Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
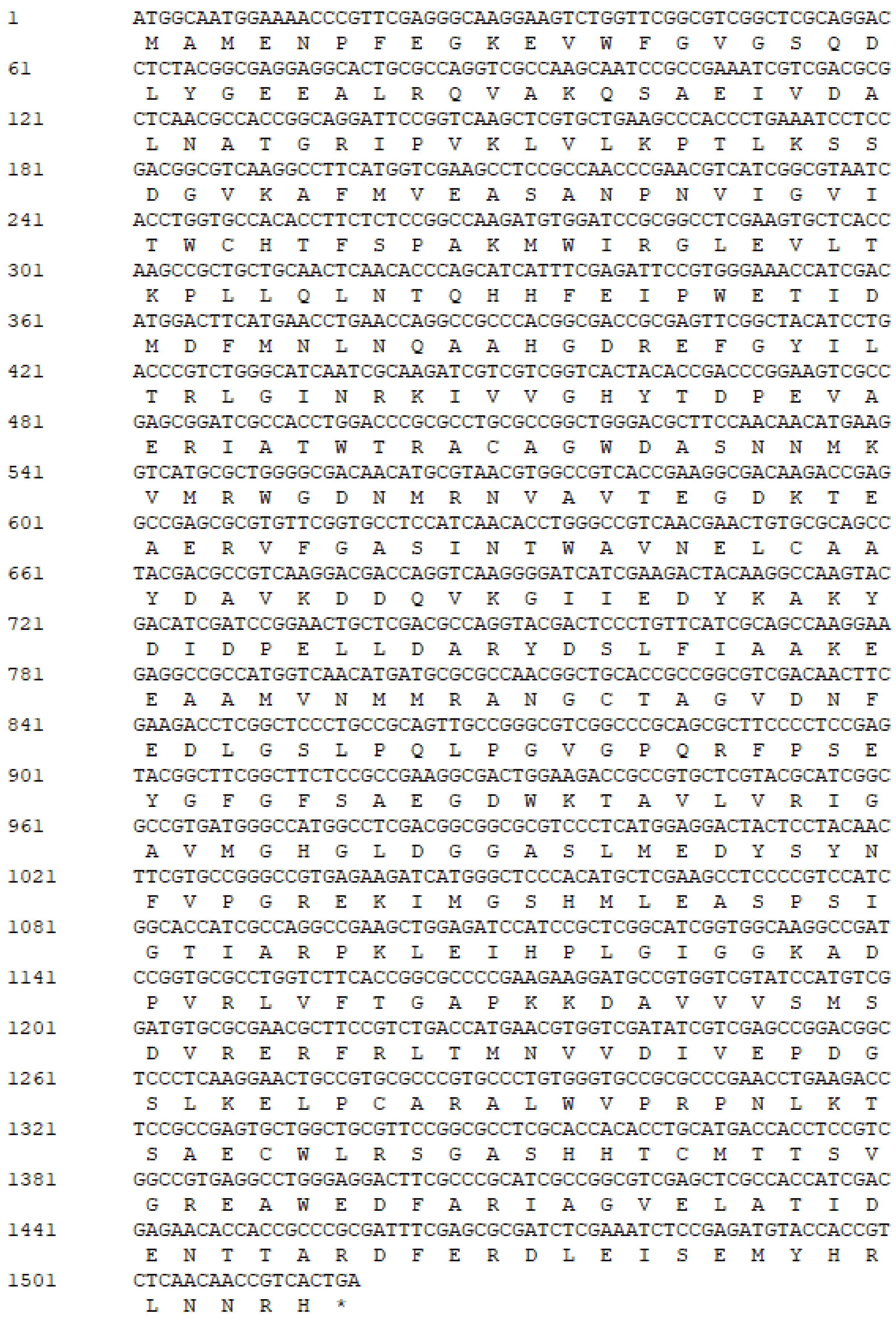
2.2. Gene Mining and Cloning of Novel L-Arabinose Isomerase
2.3. Expression and Purification of the BmAIase12
2.4. Enzyme Assay and Protein Determination
2.5. Temperature and pH Profiles
2.6. Influence of Metal Ions
2.7. Examination of the Ability of BmAIase12 to Catalyze Synthesis of D-Tagatose
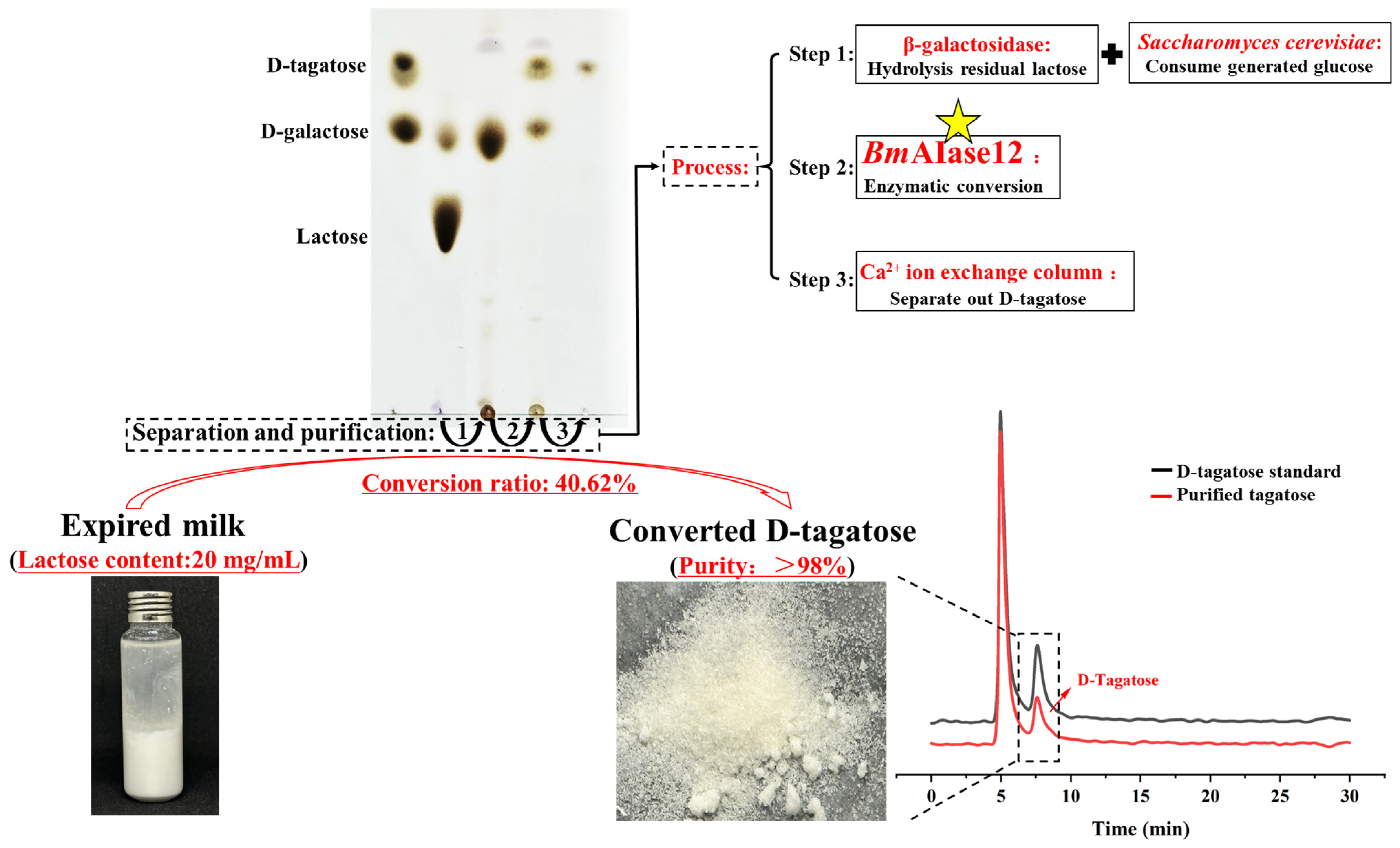
2.8. Enzymatic Recycling of Expired Milk by BmAIase12
2.9. Isolation and Purification of D-Tagatose
3. Results
3.1. BmAIase12 Recombinant Production and Purification
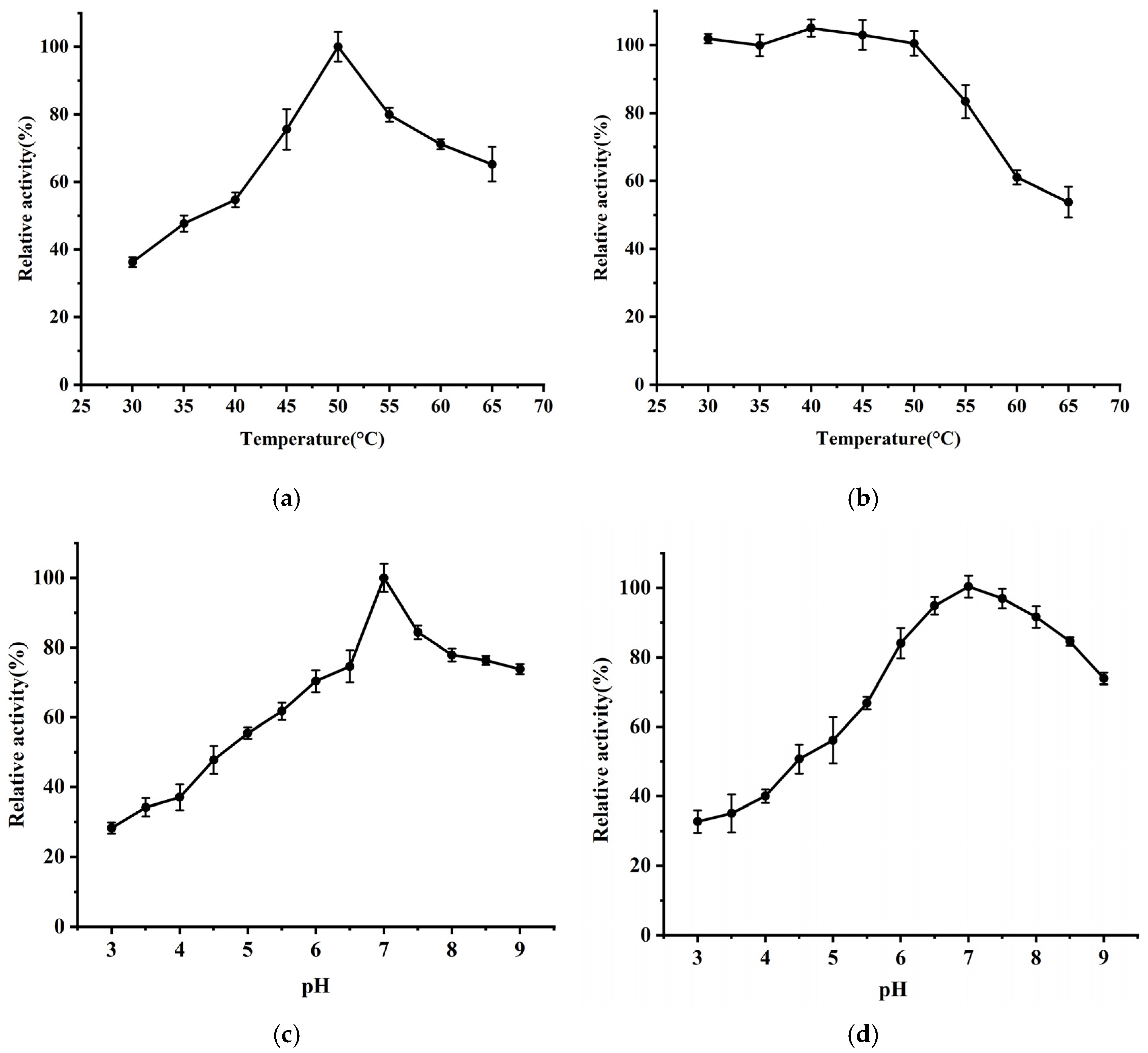
3.2. Biochemical Characterization of BmAIase12
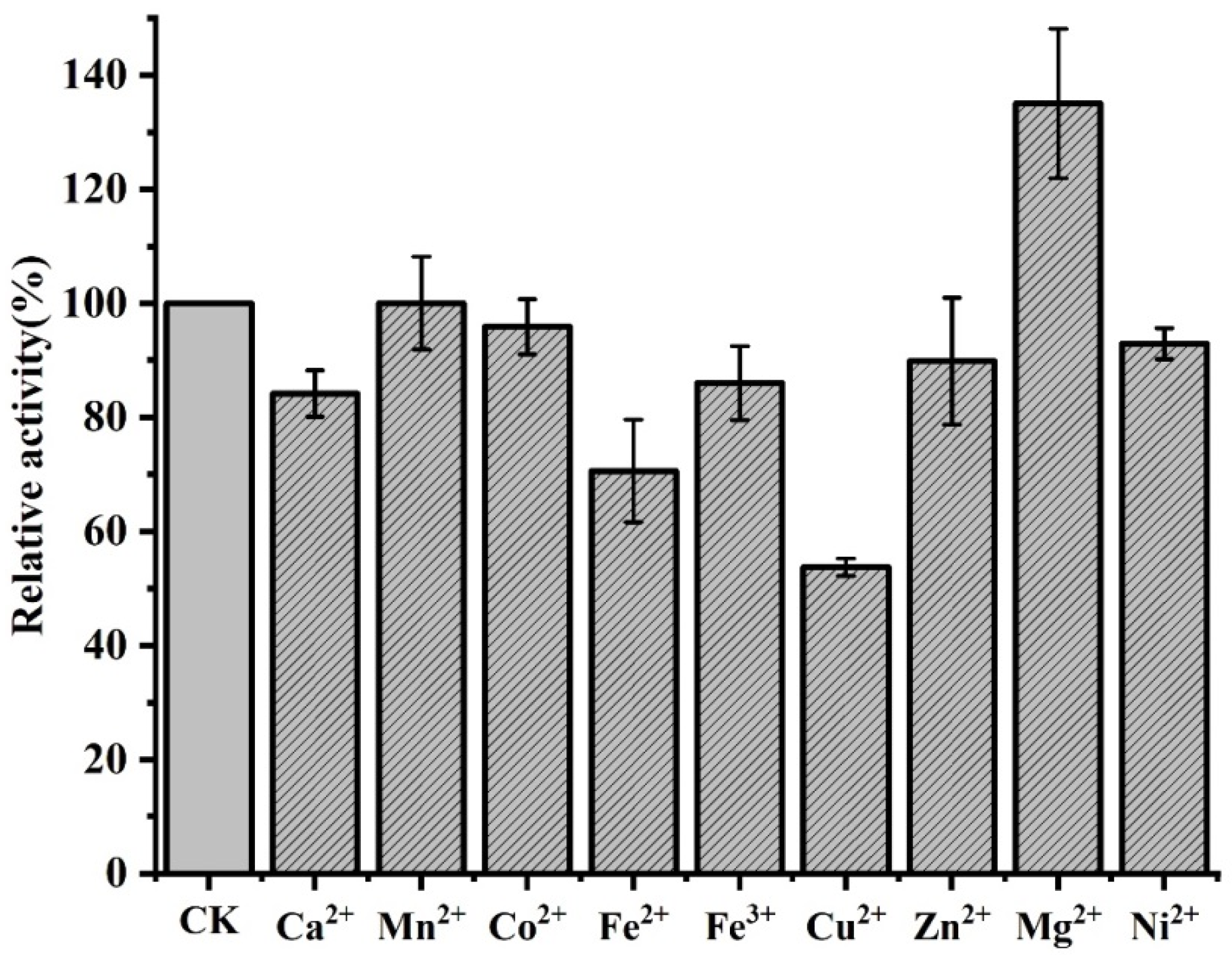
3.3. Influence of Metal Ions
3.4. Enzymatic Synthesis of D-Tagatose by BmAIase12
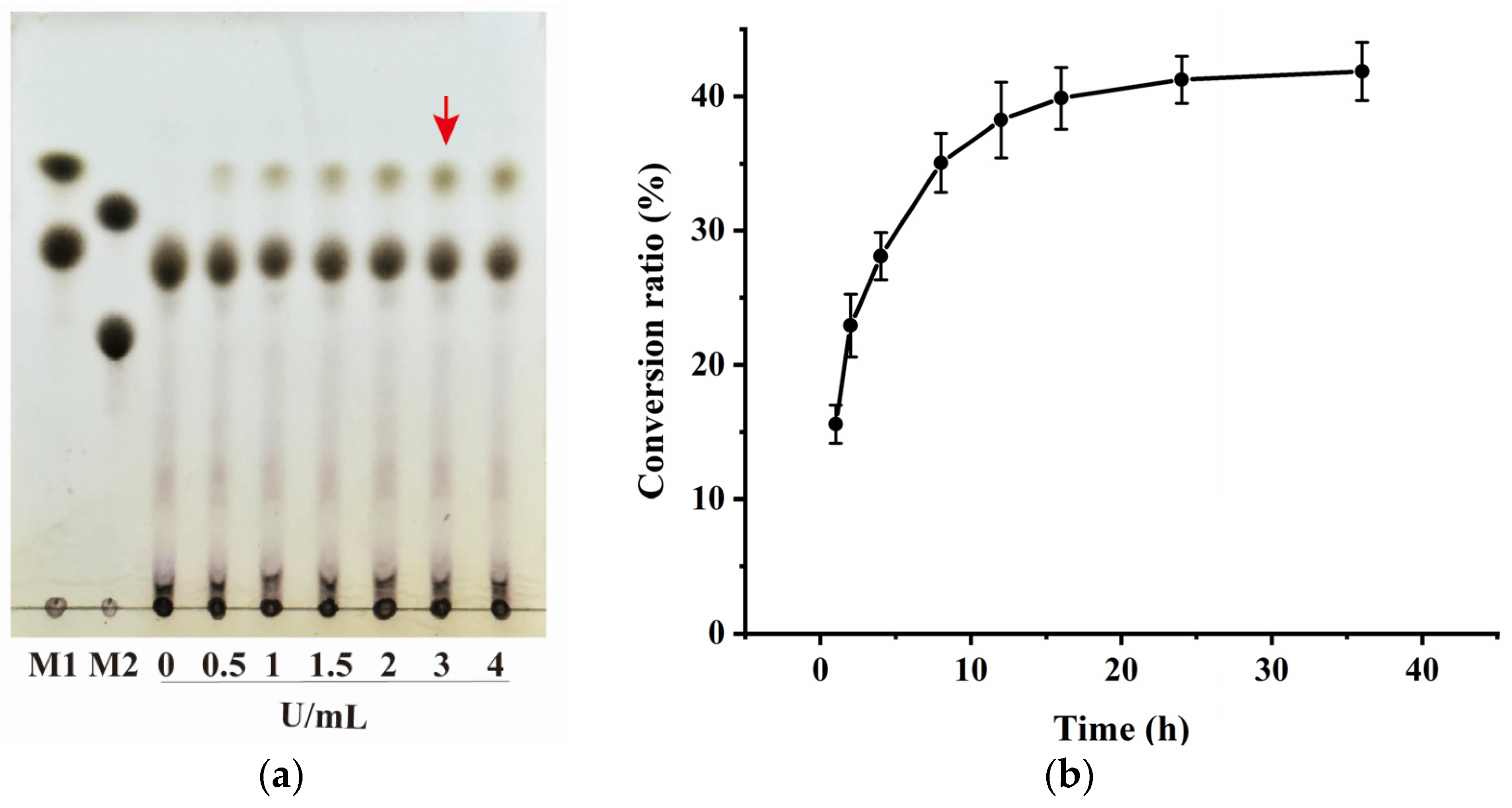
3.5. Capacity of BmAIase12 to Enhance the Conversion of Expired Milk
3.6. Isolation and Purification of the Converted D-Tagatose
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demirel, B.; Yenigun, O.; Onay, T.T. Anaerobic treatment of dairy wastewaters: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2583–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Kajla, P.; Verma, D.; Singh, T.P.; Kothakota, A.; Prasath, V.A.; Jeevarathinam, G.; Kumar, M.; Ramniwas, S.; Rustagi, S.; et al. Valorization of dairy wastes into wonder products by the novel use of microbial cell factories. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 142, 104221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization South-East Asia (WHO). Food Safety: What You Should Know; World Health Organization: New Delhi, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Gao, C.; Lin, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Shan, G.; Xie, C. Recycling of expired cow milk for constructing multifunctional biomass nonfluorinated chromatic paint with superhydrophobicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 492, 152326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Kanawaku, R.; Kawamura, S. Ethanol production from cheese whey and expired milk by the brown rot fungus Neolentinus lepideus. Fermentation 2019, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sar, T.; Harirchi, S.; Ramezani, M.; Bulkan, G.; Akbas, M.Y.; Pandey, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Potential utilization of dairy industries by-products and wastes through microbial processes: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thunuguntla, R.; Mahboubi, A.; Ferreira, J.A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Integration of membrane bioreactors with edible filamentous fungi for valorization of expired milk. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Guang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. An overview on biological production of functional lactose derivatives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3683–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granström, T.B.; Takata, G.; Tokuda, M.; Izumori, K. Izumoring: A novel and complete strategy for bioproduction of rare sugars. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 97, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felis, G.E.; Dellaglio, F. Taxonomy of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 2007, 8, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chikkerur, J.; Roy, S.C.; Dhali, A.; Kolte, A.P.; Sridhar, M.; Samanta, A.K. Tagatose as a potential nutraceutical: Production, properties, biological roles, and applications. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.K.; Kaur, H.; Kauldhar, B.S.; Yadav, S.K. Dual-enzyme metal hybrid crystal for direct transformation of whey lactose into a high-value rare sugar D-tagatose: Synthesis, characterization, and a sustainable process. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6661–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Z.; Izumori, K.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y. Enzymatic conversion of D-galactose to D-tagatose: Cloning, overexpression and characterization of L-arabinose isomerase from Pediococcus pentosaceus PC-5. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, N.; Lutz-Wahl, S.; Fischer, L. Recombinant production and characterization of a novel L-arabinose isomerase for the production of D-tagatose at acidic pH. Food Biosci. 2025, 65, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Lin, H.; Liu, G.; Ning, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Dong, N.; Lin, J.; Song, X.; et al. D-tagatose biotransformation from lactose by lactase and recombinant Bacillus subtilis expressing L-arabinose isomerase, and the product separation, purification and crystallization. Food Microbiol. 2025, 131, 104785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, C.S.; Lemos, C.M.G.d.F.; de Sousa, M.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. Enzyme immobilization onto renewable polymeric matrixes: Past, present, and future trends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.K.; Kaur, H.; Singh, A.; Kamboj, M.; Jain, G.; Yadav, S.K. Production of D-tagatose in packed bed reactor containing an immobilized L-arabinose isomerase on alginate support. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 38, 102227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, M.; Melo, V.M.M.; Hissa, D.C.; Manzo, R.M.; Mammarella, E.J.; Antunes, A.S.L.M.; García, J.L.; Pessela, B.C.; Gonçalves, L.R.B. One-step immobilization and stabilization of a recombinant Enterococcus faecium DBFIQ E36 L-arabinose isomerase for D-tagatose synthesis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, X.-W.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, M.; Wang, P. Bioconversion of D-galactose to D-tagatose: Continuous packed bed reaction with an immobilized thermostable L-arabinose isomerase and efficient purification by selective microbial degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ravikumar, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zabed, H.M.; Qi, X. L-Arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus parabuchneri and its whole cell biocatalytic application in D-tagatose biosynthesis from D-galactose. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 101034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, K.; Yan, M.; Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, T. Preparation of sweet milk and yogurt containing D-tagatose by the L-arabinose isomerase derived from Lactobacillus rhamnosus. LWT 2023, 187, 115355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, F.V.; Neifar, S.; Merdzo, Z.; Viña-Gonzalez, J.; Fernandez-Arrojo, L.; Ballesteros, A.O.; Fernandez-Lobato, M.; Bejar, S.; Plou, F.J. A three-step process for the bioconversion of whey permeate into a glucose-free D-Tagatose syrup. Catalysts 2020, 10, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, W.; Józef, K. A method for the production of D-tagatose using a recombinant Pichia pastoris strain secreting β-D-galactosidase from Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus and a recombinant L-arabinose isomerase from Arthrobacter sp. 22c. Microb. Cell Factories 2012, 11, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; An, Y.; Parvez, A.; Zabed, H.M.; Yun, J.; Qi, X. Exploring a highly D-galactose specific L-Arabinose isomerase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis for D-tagatose production. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, N.; Nyyssölä, A.; Salonen, K.; Turunen, O. Bifidobacterium longum L-arabinose isomerase—Overexpression in Lactococcus lactis, purification, and characterization. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, S.L.; Romaní, A.; Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, S.; Rocha, C.M.; Domingues, L. Galactose to tagatose isomerization by the L-arabinose isomerase from Bacillus subtilis: A biorefinery approach for gelidium sesquipedale valorisation. LWT 2021, 151, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. Improved thermostability and robustness of L-arabinose isomerase by C-terminal elongation and its application in rare sugar production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 637, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Ma, M.; Zhao, G.; Chang, R.; Si, H.; Dai, M. A novel Lactococcus lactis L-arabinose isomerase for D-tagatose production from lactose. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dische, Z.; Borenfreund, E. A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 192, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterborg, J.H.; Matthews, H.R. The lowry method for protein quantitation. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouayekh, H.; Bejar, W.; Rhimi, M.; Jelleli, K.; Mseddi, M.; Bejar, S. Characterization of an L-arabinose isomerase from the Lactobacillus plantarum NC8 strain showing pronounced stability at acidic pH. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 277, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, S.; Takahashi, S.; Nguema, P.P.M.; Fujita, S.; Kitahara, M.; Yamagiwa, J.; Ngomanda, A.; Ohkuma, M.; Ushida, K. Bifidobacterium moukalabense sp. Nov., isolated from the faeces of wild west lowland gorilla (gorilla gorilla gorilla). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64 Pt 2, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segawa, T.; Fukuchi, S.; Bodington, D.; Tsuchida, S.; Nguema, P.P.M.; Mori, H.; Ushida, K. Genomic analyses of Bifidobacterium moukalabense reveal adaptations to frugivore/folivore feeding behavior. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-H.; Lee, D.-W.; Lee, S.-J.; Choe, E.-A.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, Y.-H.; Cheigh, C.-I.; Pyun, Y.-R. Production of D-tagatose at high temperatures using immobilized Escherichia coli cells expressing L-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhimi, M.; Chouayekh, H.; Gouillouard, I.; Maguin, E.; Bejar, S. Production of D-tagatose, a low caloric sweetener during milk fermentation using L-arabinose isomerase. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3309–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-K.; Hong, M.-G.; Chang, P.-S.; Lee, B.-H.; Yoo, S.-H. Biochemical properties of L-arabinose isomerase from Clostridium hylemonae to produce D-tagatose as a functional sweetener. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Peng, S.; Liao, Y.; Li, K. L-arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus fermentum c6: Enzymatic characteristics and its recombinant Bacillus subtilis whole cells achieving a significantly increased production of D-tagatose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhimi, M.; Aghajari, N.; Juy, M.; Chouayekh, H.; Maguin, E.; Haser, R.; Bejar, S. Rational design of Bacillus stearothermophilus US100 L-arabinose isomerase: Potential applications for D-tagatose production. Biochimie 2009, 91, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Qing, Y.; Li, S.; Feng, X.; Xu, H.; Ouyang, P. A novel L-arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus fermentum cgmcc2921 for D-tagatose production: Gene cloning, purification and characterization. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 70, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Pan, B. Purification and characterization of L-arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus plantarum producing D-tagatose. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lee, D.-W.; Choe, E.-A.; Hong, Y.-H.; Kim, S.-B.; Kim, B.-C.; Pyun, Y.-R. Characterization of a thermoacidophilic L-arabinose isomerase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius: Role of lys-269 in pH optimum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7888–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, H.M.; El-Ghany, M.N.A.; Hamdi, S.A.; Abomughaid, M.M.; Ghaleb, K.I.; Kamel, Z.; Farahat, M.G. Characterization of a metallic-ions-independent L-arabinose isomerase from endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for production of D-tagatose as a functional sweetener. Fermentation 2023, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.-J. Characterization of an L-arabinose isomerase from Bacillus thermoglucosidasius for D-tagatose production. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirwantono, R.; Laksmi, F.A.; Nuryana, I.; Firdausa, S.; Herawan, D.; Giyandini, R.; Hidayat, A.A. Exploring an L-arabinose isomerase from cryophile bacteria Arthrobacter psychrolactophilus b7 for D-tagatose production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 254, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zabed, H.M.; Yun, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X. Two-stage biosynthesis of D-tagatose from milk whey powder by an engineered Escherichia coli strain expressing L-arabinose isomerase from Lactobacillus plantarum. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, W.; Wu, H.; Guang, C.; Zhang, W.; Mu, W. An overview of D-galactose utilization through microbial fermentation and enzyme-catalyzed conversion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 7161–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Song, Y.; Wi, S.G.; Bae, H.-J. Production of D-tagatose and bioethanol from onion waste by an intergrating bioprocess. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 260, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Lyu, X.; Wang, C.; Tong, Y.; Hua, X.; Yang, R. Recycling preparation of high-purity tagatose from galactose using one-pot boronate affinity adsorbent-based adsorption-assisted isomerization and simultaneous purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
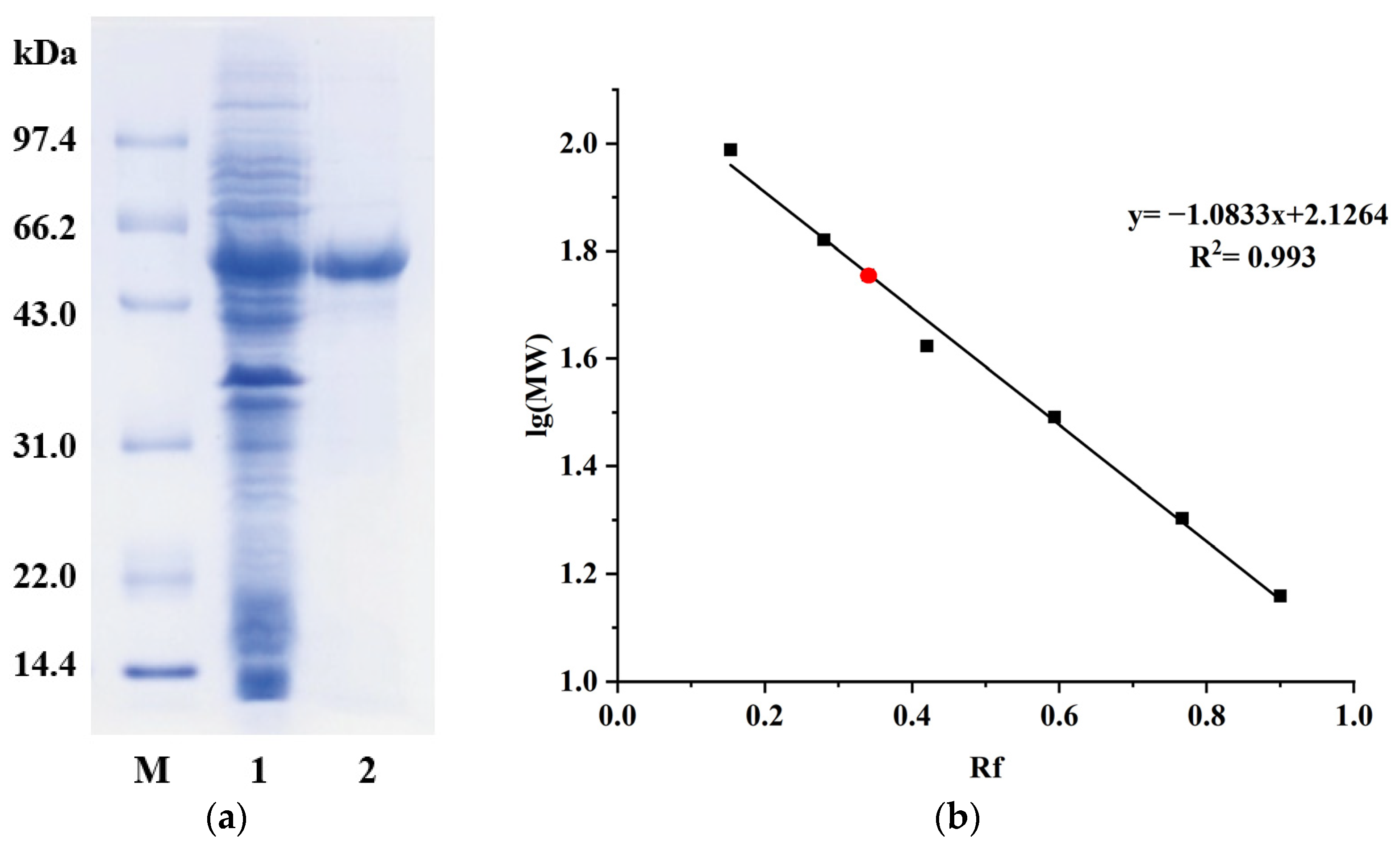

| Purification Step | Total Activity | Protein | Specific Activity | Purification | Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (U) a | (mg) b | (Units/mg) | Factor (-Fold) | (%) | |
| crude supernatant | 452.5 | 90.0 | 5.1 | 1.0 | 100.0 |
| Ni-IDA affinity chromatography | 269.8 | 25.0 | 10.7 | 2.1 | 59.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Z.; Song, Y.; Xu, J. Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk. Foods 2025, 14, 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111873
Chen Z, Yan Y, Wu Z, Song Y, Xu J. Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk. Foods. 2025; 14(11):1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111873
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhou, Yuhan Yan, Ziang Wu, Yanyin Song, and Jiangqi Xu. 2025. "Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk" Foods 14, no. 11: 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111873
APA StyleChen, Z., Yan, Y., Wu, Z., Song, Y., & Xu, J. (2025). Expression and Characterization of L-Arabinose Isomerase and Its Enzymatic Recycling of the Expired Milk. Foods, 14(11), 1873. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14111873







