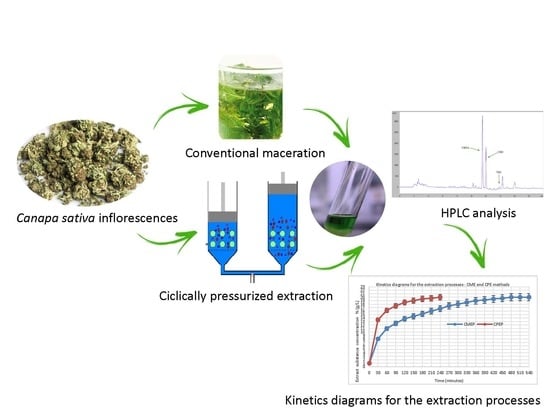
Study of the Kinetics of Extraction Process for The Production of Hemp Inflorescences Extracts by Means of Conventional Maceration (CM) and Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Materials and Solvents
2.3. Extraction Process by Conventional Maceration (CME)
2.4. Cyclically Pressurized Extraction (CPE) Process (Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE)
2.5. Determination of Solid Matrix Pieces Size
2.6. Determination of the Total Volume
2.7. Determination of the Initial Concentration of the Solid Matrix
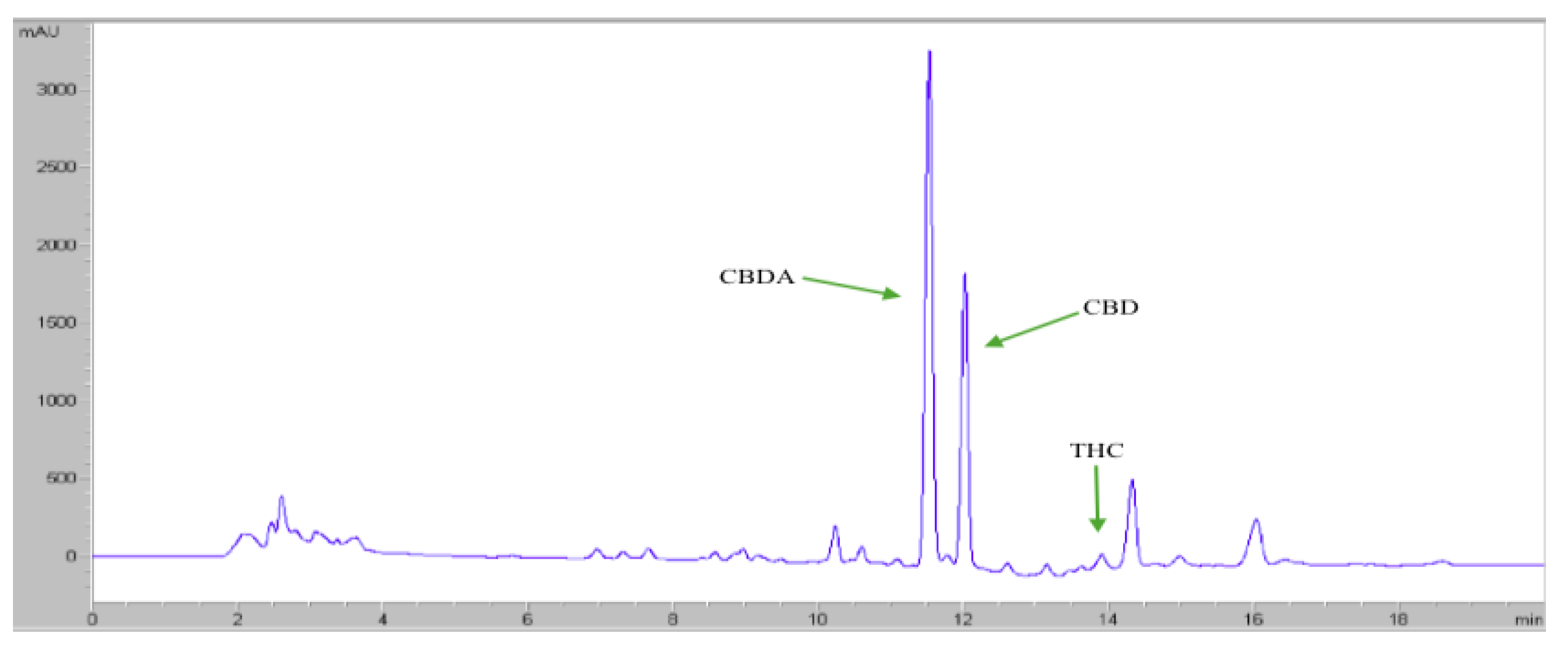
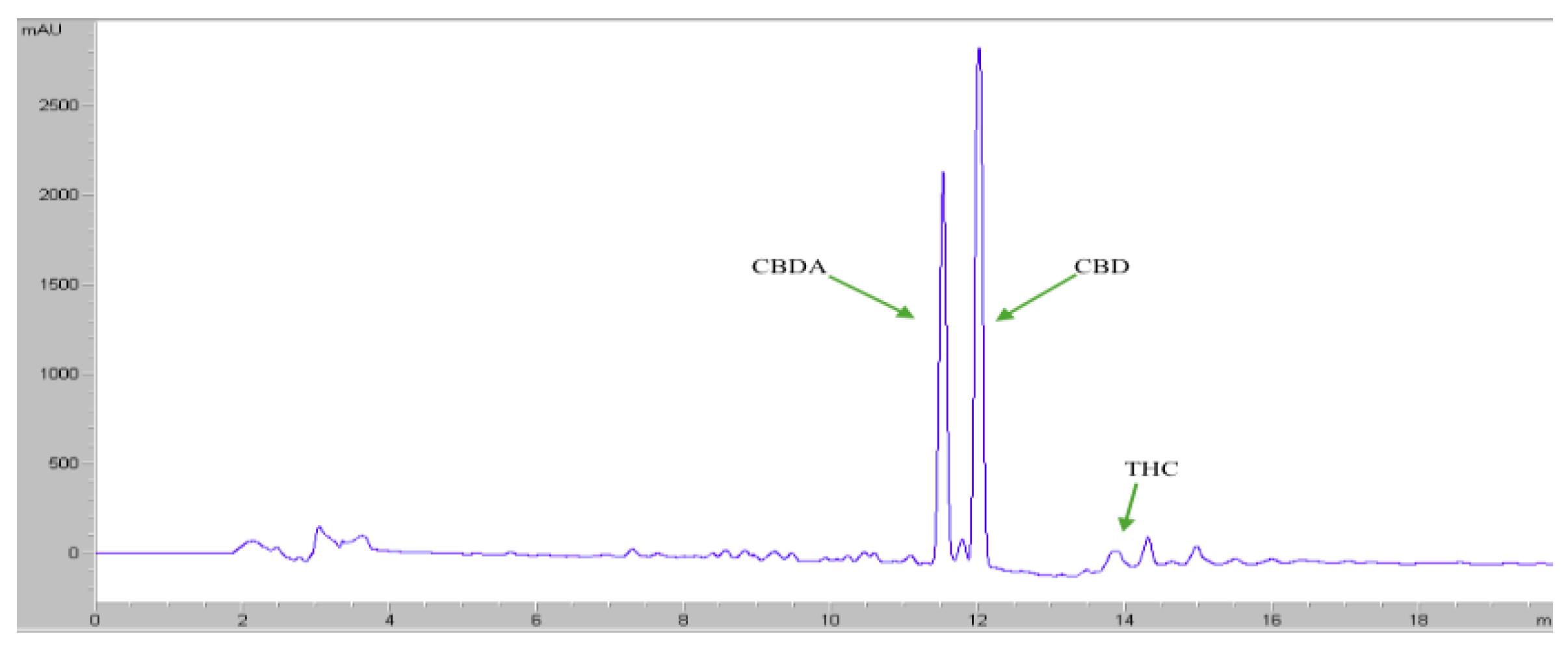
2.8. HPLC Analysis
2.9. Dry Residue
2.10. Analytical Approach
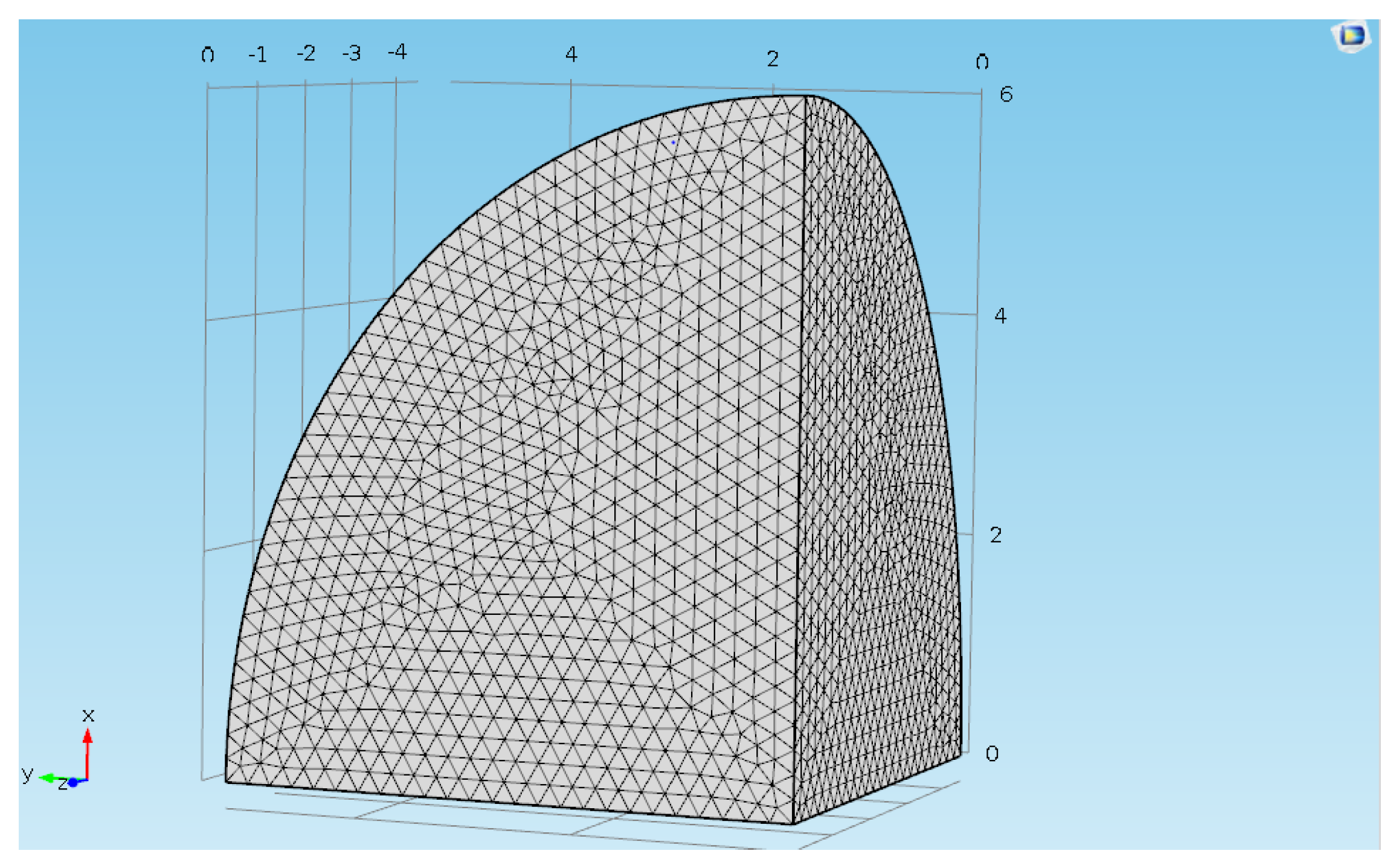
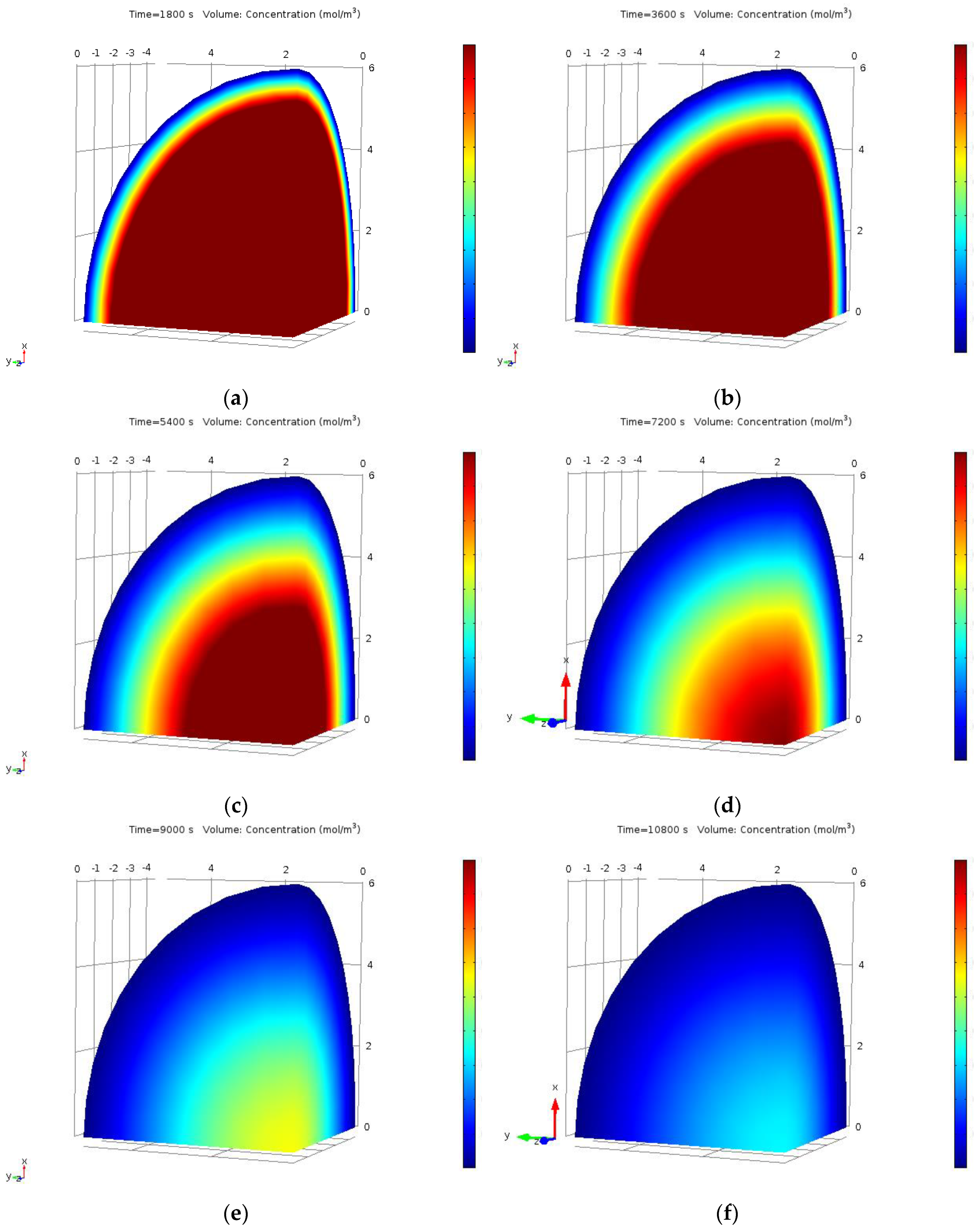
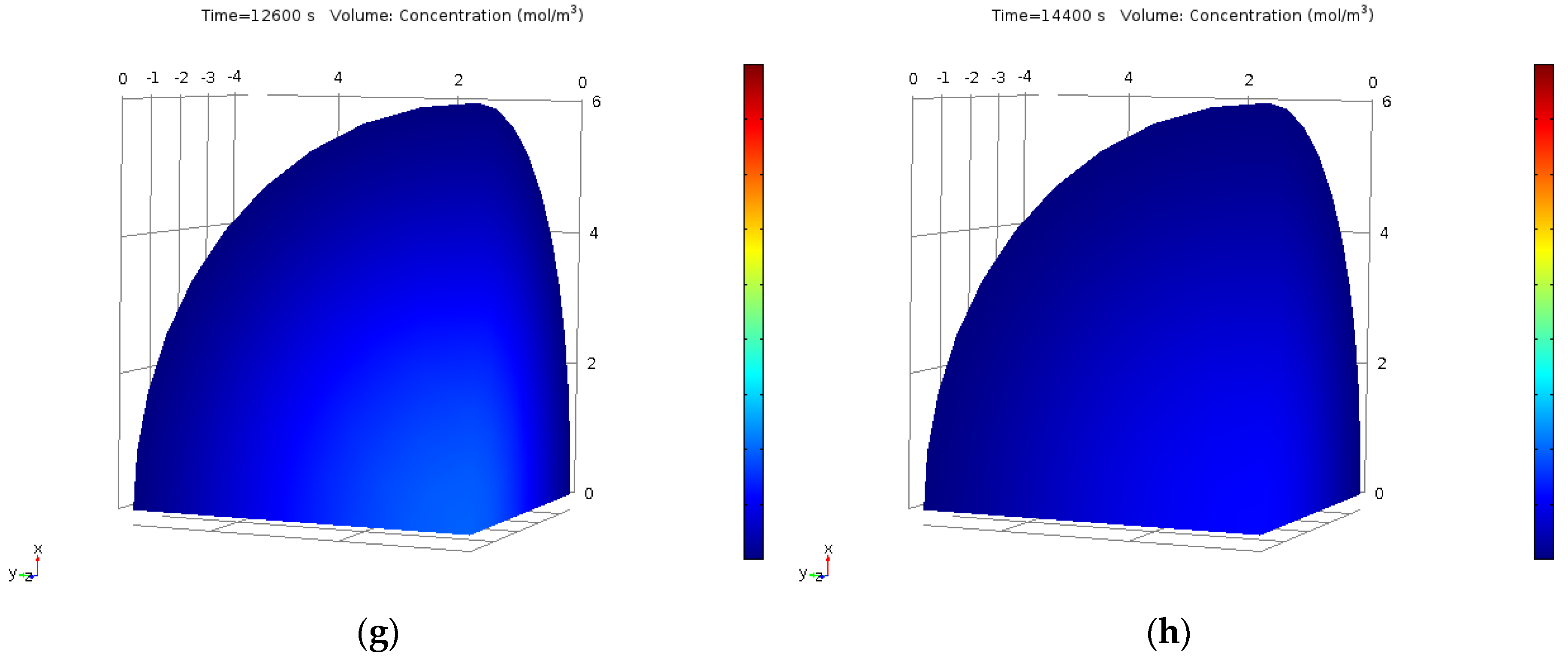
2.11. Finite Element Method Approach for CPE Process
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Drying
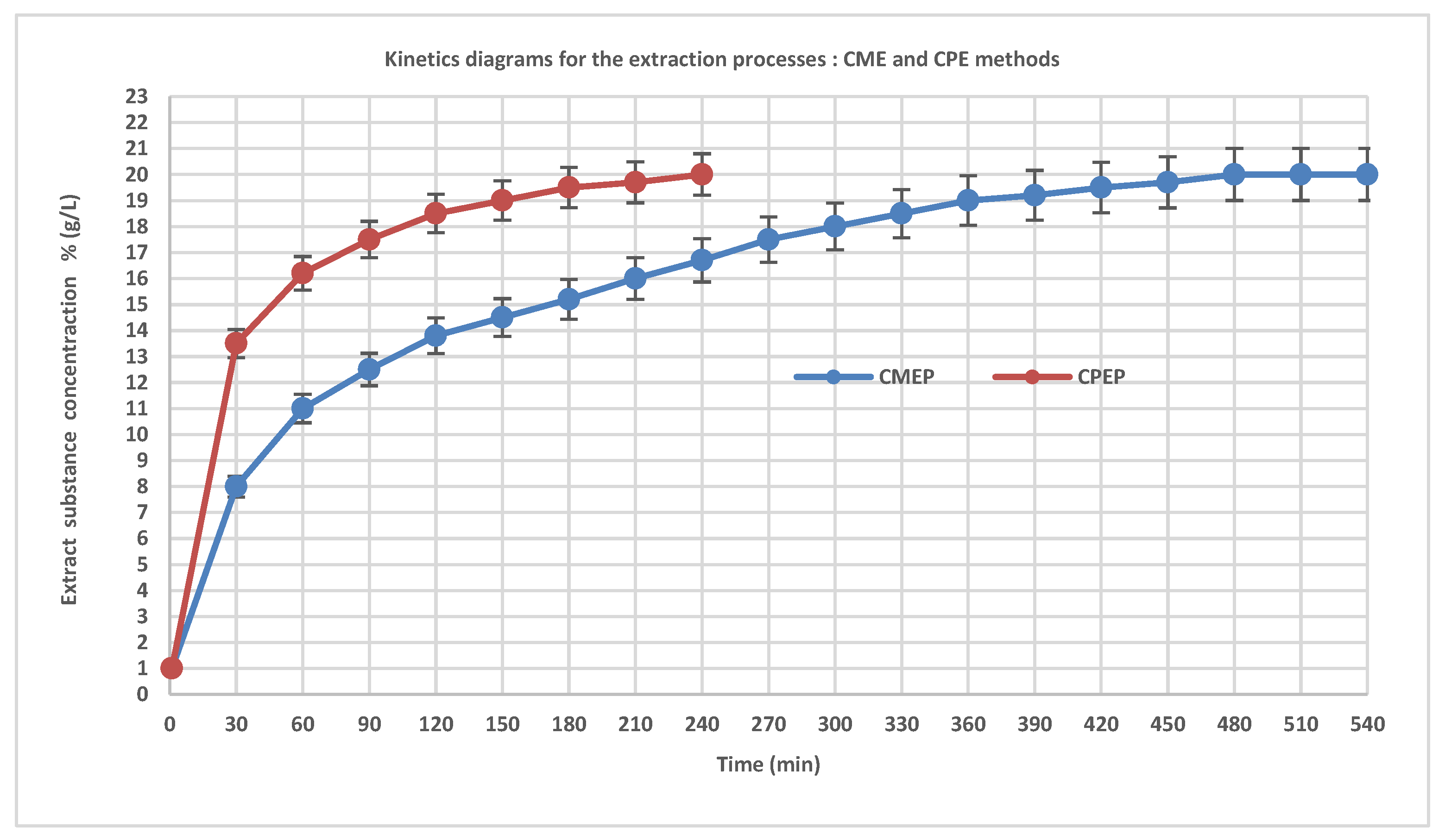
3.2. Kinetics Diagrams of CME and CPE Processes
3.3. Dry Residue
3.4. HPLC Analysis
3.5. Cyclically Pressurized Extraction (CPE) Process
3.6. Numerical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Tambaro, S.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Memo, M.; Mastinu, A. Cannabis sativa: A comprehensive ethnopharmacological review of a medicinal plant with a long history. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Moghadam, H.; Naghdi Badi, H.; Naghavi, M.R.; Salami, S.A.R. A review on agronomic, phytochemical and pharmacological aspects of cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.). J. Med. Plant. 2019, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Foti, V.T.; Scuderi, A.; Bellia, C. Actuality and future prospects of Cannabis sativa L. crops. features and problems. Quality-Access to Success 2019, 20, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Haney, M.; Hill, M.N. Cannabis and cannabinoids: From synapse to society. Neuropsychophamacology 2018, 43, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: Signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar]
- Sarne, Y. Beneficial and deleterious effects of cannabinoids in the brain: The case of ultra-low dose THC. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 2019, 45, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa: The plant of the thousand and one molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviglio, D. Naviglio’s principle and presentation of an innovative solid–liquid extraction technology: Extractor Naviglio®. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 1647–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliarelli, G.; Pagiotti, R.; Persia, D.; Marcotullio, M.C. Optimisation of a Naviglio-assisted extraction followed by determination of piperine content in Piper longum extracts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, G.; Iannarelli, R.; Sagratini, G.; Vittori, S.; Zorzetto, C.; Sánchez-Mateo, C.C.; Rabanl, R.M.; Quassinti, L.; Bramucci, M.; Vitali, L.A.; et al. Phenolic acids, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of Naviglio® extracts from Schizogyne sericea (Asteraceae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, A.; Luongo, G.; Di Marino, C.; De Tommaso, G.; Di Fabio, G.; Zarrelli, A. Silymarin from Silybum marianum by Naviglio’s extractor: A new and very efficient approach. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Williams, S., Ed.; AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists): Arlington, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R.K.; Bal, S. Properties of pearl millet. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1997, 66, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviglio, D.; Formato, A.; Gallo, M. Comparison between 2 methods of solid-liquid extraction for the production of Cinchona calisaya elixir: An experimental kinetics and numerical modeling approach. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E1704–E1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Formato, A.; Ianniello, D.; Andolfi, A.; Conte, E.; Ciaravolo, M.; Varchetta, V.; Naviglio, D. Supercritical fluid extraction of pyrethrins from pyrethrum flowers (Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium) compared to traditional maceration and cyclic pressurization extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 119, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviglio, D.; Formato, A.; Vitulano, M.; Cozzolino, I.; Ferrara, L.; Zanoelo, E.F.; Gallo, M. Comparison between the kinetics of conventional maceration and a cyclic pressurization extraction process for the production of lemon liqueur using a numerical model. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Formato, A.; Formato, G.; Naviglio, D. Comparison between two solid-liquid extraction methods for the recovery of steviol glycosides from dried stevia leaves applying a numerical approach. Processes 2018, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Formato, A.; Ciaravolo, M.; Langella, C.; Cataldo, R.; Naviglio, D. A water extraction process for lycopene from tomato waste using a pressurized method: An application of a numerical simulation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1767–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Formato, A.; Giacco, R.; Riccardi, G.; Luongo, D.; Formato, G.; Amoresano, A.; Naviglio, D. Mathematical optimization of the green extraction of polyphenols from grape peels through a cyclic pressurization process. Heliyon 2019, e01526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Gaston, A.L.; Abalone, R.M.; Giner, S.A.; Bruce, D.M. Effect of modelling assumptions on the effective water diffusivity in wheat. Biosyst. Eng. 2004, 88, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, A.L.; Abalone, R.M.; Giner, S.A. Wheat drying kinetics. Diffusivities for sphere and ellipsoid by finite elements. J. Food Eng. 2002, 52, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, M.; Formato, A.; Fabiani, A.; Scaglione, G.; Pucillo, G.P. An inertizing and cooling process for grapes cryomaceration. Elect. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviglio, D.; Formato, A.; Scaglione, G.; Montesano, D.; Pellegrino, A.; Villecco, F.; Gallo, M. Study of the grape cryo-maceration process at different temperatures. Foods 2018, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, W.L.; Smith, J.C.; Harriott, P. Unit Operation of Chemical Engineering, 7th ed.; McGraw Hill, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ahromrit, A.; Ledward, D.A.; Niranjan, K. High pressure induced water uptake characteristics of Thai glutinous rice. J. Food Eng. 2006, 72, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cissé, M.; Bohuon, P.; Sambe, F.; Kane, C.; Sakho, M.; Dornier, M. Aqueous extraction of anthocyanins from Hibiscus sabdariffa: Experimental kinetics and modeling. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, A.R.; Hase, S.L.; Vergara, M.L.; Resnik, S.L. Modeling yerba mate aqueous extraction kinetics: Influence of temperature. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.H.; Kim, C.J.; Wilson, L.A. Factors affecting water uptake of soybeans during soaking. Cereal Chem. 1983, 60, 208–211. [Google Scholar]
- Plhak, L.C.; Caldwell, K.B.; Stanley, D.W. Comparison of methods used to characterize water imbibition in hard-to-cook beans. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
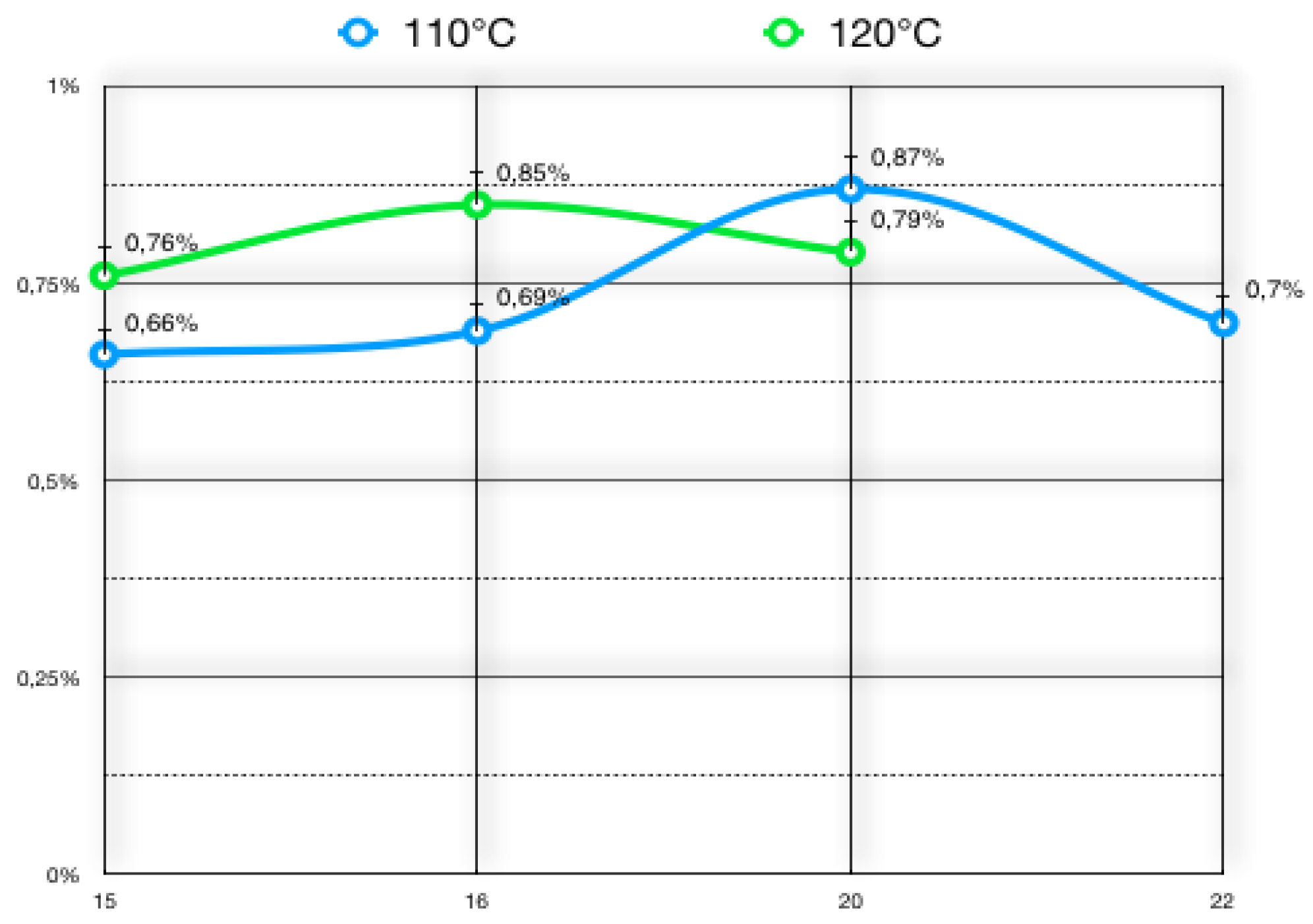
| n. | Grams of Hemp at t = 0 | Grams of Hemp at t = 1 | T° | Time | % Grams Lost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.1619 | 39.8500 | 110 °C | 15 | 11.76 |
| 2 | 45.1474 | 40.0400 | 110 °C | 16 | 11.31 |
| 3 | 45.0302 | 39.9800 | 110 °C | 20 | 11.21 |
| 4 | 46.6100 | 41.3510 | 110 °C | 22 | 11.28 |
| 5 | 45.2654 | 40.2468 | 120 °C | 15 | 11.08 |
| 6 | 45.5648 | 39.7742 | 120 °C | 16 | 12.70 |
| 7 | 45.0396 | 39.4000 | 120 °C | 20 | 12.52 |
| n. | Liquid Sample | Dry Sample | Dry Residue % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.7875 | 0.0249 | 0.66 |
| 2 | 4.0039 | 0.0277 | 0.69 |
| 3 | 4.0221 | 0.035 | 0.87 |
| 4 | 3.8434 | 0.0269 | 0.7 |
| 5 | 3.9221 | 0.03 | 0.76 |
| 6 | 4.0285 | 0.0339 | 0.85 |
| 7 | 4.0132 | 0.032 | 0.79 |
| n. | %CBDA | %CBD | %THCA | %THC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.84 | 2.30 | 0% | <0.6% |
| 2 | 13.48 | 2.82 | 0% | <0.6% |
| 3 | 12.35 | 3.30 | 0% | <0.6% |
| 4 | 12.23 | 3.36 | 0% | <0.6% |
| 5 | 8.61 | 2.92 | 0% | <0.6% |
| 6 | 8.60 | 4.41 | 0% | <0.6% |
| 7 | 7.58 | 4.71 | 0% | <0.6% |
| Minutes | L1 Length (mm) | L2 Width (mm) | L3 Thickness (mm) | fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.05 ± 0.81 | 5.22 ± 0.78 | 4.51 ± 0.80 | 0.986756 | 1.003385 |
| 60 | 6.01 ± 0.78 | 5.01 ± 0.61 | 4.49 ± 0.78 | 0.984958 | 1.012366 |
| 90 | 5.93 ± 0.69 | 4.98 ± 0.71 | 4.46 ± 0.65 | 0.985755 | 1.01131 |
| 120 | 5.9 ± 0.68 | 4.95 ± 0.75 | 4.43 ± 0.69 | 0.985606 | 1.011373 |
| 150 | 5.86 ± 0.70 | 4.93 ± 0.69 | 4.4 ± 0.74 | 0.985761 | 1.010711 |
| 180 | 5.84 ± 0.67 | 4.90 ± 0.65 | 4.36 ± 0.60 | 0.985288 | 1.010752 |
| 210 | 5.81 ± 0.65 | 4.86 ± 0.64 | 4.33 ± 0.62 | 0.985015 | 1.011309 |
| 240 | 5.78 ± 0.72 | 4.83 ± 0.70 | 4.29 ± 0.66 | 0.984722 | 1.011117 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallo, M.; Formato, A.; Ciaravolo, M.; Formato, G.; Naviglio, D. Study of the Kinetics of Extraction Process for The Production of Hemp Inflorescences Extracts by Means of Conventional Maceration (CM) and Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE). Separations 2020, 7, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020020
Gallo M, Formato A, Ciaravolo M, Formato G, Naviglio D. Study of the Kinetics of Extraction Process for The Production of Hemp Inflorescences Extracts by Means of Conventional Maceration (CM) and Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE). Separations. 2020; 7(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallo, Monica, Andrea Formato, Martina Ciaravolo, Gaetano Formato, and Daniele Naviglio. 2020. "Study of the Kinetics of Extraction Process for The Production of Hemp Inflorescences Extracts by Means of Conventional Maceration (CM) and Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE)" Separations 7, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020020
APA StyleGallo, M., Formato, A., Ciaravolo, M., Formato, G., & Naviglio, D. (2020). Study of the Kinetics of Extraction Process for The Production of Hemp Inflorescences Extracts by Means of Conventional Maceration (CM) and Rapid Solid-Liquid Dynamic Extraction (RSLDE). Separations, 7(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations7020020