Non-Alcoholic Fermentation of Maize (Zea mays) in Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Composition of Maize Grains
3. Lactic Acid Fermentation in Food and Beverages
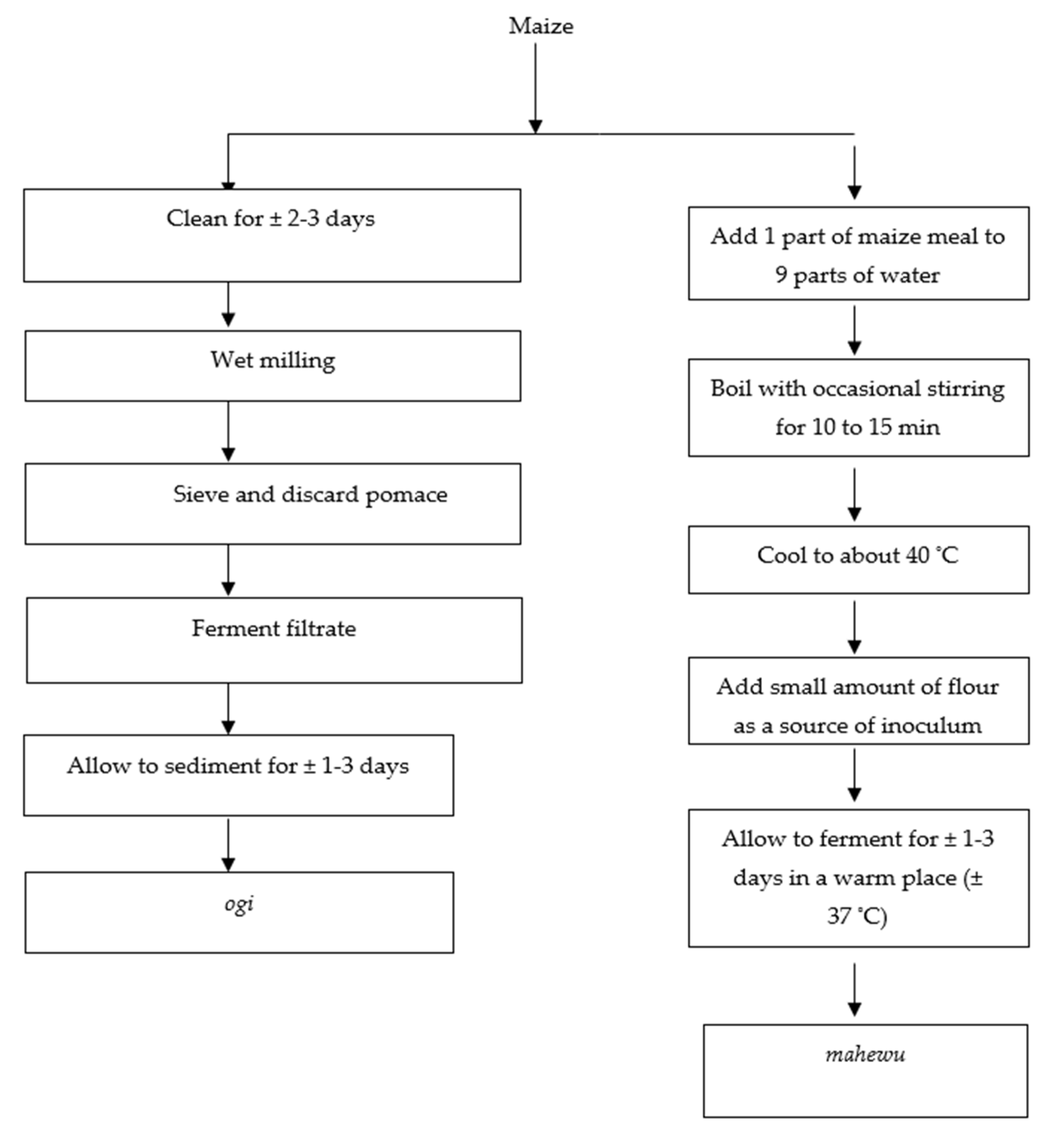
4. Types of Non-Alcoholic Maize-Fermented Gruels and Beverages in Sub-Saharan Africa
4.1. Mahewu
4.2. Ogi
4.3. Uji
4.4. Togwa
4.5. Borde
4.6. Munkoya
5. Nutritional Characteristics and Health Benefits of Maize-Based Non-Alcoholic Fermented Beverages
6. Preservative Effects, Safety and Risk Factors of Maize Based Non-Alcoholic Fermented Beverages
7. Current and Future Research on Maize-Based Non-Alcoholic Fermented Beverages
| Product | Ingredients | Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mahewu | Aloe vera powder | Increased titratable acidity and reduced pH | [113] |
| Moringa oleifera powder | Increased ash and fat contents, dietary fibre and selected mineral elements | [114] | |
| Bambara groundnut flour | Increased protein and crude fibre contents, essential amino acids and titratable acidity Reduced phytate content and pH | [115] | |
| Provitamin A biofortified maize meal | Retained provitamin A High sensory acceptability | [116] | |
| Bambara groundnut flour (raw, germinated and roasted) | Increased protein and lysine contents Increased protein digestibility Improved colour, aroma and taste | [117] | |
| Watermelon pulp powder | Increased protein, ash, titratable acidity, vitamin C and total carotenoid contents | [118] | |
| Ogi | Okra seed flour | Increased proximate composition (moisture, ash, protein and fat contents) and minerals (iron, calcium and potassium) | [119] |
| Defatted and roasted okra seed meal | Increased ash, protein and fat contents Higher viscosity and sensory scores for colour and taste | [120] | |
| Pigeon pea flour | Increased protein content and dietary fibre, B complex vitamins and essential amino acids Reduced anti-nutritional factors | [121] | |
| Whey | Increased protein, ash and fat contents and essential amino acids | [122] | |
| Groundnut seed powder | Increased protein, ash and fat contents | [123] |
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nout, M.J.R. Rich nutrition from the poorest–cereal fermentations in Africa and Asia. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultosa, G.; Hamaker, B.R.; BeMiller, J.N. An SEC-MALLS study of molecular features of water-soluble amylopectin and amylase of tef [Eragrostis tef (Zucc) Trotter] starches. Starch/Staerke 2008, 60, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jideani, I.A.; Jideani, V.A. Developments on the cereal grains Digitaria exilis (acha) and Digitaria iburua (iburu). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haard, N.F.; Odunfa, S.A.; Cherl-Ho, L.; Quintero-Ramirez, R. Food and Agricultural Organization Bulletin No. 38. In Fermented Cereals; A Global Perspective; Food and Agricultural Organisation of United Nation: Rome, Italy, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, C.O.; Ascheri, J.L.R.; Carvalho, C.W.P.; Chávez, D.W.H.; Martins, I.B.A.; Deliza, R.; de Freitas, D.G.C.; Queiroz, V.A.V. Impact of extruded sorghum genotypes on the rehydration and sensory properties of soluble beverages and the Brazilian consumers’ perception of sorghum and cereal beverage using word association. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekata, P.E.S.; Domínguez, R.; Budaraju, S.; Roselló-Soto, E.; Barba, F.J.; Mallikarjunan, K.; Roohinejad, S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Effect of innovative food processing technologies on the physicochemical and nutritional properties and quality of non-dairy plant-based beverages. Foods 2020, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.G.; Sonawane, S.K.; Arya, S.S. Cereal based functional beverages: A review. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2018, 8, 914–919. [Google Scholar]
- Phiri, S.; Schoustra, S.E.; van den Heuvel, J.; Smid, E.J.; Shindano, J.; Linnemann, A. Fermented cereal-based Munkoyo beverage: Processing practices, microbial diversity and aroma compounds. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, A.; Al-Aseeri, M.E.; Pandiella, S.S.; Cantero, D.; Webb, C. Cereal-based fermented foods and beverages. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves-López, C.; Rossi, C.; Maggio, F.; Paparella, A.; Serio, A. Changes occurring in spontaneous maize fermentation: An overview. Fermentation 2020, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achi, O.K.; Ukwuru, M. Cereal-based fermented foods of Africa as functional foods. Int. J. Microbiol. Appl. 2015, 2, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mbugua, S.K. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria during the traditional fermentation of uji. East Afri. Agric. For. J. 1984, 50, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, E.; Mejia, D. Diversification Booklet Number 21: Traditional Fermented Food and Beverage for Improved Livelihoods; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Adebiyi, J.A.; Kayitesi, E.; Adebo, O.A.; Changwa, R.; Njobeh, P.B. Food fermentation and mycotoxin detoxification: An African perspective. Food Control 2019, 106, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Kayitesi, E.; Tugizimana, F.; Njobeh, P.B. Differential metabolic signatures in naturally and lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermented ting (a Southern African food) with different tannin content, as revealed by gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC–MS)-based metabolomics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Mutanda, T.; Olaniran, A.O. Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, M.N. Chlorogenic acids and other cinnamates-nature, occurrence, and dietary burden. J. Sci Food. Agric. 1999, 79, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Taylor, J.R.N. Protein biofortified sorghum: Effect of processing into traditional African foods on their protein quality. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; Neysens, P. The sourdough microflora: Biodiversity and metabolic interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesokan, I.A.; Fawole, A.O.; Ekanola, Y.A.; Odejayi, D.O.; Olanipekun, O.K. Nutritional and sensory properties of soybean fortified composite ogi–A Nigerian fermented cereal gruel. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 3144–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, J.K.; Kadam, S.S.; Beuchat, L.R. Nutritional improvement of cereals by fermentation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutri. 1989, 28, 348–400. [Google Scholar]
- Katangole, J.N. The Microbial Succession in Indigenous Fermented Maize Products. Master’s Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Steinkraus, K.H. Fermentations in world processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2002, 1, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arngren, M.; Pedersen, C.S. Technical Report: 3-Way Modeling of Maize Kernels Using Hyperspectral Image Analysis; Faculty of Science, University of Copenhagen: Frederiksberg, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brockway, B.E. Maize. In Cereals and Cereal Products: Chemistry and Technology; Dendy, D.A.V., Dobraszczyk, B.J., Eds.; Springer publishers Inc.: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Sangwan, S.; Kumar, S.; Goyal, S. Maize utilisation in food bioprocessing: An overview. In Maize: Nutritional Dynamics and Novel Use; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanna, B.M.; Vasal, S.K.; Kassahun, B.; Singh, N.N. Quality protein maize. Curr. Sci. 2001, 8, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, S.A. Structure and composition. In Corn: Chemistry and Technology; Watson, S.A., Ramstad, P.E., Eds.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St Paul, MN, USA, 1987; pp. 53–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, A.; Bergvinson, D.; Miller, S.; Atkinson, J.; Gary, F.R.; Thor, A.J. Distribution and microchemical detection of phenolic acids, flavonoids, and phenolic acid amides in maize kernels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1879–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Y.S.; Hernandez, D.R.; Velazquez, A.D. Extraction and use of pigments from maize grains (Zea mays L.) as colorants in yogurt. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2005, 55, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Hayek, S.A.; Ibrahim, S.A. Current Limitations and Challenges with Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Review. Food Nutri. Sci. 2013, 4, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplice, E.; Fitzgerald, G.F. Food fermentations: Role of microorganisms in food production and preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 50, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, G.; Smit, B.A.; Engels, W.J. Flavour formation by lactic acid bacteria and biochemical flavour profiling of cheese products. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 591–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefyedi, M.L.; Marais, G.J.; Dutton, M.F.; Taylor, J.R.N. The microbial contamination, toxicity and quality of turned and unturned outdoor floor malted sorghum. J. Inst. Brew. 2005, 111, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhoro, C.T.; Jackson, D.S. Starch related changes in stored soft sorghum porridge. J. Food Sci. 1995, 60, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byaruhunga, Y.B. Inhibition of Bacillus Cereus by Lactic Acid Bacteria in Mageu, A Sour Maize Beverage. Master’s Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, A.; Halm, M.; Jakobsen, M. The antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria from fermented maize (Kenkey) and their interactions during fermentation. J. Appl Bacteriol. 1995, 79, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, L.L.; Baldwin, K.A. Applications for biotechnology: Present and future improvements in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 87, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskovic, J.; Kos, B.; Matosic, S.; Maric, V. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 35, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Oyewole, O.B. Lactic fermented foods in Africa and their benefits. Food Control 1997, 8, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, K.A.R.J. The role of lactic acid bacteria in colon cancer prevention: Mechanistic considerations. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999, 76, 391–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chelule, P.K.; Mokoena, M.P.; Gqaleni, N. Advantages of traditional lactic acid bacteria fermentation of food in Africa. In Current Research, Technology and Education Topics in Applied Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology; Mendez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Spain, 2010; pp. 1160–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Chelule, P.K.; Galeni, N. Reduction of fumonisin B1 and zearalenone by lactic acid bacteria in fermented maize meal. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2095–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyanzi, R.; Jooste, P.J. Cereal-Based Functional Food. In Probiotics; Rigobelo, E.C., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 161–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ghoshal, G.; Kansal, S.K. The Emerging Trends in Functional and Medicinal Beverage Research and Its Health Implication. In Functional and Medicinal Beverages; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schweigart, F.; Fellilngham, J.A. A study of fermentation in the production of ‘mahewu’, an indigenous sour maize beverage of Southern Africa. Milchwissenschaft 1963, 18, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Gqaleni, N.; Shandu, N.R.; Sibiya, P.; Dutton, M.F. Indigenous nonalcoholic fermentations and mycotoxin degradation. In International Symposium on Mycotoxins in the Food Chain: A Satellite Symposium of the IUTOX 8th International Congress of Toxicology; Le Bars, J., Ed.; Reveue de Medecine Veterinaire: Toulose, France, 1998; pp. 149–563. [Google Scholar]
- Osungbaro, W.; Taiwo, O. Physical and nutritive properties of fermented cereal foods. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2009, 3, 023–027. [Google Scholar]
- Mugula, J.K.; Nnko, S.A.M.; Narvuhus, J.A.; Sorhaug, T. Microbiological and fermentation characteristics of togwa, a Tanzanian fermented food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 80, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegaz, K. Isolation, characterization and identification of lactic acid bacteria involved in traditional fermentation of borde, an Ethiopian cereal beverage. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Anteneh, T.; Tetemke, M.; Mogessie, A. Antagonism of lactic acid bacteria against foodborne pathogens during fermentation and storage of borde and shamita, traditional Ethiopian fermented beverages. Int. Food Res. J. 2011, 18, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Zulu, R.M.; Dillon, V.M.; Owens, J.D. Munkoyo beverage, a traditional Zambian fermented maize gruel using Rhynchosia root as amylase source. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1997, 34, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoustra, S.E.; Kasase, C.; Toarta, C.; Kassen, R.; Poulain, A.J. Microbiological characterization and community evolution of three traditional Zambian fermented products: Mabisi, Chibwantu and Munkoyo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, G.B.; Otunola, G.A.; Ajao, T.A. Physicochemical, microbiological and sensory characteristics of kunu prepared from millet, maize and Guinea corn and stored at selected temperatures. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffa, T.; Jideani, I.A.; Nkama, I. Traditional production, consumption and storage of kunu—A non-alcoholic cereal beverage. Plant Foods Hum. Nutri. 2002, 57, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffa, T.; Jideani, I.A.; Nkama, I. Nutritional composition of different types of kunu produced in Bauchi and Gombe States of Nigeria. Int. J. Food Prop. 2001, 5, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Van Noort, G.; Spence, C. The mahewu Industry, South African Food Review; South African Association for Food Science and Technology: Durban, South Africa, 1976; p. 129. [Google Scholar]
- Steinkraus, K.H. Industrialisation of Indigenous Fermented Foods, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Odunfa, S.A. African Fermented Foods. In Microbiology of Fermented Foods; Wood, B.J.B., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science Publisher: London, UK, 1985; Volume 2, pp. 155–191. [Google Scholar]
- Inyang, C.U.; Idoko, C.A. Assessment of the quality of ogi made from malted millet. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 5, 2334–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Odunfa, S.A.; Nordstrom, J.; Adeniran, S.A. Development of starter cultures for nutrient enrichment of ogi, a West African fermented cereal gruel. In Report Submitted to HBVC Research, Grants Program; USAID: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bamiro, F.O.; Esuoso, K.O.; Adetunji, N.T. Fortified corn flour feed as infant formulae substitute. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1994, 37, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ohenhen, R.E.; Ikenemoh, M.J. Shelf stability and enzyme activity studies of ogi: A corn meal fermented product. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 3, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wanjala, W.G.; Onyango, A.; Makayoto, M.; Onyango, C. Indigenous technical knowledge and formulations of thick (ugali) and thin (uji) porridges consumed in Kenya. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2016, 10, 385–396. [Google Scholar]
- Masha, G.G.K.; Ipsen, R.; Petersen, M.A.; Jakobsen, M. Microbiological, rheological and aromatic characteristics of fermented Uji (an East African sour porridge). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 14, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nout, M.J.R. Fermented foods and food safety. Food Res. Int. 1994, 27, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, C.; Noetzold, H.; Bley, T.; Henle, T. Proximate composition and digestibility of fermented and extruded uji from maize-finger millet blend. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 37, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitabatake, N.; Gimbi, D.M.; Oi, Y. Traditional non-alcoholic beverage, Togwa, in East Africa, produced from maize flour and germinated finger millet. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutri. 2003, 54, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugula, J.K.; Nnko, S.A.M.; Sørhaug, T. Changes in quality attributes during storage of togwa, a lactic acid fermented gruel. J. Food Saf. 2001, 21, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foma, R.K.; Destain, J.; Mobinzo, P.K.; Kayisu, K.; Thonart, P. Study of physicochemical parameters and spontaneous fermentation during traditional production of munkoyo, an indigenous beverage produced in Democratic Republic of Congo. Food Control 2012, 25, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwale, M.M. Microbiological Quality and Safety of the Zambian Fermented Cereal Beverage: Chibwantu. Ph.D. Thesis, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Simwamba, C.G.; Elahi, M. Studies on the nutrient composition of Rhynchosia venulosa (munkoyo Roots) and physicochemical changes in munkoyo roots and maize porridge mixture during preparation of munkoyo beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1986, 34, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbo, M.R.; Bevilacqua, A.; Petruzzi, L.; Casanova, F.P.; Sinigaglia, M. Functional beverages: The emerging side of functional foods. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1192–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Aggett, P.J.; Bindels, J.G.; Bung, P.; Ferré, P.; Gil, A.; Lentze, M.J.; Roberfroid, M.; Strobel, S. Growth, development and differentiation: A functional food science approach. Br. J. Nutr. 1998, 80, S5–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyanja, C.; Birungi, S.; Ahimbisibwe, M.; Semanda, J.; Namugumya, B.S. Traditional processing, microbial and physicochemical changes during fermentation of malwa. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutri. Dev. 2010, 10, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Estepa, R.M.; Eduardo Guerra-Hernandez, E.; Garcia-Villanova, B. Phytic acid content in milled cereal products and breads. Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhou, J.R.; Erdman, J.V. Phytic acid in health and disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutri. 1995, 35, 495–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ignat, M.V.; Salant, L.C.; Pop, O.L.; Pop, C.R.; Tofana, M.; Mudura, E.; Coldea, T.E.; Bors, A.; Pasqualone, A. Current functionality and potential improvements of non-alcoholic fermented cereal beverages. Foods 2020, 9, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, Y.; Gordon, D.T.; Field, M.L. Release of phosphorus from phytate by natural lactic acid fermentation. J. Food Sci. 1983, 48, 933–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titcomb, T.J.; Tanumihardjo, S.A. Global concerns with B vitamin statuses: Biofortification, fortification, hidden hunger, interactions, and toxicity. Comp. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1968–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badawy, A.A.-B. Kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism: Regulatory and functional aspects. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2017, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odunfa, S.A. Review: African fermented foods: From art to science. MIRCEN J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1988, 4, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, C.; O’Connell-Motherway, M.; Sybesma, W.; Hugenholtz, J.; van Sinderen, D. Riboflavin production in Lactococcus lactis: Potential for in situ production of vitamin-enriched foods. Appl. Enviro. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5769–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Duodu, K.G. Effects of processing sorghum and millets on their phenolic phytochemicals and the implications of this to the health-enhancing properties of sorghum and millet food and beverage products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota de Carvalho, N.; Costa, E.M.; Silva, S.; Pimentel, L.; Fernandes, T.H.; Estevez Pintado, M. Fermented foods and beverages in human diet and their influence on gut microbiota and health. Fermentation 2018, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tannock, G.W. Identification of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 1999, 1, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Schachtsiek, M.; Hammes, W.P.; Hertel, C. Characterization of Lactobacillus coryniformis DSM 20001T surface protein CPF mediating coaggregation with and aggregation among pathogens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 7078–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelschlaeger, T.A. Mechanisms of probiotic actions—A review. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 300, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nova, E.; Warnberg, J.; Gomez-Martinez, S.; Diaz, L.E.; Romeo, J.; Marcos, A. Immunodulatory effects of probiotics in different stages of life. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, S90–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, C.; Lambert, J. Production of anti-microbial substances by probiotics. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 5, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Markowiak, P.; Slizewska, K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbanwo, S.T.; Ogunsanya, B.T. Quality assessment of oti-oka like beverage produced from pearl millet. J. Appl. Biosci. 2012, 51, 3608–3617. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R.P.; Morgan, S.; Hill, C. Preservation and fermentation: Past, present and future. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 79, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawadogo-Lingani, H.; Diawara, B.; Traore, A.S.; Jakobsen, M. Technological properties of Lactobacillus fermentum involved in the processing of dolo and pito, West African sorghum beers, for the selection of starter cultures. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aka, S.; N’Guessan, K.F.; Nanga, Y.Z.; Loukou, Y.G.; Mazabraud, A.I.; Djè, K.M. Characterization of Lactobacillus species isolated from mash, sour wort and tchapalo produced in Côte d’Ivoire. Food 2010, 4, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Holzapfel, W.H. Industrialization of mageu fermentation in South Africa. In Industrialization of indigenous Fermented Foods; Steinkraus, K.H., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 285–328. [Google Scholar]
- Fadahunsi, I.F.; Ogunbanwo, S.T.; Fawole, A.O. Microbiological and nutritional assessment of burukutu and pito (indigenously fermented alcoholic beverages in West Africa) during storage. Nat. Sci. 2013, 11, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sanni, A.I.; Oniludu, A.A.; Fadahunsi, I.F.; Afolabi, R.O. Microbial deterioration of traditional alcoholic beverages in Nigeria. Food Res. Int. 1999, 32, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaga, H.T.; Mutukumira, A.N.; Narvhus, J.A.; Feresu, S.B. A review of traditional fermented food beverages of Zimbabwe. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, A.O. African sorghum-based fermented foods: Past, current and future prospects. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutyauripo, J.; Parawira, W.; Tinofa, S.; Kudita, I.; Ndengu, C. Investigation of shelf-life extension of sorghum beer (chibuku) by removing the second conversion of malt. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 129, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, V.C.; Eleke, O.I.; Omeh, Y.S. Microbiological and nutritional qualities of burukutu sold in mammy market Abakpa, Enugu State, Nigeria. Am. J. Food Nutr. 2011, 1, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Amartey, E.O.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.B.; Adjei, C.A.; Quashie, F.K.; Nsiah-Akoto, I.; Ayanu, G. Mineral profile of pito from Accra, Tamale, Bolgatanga and Wa in Ghana. Food Public Health 2012, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solange, A.; Georgette, K.; Gilbert, F.; Marcellin, D.K.; Bassirou, B. Review on African traditional cereal beverages. Am. J. Res. Commun. 2014, 2, 103–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aadil, R.M.; Roobab, U.; Sahar, A.; ur Rahman, U.; Khalil, A.A. Functionality of Bioactive Nutrients in Beverages; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128168424. [Google Scholar]
- McGovern, P.E.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hall, G.R.; Moreau, R.A.; Nuñez, A.; Butrym, E.D.; Richards, M.P.; Wang, C.S. Fermented beverages of pre-and proto-historic China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17593–17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, G.; Wang, R.; Patel, H.; Pandiella, S.S. Use of mixed cultures for the fermentation of cereal-based substrates with potential probiotic properties. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uifalean, A.; Schneider, S.; Ionescu, C.; Lalk, M.; Iuga, C.A. Soy isoflavones and breast cancer cell lines: Molecular mechanisms and future perspectives. Molecules 2015, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequencing-based analysis of the bacterial and fungal composition of kefir grains and milks from multiple sources. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shori, A.B. Influence of food matrix on the viability of probiotic bacteria: A review based on dairy and non-dairy beverages. Food Biosci. 2016, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Procopio, S.; Becker, T. Influence of malting and lactic acid fermentation on functional bioactive components in cereal-based raw materials: A review paper. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.S.; Park, S.K.; Kim, D.S. Biostabilization of kefir with a non-lactose-fermenting yeast. J. Dairy Sci. 1996, 79, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P. Health benefits of dietary whole grains: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. J. Chiropr. Med. 2017, 16, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer-Lequart, C.; Lehmann, U.; Ross, A.B.; Roger, O.; Eldridge, A.L.; Ananta, E.; Bietry, M.F.; King, L.R.; Moroni, A.V.; Srichuwong, S.; et al. Whole grain in manufactured foods: Current use, challenges and the way forward. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashau, M.E.; Jideani, A.I.O.; Maliwichi, L.L. Evaluation of the shelf-life extension and sensory properties of mahewu–A non-alcoholic fermented beverage by adding Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) powder. Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 3419–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olusanya, R.N.; Kolanisi, U.; van Onselen, A.; Ngobese, N.Z.; Siwela, M. Nutritional composition and consumer acceptability of Moringa oleifera leaf powder (MOLP)-supplemented mahewu. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaku, X.W.; Adetunji, A.; Dlamini, B.C. Fermentability and nutritional characteristics of sorghum mahewu supplemented with Bambara groundnut. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awobusuyi, T.D.; Siwela, M.; Kolanisi, U.; Amonsoua, E. Provitamin A retention and sensory acceptability of amahewu, a non-alcoholic cereal based beverage made with provitamin A-biofortified maize. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1356–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awobusuyi, T.D.; Siwela, M. Nutritional properties and consumer’s acceptance of provitamin a-biofortified amahewu combined with Bambara (Vigna subterranea). Nutrients 2019, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maakelo, P.K.; Bultosa, G.; Kobue-Lekalake, R.I.; Gwamba, J.; Sonno, K. Effects of watermelon pulp fortification on maize mageu physicochemical and sensory acceptability. Heliyon 2021, 7, e071285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aderonke, A.; Moronkeji, A.; Vivian, I.; Chinwe, O.; Rotimi, S.; Henry, O.; Olalekan, O. Dietary fortification of ogi (maize slurry) with okra seed flour and its nutritional value. Sch. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 4, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Aminigo, E.R.; Akingbala, J.O. Nutritive composition of ogi fortified with okra seed meal. J. Appl. Sci. Env. Manage. 2004, 8, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Uchechukwu, I.O.; Omemu, A.M.; Obadina, A.O.; Bankole, M.O.; Adeyeye, S.A.O. Nutritional composition and antinutritional properties of maize ogi co-fermented with pigeon pea. Food Sci. Nutri. 2018, 6, 424–439. [Google Scholar]
- Omole, J.O.; Ighodaro, O.M.; Durosinolorun, O. Fortification of ogi with whey increases essential amino acids content of fortified product. Int. Sch. Res. Notices. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajanaku, K.O.; Ajanaku, C.O.; Edobor-Osoh, A.; Nwinyi, O.C. Nutritive Value of Sorghum ogi fortified with groundnut seed (Arachis hypogaea L.). Am. J. Food Technol. 2012, 7, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genera of LAB | Cell Form | Catalase Activity | Gram (±) Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | Rods (Bacilli; cocobacilli) | − | + |
| Streptococcus | Spheres in chains (Cocci) | − | + |
| Pediococcus | Spheres in tetrads (Cocci) | − | + |
| Lactococcus | Cocci | − | + |
| Leuconostoc | Spheres in chains (Cocci) | − | + |
| Bifidobacterium | Branched rods | − | + |
| Carnobacterium | Cocci | − | + |
| Enterococcus | Cocci | − | + |
| Sporolactobacillus | Rod | − | + |
| Lactosphaera | Cocci | − | + |
| Oenococcus | Cocci | − | + |
| Vagocuccus | Cocci | − | + |
| Aerococcus | Cocci | − | + |
| Weisella | Cocci | − | + |
| Product | Region | Countries | Substrate | Microorganisms | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahewu | Southern Africa | South Africa, Botswana and Zimbabwe | Maize, water | Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis | [46] |
| Incwancwa | Southern Africa | South Africa | Maize, water | Lactobacillus species | [47] |
| Ogi (Akamu) | West Africa | Nigeria, Ghana | Maize, Sorghum, millet, water | Lactobacillus species, Aerobacter and yeasts | [48] |
| Togwa | East Africa | Tanzania | Maize, finger millet malt, water | Lactobacillus species, Issatchenkia orientalis and Saccharomyes cerevisiae | [49] |
| Borde (shamita) | East Africa | Ethiopia | Maize, wheat, barley, water | Lactobacillus species, Enterobacteriaceae | [50,51] |
| Munkoyo | Southern Africa | Zambia | Maize, Rhynchosia heterophylla root extract, water | Lactobacillus plantarum, Weissella confusa, Lactococcus lactis and Enterococcus italicus | [52,53] |
| Uji | East Africa | Kenya, Uganda | Maize, Sorghum, millet, water | Leuconostoc mesenteriodes, Lactobacillus platarum, Pediococcus acidilactici and P. pentosaceus | [1,9] |
| Kunu | West Africa | Nigeria, Cameroon, Niger | Maize, sorghum, millet, water | Bacillus subtilis, Micrococcus sp., Staphylococcus Aureus | [54,55,56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mashau, M.E.; Maliwichi, L.L.; Jideani, A.I.O. Non-Alcoholic Fermentation of Maize (Zea mays) in Sub-Saharan Africa. Fermentation 2021, 7, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030158
Mashau ME, Maliwichi LL, Jideani AIO. Non-Alcoholic Fermentation of Maize (Zea mays) in Sub-Saharan Africa. Fermentation. 2021; 7(3):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030158
Chicago/Turabian StyleMashau, Mpho Edward, Lucy Lynn Maliwichi, and Afam Israel Obiefuna Jideani. 2021. "Non-Alcoholic Fermentation of Maize (Zea mays) in Sub-Saharan Africa" Fermentation 7, no. 3: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030158
APA StyleMashau, M. E., Maliwichi, L. L., & Jideani, A. I. O. (2021). Non-Alcoholic Fermentation of Maize (Zea mays) in Sub-Saharan Africa. Fermentation, 7(3), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030158