V.A.d.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), Brazil (CNPq: Process N° 314551/2023-9) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Federal University of Mato Grosso do Sul, Faculty of Medicine, for their scientific support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Cr | chromium |
| Cd | cadmium |
| Co | cobalt |
| Cu | copper |
| Fe | iron |
| Mn | manganese |
| Mo | molybdenum |
| Ni | nickel |
| As | arsenic |
| Al | aluminum |
| Pb | lead |
| Ba | barium |
| Ag | silver |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| IUPAC | International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry |
| ICP OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy |
| OJEU | Official Journal of the European Union |
| ATSDR | Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry |
| HQ | Hazard Quotient |
| HI | Hazard Index |
| CR | Cancer Risk |
| USEPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| ANVISA | Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária |
References
- Lavilla, I.; Cabaleiro, N.; Costas, M.; DE LA Calle, I.; Bendicho, C. Ultrasound-assisted emulsification of cosmetic samples prior to elemental analysis by different atomic spectrometric techniques. Talanta 2009, 80, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Yu, T.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ren, Q.; Shen, H. Investigation on the 2D-Distribution of Metallic Elements after Hair Dyeing. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafaii, G.; Karamali, F.; AbooSaedi, Z.; Atoof, F.; Hesami Arani, M.; Miranzadeh, M.B. Determination of Heavy Metals in Hair Dye Sale in Iranian Market: Dermal Sensitivity and Carcinogenicity Assessment. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashim, Z.I.; Dallatu, Y.A.; Bolarin-Akinwade, O.O.; Obebe, E.O. Evaluation of heavy metals level in hair dyes and their potential health risk. Niger. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2020, 8, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, H.; Mehmood, M.Z.; Shah, M.H.; Abbasi, A.M. Evaluation of heavy metals in cosmetic products and their health risk assessment. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA’s Testing of Cosmetics for Arsenic, Cadmium, Chromium, Cobalt, Lead, Mercury, and Nickel Content [Internet]; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/cosmetics/potential-contaminants-cosmetics/fdas-testing-cosmetics-arsenic-cadmium-chromium-cobalt-lead-mercury-and-nickel-content (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Official Journal of the European Union (OJEU). Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on Cosmetic Products; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2009; pp. 59–208. [Google Scholar]
- Raza-Naqvi, S.A.; Idrees, F.; Sherazi, T.A.; Anjum-Shahzad, S.; Ul-Hassan, S.; Ashraf, N. Toxicology of heavy metals used in cosmetics. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2022, 67, 5615–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on Cosmetic Products [Internet]; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32009R1223 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Iwegbue, C.M.A.; Bassey, F.I.; Tesi, G.O.; Onyeloni, S.O.; Obi, G.; Martincigh, B.S. Safety evaluation of metal exposure from commonly used moisturizing and skin-lightening creams in Nigeria. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, T.M.; Santos, E.V. Determinação de Chumbo em Amostras de Corante Usando um Sensor Composto de Cortiça e Grafite. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Natal, Brazil, 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.ufrn.br/handle/123456789/44551 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Heavy metals: Toxicity and human health effects. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 153–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 643972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da França, S.A.; Dario, M.F.; Esteves, V.B.; Baby, A.R.; Velasco, M.V.R. Types of Hair Dye and Their Mechanisms of Action. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Michailidou, F.; Gahlon, H.L.; Zeng, W. Hair Dye Ingredients and Potential Health Risks from Exposure to Hair Dyeing. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Hair Dyes and Cancer Risk [Internet]; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/risk-prevention/chemicals/hair-dyes.html (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Lead Poisoning and Health [Internet]; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lead-poisoning-and-health (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Cobalt, Antimony Compounds, and Weapons-Grade Tungsten Alloy [Internet]; IARC: Lyon, France, 2023. Available online: https://publications.iarc.who.int/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Cobalt-Antimony-Compounds-And-Weapons-grade-Tungsten-Alloy-2023 (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Barium toxicity after exposure to contaminated contrast solution—Goias State, Brazil, 2003. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2003, 52, 1047–1048. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14586298/ (accessed on 3 July 2025). [PubMed]
- Åkesson, A.; Barregard, L.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Nordberg, G.F.; Nordberg, M.; Skerfving, S. Non-renal effects and the risk assessment of environmental cadmium exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, K.; Roberts, J. A comprehensive summary of disease variants implicated in metal allergy. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2022, 25, 279–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocca, B.; Pino, A.; Alimonti, A.; Forte, G. Toxic metals contained in cosmetics: A status report. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 68, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, F.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nasseri, S.; Yunesian, M.; Yaseri, M.; Djahed, B. Health Risk Assessment of Dermal Exposure to Heavy Metals Content of Chemical Hair Dyes. Iran. J. Public Health 2019, 48, 902–911. Available online: https://ijph.tums.ac.ir/index.php/ijph/article/view/16759 (accessed on 6 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.M.; Goher, A.S.; Alzubaidi, A.A.A.M. Risk assessment of heavy metals content in different hair dyes and their users’ urine samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 101, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A. The Triple Frontier: Illegal Trade and Globalization at the Intersection of Brazil, Paraguay and Argentina [Internet]. Master’s Thesis, The George Washington University, Washington, DC, USA, 2005. Available online: https://www2.gwu.edu/~ibi/minerva/Spring2005/Adriana.Barreto.de.Oliveira.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Conducting Scientific Evaluations: Hazard Quotients and Cancer Risk; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/pha-guidance/conducting_scientific_evaluations/epcs_and_exposure_calculations/hazardquotients_cancerrisk.html (accessed on 3 July 2025).
- Pehlić, E.; Nanić, H.; Jukić, H.; Aldžić, A. Determination of Heavy Metals in Hair Dyes by the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. New Technol. Dev. Appl. (LNNS) 2019, 42, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed.; The “Gold Book”; Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Exposure Dose Guidance for Soil/Sediment Dermal Absorption; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/pha-curriculum/php/training-topic/exposure-dose-guidance-edg-documents.html (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Zheng, N.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition (Final Report); EPA/600/R-09/052F; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/exposure-factors-handbook (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Da Silva Alves Junior, A.; Ancel, M.A.P.; Garcia, D.A.Z.; de Pádua Melo, E.S.; de Cássia Avellaneda Guimarães, R.; de Cássia Freitas, K.; Bogo, D.; Hiane, P.A.; Vilela, M.L.B.; do Nascimento, V.A. Monitoring of Metal(loid)s Using Brachiaria decumbens Stapf Leaves along a Highway Located Close to an Urban Region: Health Risks for Tollbooth Workers. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddig, M.M.S.; Brevik, E.C.; Sauer, D. Human health risk assessment from potentially toxic elements in the soils of Sudan: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Regional Screening Level (RSL) Summary Table (TR = 1E − 06, HQ = 1). November 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Guidelines for Human Exposure Assessment. (EPA/100/B-19/001). Risk Assessment Forum; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recentadd.cfm (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Shomar, B.; Rashkeev, S.N. A comprehensive risk assessment of toxic elements in international brands of face foundation powders. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oni, A.A.; Babalola, S.O.; Adeleye, A.D.; Olagunju, T.E.; Amama, I.A.; Omole, E.O.; Adegboye, E.A.; Ohore, O.G. Non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic health risks associated with heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in well-water samples from an automobile junk market in Ibadan, SW-Nigeria. Heliyon 2022, 22, e10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS) Part E—Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment [Internet]; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/part_e_final_revision_10-03-07.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Health Canada. Draft Guidance on Heavy Metal Impurities in Cosmetics [Internet]; Health Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/consumer-product-safety/reports-publications/industry-professionals/guidance-heavy-metal-impurities-cosmetics.html (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Resolução RDC nº 44, de 9 de agosto de 2012. Dispõe Sobre os Requisitos para Substâncias e Preparações Usadas Como Corantes em Produtos de Higiene Pessoal, Cosméticos e Perfumes. Diário Oficial da União. 2012 Ago 10; Seção 1:72. Available online: https://anvisalegis.datalegis.net/action/ActionDatalegis.php?acao=detalharAto&tipo=RDC&numeroAto=00000044&seqAto=000&valorAno=2012&orgao=RDC/DC/ANVISA/MS&nomeTitulo=codigos (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Amhimmid, W.K.; Fatah, S.A.; Altabeeb, S.S. Determination of Typical Heavy Metals in Hair Dyes Brands Selected from Libyan Markets. WJPMR 2022, 8, 5–10. Available online: https://www.wjpmr.com/ (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Al-Qutob, M.A.; Alatrash, H.M.; Abol-Ola, S. Determination of different heavy metals concentrations in cosmetics purchased from the Palestinian markets by ICP/MS. AES Bioflux. 2013, 5, 287–293. Available online: http://www.aes.bioflux.com.ro (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Johnson, W., Jr.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G., Jr.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of Barium Sulfate as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37 (Suppl. S5), 5S–11S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerny, B.; Krupka, K.; Ożarowski, M.; Seremak-Mrozikiewicz, A. Screening of trace elements in hair of the female population with different types of cancers in Wielkopolska region of Poland. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 953181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Lead; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp13.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2025).
- Li, H.; Toh, P.Z.; Tan, J.Y.; Zin, M.T.; Lee, C.Y.; Li, B.; Leolukman, M.; Bao, H.; Kang, L. Selected Biomarkers Revealed Potential Skin Toxicity Caused by Certain Copper Compounds. Sci. Rep. 2016, 28, 37664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, A.K.; Singhi, S.C. Acute iron poisoning: Management guidelines. Indian Pediatr. 2003, 40, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Guy, R.H. Metals and the Skin: Topical Effects and Systemic Absorption; CRC Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Chromium; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp7.pdf (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Manganese; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp151.pdf (accessed on 2 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Chapter 2, Health Effects. In Toxicological Profile for Molybdenum; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK590366/ (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Appendix E, Background Information for Strontium-90. In Interaction Profile for: Arsenic, Hydrazines, Jet Fuels, Strontium-90, and Trichloroethylene; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK601912/ (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Rahmanian, E.; Tanideh, N.; Karbalay-doust, S.; Mehrabani, D.; Rezazadeh, D.; Ketabchi, D.; EskandariRoozbahani, N.; Hamidizadeh, N.; Rahmanian, F.; Namazi, M.R. The effect of topical magnesium on healing of pre-clinical burn wounds. Burns 2024, 50, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, G.; March, C.; Gowdey, J. Magnesium in epidermis, dermis, and whole skin of normal and atopic subjects. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1964, 2, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Arsenic, metals, fibres, and dusts. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2012, 100C, 41–93. Available online: https://publications.iarc.who.int/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Arsenic-Metals-Fibres-And-Dusts-2012 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Arsenic; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. Available online: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=22&tid=3 (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Aluminum; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp22.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Silver; U.S. Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1990. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp146.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Enei, M.L.; Paschoal, F.M.; Valdés, R. Argyria mimicking a blue nevis: Dermoscopy features. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 452–455. Available online: https://www.scielo.br/j/abd/a/4JQh3V9ZRgDRwqDnr6ZW4Qf/?format=pdf&lang=en (accessed on 12 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Health Effects. In Toxicological Profile for Barium and Barium Compounds; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2007. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK598777/ (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Gates, A.; Jakubowski, J.A.; Regina, A.C. Nickel Toxicology. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK592400/ (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Zirwas, M.J.; Molenda, M.A. Dietary nickel as a cause of systemic contact dermatitis. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2009, 2, 39–43. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2923958/ (accessed on 12 July 2025). [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). IRIS Chemical Assessment Summary: Chromium (VI) (CASRN 18540-29-9); U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/iris (accessed on 12 July 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).