Abstract
Ginkgo biloba seed (GBS) contains rich nutrients, such as starch, protein, oil, and trace components, such as flavonoids and terpene lactones. Due to its high protein content, it can be used as a raw material for fermentation and brewing. In this study, GBS was selected as the object of a fermentation process optimization test. Six kinds of fermentation starter were selected to brew ginkgo wine. The results showed that different fermentation starters have significant impacts on the composition of the wine. The yeast group had higher total sugar content and comprehensive evaluation scores than the Jiuqu group, while the total acid and total free amino acid contents showed the opposite result. The total flavonoid and total terpene lactone contents of the yeast group were 21.0% and 12.8% higher than those of the Jiuqu group, respectively. However, the 4′-O-methylpyridoxine (MPN) and 4′-O-methylpyridoxine-5′-glucoside (MPNG) contents of the yeast group were also 12.6% and 2.3% higher than those of the Jiuqu group, respectively. The common volatile components in the two groups of samples were isoamyl alcohol, phenethyl alcohol, ethyl octanoate, and phenethyl acetate. The antioxidant capacity of ginkgo wine fermented by yeast was significantly higher than that of the Jiuqu group sample.
1. Introduction
Ginkgo biloba L. is a gymnosperm belonging to Ginkgoaceae. The seed of Ginkgo biloba, also known as white nut, contains starch, protein, oil, and some trace nutrients [1]. Ginkgo biloba seed (GBS) has the characteristic of being both a food and a medicinal herb and is commonly used as such in Asian regions. Its starch content accounts for 60–70% of the seed’s dry weight and contains 9–13% protein and 3–7% oil [2]. It has a similar nutritional composition to those of maize and wheat, making it a potential grain substitute for food processing. In addition, GBS contains active components such as terpenoids, flavonoids, organic acids, phenylpropanoids, and lignan glycosides, which give it significant antibacterial, antioxidant, and lung-moistening, and cough-relieving effects [3].
Due to its high starch content, GBS can be used as a raw material for brewing alcohol [4]. However, its slightly bitter taste poses some obstacles in the fermentation process, requiring technological improvements such as enzymatic hydrolysis and flavoring [5]. For example, starch needs to be hydrolyzed into small sugar molecules before it can be utilized by a starter, and the protein and oil contents of white nut impact hydrolysis and fermentation, adding complexity to the process [6]. Additionally, similar to cereal brewing, GBS can act as a rich source of amino acids during enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation due to its high protein content [7]. Therefore, brewing white nut wine that is both nutritious and palatable and can be accepted by the public is a breakthrough in the development and utilization of ginkgo resources, not only enriching the variety of fruit wines, but also helping to solve the problem of excessive white nut production, as well as promoting and advertising this economic forest product. Currently, most ginkgo wines on the market are made by adding GBS extract to fermented grain liquor or by directly soaking GBS in liquor, while few directly use white nuts as raw fermentation materials. GBS, as a food with medicinal properties, can improve the quality of wine due to its rich nutrition and health benefits, enabling people to enjoy wine while also benefiting from its health-promoting effects [8]. Several researchers have previously conducted some research on the production of ginkgo wine. Zhao used GBS as the main raw material and brewed ginkgo wine using the liquid fermentation method. Preliminary research was conducted on yeast screening and composite strain fermentation, and using ginkgo as the raw material, ginkgo wine with an alcohol content of 13.62% vol, a residual sugar content of 28.3 g/L, and a total acid content of 4.5 g/L was produced [9]. Chen studied the brewing process of ginkgo brandy using wine technology [10].
The fermentation starters that are commonly employed in the brewing process include yeast, Jiuqu, Koji, and others [11]. Yeast, as a widely used fermentation starter for fruit wine, finds extensive application worldwide. In China, Jiuqu is typically utilized to brew Chinese rice wine, Baijiu, and others [12]. Meanwhile, Koji is commonly used for the production of sake in Japan [13]. The yeast fermentation starter primarily involves the selection of pure or compound yeast strains that are often sourced from the natural environment. These strains can be further isolated and purified to enhance their characteristics. Jiuqu, is a compound starter that generally comprises various Aspergillus and Rhizopus microorganisms. Sometimes a small amount of yeast will be added to Jiuqu to assist with alcohol production during fermentation. Here are some commonly used fermentation starter products: The yeast strain in BV818 is Saccharomyces Bayanus, which is a naturally excellent strain with low nutritional requirements. After inoculation, it rapidly reproduces and becomes dominant. It is suitable for safe and stable fermentation under adverse conditions, such as low temperatures and poor raw material quality, making it ideal for the brewing of various fruit wines, including wine. The RW and SY yeast species are Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The RW style is suitable for brewing grape, mulberry, blueberry, strawberry, raspberry, and other fruit wines. The SY style is suitable for brewing fruit wines like apple, pineapple, orange, pear, peach, and more. Jiuqu used for brewing mainly contains yeast, Rhizopus, α-amylase, glucose amylase, and phytase. It is a compound distiller’s yeast with excellent acid resistance and temperature resistance, making it suitable for Baijiu, yellow rice wine, and other brewing fields. Baijiu Jiuqu primarily consists of yeast, Rhizopus, and complex enzyme preparations. It is also classified as a type of complex distiller’s yeast that is suitable for Baijiu, yellow rice wine, and other brewing fields. Sweet Wine Jiuqu mainly contains Aspergillus oryzae and Rhizopus and is suitable for the brewing of rice wine and similar beverages.
Based on the optimized white nut wine fermentation process obtained from previous team experiments [14], further research is planned to investigate the effects of different fermentation agents on the quality and flavor of GBS wine. Through response surface experiments combined with a fuzzy mathematics sensory evaluation, the effects of different fermentation agents on the quality and flavor characteristics of GBS wine are compared, and the changes in the flavor components of white nut wine are further explored. This provides a reference for further optimizing the fermentation process of GBS wine.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Equipment
Table 1 provides information on the main materials and equipment used in this experiment.

Table 1.
Test materials and equipment.
2.2. Material Pretreatment and Fermentation Method
Take fresh GBS and use a blunt instrument to remove the hard outer seed shell and inner seed coat. Boil the seeds in water for 20 min until they become gelatinous. After draining the water, add an appropriate volume of pure water (2~10 times the mass of the raw material) and mix it with the seeds. Then, crush them. Then, transfer the mixture to a conical flask, weigh appropriate amounts of α-amylase (0.1~0.6% of the mass of GBS, equivalent to 9.1~54.6 U/mL) and pullulanase (0.1~0.6% of the mass of GBS, equivalent to 1.4~8.4 U/mL), put them into an inverted conical flask, and mix evenly. The conical bottle mouth is sealed with a sealing film, and amylase hydrolysis is carried out in a 60 °C oscillating water bath for 1 h. Adjust the solution to pH 4.0 with citric acid, weigh and add glucoamylase (0.5~3.0% by mass of GBS, equivalent to 72.4~434.4 U/mL), mix well, and continuously saccharify at 75 °C for 1 h. Boil for 3 min to inactivate the enzyme. Take 200 mL of enzymatic hydrolysate. At this point, the sugar content of the enzymatic hydrolysate should be 34~170 g/L (based on the solid–liquid ratio during mixing). Add appropriate amounts of sugar and activated fermentation starter (six types of starter produced by biological companies were selected for the experiment, represented by A–F, where A is RW; B is SY; C is BV818; D is Brewing Jiuqu; E is Baijiu Jiuqu; and F is Sweet Wine Jiuqu). The activation method and dosage were determined according to the operating instructions of enzyme preparation products. Place the solution into a 28 °C constant-temperature incubator for anaerobic fermentation for 5~9 d and filter it after fermentation. Measure and analyze the physicochemical indicators and active ingredients and conduct a sensory evaluation of the ginkgo wine.
2.3. Response Surface Design of Experiments of GBS Fermentation
2.3.1. Single Factor Experiments
A preliminary investigation was conducted to explore the factors influencing the taste and quality of fermented ginkgo wine. Single-factor experiments were performed on three factors, namely the solid–liquid ratio, sugar addition, and fermentation time. The solid–liquid ratios investigated were 1:2, 1:4, 1:6, 1:8, and 1:10; the sugar additions included 60, 120, 180, 240, and 300 g/L; and the fermentation times were set at 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 days. The experiment employed control variables to maintain constant conditions for the three factors: the material-to-liquid ratio (1:6), the added sugar amount (180 g/L), and the fermentation time (7 d). After the fermentation process, the alcohol content and sensory score indicators were measured for each sample. Data visualization and analysis were performed using Origin 8.5 software.
2.3.2. Experimental Design
A Box–Behnken design (BBD) was employed to optimize the fermentation process, encompassing three factors, each with three levels. Based on the results of the preliminary single-factor experiments, a response surface methodology was selected to determine the optimal fermentation conditions for ginkgo wine. The key independent variables identified as having the most significant impacts on the experimental design were the solid–liquid ratio (1:4, 1:6, and 1:8), sugar addition (60, 120, and 180 g/L), and fermentation time (7, 8, and 9 days), and BV818 was selected as the fermentation starter. The BBD approach was utilized to assess the combined effects of these three independent variables. A total of 17 experimental runs were conducted, with the central point (triplicate) utilized for the optimization of fermentation conditions. The levels of the independent variables were coded as −1, 0, and +1, as presented in Table 2. The dependent variables under evaluation were the alcohol content (Y1) and sensory score (Y2). The levels of the independent variables and the design matrix are shown in Table 3. All experimental data obtained from the designed experiments were fitted with a quadratic model using Equation (1):
where Y is the predicted response, and A, B, and C correspond to the independent variables for the solid–liquid ratio, sugar content, and fermentation time. β0 represents the intercept; β1, β2, and β3 are the linear coefficients; β12, β13, and β23 are the interaction coefficients; β11, β22, and β33 are the quadratic coefficients; and Y is the response value.
Y = β0 + β1A + β2B + β3C + β11A2 + β22B2 + β33C2 + β12AB + β13AC + β23BC

Table 2.
The coded and actual values of factors in the BBD.

Table 3.
The BBD matrix and responses.
2.4. Determination of Physicochemical Indicators
The contents of alcohol, total residual sugar, free amino acids, and total acids were determined according to the standard GB/T 15038–2006 “Analytical methods for wine and fruit wine” [15]. After referring to the literature, the total flavonoid content was determined using the spectrophotometric method with aluminum chloride [16]. The terpene lactone content was determined using the spectrophotometric method [17]. The MPN and MPNG contents were detected using high performance liquid chromatography [18].
2.5. Fuzzy Mathematics Sensory Evaluation
The sensory evaluation was based on this method with slight modifications [19]. The sensory evaluation panel consisted of eight trained evaluators (four females and four males) who conducted the evaluation independently in separate rooms. The quality evaluation considered multiple factors, including the aroma, flavor, color, and palatability, which were graded as excellent, good, fair, or poor, corresponding to score ranges of 60–100 points for each evaluation criterion. The overall sensory evaluation criteria are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comprehensive sensory evaluation standard.
The four indicators, namely aroma, color, taste, and palatability, significantly influence the quality of wine-making. To achieve a more objective assessment of the fruit wine quality, it is essential to determine the relative importance of each indicator through mathematical methods based on their respective impacts. A pairwise comparison method was employed to assess two indicators against each other. Volunteers were asked to indicate whether they perceived one indicator to be more important than the other, recording a value of 1 if so, and 0 otherwise. Indicators were not compared against themselves. In cases where the same indicator was compared, a value of 1 was recorded to indicate its necessity. The sum of the weights assigned to all indicators amounted to 1. The evaluation results for the weights of each indicator are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Evaluation index weight distribution.
Two evaluation domains were established in this experiment: the factor set, which includes sensory quality indicators A = {aroma, flavor, color, palatability}, and the comment set, which includes sensory quality comments B = {excellent B1, good B2, fair B3, poor B4}. The weight domain matrix U = (a1, a2, …, an) was obtained based on the weight scores of each indicator, where a1, a2, …, an [ai (0, 1)] are the corresponding membership degrees of each evaluation indicator, and they satisfy the condition a1 + a2 + … + an = 1. The evaluation system Y = U × R = (b1, b2, …, bm) was established through the following process:
R represents the set of rating scores for each sample, where r represents the rating score for each indicator, and rij = j(xi) represents the i-th evaluation belonging to the j-th level of the corresponding evaluation item, where i = 1, 2, …, n and j = 1, 2, …, m. The evaluation results of each sample were transformed into the product of matrices U and R. The overall sensory score H of each sample was obtained by multiplying the evaluation result vector Y with the corresponding score for each level, resulting in the final comprehensive sensory score for the sample.
The sensory weight factors of the white fruit wine were obtained based on the weight scores of each indicator, shown in Table 3, resulting in the weight matrix = (0.02, 0.31, 0.37, 0.31). The formula for calculating the comprehensive score is as follows:
2.6. GC-MS Analysis for the Determination of Volatile Components
Compared to previously published research [20], our method was modified slightly. For the aroma component extraction method: use solid phase microextraction (SPME) with headspace sampling. For this method, accurately weigh 4.0 g of the sample into a 20 mL headspace vial. Place it in a 60 °C water bath for 10 min to reach equilibrium and then insert an aged extraction needle (aged for 30 min at 250 °C) for headspace adsorption and extraction for 30 min. Insert the extraction needle into the GC-MS inlet for analysis for 10 min.
Regarding the chromatographic conditions, use a DB-Wax (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm) capillary column; high-purity helium (99.999%) as the carrier gas, a flow rate of 1.000 mL/min, and an inlet temperature of 250 °C. For the temperature program, start at 50 °C, hold for 2 min, and then increase at a rate of 5 °C/min to 200 °C, and finally increase at a rate of 10 °C/min to 220 °C.
For the mass spectrometry conditions, use electron ionization (EI) as the ion source; an electron energy of 70 eV; an ion source temperature of 250 °C; and an interface temperature of 250 °C.
2.7. Antioxidant Activity Experiment
The sample preparation was conducted as follows: ginkgo wines fermented with six kinds of fermentation starters were tested. Based on previous research [21], the antioxidant activity was analyzed through DPPH and ABTS+, and some modifications were made [15].
2.7.1. Determination of the (DPPH) Scavenging Rate
In a 96-well plate, a suitably prepared sample solution was mixed with a DPPH solution. After allowing the mixture to react at room temperature for 30 min, the absorbance (A) was measured at 517 nm. Vitamin C (VC) was utilized as the positive control. The absorbance of the sample–DPPH mixture was recorded as A1. The absorbance of the sample blended with ethanol was noted as A2, and the absorbance of ethanol mixed with the DPPH solution was labeled as A0. The scavenging rate of the compound was calculated using the formula shown in Equation (4):
2.7.2. Determination of the (ABTS+) Scavenging Rate
Each sample was mixed with an ABTS solution in a 96-well clear plate and allowed to react for 5 min at room temperature. Subsequently, the absorbance of the samples was measured at 734 nm. VC was employed as the positive control. The absorbance of the sample–ABTS mixture was denoted as A1, and for the absorbance control, the sample was replaced with ethanol and denoted as A0. The scavenging rate of the compound was calculated using the formula shown in Equation (5):
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimal Fermentation Conditions for Ginkgo Wine
3.1.1. Single-Factor Experiment Results
Effect of the Solid–Liquid Ratio on Fermentation
Utilizing GBS as the fermentation material offers numerous advantages, including high starch and protein contents, as well as organic components such as flavonoids and terpene lactones. This aligns with the modern trend in fruit wine development that is characterized by the utilization of new raw materials, a low alcohol content (<40% vol), and enhanced nutritional value. In this experiment, two variables were held constant: the sugar addition ratio (180 g/L) and the fermentation time (7 d). The study focused on investigating the impact of the solid–liquid ratio within the range of 1:2 to 1:10 on the fermentation process. The effects on sensory scores and the alcohol content are illustrated in Figure 1a. With an increasing solid–liquid ratio, both the alcohol content and sensory scores exhibited an initial rise followed by a decline. The optimal condition was achieved when the solid–liquid ratio fell between 1:6 and 1:8, resulting in the highest sensory score, while the highest alcohol content was observed between 1:4 and 1:6. Consequently, a solid–liquid ratio of 1:6 was considered ideal for subsequent experiments in this study.
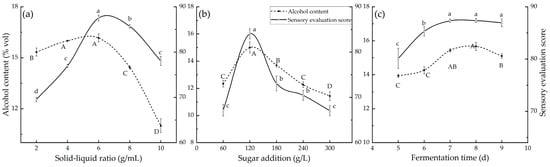
Figure 1.
The results of the single-factor test. Note that the error line represents the standard deviation, with different lowercase letters indicating significant differences in the sensory evaluation (p < 0.05) and different uppercase letters indicating significant differences in the alcohol content (p < 0.05). (a) The effects on sensory scores and the alcohol content. (b) The changes in sensory scores and the alcohol content during the fermentation process. (c) The effect of the fermentation time on the sensory scores and alcohol content.
Influence of the Sugar Addition Ratio on Fermentation
The starch content in the GSB selected for the experiment was about 68% of the dry weight of the seed. If the material liquid ratio is 1:6, the sugar content of the enzymatic hydrolysis solution is about 60 g/L. However, when calculating the alcohol content by converting 17 g/L of sugar into 1% vol during fermentation, it was observed that the sugar content in the fermentation broth was insufficient to yield an adequate amount of alcohol. To achieve an appropriate alcohol content in the wine, it was necessary to add an appropriate amount of sugar before fermentation. In this experiment, three variables were kept constant: the solid–liquid ratio (1:6), the fermentation time (7 d), and the fermentation starter (BV818). The primary objective of this study was to examine the influence of sugar addition within the range of 1:1 to 1:5 on the fermentation process. The changes in sensory scores and the alcohol content during the fermentation process are depicted in Figure 1b. With increasing amounts of added sugar, both the alcohol content and sensory scores initially experienced rapid increments, followed by gradual decreases. An excessive alcohol concentration can also accentuate the alcohol aroma, diminishing the intricate fruit wine bouquet and disrupting the overall taste equilibrium. In the single-factor experiment, the addition of more sugar to the fermentation substrate resulted in a reduction in the alcohol content of the fruit wine during the later stages. It is speculated that the potential reason for this is that the rise in the alcohol content led to a decrease or even the deactivation of yeast activity. Following the loss of the dominant yeast strain, lactic acid bacteria or certain spoilage microorganisms (such as acetic acid bacteria) in the wine convert ethanol into metabolic byproducts like acetic acid, causing a decline in the wine’s alcohol content. Consequently, a sugar addition ratio of 120 g/L was selected as the optimal condition. At this point, the resulting ginkgo wine exhibited an alcohol content of 14.9% vol and a sensory score of 84. The wine achieved a harmonious and rich taste profile, coupled with fruity notes, indicative of a well-balanced combination of aroma and taste.
Influence of the Fermentation Time on Fermentation
During the entire fermentation process, fermentation time is an important factor affecting the taste of ginkgo wine. For example, prolonged fermentation can lead to the depletion of the residual sugar content in wine. If the fermentation time is too short, it will lead to incomplete fermentation, a high sugar content, a low alcohol content, and even fewer flavor components. In this experiment, three variables were held constant: the solid–liquid ratio (1:6), the amount of sugar added (180 g/L), and the fermentation starter (BV818). The focus of the study was to investigate the impact of varying fermentation times in the range of 5~9 d on the fermentation process. The effect of the fermentation time on the sensory scores and alcohol content is shown in Figure 1c. As the fermentation time increased, the alcohol content of white fruit wine first increased, then decreased, and then remained stable. The sensory score also increased first and then decreased. When the fermentation time was less than 7 d, the alcohol content and sensory evaluation scores were relatively low, and the aroma of fruit wine was not strong enough. Therefore, 7–8 d is the optimal fermentation cycle. At this temperature, the alcohol content of elderberry wine is approximately 15% vol, with a sensory score of 87. The ginkgo wine brewed from this has a good sweetness level and balanced aroma components.
3.1.2. Fitting the Response Surface Models
The influences of the solid–liquid ratio, sugar addition, and fermentation time on the alcohol content and sensory score were investigated using RSM. The alcohol content and sensory score were chosen as the response values. To examine the statistical significance of the factors in the model, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) and regression analysis were conducted; the results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
The ANOVA evaluation of linear, interaction, and quadratic terms for the sensory score and alcohol content response variables and the coefficients of the model prediction.
The role of each variable and its second-order interactions is explained by a second-order polynomial model in coded units based on a multiple regression analysis conducted using experimental data. The developed models are shown in Equations (6) and (7).
Alcohol content: Y1 = −1.22 + 2.46A − 0.66B + 2.88C + 0.94A B − 0.16A C + 0.31B C − 0.29A 2 − 1.66B 2 − 0.17C 2
Sensory score: Y2 = 88.21 + 0.60A + 4.23B − 0.39C + 1.20A B − 0.01A C + 0.39B C − 3.31A 2 − 3.57B 2 − 1.56C 2
A linear regression model was constructed. and the coefficient of determination, R2, and F value were found. Based on Table 6, the overall results for the performance parameters are shown as listed below: the R2 for the responses of both the sensory score and alcohol content were 0.9736 and 0.7943. The F values of both regression models were 28.63 and 3.38, and the p-values of both regression models were 0.0001 < 0.05 and 0.06; the p-values of both occasions where the lack of fit was non-significant were 0.1554 and 0.1282 > 0.05. This indicates that the sensory evaluation model is more meaningful. This also indicates that the sensory evaluation prediction model can be tested with the mathematical model in the equation.
Fermentation is a complex multi-step process that requires the coordination of many factors, including the physical and chemical factors of the agent, sugar, acidity, etc. [22]. These different factors can affect the results of brewing research. The significance levels of the F and p-values on the linearity, interaction, and quadratic terms of the solid–liquid ratio, sugar addition, and fermentation time are shown in Table 6. The optimized simulated results revealed the interaction of two out of the three major factors on the sensory evaluation score when the third one was fixed at a certain level in the 3D curved surface and 2D contour plots (Figure 2). The model items B, A B, A2, B2, and C2 showed significant differences (p < 0.05) and were positively affected. Other terms, A, A C, and B C, were irrelevant (p > 0.05) and were negatively affected.
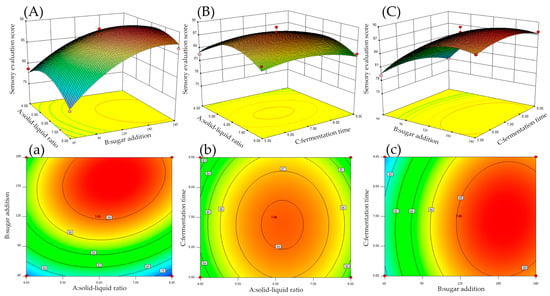
Figure 2.
Response surface and contour plots for the sensory score. (A,a) Effect of the solid–liquid ratio and sugar addition. (B,b) Effect of the solid–liquid ratio and fermentation time. (C,c) Effect of the sugar addition and fermentation time.
It can be found that the three factors tested have significant impacts on the taste and mouthfeel of ginkgo wine. By analyzing the influences of the main factors and their F-values, it can be concluded that the influence of these factors occurs in the following order: sugar addition > solid–liquid ratio > fermentation time. In addition, the quadratic response 3D surface plot presented in Figure 2 clearly illustrates the optimization model for the sensory evaluation, including the solid–liquid ratio, sugar addition, and fermentation time, to determine the sensory score. As shown in Figure 2A–C, with increases in the solid–liquid ratio and sugar addition, the sensory score shows an upward trend with noticeable changes. The amount of sugar added will affect the alcohol content and flavor components of ginkgo wine [23]. The taste and aroma of wine fermented at different sugar levels will vary significantly. During fermentation, increasing the sugar addition may increase the starter’s growth rate, fermentation rate, and cell vitality, as well as the sweetness of the alcohol produced. On the contrary, having an insufficient sugar content will affect the growth and fermentation rate of the starter and ultimately affect the composition of the fermentation products. The effects of the solid–liquid ratio and fermentation time on measurement are similar. When the solid–liquid ratio and fermentation time are large, they will have negative impacts on the flavor and taste of the wine. On the contrary, if the fermentation time is too short and the solid–liquid ratio is too low, the overall fermentation process will also be inhibited, leading to the insufficient fermentation of ginkgo wine [24]. In Figure 2a–c, from the perspective of 2D contours, the oval and circular contours indicate that the interaction between these two factors is significant or non-significant, respectively. The interaction between the solid–liquid ratio and fermentation time is significant, while the interaction between the solid–liquid ratio and sugar addition as well as the interaction between the fermentation time and sugar addition are not significant. The predicted sensory scores were 89.42, 87.67, and 87.49, respectively.
3.1.3. Validation and Verification of the Optimized Conditions
The obtained response surfaces (Figure 2) were used as a basis for optimizing the investigated parameters for the fermentation of ginkgo wine. The resulting response surfaces showed the effects of the solid–liquid ratio, fermentation temperature, and yeast inoculum on the ethanol and sensory scores. According to our previous experiments, the value determination coefficient of the alcohol model (R2 = 0.7943) is too low, so optimization should target high scores in the sensory evaluation. The predicted sensory score was set to the maximum value, and the optimized values for the solid–liquid ratio, sugar addition, and fermentation time obtained from this model were 1:6.4, 157.2 g/L, and 8 d, respectively. Under these conditions, the highest sensory score may be 87.35 with an alcohol content of 12.7% vol.
The fermentation conditions were adjusted to a solid–liquid ratio of 1:6.4, sugar addition of 157.2 g/L, and a fermentation time of 8 d, based on the results of the response surface optimization experiment and the actual situation. Verification tests can also be carried out under optimized fermentation conditions in a 10 L fermenting tank.
The physical and chemical indicators of the fermented products are shown in Table 7, as follows: reducing sugar of 14.9 g/L, total sugar of 16.21 g/L, volatile acid of 0.076 g/L, total acid of 3.24 g/L, alcohol of 12.7% vol, dry extract of 12.92 g/L, and a free amino acid content of 2.18 g/L in ginkgo wine. According to the Green Fruit Wine Standard NY/T 1508-2017 formulated by the Ministry of Agriculture of China, the ginkgo wine prepared by this process is of the semi-sweet type. The total acidity of the ginkgo wine is slightly below the national fruit wine standard, and the content of volatile acids is also exceptionally low. This could be attributed to the inherent low acidity of the raw ginkgo material itself and the relatively low fermentation temperature, resulting in reduced acid production. In contrast, other fruit-based brewing materials, such as grapes, typically contain a significant amount of organic acids [25]. Grape varieties with higher acidity are often chosen for brewing purposes, contributing to higher acidity levels in the final product. All other indicators meet the standard for green fruit wine. In addition, the overall taste of fermented wine is sour and sweet with a light-yellow color and clear transparency.

Table 7.
Evaluation of basic components of ginkgo wine.
3.2. Differences in Physical and Chemical Indexes of Ginkgo Wine Fermented by Different Starters
Table 8 shows the nutritional and active ingredient contents of the GBS. The starch content is 68.02%, the protein content is 10.97%, and the fat content is 4.74%. Among these three indicators, starch has a more significant impact on the fermentation of fruit wine, affecting the alcohol content and residual sugar level. Meanwhile, protein and fat influence the flavor components and clarity of the fruit wine. Furthermore, the total acidity is 0.37%, and the content of free amino acids is 1.49%. In terms of active components, the flavonoid content is 410.75 µg/g, and the terpene lactone content is 62.25 µg/g. Flavonoids and terpene lactones are two characteristic components of Ginkgo biloba and are important medicinal constituents in the field of medicine. Although the contents of these active components in GBS are one to two orders of magnitude lower than in ginkgo leaves, they still have positive impacts on health, even when present in trace amounts. Studies have indicated that the toxicity of the two distinctive components of GBS, namely MPN and MPNG, is the primary factor responsible for adverse reactions in children. This is primarily due to their chemical structures, which closely resemble that of vitamin B6 (also known as pyridoxine, VB6), leading to their binding to receptors and resulting in a deficiency of VB6 in the human body [26]. However, in vivo toxicity tests have revealed that the contents of MPN and MPNG in GBS are relatively low. In general, it is unlikely for individuals to consume such a significant amount of GBS that would lead to toxicity reactions [27].

Table 8.
Nutritional and active components of the gingko biloba seeds.
Table 9 shows the results of the determination of the physicochemical indicators of six fermented white fruit wines, including the reducing sugar, total sugar, volatile acid, total acid, alcohol content, and dry extract content. According to the sweetness grading standard for green fruit wines in NY/T 1508 (total sugar content/g·L−1), the dry type is ≤4; the semi-dry type is 4.1~12.0; the semi-sweet type is 12.1~50.0; and the sweet type is >50.1. In the experiment, sample D had the highest reducing sugar and total sugar contents, which were 24.57 g/L and 26.31 g/L, respectively, and was of the semi-sweet type. C and E were also semi-sweet, while B was semi-dry. In addition, the reducing sugar and total sugar contents of sample F were the lowest, 2.35 g/L and 2.98 g/L, respectively, and were not significantly different from A (p > 0.05). Both of these wines belonged to the dry fruit wine.

Table 9.
Effects of different starters on the physicochemical properties of ginkgo wine.
The reducing sugar and total sugar contents of the six fermented wines were significantly correlated (p < 0.05), with relative standard deviations (RSDs) of 17.23% and 16.64%, respectively, indicating that the degrees of change in the reducing sugar and total sugar contents were consistent and were more affected by the fermentation agent than by other physicochemical indicators. The volatile acid content of the samples ranged from 0.072 to 0.106 g/L, and the total acid content ranged from 2.79 to 4.35 g/L. The total acid contents of samples A and F were significantly higher than those of the other samples (p < 0.05), both exceeding 4 g/L. The alcohol content of the samples ranged from 8.0 to 10.0% vol, with an RSD of 1.91%, and was less affected by the fermentation agent. Sample B had the highest alcohol content, at 10% vol, while sample E had the lowest, at 8% vol. The dry extract content of the fermented white fruit wines ranged from 8.49 to 13.49 g/L.
According to the requirements of NY/T 1508 for green food fruit wines, the alcohol content should be 7~18% vol, the total acid content should be 4.0~9.0 g/L, the volatile acid content should be ≤1.0 g/L, and the dry extract content should be ≥12.0 g/L. Some of the total acid and dry extract contents of the white fruit fermented wines were slightly lower than the standard. The reason for the low total acid content may be an insufficient secondary fermentation time or a low fermentation temperature, resulting in an insufficient amount of acid production to meet the standard requirements. Additionally, the low total acid content may also be due to the characteristics of the raw materials, which are different from those of typical fruit wine raw materials [28]. Similarly, the dry extract content includes free acid and salts, tannins, pigments, pectin, low sugar, minerals, and other substances, and the contents of these substances are closely related to the raw fermentation materials and the amount of raw materials added [29,30,31]. For example, research has reported that the dry extract content in white wine is as high as 29.4 g/L, and such a high dry extract concentration can reduce the volatile acid content [32].
According to Figure 3, different fermentation agents have different effects on the content of free amino acids in fermented wine. The total free amino acid content in sample D is the highest, at 1985.4 mg/L, while sample B has the lowest content at 1591.8 mg/L. The essential amino acid content is between 373.6 and 431.4 mg/L, accounting for approximately 22% of the total free amino acid content. Sample C has the highest essential amino acid content, while sample A has the lowest. White fruit fermented wine contains a considerable amount of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), ranging from 33.5 to 44.9 mg/L, accounting for approximately 2.4% of the total free amino acid content. The physiological function of GABA has been recognized by researchers, and studies have shown that supplementing with GABA can regulate bodily functions and relieve fatigue [33]. The free amino acid content in ginkgo wine is several times higher than that in grape wine [34], mainly due to the higher protein content in GBS. Therefore, it can be determined that white fruit fermented wine has its unique advantages in terms of nutrition and functionality.
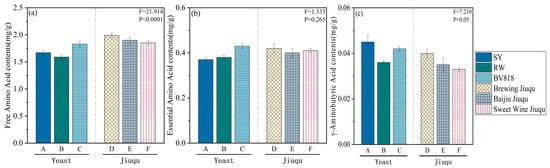
Figure 3.
The effect of different starters on the free amino acid content in ginkgo wine. (a) The free amino acid content. (b) The essential amino acid content. (c) The γ-aminobutyric acid content. (values represent the mean ± SD. A is RW; B is SY; C is BV818; D is Brewing Jiuqu; E is Baijiu Jiuqu; and F is Sweet Wine Jiuqu.).
Overall, the average total free amino acid content in ginkgo wine fermented with Jiuqu was 1911.49 mg/L, while it was 1696.55 mg/L in these samples fermented with yeast, which is 11.2% lower than the former. In terms of the essential amino acid content, the wine fermented with Jiuqu also had a higher content than that fermented with yeast (409.86 mg/L > 395.66 mg/L). However, the opposite was true for the content of GABA, with the yeast wine sample containing 41.04 mg/L of GABA, which is 13.8% higher than the 36.08 mg/L in the Jiuqu sample.
Table 10 and Figure 4 show the effects of different fermentation agents on the active components of fermented ginkgo wine. The standard deviations of the total flavonoid, total terpenoid, MPN, and MPNG contents were 19.3%, 8.5%, 14.0%, and 4.7%, respectively, indicating that the total flavonoid content was most affected by the fermentation agent. The contents and proportions of MPN and MPNG, the toxic components of GBS, changed in both the raw materials and wine. After converting to the water addition ratio, the content of ginkgo toxins in fermented ginkgo wine decreased by 39.8%, and 86.0% of the MPN was converted to MPNG. Among the wines, sample C had the total flavonoid and total terpenoid contents, which were 72.2 µg/g and 10.28 µg/g, respectively, and sample B had the lowest total flavonoid content of 57.62 µg/g, while sample E had the lowest total terpenoid content of 9.05 µg/g. Comparing different types of fermentation agents, yeast fermentation agents were shown to produce ginkgo wine with higher total flavonoid and total terpenoid contents than Jiuqu fermentation, with increases of 21.0% and 12.8%, respectively. However, the contents of MPN and MPNG in yeast fermentation agents were also 12.6% and 2.3% higher than those in Jiuqu fermentation. This suggests that the overall content of active components in ginkgo wine after yeast fermentation is higher than that in Jiuqu fermentation, and it is speculated that microorganisms such as Aspergillus in Jiuqu may decompose and utilize these active components, leading to a decrease in their content. Previously, researchers used Eurotium cristatum to ferment GBS and found that the contents of active ingredients and TMPN decreased [2].

Table 10.
Effects of different agents on the active components of ginkgo wine.
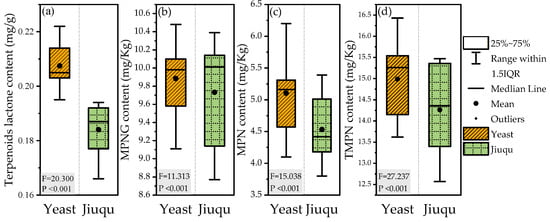
Figure 4.
Contents of metabolites in ginkgo wine between the yeast and Jiuqu groups. (a) The terpenoid lactone content. (b) The MPNG content. (c) The MPNG content. (d) The TMPN content.
3.3. Effects of Different Fermenting Agents on the Sensory Evaluation of Ginkgo Wine
Ginkgo wine is made from GBS. Through a sensory analysis survey, the importance levels of four evaluation indicators of ginkgo wine were investigated by the sensory analysis team using a questionnaire voting form. The sensory weight factor = (0.02, 0.31, 0.37, 0.31) was calculated. The weight of aroma was the lowest, only 0.02, while the weight of color was the highest, indicating that the experimenters believed that the importance of the aroma of the wine was very low, and a clear color could better highlight the quality of the wine. By multiplying the obtained weight factor by the evaluation score matrix of the four indicators, the group members obtained the evaluation result vector (Y). Finally, the comprehensive sensory evaluation score was calculated by averaging the evaluation scores of the four indicators by the group members with Y. The results are shown in Table 11, and the comprehensive evaluation scores of the sensory evaluations are ranked in the order of F, C, D, B, A, E, with scores of 88.59, 87.82, 83.54, 82.72, 79.58, and 76.83, respectively. This indicates that using the agent of Baijiu Jiuqu and BV818 yeast for ginkgo wine fermentation can result in better tasting ginkgo wine. The taste of ginkgo wine fermented with Baijiu Jiuqu is slightly sour and sweet, while the taste of ginkgo wine fermented with BV818 yeast is relatively sweet.

Table 11.
Sensory evaluation scores obtained with fuzzy mathematics for ginkgo wine brewed with six agents.
3.4. Comparison Analysis of Volatile Components in Fermented Ginkgo Wine
Table 12 shows the percentage contents of volatile compounds in the white nut enzymatic hydrolysate, including seven aldehydes, three alcohols, two esters, and one hydrocarbon. The compound with the highest volatile component content was pentadecanal, accounting for 17.45% of the 18 compounds, followed by n-hexanal at 14.1%. According to other researchers’ reports [35], aldehydes are the main volatile compound components in white nut, accounting for up to 71.46% of the total. They are mainly unsaturated aldehydes, and they contribute significantly to the characteristic flavor of white nut with their aldehyde, wax, fat, grass, and clean fragrances. A small concentration of saturated aldehydes is mainly produced by the degradation of unsaturated fatty acids, with myristic aldehyde having the highest content and a waxy and fruity taste. The aldehyde components also accounted for the largest proportion of volatile components after the enzymatic hydrolysis of white nut, reaching 50.53%.

Table 12.
Analytical results of the GS-MS identification of volatile components in GBS enzymatic hydrolysate.
Table 13 presents the GC-MS identification results of volatile components in ginkgo wine samples fermented with different fermentation agents. It can be found that the volatile components commonly found in ginkgo wine fermented with different agents include ethanol, isopentanol, phenethyl alcohol, ethyl caprylate, and phenethyl acetate. More than half of the samples contained compounds such as isopentyl acetate, ethyl decanoate, benzaldehyde, and decanal. These volatile compounds are important components of flavor and contribute to the aroma characteristics of ginkgo wine. The top five substances with the highest volatile component contents of the wine samples are ethanol (43.17%), isopentanol (29.09%), phenethyl alcohol (18.21%), octanol (3.01%), and isopentyl acetate (1.87%). Of the 27 volatile compounds listed in the table, the nine ester compounds accounted for the largest proportion, followed by six alcohol and hydrocarbon compounds, five aldehyde compounds, and one acid compound. Compared with white nut and enzymatic hydrolysate, the proportion of aldehyde volatile components in fermented wine decreased to 0.81%. It is speculated that the substances that produce aldehyde volatile components are decomposed during fermentation, and sugars and other substances are fermented into more volatile alcohols and esters, causing a sharp drop in the proportion of aldehyde components [36].

Table 13.
Analytical results of the GS-MS identification of volatile components in ginkgo wine.
Ester substances are important metabolic products in the process of wine fermentation. During fermentation, ester compounds are mainly produced by microorganisms such as yeast and fungi. In addition, acid and alcohol can also generate ester compounds through alcohol acyl transfer under the action of enzymes or microorganisms. Two common components, ethyl caprylate (brandy aroma) and phenethyl acetate (peach aroma), were detected in all six samples. Ethyl acetate, ethyl hexanoate (fruit aroma), 3-methyl ethyl pentanoate (fruit aroma), and ethyl palmitate (butter aroma) were detected in different wine samples. Ester compounds produced by different fermentation agents have significant impacts on their volatile components. As shown in Table 6, ethyl hexanoate with a fruity aroma was detected in sample A, 3-methylbutyl acetate with a pineapple aroma was detected in sample B, and ethyl palmitate with a milky aroma was detected in sample C. Undecyl acetate with a fatty, fruity, and nutty aroma was detected in samples D and F. Decyl acetate with a coconut aroma was detected in samples A, B, C, and D. Ethyl isovalerate (banana aroma) was present significantly higher concentrations in samples A and B than in other samples. These differences in volatile components are the main reasons for the characteristic aroma differences in fermented wines [20].
The production of alcohols is mainly generated by the synthetic and degradative metabolism of yeast or microorganisms, mainly through the synthetic pathway of glucose. Degradative metabolism mainly produces alcohols through the deamination pathway of amino acids. Among the volatile components of the six kinds of wine samples, alcohols accounted for 81.35% to 95.82% of the total and were the main components of the volatile components.
Aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and phenylacetaldehyde are produced along with alcohol fermentation during the fermentation process. Through investigation, it was found that aldehyde compounds accounted for a large proportion of the volatile components of white fruit, and a small amount of aldehyde compounds may be retained after fermentation, such as nonanal and decanal components.
In addition, different fermentation agents have significant impacts on the volatile components of fermented wine. For example, the concentration of volatile ester components produced by yeast in ginkgo wine is twice as high as that produced by Jiuqu (6.66% > 3.13%). The high-content ester components include isoamyl acetate and ethyl caprylate. In terms of alcohol components, the ethanol content in the sample with the yeast group (57.81%) was 1.03 times higher than that in the Jiuqu group (28.53%). However, the contents of isoamyl alcohol and phenethyl alcohol produced during Jiuqu fermentation (34.04% and 30.30%, respectively) were 0.41 and 3.78 times higher than those produced by yeast (24.14% and 6.09%, respectively). The reason for these differences in components may be that microorganisms in wine Jiuqu utilize the free amino acids in the GBS hydrolysate, resulting in higher levels of ethyl phenethyl acetate, isoamyl alcohol, and phenethyl alcohol in the wine samples. Research has also shown that an increase in the leucine content can increase the contents of isoamyl alcohol and ethyl caprylate, while an increase in the phenylalanine content can increase the production of phenethyl alcohol and ethyl phenethyl acetate.
3.5. Experimental Results and Analysis of Antioxidant Activity
3.5.1. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Ability
GBS contains some antioxidant substances, including flavonoids and terpene lactones. Therefore, ginkgo wine has a positive effect on the antioxidant activity.
The effect of ginkgo wine on the antioxidant capacity is shown in Figure 5. As the sample size increases, the scavenging ability of DPPH free radicals gradually increases. When the addition amount of the two groups of samples was 0.2 mL, the clearance rate of the DPPH free radicals rapidly increased to nearly 45%, and at this time, the clearance rate of the Jiuqu group was higher than that of the yeast group. After 0.4 mL, the clearance rate of both groups of samples slowed down, and the clearance rate of the yeast group was higher than that of the Jiuqu group. Finally, when the addition amount was 1.0 mL, the DPPH free radical clearance rates of the yeast group and the Jiuqu group reached the maximum values within the experimental range, which were 75.48% and 70.05%, respectively. The results showed that the scavenging effects of the two types of fermentation starter on the DPPH free radicals were similar. Through fermentation, the DPPH free radical clearance rate of the yeast group samples was generally higher than that of the yeast group samples, which may be related to the more active components of ginkgo wine after yeast fermentation [21]. However, overall, compared to other fruit and fruit wines, ginkgo wine has a weaker antioxidant capacity [37].
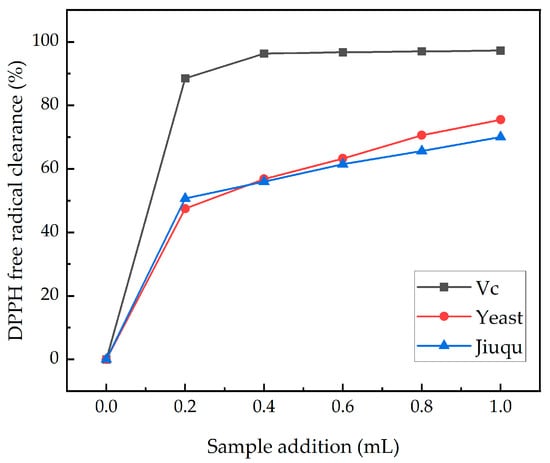
Figure 5.
DPPH free radical clearance ability. (Yeast includes RW, SY, and BV818, and Jiuqu includes Brewing Jiuqu, Baijiu Jiuqu, and Swet Wine Jiuqu).
3.5.2. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Ability
The scavenging ability of ABTS+ cation radicals is shown in Figure 6. The clearance rates of the two samples gradually increased with increased sample addition, and rapidly increased at 0.2 mL. After 0.2 mL, the clearance rates of the ABTS+ cationic free radicals in the two groups of samples steadily increased. At 1 mL, the clearance rates of the yeast group and the Jiuqu group were 75.49% and 73.68%, respectively. The results indicate that the yeast group sample has a greater ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. The ABTS+ clearance rate of the yeast group sample was slightly higher than that of the Jiuqu group, indicating that yeast fermentation produces more active ingredients in ginkgo wine, which has substances that enhance the antioxidant capacity [38].
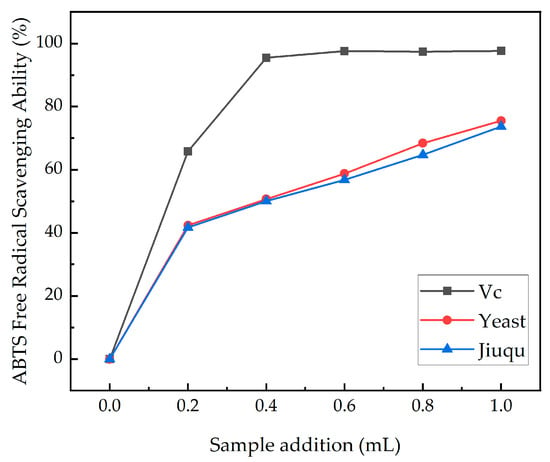
Figure 6.
ABTS free radical clearance ability. (Yeast includes RW, SY, and BV818, and Jiuqu includes Brewing Jiuqu, Baijiu Jiuqu, and Sweet Wine Jiuqu).
4. Conclusions
This study prepared a new type of fruit wine using GBS as the raw material. Based on the results of single-factor experiments, response surface methodology was used to further optimize three factors: the solid–liquid ratio (A), sugar addition (B), and the fermentation time (C). This model can better predict and explain the sensory evaluation results of fermented ginkgo wine. The optimization results show that the optimal fermentation conditions were a solid–liquid ratio of 1:6.4, sugar addition of 157.2 g/L, and a fermentation time of 8 d. Under these conditions, a 10 L ferment tank was selected for validation testing. The ginkgo wine is light yellow, clear, and transparent with rich nutritional value and a refreshing taste, and it belongs to the semi-sweet type of fruit wine. Six kinds of fermentation starter were used to ferment GBS, and the effects of different types of starter on the physical and chemical indexes, flavor components, and the in vitro antioxidant capacity of ginkgo wine were studied. The results show that different groups had great influences on the sugar, total flavonoid, and MPN contents of ginkgo wine. The flavonoid and terpene lactone components in the yeast group were higher than those in the Jiuqu group. Aldehydes are the main volatile components in both GBS and the seed enzymatic hydrolysates, and they greatly contribute to the flavor of GBS. The main volatile components in ginkgo wine are alcohols, esters, and a small amount of aldehydes. A total of 27 volatile components were detected in the ginkgo wine samples, among which different starters caused differences in the individual aroma components. In vitro antioxidant experiments have shown that ginkgo wine has a certain ability to clear DPPH and ABTS, and the antioxidant capacity of the yeast group sample is stronger than that of the Jiuqu group.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.S. and F.C.; methodology, E.S. and Q.G.; software, B.C.; validation, B.C. and E.S.; formal analysis, B.C., F.Z. and Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, B.C., F.Z., Z.L. and Y.H.; writing—review and editing, B.C. and Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research Program of China, grant number: 2017YFD0600701, and the 333 Project of Jiangsu Province, grant number: BRA2017458.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Deng, Q.; Wang, L.; Wei, F.; Xie, B.; Huang, F.H.; Huang, W.; Shi, J.; Huang, Q.; Tian, B.; Xue, S. Functional properties of protein isolates, globulin and albumin extracted from Ginkgo biloba seeds. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Q.; Tang, C.; Cao, F.; Su, E. Submerged fermentation ofGinkgo biloba seed powder using Eurotium cristatum for the development of ginkgo seeds fermented products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lihu, Z.; Tingting, W.; Wei, X.; Zhenzhong, W.; Gang, D.; Linguo, Z. Enrichment and Purification of Total Ginkgo Flavonoid O-Glycosides from Ginkgo Biloba Extract with Macroporous Resin and Evaluation of Anti-Inflammation Activities In Vitro. Molecules 2018, 23, 1167. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.X.; Xu, Y. Brewing of Chinese rice wine from rice roasted using superheated steam. J. Inst. Brew. 2012, 118, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, I.T.; Gustafsson, I.B.; HAGLUND, Å.; Johansson, L.; Noble, A.C. Flavor changes produced by wine and food interactions: Chardonnay wine and hollandaise sauce. J. Sens. Stud. 2010, 16, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Tan, J. Influence of fermentation temperature and source of enzymes on enological characteristics of rice wine. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, B.; Cui, S.W.; Zhang, T. Structure and functional properties of starches from Chinese ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.) nut. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, S.; Park, Y.; Park, Y. Modulation of cholesterol metabolism by Ginkgo biloba L. nuts and their extract. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, J. Study on the Fermenting Conditions of Ginkgo Fruit Wine. Liquor-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2014, 240, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Brewing Technology for Ginkgo Brandy. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2013, 5, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ciani, M.; Comitini, F. Yeast interactions in multi-starter wine fermentation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Wang, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Kida, K. Characterization of the microbial community in three types of fermentation starters used for Chinese liquor production. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allwood, J.G.; Wakeling, L.T.; Bean, D.C. Fermentation and the microbial community of Japanese koji and miso: A review. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2194–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Su, E.; Cao, F. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation conditions of Ginkgo biloba wine using response surface methodology. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2022, 46, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Bai, M.; Lou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Lu, K.; Zhang, P. Optimization of the Brewing Process and Analysis of Antioxidant Activity and Flavor of Elderberry Wine. Fermentation 2023, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Min, Z. Determination of the Flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba Extract by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2002, 13, 968–970. [Google Scholar]
- Beek, T.A.V.; Montoro, P. Chemical analysis and quality control of Ginkgo biloba leaves, extracts, and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2002–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.J.; Li, T.T.; Wang, T. Determination and Comparison of 4′-O-Methylpyridoxine Analogues in Ginkgo biloba Seeds at Different Growth Stages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Shi, Y.; Tu, Z. Optimization of Processing Formula of Kiwifruit Cake by Fuzzy Mathematical Sensory Evaluation. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y. Changes in Volatile Compounds of Chinese Rice Wine Wheat Qu During Fermentation and Storage. J. Inst. Brew. 2009, 115, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.; Junli, H.; Chuang, W. Anti-oxidation and anti-aging activity of polysaccharide from Malus micromalus Makino fruit wine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 121, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinzurik, M.I.; Deed, R.C.; Herbst-Johnstone, M.; Slaghenaufi, D.; Fedrizzi, B. Addition of volatile sulfur compounds to yeast at the early stages of fermentation reveals distinct biological and chemical pathways for aroma formation. Food Microbiol. 2020, 89, 103435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonin, S. Effects of magnesium ions on both VHG batch and continuous fruit wine fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Zhang, B.Q.; Duan, C.Q.; Yan, G.L. Effects of different pre-fermentation cold maceration time on aroma compounds of Saccharomyces cerevisiae co-fermentation with Hanseniaspora opuntiae or Pichia kudriavzevii. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, Z.; Su, H.; Ren, X. Amino Acid and Microbial Community Dynamics during the Fermentation of Hong Qu Glutinous Rice Wine. Food Microbiol. 2020, 90, 103467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenz, A.; Klein, M.; Fiehe, K.; Gross, J.; Drewke, C.; Hemscheidt, T.; Leistner, E. Occurrence of Neurotoxic 4′-O-Methylpyridoxine in Ginkgo biloba Leaves, Ginkgo Medications and Japanese Ginkgo Food. Planta Med. 1996, 62, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Yoshimura, T.; Johno, A.; Sasaki, K.; Wada, K. Toxicity of 4′-O-methylpyridoxine-5′-glucoside in Ginkgo biloba seeds. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Shi, R.; Qayum, A.; Bilawal, A.; Gantumur, M.A.; Hussain, M.A.; Jiang, Z.; Tian, B. Comparison in bioactivity and characteristics of Ginkgo biloba seed polysaccharides from four extract pathways. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X.; Cai, Y.; Bai, Y. HPTLC-bioautography/SERS screening nifedipine adulteration in food supplement based on Ginkgo biloba. Microchem. J. Devoted Appl. Microtech. All Branches Sci. 2020, 154, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanniotis, S.; Kotseridis, G.; Orfanidou, A.; Petraki, A. Effect of ethanol, dry extract and glycerol on the viscosity of wine. J. Food Eng. 2007, 81, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teslić, N.; Berardinelli, A.; Ragni, L.; Iaccheri, E.; Parpinello, G.P.; Pasini, L.; Versari, A. Rapid assessment of red wine compositional parameters by means of a new Waveguide Vector Spectrometer. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versari, A.; Ferrarini, R.; Tornielli, G.B.; Parpinello, G.P.; Celotti, E. Treatment of Grape Juice by Osmotic Evaporation. J. Food Sci. 2015, 69, E422–E427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Xiao, G.; You, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Mao, J. Effect of γ-aminobutyric acid supplementation on the composition of Chinese rice wine. J. Inst. Brew. 2019, 125, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, A.; Jing, J.; Wang, J. Determination of free amino acids and 18 elements in freeze-dried strawberry and blueberry fruit using an Amino Acid Analyzer and ICP-MS with micro-wave digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I.D.; Yang, X.M. Thermal and non-thermal processing affect Maillard reaction products, flavor, and phytochemical profiles of Ginkgo biloba seed. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Su, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Molecular structures of nonvolatile components in the Haihong fruit wine and their free radical scavenging effect. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129298. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W.; Miao, M. Characterization and antioxidant activity of Ginkgo biloba exocarp polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mridula, C.; Fitzsimons, P.E.; Strain, J.J.; Thurnham, D.I.; Howard, A.N. Nonalcoholic Red Wine Extract and Quercetin Inhibit LDL Oxidation without Affecting Plasma Antioxidant Vitamin and Carotenoid Concentrations. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).