- Review
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Long COVID Symptoms: A Breath of Fresh Air
- Federica Zoccali,
- Chiara Fratini and
- Antonio Minni
- + 5 authors
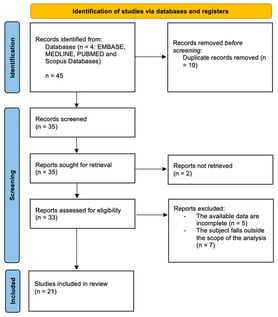
Long COVID is defined as “the continuation or development of new symptoms 3 months after the initial SARS-CoV-2 infection, with these symptoms lasting for at least 2 months with no other explanations”, as reported by the World Health Organization. A growing number of people are dealing with a variety of lingering symptoms even after recovering from an acute infection. These can include fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, headaches, cognitive issues, neurodegenerative symptoms, anxiety, depression, and a feeling of hopelessness, and therapeutic options for long COVID are investigated. The potential of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) to improve chronic fatigue, cognitive impairments, and neurological disorders has been established; therefore, the use of HBOT to treat long COVID has also been studied. The aim of this literature search is to analyze the state of the art of a potential role of HBOT to improve chronic fatigue, cognitive impairments and neurological disorders. A literature analysis was performed, focusing on the clinical efficacy of HBOT for treating long COVID symptoms. The results from January 2021 to October 2025, using a standard registry database, showed 21 studies, including one case report, ten randomized controlled trial, eight systematic reviews and three studies regarding the molecular mechanism and markers changing after HBOT. They suggested that HBOT can improve quality of life, fatigue, cognition, neuropsychiatric symptoms and cardiopulmonary functions. HBOT is a safe treatment and has shown some benefits for long COVID symptoms. To precisely define indications, protocols, and post-treatment evaluations, we need to conduct more in-depth, large-scale studies.
7 February 2026