Abstract
Plant oils are increasingly explored as sustainable functional ingredients in topical emulsions due to their emollient properties and reported photoprotective potential. This study aimed to formulate physically stable W/O emulsions containing selected plant oils (olive, avocado, sesame, flaxseed, and grape seed oils) at two concentrations (15% and 30%) and to evaluate their physicochemical, rheological, occlusive, and UV-protective properties. All formulations were confirmed as W/O systems with skin-compatible pH values and demonstrated shear-thinning, non-Newtonian flow with varying degrees of thixotropy. Increasing oil content from 15% to 30% reduced shear stress, consistency index, and viscoelastic moduli, indicating a softer internal structure. Moreover, the viscosities of the emulsions were not solely determined by the viscosities of the individual oils, suggesting significant interactions with the emulsifier system. High occlusion factors were demonstrated for all emulsions, with the highest values observed for 30% olive- and grape seed oil–based formulations. Spectrophotometric SPF assessment revealed measurable UV-protective activity only for emulsions containing 30% olive, avocado, or flaxseed oil (SPF > 1). All formulations exhibited satisfactory physical stability under mechanical and thermal stress. These findings demonstrate that plant oils can modulate the structure and performance of W/O emulsions and may serve as valuable supportive ingredients in the development of photoprotective cosmetic products.
1. Introduction
The skin is the largest organ of the human body and acts as the primary barrier between the body and the external environment, playing a crucial role in protection against harmful external factors. One of these factors is ultraviolet (UV) radiation, to which the skin is regularly exposed. While UV radiation is indispensable for the endogenous synthesis of vitamin D3 and exerts certain beneficial physiological effects, excessive exposure is associated with adverse outcomes such as erythema, oxidative stress, photoaging, and photocarcinogenesis. Chronic overexposure to UV radiation constitutes a significant risk factor for the development of various skin cancers, the incidence of which has markedly increased in recent decades [1,2]. According to the GLOBOCAN 2022 report by the Global Cancer Observatory, the highest incidence rates of skin cancer were recorded in North America, Oceania, and Europe, regions characterized by predominantly fair-skinned populations. In Europe, the incidence of melanoma skin cancer ranges from 10 to 25 new cases per 100,000 inhabitants, making it the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer on this continent [3,4]. Numerous studies have shown that frequent sunburns throughout life are associated with an increased risk of skin cancer [5,6].
To mitigate the deleterious effects of UV radiation, regular and proper application of sunscreens represents the primary preventive strategy, serving as a crucial factor in preventing the development of skin cancer and reducing the occurrence of various types of skin damage [7,8]. Nevertheless, although commercial sunscreens are highly effective, some of their active ingredients (UV filters) may pose risks to human health and the environment. The safety of both organic and inorganic UV filters has been extensively investigated, as numerous studies have reported their susceptibility to photodegradation. Irreversible photodegradation not only decreases the photoprotective efficiency of UV filters but may also result in the formation of toxic or reactive byproducts capable of inducing photoirritation or photoallergic reactions in humans [9,10,11]. While inorganic UV filters generally exhibit greater photostability, exposure to UV radiation can lead to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which may penetrate the stratum corneum and cause oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA [8,12]. Furthermore, several studies have shown that certain organic UV filters can be absorbed through the skin, enter systemic circulation, and exert potential endocrine-disrupting effects [13,14].
In 2019, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classified 16 approved over-the-counter (OTC) sunscreen active ingredients into three categories based on available safety and efficacy data. UV filters in Category I are Generally Recognized as Safe and Effective (GRASE), whereas those in Category II are considered non-GRASE. Category III requires additional data before a GRASE determination can be made. As a result, two ingredients, para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) and trolamine salicylate, were designated as Category II and subsequently banned from use in sunscreen products in the United States due to safety concerns [15,16].
To identify safer alternatives, there is a growing demand for natural ingredients in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries [17]. Plant oils, natural triglyceride-based oils of botanical origin (commonly known as vegetable oils) have attracted considerable interest due to their abundant availability, renewability, and numerous beneficial effects on humans, making them a natural and environmentally friendly choice for cosmetic applications. In topical preparations, plant oils are primarily used for their emollient and moisturizing properties [18]. According to literature reports, certain plant oils also exhibit UV-protective properties. For instance, sesame oil has been described as having strong antioxidant activity and providing approximately 30% resistance to UV radiation, with an estimated sun protection factor (SPF) of around 2. Coconut oil, peanut oil, olive oil, and cottonseed oil have been reported to exhibit about 20% UV resistance, and olive oil has been cited as having one of the higher SPF values among plant oils, with reported values ranging from approximately 7.5 to 8 [19,20].
Sunscreens are intended to remain on the skin surface or accumulate in the upper layers of the stratum corneum, with minimal penetration beyond the epidermis to achieve their effect [21]. Excessive penetration of UV filters into deeper layers may reduce their effectiveness and safety, leading to systemic absorption and increased risk of adverse effects [22]. Currently, various sunscreen formulations are available, among which emulsions remain the most widely used worldwide. Oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions are preferable because the external water phase evaporates after application, creating a cooling, namely refreshing sensation on the skin [23]. However, oil-based formulations provide superior emollient properties and form a long-lasting film on the skin surface, which enhances their suitability for sunscreen applications [24].
The choice of formulation type is crucial for ensuring efficacy, safety, and consumer acceptance. Increasing attention is now devoted to the esthetic properties of topical products, including appearance and sensory feel, as these factors strongly influence consumer acceptance [22,23]. Rheological measurements can provide useful insights into sensory-related properties; however, they cannot fully replace dedicated sensory evaluation. Although they have certain limitations, instrumental measurements have been shown to correlate well with sensory tests [25]. By analyzing rheological behavior, it is possible to gain insight into how a product will perform under real-life conditions, including manufacturing, packaging, and application to the skin. The flow behavior and viscosity of formulations, as determined by rheological measurements, may reflect their spreadability and ease of application on the skin. Therefore, rheological analysis represents a valuable tool in developing formulations optimized for both efficacy and sensory appeal [26,27].
Therefore, the aim of this study was to formulate stable water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions for topical application and to investigate the influence of different types and concentrations of plant oils on their rheological properties, occlusive capacity, and sun-protective potential.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
Plant oils (olive oil, avocado oil, sesame oil, flaxseed oil and grape seed oil) were obtained from Alekpharm (Belgrade, Serbia). Dehymuls® K (BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) was used as a base and consisted of: soft paraffin, decyl oleate, dicocoyl pentaerythritol distearyl citrate, sorbitan sesquioleate, microcrystalline wax, paraffin oil, beeswax, and aluminum stearate.
2.2. Formulation Design and Preparation Method
Ten formulations were prepared using five different plant oils (olive oil, avocado oil, sesame oil, flaxseed oil, and grape seed oil) at two concentrations (15% and 30%) (Table 1). Additionally, a control formulation (F0) containing no plant oil was included.

Table 1.
Composition of emulsions (%, w/w).
The oil phase was prepared by incorporating the required amount of plant oil into the Dehymuls® K base and heating the mixture to 70 °C under continuous stirring. In parallel, the aqueous phase was heated separately to the same temperature. The emulsion was formed by gradually adding the aqueous phase to the oil phase under continuous stirring using Boeco mechanical overhead stirrer (Hamburg, Germany) at a constant speed of 500 rpm. After addition, emulsification was continued for an additional 10 min at 70 °C to ensure homogeneity.
The prepared emulsions were then allowed to cool to room temperature under continuous gentle stirring, after which they were transferred to suitable glass containers and stored well closed, protected from light at room temperature prior to further characterization.
2.3. Physical Characterization and PH Value of Emulsions
The type of emulsion was determined using an electric conductivity measurement with a Boeco CT-600 conductivity meter (Hamburg, Germany).
The emulsions were visually examined for color and phase separation. Additionally, the pH value of each formulation was determined at 25 ± 0.1 °C using a digital pH meter (WTW Inolab, Weilheim, Germany).
2.4. Rheological Properties
Rheological behavior of prepared formulations was examined by Haake Mars rheometer (Thermo Scientific, Karlsruhe, Germany) equipped with a cone-plate geometry C35/2°/Ti at 25 ± 0.1 °C.
Flow curves were determined in continuous hysteresis loop tests where samples were exposed to a gradual increase in shear rate from 0.005 to 150 s−1 over 120 s, followed by a 60 s period at a constant shear rate of 150 s−1, and finally a decrease to 0 s−1 over the next 120 s. The same procedure was performed for the pure plant oils using a coaxial cylinder geometry with CC25 DIN/Ti rotor to determine their apparent viscosities. The obtained flow curves were fitted using the Herschel–Bulkley model:
where τ (Pa) is shear stress, is the yield stress, (s−1) is the shear rate, n (non-dimensional) is the flow behavior index, and K (Pa·sn) is the consistency index.
Apparent viscosity values were recorded throughout the flow curve measurement, and the apparent viscosities of the formulations at 100 s−1 were correlated with those of the corresponding pure plant oils to assess whether emulsion rheology was primarily influenced by oil viscosity.
Additionally, amplitude sweep tests were performed to determine the linear viscoelastic region (LVR). The storage (elastic) modulus (G′) and loss (viscous) modulus G″ were recorded versus shear stress (0.1–100 Pa) at a constant frequency of 1 Hz. Based on the amplitude sweep results, a shear stress of 1 Pa, corresponding to the midpoint of the LVR, was selected and applied in the subsequent frequency sweep tests. In the frequency sweep tests G′ and G″ moduli were recorded as a function of frequency (0.1–10 Hz) at a constant shear stress of 1 Pa.
2.5. Determination of Occlusion Factor
The occlusive properties were investigated using an in vitro occlusion test [28]. Beakers with a capacity of 100 mL and a diameter of 5.8 cm were filled with 50 mL of distilled water and covered with filter paper (Whatman number 4, pore size: 20–25 µM). An equal amount of each sample (0.5 g) was uniformly spread over the surface of the filter paper (26.4 cm2), resulting in an applied emulsion amount of 18.9 mg/cm2. The beakers with the samples were then incubated at 32 ± 0.5 °C, corresponding to the skin surface temperature. After 24 and 48 h, the beakers were weighed to determine water loss. The occlusion factor (F) was calculated according to the following equation:
where A represents the water loss in the control and B represents the water loss in the samples. An F value close to 0 indicates no occlusive effect, whereas a value close to 100 indicates maximal occlusion.
2.6. Determination of SPF Values
SPF values were determined by the spectrophotometric method [29]. Samples (1 g) were dissolved in 100 mL of absolute ethanol using an ultrasonic bath for 5 min and then diluted 5-fold. The absorbance of each formulation was measured in the UVB spectral range (290–320 nm), at 5 nm intervals, using ethanol as a blank. The SPF values were calculated using Mansur’s equation:
where CF is the correction factor (10), EE is the erythmogenic effect of radiation of wavelength λ, I is the intensity of solar light at wavelength λ, and Abs represents the absorbance of emulsion at the corresponding wavelength λ. The values of EE × I are constants, previously described in the literature and shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Values of the product of the erythemogenic effect of radiation (EE) and the intensity of solar light (I) at each wavelength (λ).
2.7. Stability Study
The stability of the formulations was evaluated under different storage conditions. The formulations were subjected to centrifugation and temperature cycle tests [30], after which visual characteristics indicative of instability, such as color changes or phase separation, were examined.
Samples (5 g) were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min at room temperature. In the temperature cycle test, samples (10 g) were exposed to heat stress for 48 h, where one temperature cycle lasted 24 h and consisted of incubation at 4 °C for 8 h followed by incubation at 40 °C for 16 h.
In addition, samples (10 g) were stored in closed glass containers at room temperature for 30 days. After this period, rheological measurements were repeated to assess possible changes in the structure of the formulations during storage.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All measurements were performed in triplicate, and all values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical significance between the examined groups was determined at a significance level (α) of 0.05 using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, performed in OriginPro 2019.
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characterization and PH Value
Visual examination of the prepared formulations showed that all emulsions were of milky-white to light-yellow color, smooth, shiny, and homogenous, with no visible signs of phase separation. The pH values ranged from 5.85 for F0 to 6.21 for F1. Low electrical conductivity values (0.01–0.03 μS/cm) indicated that all prepared formulations were W/O emulsions.
3.2. Rheological Properties of the Emulsions
As part of the pre-formulation evaluation, the apparent viscosities of the plant oils used in the emulsion formulations were first determined. Their apparent viscosities ranged from 39.75 mPa·s for flaxseed oil to 94.45 mPa·s for avocado oil (Table 3).

Table 3.
Apparent viscosities of the plant oils used in the emulsion formulations.
Flow curves of the prepared emulsions are presented in Supplementary Figure S1. All formulations exhibited pseudoplastic (e.g., shear-thinning) flow, characterized by a substantial decline in apparent viscosity as the shear rate increased. In several formulations, a certain degree of thixotropy was also observed, indicated by the hysteresis area between the forward and backward curves. The concentration of plant oil strongly influenced the flow behavior; emulsions containing 15% oil (F1, F3, F5, F7, F9) reached approximately half the shear stress values of the control formulation without plant oil (F0), while increasing the oil proportion to 30% further significantly reduced shear stress. The lowest shear stress values were recorded for the formulation F8 containing 30% flaxseed oil.
Rheological parameters calculated by fitting the flow curves to the Herschel–Bulkley model are summarized in Table 4. Analysis of the forward curves showed that only the control formulation F0 and the emulsions containing avocado oil (F3 and F4) exhibited a yield stress (τ0), indicating that an initial shear force was required to initiate flow in these emulsions. In contrast, yield stress values were obtained for all formulations when calculated from the backward curves, with the control formulation showing the highest τ0. Increasing the oil content from 15% to 30% resulted in an approximately 10-fold decrease in yield stress. Similar trend was observed for the consistency index (K), which also decreased with higher oil content. For all emulsions, K values obtained from the forward curves were higher than those obtained from the backward curves, confirming the thixotropic behavior of the formulations. The flow behavior index (n) calculated from the forward curves ranged from 0.13 to 0.45 for emulsions containing plant oils and was 0.55 for the control. When derived from the backward curves, n values were significantly higher (0.57–0.79), indicating that the disrupted structures behaved more like Newtonian fluids, i.e., their viscosities changed slightly with shear rate.

Table 4.
Yield stress (τ0), consistency index (K) and flow behavior index (n) values of the emulsions obtained from Herschel–Bulkley model fitting.
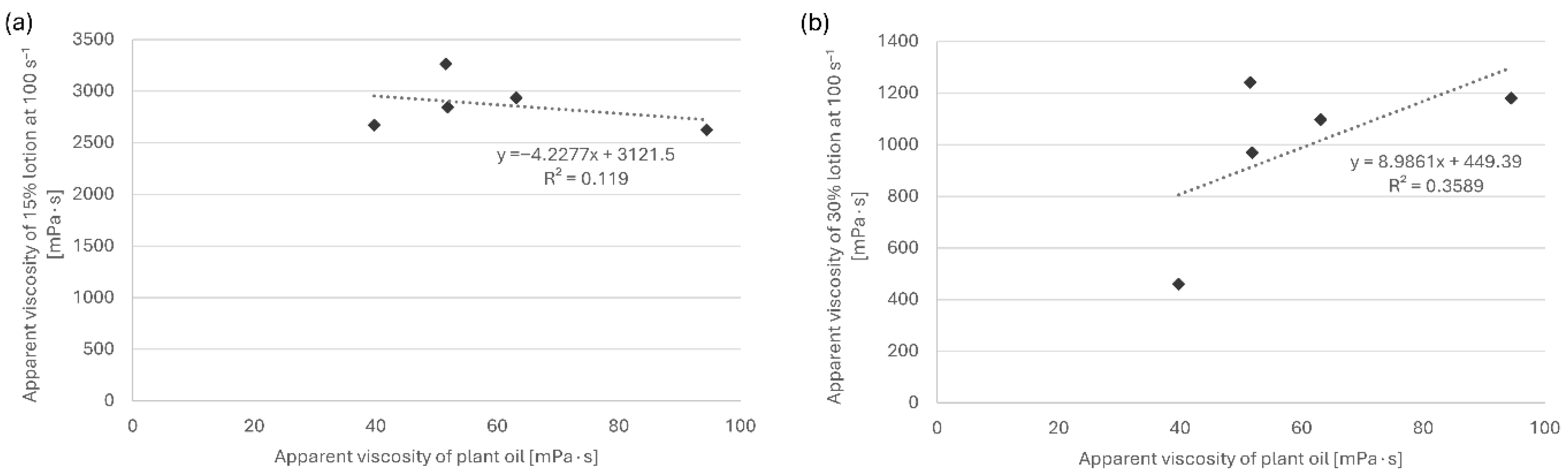
Correlation analysis between the apparent viscosities of the pure plant oils and those of the corresponding emulsions showed no statistically significant relationship (Figure 1). In the formulations containing 30% oil, emulsions prepared with more viscous oils tended to exhibit higher apparent viscosities (Pearson r = 0.60), while no such trend was observed for the 15% oil group. These findings suggest that the rheological behavior of the emulsions is not determined solely by the viscosity of the plant oils but also by interactions among the formulation components.
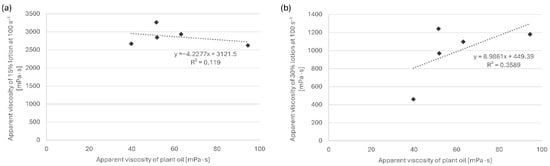
Figure 1.
Correlation between apparent viscosities of plant oils and the corresponding emulsions prepared with (a) 15% oil and (b) 30% oil.
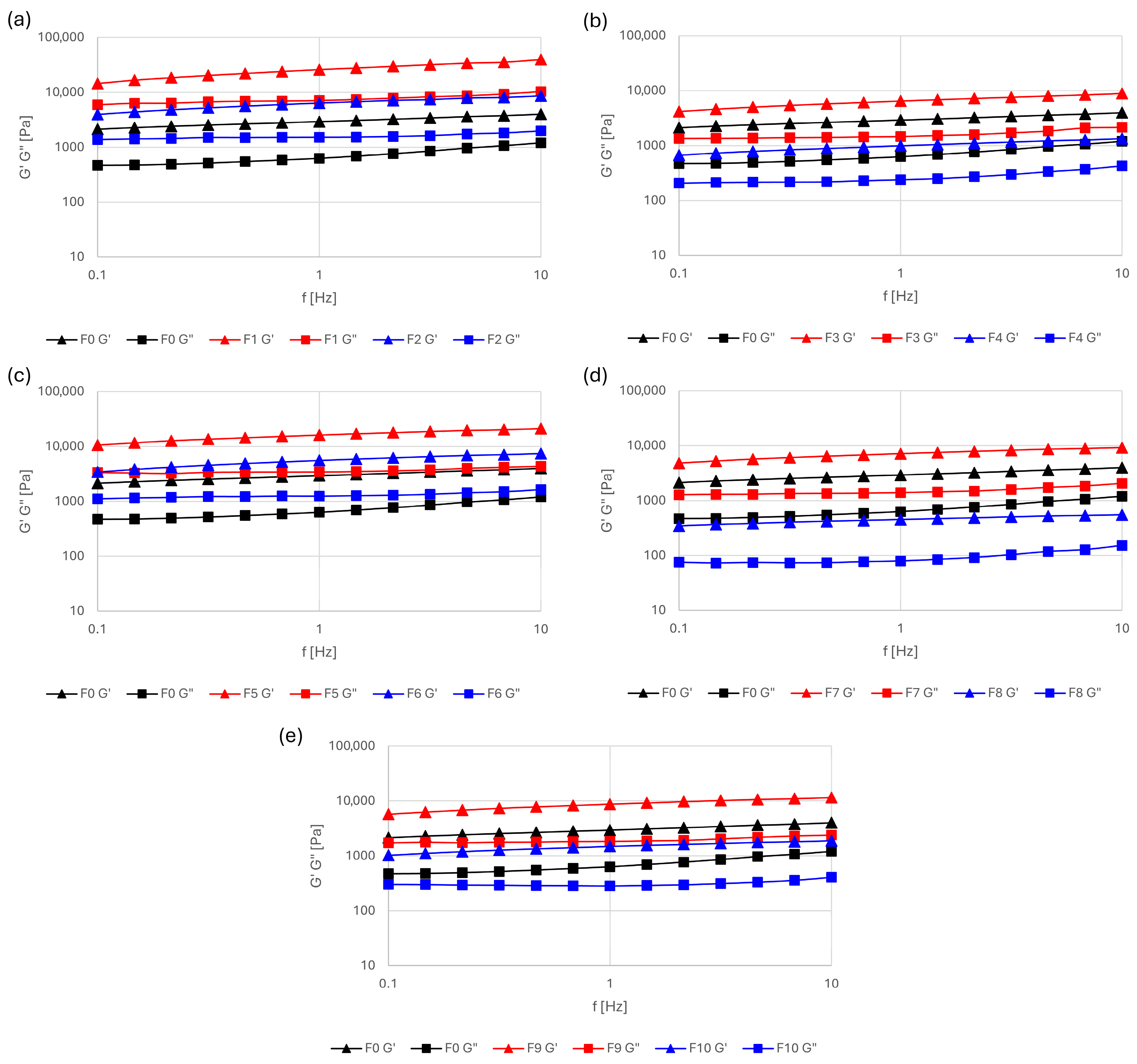
Viscoelastic properties were evaluated by amplitude sweep tests, which confirmed the existence of a linear viscoelastic region (LVR) for all formulations within the stress range of 0.1–10 Pa. Shear stress of 1 Pa was therefore selected for the frequency sweep. Figure 2 shows the frequency dependence of the storage modulus (G″) and loss modulus (G″) for all emulsions. G′ exceeded G″ values in all formulations, indicating that solid-like behavior predominated over viscous behavior. As expected, both moduli increased with frequency.
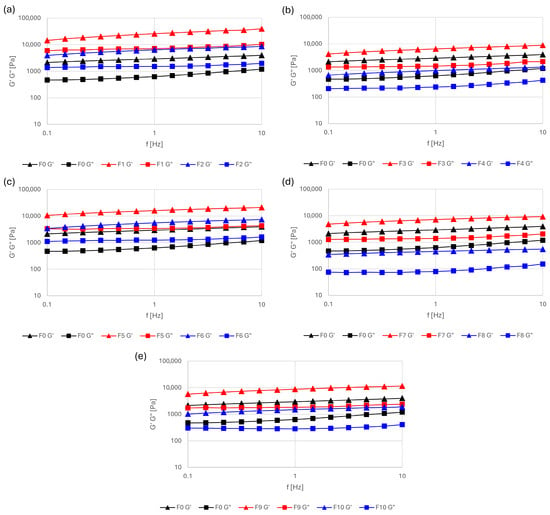
Figure 2.
Changes in storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of the emulsion lotions as a function of frequency (0.1–10 Hz) at a constant shear stress of 1 Pa: (a) F1 and F2, (b) F3 and F4, (c) F5 and F6, (d) F7 and F8, and (e) F9 and F10, each compared with the control formulation F0.
Increasing the plant oil content from 15% to 30% resulted in a marked decrease in both G′ and G″ values. All formulations containing 15% oil exhibited higher viscoelastic moduli than the control formulation without oil. The highest moduli were observed for the formulation with 15% olive oil (F1), whereas the lowest values were recorded for the emulsion with 30% flaxseed oil (F8).
3.3. Occlusivity of the Emulsions
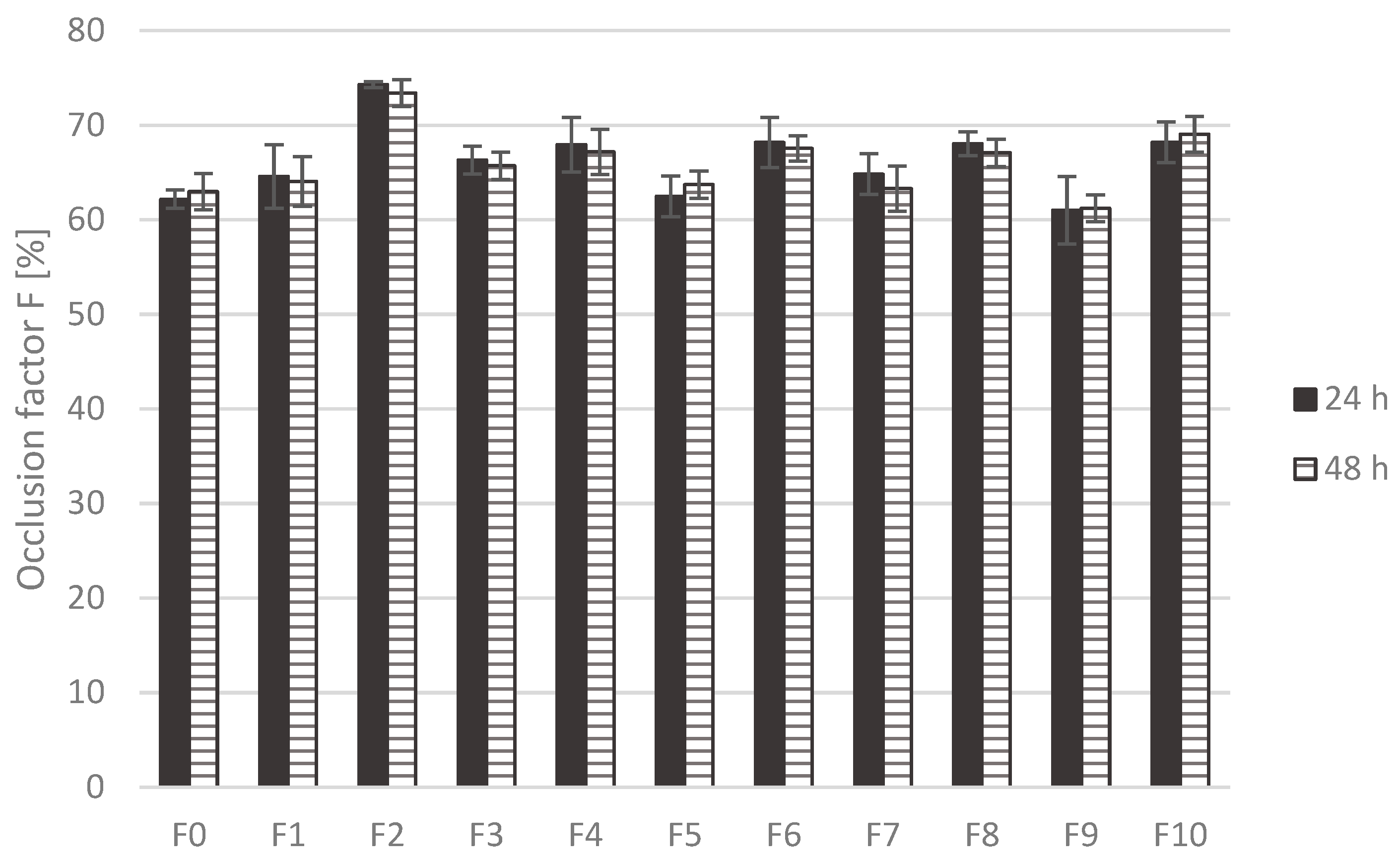
The in vitro occlusion test demonstrated that all formulations exhibited high occlusion factors (F > 60%) after both 24 h and 48 h (Figure 3). The occlusion factors of individual formulations did not change significantly between the two time points. The incorporation of plant oils increased occlusivity in both concentration levels, although statistically significant higher values (p < 0.05) were recorded only for the formulations containing 30% olive oil (F2) at both time points and 30% grape seed oil (F10) after 48 h. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) were also confirmed emulsions containing the same type of oil at the two tested concentrations (olive oil: F1 vs. F2; grape seed oil: F9 vs. F10), at both 24 h and 48 h.
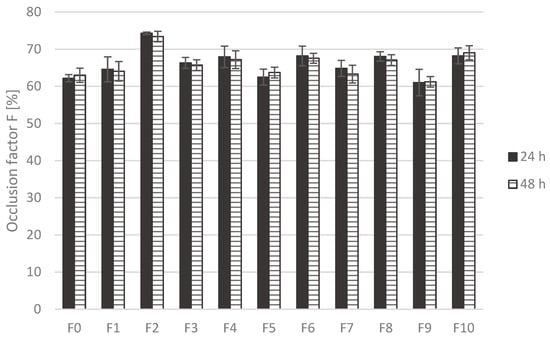
Figure 3.
Occlusion factor (F) of the emulsions measured after 24 h and 48 h.
3.4. UV-Protective Properties
SPF values determined from UVB absorbance spectra (290–320 nm) are shown in Table 5. Although all formulations containing 30% oil had higher SPF values compared with the corresponding 15% formulations, only emulsions with 30% olive oil (F2), 30% avocado oil (F4), and 30% flaxseed oil (F8) achieved SPF value more than 1, indicating measurable UV-protective activity. Formulations F4 and F8 exhibited SPF values of approximately 3, which were significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that of F2, while there was no significant difference between the SPF values of F4 and F8.

Table 5.
Sun protection factor (SPF) values of the emulsions.
3.5. Stability of the Emulsions
Stability assessment included centrifugation tests and temperature-cycling. No phase separation or notable changes in organoleptic properties were observed in any formulation, indicating adequate physical stability. After 30 days of storage at room temperature, the emulsions retained their visual appearance and did not undergo phase separation.
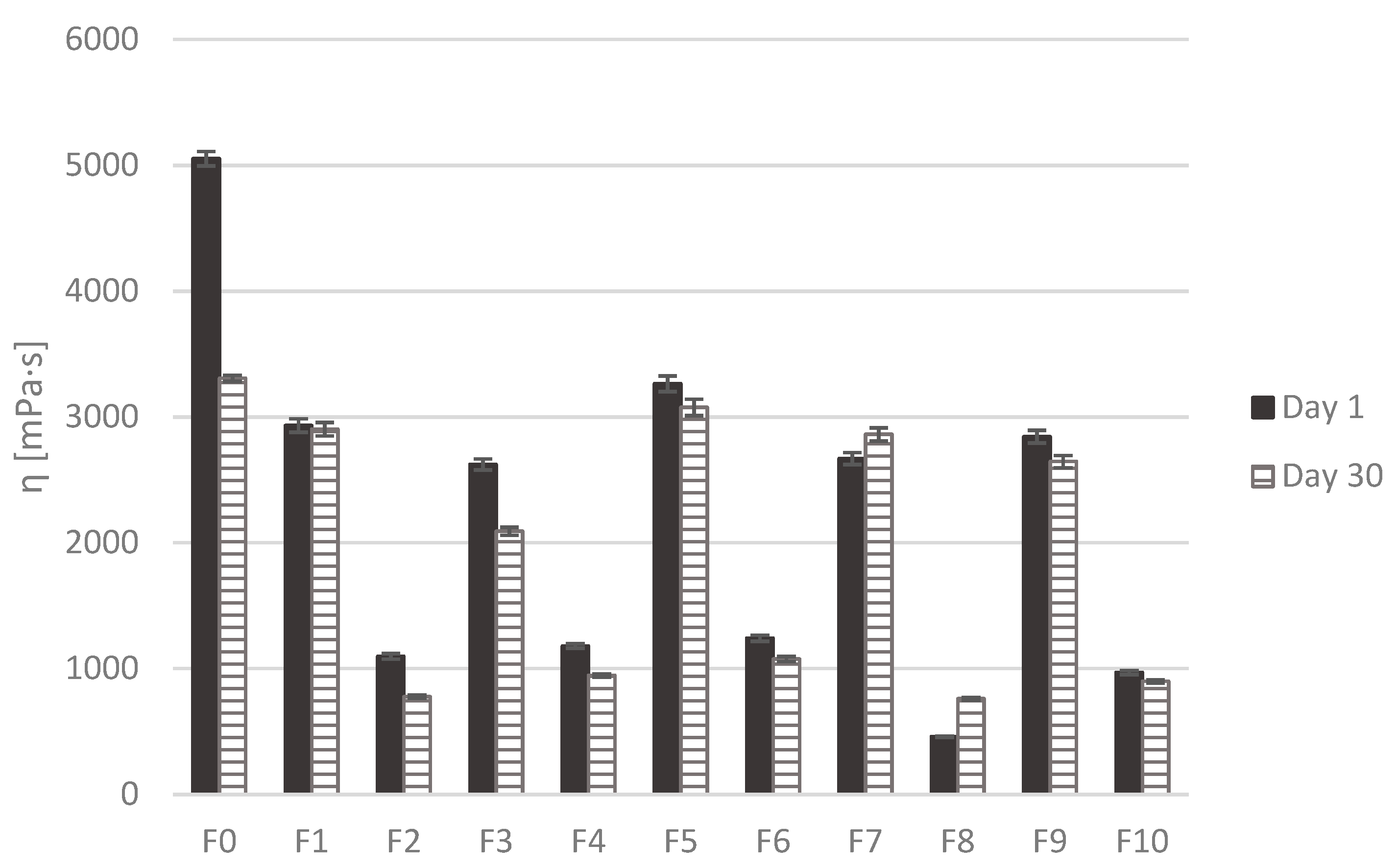
Rheological analysis after storage showed that the flow curves remained mostly unchanged for all formulations. However, when apparent viscosity at 100 s–1 was compared between day 1 and day 30, a decrease was observed in most formulations (Figure 4). This decrease was statistically significant only for control formulation F0. In contrast, formulations containing flaxseed oil (F7 and F8) showed a slight increase in apparent viscosity over the 30-day storage period, although that increase was not statistically significant.
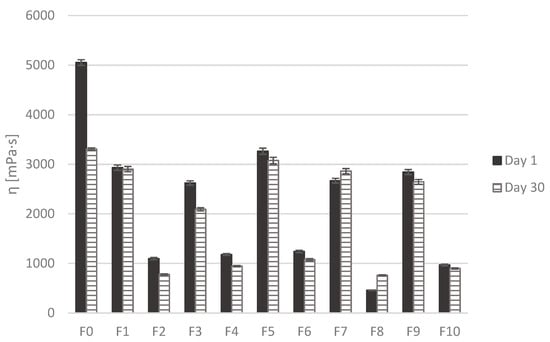
Figure 4.
Apparent viscosity of the emulsions at a shear rate of 100 s–1 measured on day 1 and day 30.
4. Discussion
With the heightened awareness of the detrimental consequences of the climate change and the harmful effects associated with repeated exposure to solar radiation, coupled with the increasing incidence of skin cancers (and other related skin conditions and diseases) among the aging population—which have escalated into a global public health concern—the use of photoprotective agents has risen notably over the past few decades. On the other hand, controversies surrounding the health and environmental safety of certain UV filters, along with the growing awareness of sustainability-related challenges and the rise of green consumerism, have created new opportunities for researchers and formulators to develop optimized sunscreen products, prompted by advancements in scientific knowledge and technology [30,31,32,33]. Additionally, the cost of topical photoprotectants is an important consideration in the formulation development process, as regular application is required to prevent photodamage and may significantly impact consumer use and compliance [34]. Notable attention has been directed towards the use of plant oils, due to their accessibility, diverse biological activities and favorable technological properties [24]. Thus, this study aimed to develop and characterize topical cosmetic emulsions using selected plant oils as functional and added-value ingredients with sun-protective potential. Since plant oils were considered as the key formulation variables to be tested, their concentrations were not compensated by an alternative non-functional oil. The control formulation (F0) represents a conventional W/O emulsion base, while formulations F1–F10 reflect progressive enrichment of this base with plant oils at two concentration levels. Consequently, the total oil phase fraction differed between the control and oil-containing formulations by design. This approach does not aim to isolate oil-type effects under constant oil volume conditions, but rather to evaluate how incorporation of different plant oils at practically relevant concentrations modulates the physicochemical, rheological, occlusive, and photoprotective performance of W/O emulsions. While this design limits strict attribution of observed effects solely to oil identity, it reflects realistic formulation strategies in cosmetic development, where functional oils are added to base systems to impart added value.
A wide range of photoprotective products intended for application on different body areas is currently available on ever growing market. According to the FDA, dosage forms including oil, lotion, cream, gel, butter, paste, ointment, stick, spray, and powder formulations are considered GRASE for OTC use. However, dosage forms such as sunscreen wipes, towelettes, body washes and shampoos cannot currently be legally marketed without an approved application [35]. It is widely reported that the selection of a vehicle strongly affects both the performance of sunscreen products and their cosmetic appeal, which are strongly related to the consumers’ preference and compliance [24,36]. In this study, we opted to formulate sunscreen emulsions, which are generally considered more cosmetically appealing and preferable to oils, ointments and creams. They are characterized by a lighter texture, ease of application, moisturizing and cooling effect [37]. Firstly, we confirmed that all formulations were W/O emulsions. The electrical conductivity determines the type of emulsion, where W/O emulsions exhibit very low conductivity values (near zero), because the continuous oily phase obstructs the conduction in the dispersed aqueous phase [38,39]. Oil-based vehicles are considered suitable for photoprotective formulations, due to their ability to form a thin, continuous and long-lasting film on the skin surface, which further helps prevent skin dehydration caused by the environmental conditions [24]. In comparison to O/W systems, W/O emulsions have several advantages relevant to photoprotective applications, such as superior water resistance, enhanced substantivity on the skin, improved photostability of lipophilic UV filters, and higher occlusivity. These properties arise primarily from the hydrophobic nature of the continuous phase, which promotes film persistence and reduced susceptibility to wash-off during sweating or water exposure. For these reasons, W/O emulsions are frequently selected for durable sunscreen and protective topical formulations [40,41].
Cosmetic elegance can be defined as any feature associated with skin sensation upon application, color or a scent [42]. Regarding color, all formulations displayed a typical milky white to light-yellow shiny appearance, with homogenous texture. Sunscreen color is one of the key cosmetic appeal determinants, since transparent or skin-blending formulations are generally preferred by consumers, regardless of their skin tone or Fitzpatrick skin type. An unfavorable visual appearance can lower perceived value of the product, represents a barrier to regular sunscreen use and may even exclude it from purchase consideration [34,43]. It is anticipated that W/O emulsions, especially those with increased oil content, will exhibit lower friction and increased spreadability upon application, and form colorless film on the skin surface [44]. Furthermore, all formulations exhibited pH values around 6.0, which is compatible with the skin and approximates its average pH. Thus, these emulsions are unlikely to cause irritation and can be considered appropriate for topical application [36].
Analysis of consumer reviews for the top 65 sunscreen products available on Amazon.com online catalog revealed that cosmetic elegance was the most cited positive attribute, followed by product performance, skin compatibility and ingredient composition. In addition, the analysis showed that a pleasant tactile skin feel and ease of rubbing out were rated as the most desirable attributes, while product residue and thickness were the least desirable [42]. Indeed, these findings further highlight the need for a comprehensive sensory analysis in the development of topical sunscreen formulations. Although sensory analysis performed by a well-trained panel has proven to be a reliable method for assessing skin feel properties, it is both time-consuming and costly. Moreover, panelist subjectivity cannot be completely eliminated. Consequently, various instrumental techniques have been introduced to predict and estimate product sensorial perception. Among them, rheology is one of the most extensively studied and applied, as it provides insight into flow behavior, textural properties, and the stability of cosmetic formulations [44,45,46]. Thus, rheological measurements were carried out to gain deeper insight into the characteristics of the prepared sunscreen formulations. Nevertheless, it should be emphasized that sensory attributes such as after-feel, residue, and greasiness require dedicated in vivo sensory studies or complementary instrumental approaches for comprehensive evaluation, which will be addressed in future work.
Steady state (continuous) rheological measurements can help predict behavior of the formulated product during manufacturing and application [45]. Initially, the viscosities of the plant oils used were determined. The results showed that their viscosities increased in the following order: flaxseed oil < sesame oil < grape seed oil < olive oil < avocado oil. Plant oils are typical Newtonian fluids with an independent shear rate viscosity, but temperature dependence [47]. However, all formulations demonstrated a non-Newtonian, shear-thinning character and showed some extent of time-dependent (thixotropic) behavior, although the magnitude of thixotropy varied, as indicated by the different hysteresis loop areas. A grouping of the flow curves according to plant oil concentration was also noticeable. The highest shear stress value was recorded for the control formulation (F0), while the addition of 15% plant oil reduced the shear stress values by approximately half (F1, F3, F5, F9). The lowest shear stress value was observed in the formulation containing 30% flaxseed oil (F8), which also displayed the lowest apparent viscosity. Shear-thinning flow behavior is a type of non-ideal behavior commonly observed in emulsion systems, where the apparent viscosity decreases with increasing shear rate. A relatively weak three-dimensional network that exists within emulsion ruptures easily after it is subjected to shear over a period of time. Thus, its viscosity decreases with shear time. It is considered a desirable property of topical preparations, as they thin during application and thicken afterwards [48,49]. Together with thixotropy, which reflects the time-dependent recovery of a system’s structure after the applied stress is discontinued, this rheological profile has a key role in application performance. Thixotropy facilitates application and uniform distribution on the skin, enhancing spreadability and user acceptance, as formulations can flow easily under shear and require lower stress to initiate spreading [50,51,52]. In addition, thixotropy promotes film formation by enabling spreading under shear and viscosity recovery once the applied stress is removed, supporting film stability on the skin [53]. In sunscreen and other topical products, thixotropic behavior has been shown to promote the formation of thinner and more uniform films, enhancing consistent UV protection and overall product performance [54].
Furthermore, the values of yield stress (τ0), consistency index (K) and flow behavior index (n) were obtained by fitting flow curves. A yield stress was obtained from the forward curves only for F0 and the avocado oil-containing formulations (F3, F4), which exhibited the highest apparent viscosity among used plant oils. Since yield stress represents the minimum stress required to initiate material flow, these formulations appear to be the most resistant to flow and are expected to be somewhat harder to spread on the skin [55]. According to the prior studies, consumers apply more sunscreen product if it spreads easily, leading to increased photoprotection efficacy [42]. The inability to reliably determine yield stress from the ascending (forward) flow curves is characteristic of thixotropic systems, in which structural breakdown under increasing shear occurs more rapidly than structural recovery at low shear rates. During the ascending sweep, the internal structure of the emulsion remains largely intact until shear rate begins to increase, at which point rapid break-down occurs, leading the model to converge toward the yield stress values close to zero. Literature data show that thixotropy and rheological aging can prevent the emergence of measurable yield stress during the forward sweep [56]. In addition, wall slip and transient inhomogeneities were shown to potentially interfere with accurate as-assessment of yield behavior [57,58]. In contrast, during the backward (descending) curve the material has already undergone shear-induced disruption and begins to partially rebuild its structure. Under these conditions, the Herschel–Bulkley model more readily captures the residual stress required to maintain flow, producing stable τ0 values. Similar behavior has been reported for structured suspensions and emulsions, where yield stress becomes apparent only after shear-induced breakdown [59,60]. Accordingly, the yield stress values fitted from backward curves in this study should be interpreted not as the stress required to initiate flow in undisturbed system, but rather the stress required to sustain flow in a partially restructured material.
The consistency index is closely correlated with the consumers’ visual perception of the product. We observed that the emulsions containing 15% plant oil exhibited higher consistency index than their counterparts containing 30% plant oil. Consistency index is also well correlated with the apparent viscosity of the emulsions. However, when assessing the correlation between the apparent viscosity of the pure plant oils and that of their corresponding emulsions, no statistically significant correlation was found. This observation highlights that emulsion viscosity is governed not only by the viscosity of the oil phase but also by microstructural factors, such as droplet volume fraction, droplet size distribution, and interfacial film properties, which are strongly influenced by oil-emulsifier interactions and overall formulation architecture [47,48,49]. The flow behavior index indicates the extent of shear thinning behavior as it deviates away from 1 [47]. The values of n for the examined emulsions were lower than 1 in all formulations, including both the ascending and descending flow curves, which further reiterates their pseudoplastic character. However, it was observed that after the structural breakdown, the emulsions behaved more like Newtonian fluids, i.e., pure plant oils, as evidenced by the higher values of the non-Newtonian behavior index n calculated from the descending curves. Similar rheological properties have been reported for sunscreen emulgels containing Cinnamomum burmannii stem bark extract and olive oil, for emulsions with varying ratios of avocado and sacha inchi oils and hydrogel containing sesame oil microemulsion [19,47,61].
To gain a deeper insight into the microstructural characteristics and viscoelastic properties of the prepared emulsions, dynamic rheological measurements were performed under oscillatory shear conditions. The results of the oscillatory rheological measurements performed under shear stress within the LVR revealed that all emulsions exhibited viscoelastic behavior, with more pronounced elastic than viscous component, as indicated by the dominance of G′ over G″ across all frequencies in the measurement range. This further indicates the presence of a weak internal gel-like structure, which is characteristic of many emulsion systems [45]. In terms of sensorial attributes, this behavior often correlates with a more robust texture and resistance to deformation, enhancing the perception of firmness or stability [62]. To further assess whether the observed differences among emulsions were qualitative or only quantitative, the damping factor (tan δ = G″/G′) was evaluated. All formulations exhibited tan δ values well below 1 (range: 0.21–0.28) across the investigated frequency range, confirming predominantly elastic, solid-like behavior. While slight variations in tan δ values were observed depending on oil type and concentration, the overall viscoelastic behavior remained similar among formulations. These findings indicate that the observed differences among emulsions are primarily quantitative, reflecting differences in structural strength rather than changes in viscoelastic character. Although the values of G′ and G″ in all formulations containing 15% plant oil were higher than those in control formulation, an increase in plant oil concentration to 30% led to a several-fold reduction in the value of both parameters. The lowest G′ and G″ were observed in the sample containing 30% (the least viscous) flaxseed oil (F8). The same formulation had previously exhibited low shear stress values. Conversely, the formulation containing 15% olive oil (F1) demonstrated the most rigid structure. This could be attributed to the presence of palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid found in olive oil, while the low G′ and G″ in the formulation containing 30% flaxseed oil may be explained by the high proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids in this particular oil [63,64]. Rheological analysis demonstrated that increasing oil concentration influenced the internal structure of the emulsions in a non-linear and oil-dependent manner. Moderate oil addition (15%) generally enhanced structural rigidity, as reflected by increased consistency index K and viscoelastic moduli G′ and G″, whereas further increasing oil content to 30% led to a reduction in these parameters. This suggests that, beyond a certain concentration, plant oils act predominantly as a diluting component of the continuous phase rather than as structural enhancers.
According to the previous reports, consumers prefer and value sunscreen products that are non-greasy, moisturizing and water/sweat resistant [42]. In fact, the use of sunscreen products is most common during outdoor physical activities that typically involve exposure to water (such as swimming and bathing) and hot, humid environments. To maintain the photoprotection in such conditions, sunscreens should be formulated in a way that their protective effect is minimally disrupted after water immersion, or designed to be water repellent to some extent. Common strategies to improve sunscreen water resistance include enhancing sunscreen-skin adhesion or increasing the hydrophobicity of the formulation. However, it is also of vital importance to maintain the “breathability” and hydration of the skin in such environmental conditions [65,66,67]. The occlusive potential of a cosmetic emulsion depends on the type of colloidal system, the amount of product applied, the size of the globules, and the concentration of fatty acids [68]. In this study, the occlusive properties of formulated W/O emulsions were examined, in which oily phase consisted of plant oils, known to act as a protective barrier by their emollient or occlusive effect, allowing the skin to retain its moisture and reduce transepidermal water loss (TEWL). Since the oil serves as the external phase, W/O emulsions generally feel heavier on the skin, which may be a desirable feature of sun care products, contributing to a perceived “protective” sensation [23,63,69]. The most occlusive formulation in our study was the emulsion containing 30% olive oil (F2), followed by 30% grape seed oil (F10). Conversely, the least occlusive one was the emulsion containing 15% grape seed oil as external phase. Although high occlusivity may be advantageous for photoprotective products by enhancing film persistence, water resistance, and skin barrier support, excessive occlusion may negatively affect cosmetic elegance. Therefore, future formulation strategies may focus on reducing occlusivity through optimization of the oil phase, such as partial substitution of highly film-forming oils with lighter emollients or fine-tuning of emulsion microstructure [70,71]. The cosmetic suitability of plant oils depends on their composition, including saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Oils rich in essential fatty acids are known to improve skin hydration and regenerate epidermal lipid barrier [72]. It is worth the notice that recent studies associate plant oils rich in oleic acid, such as olive oil, with skin’s lipid barrier disruption. However, a recent review of clinical studies implies that such plant oils seem to be non-irritating towards healthy skin [73]. Grape seed oil is commonly used in the cosmetic industry for its softening, soothing and moisturizing effects. Owing to its high content of omega−6 fatty acids, vitamin E and phenolic compounds, it helps prevent excessive water loss and combats photodamage, which makes it a suitable ingredient for use in sunscreen formulations [74].
SPF refers to the ability of a photoprotective formulation to prevent the development of erythema upon exposure to UV radiation, resulting from the presence of ingredients capable of absorbing, reflecting or scattering certain energy certain wavelengths of solar radiation [36,75]. Current guidelines and procedures established by regulatory bodies suggest that SPF determination studies should be conducted in vivo on human test subjects [35,76]. However, in vivo testing is ethically challenging, invasive, costly and time-consuming. Thus, much effort has been directed towards developing reliable in silico and in vitro techniques for assessing the photoprotective efficacy of sunscreen products. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has recently published a procedure for in vitro determination of SPF (ISO 23675:2024) [77]. Typically, in vitro methods utilize spectrophotometric analysis to assess the UV absorption characteristics of sunscreen agents. To determine SPF values of formulated W/O emulsions, spectrophotometric measurement proposed by Mansur et al. was conducted, which is useful as a rough estimation of product’s photoprotective potential during development stage. It is a fast method that utilizes low-cost solvents and conventional laboratory spectrophotometers [78]. The results of our study showed that only formulations containing 30% olive oil (F2), avocado oil (F4) and flaxseed oil (F8) exhibited certain UV-protective effect, i.e., SPF > 1. These findings are in accordance with the results reported by Kaur et al. who found that SPF of olive oil was 7.549. The same study reported the SPF of 1.771 for sesame oil [20]. Priani et al. reported the SPF of 1.092 ± 0.141 for emulgel base containing 20% olive oil [61]. According to previous studies, sesame oil can block 30% of UV rays, whereas olive oil blocks around 20%. SPF values were also calculated for numerous other fixed and essential oils, including carrot seed oil, babassu nut oil, castor oil, peppermint oil, lemon grass oil and others [20,68,79]. According to the FDA, the finished sunscreen product should provide a minimum SPF value of not less than 2, measured by the established test procedures [35]. Plant oils may exhibit photoprotective properties through two main mechanisms: acting as UV filters and/or functioning as antioxidants that scavenge UV-induced free radicals. Owing to their unique composition (rich in phenolic compounds, vitamins, and various fatty acids), plant oils can display strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Thus, they may not be considered conventional sunscreen, but valuable additives to sunscreen formulations that offer stabilizing and antioxidative effect, protecting the skin from oxidative damage and reducing the overall risk of photodamage [63,75]. Also, incorporation of plant oils may be a useful strategy to improve SPF values of formulations containing reduced concentrations of conventional UV filters [24]. It is also worth the notice that other components of the formulation vehicle, including emulsifiers, may affect the efficacy of sunscreens [20].
The ideal sunscreen should also exhibit suitable stability, to ensure the product’s desired physicochemical properties and sufficient shelf-life [36,48]. Therefore, physical stability of the prepared W/O emulsions was assessed by exposing them to mechanical stress (centrifugal testing) and thermal stress (temperature cycle testing). All formulations remained stable throughout testing, showing no visible phase separation and retaining their organoleptic characteristics. In addition, storage for 30 days did not result in any detectable changes in appearance or texture. Overall, the emulsions demonstrated satisfactory physical stability over the entire testing period. However, the relatively short duration of the stability study represents a limitation of the present work. Prolonged accelerated stability studies would be required in the future to more reliably predict long-term behavior and shelf-life of these W/O emulsions. Furthermore, it should be noted that oxidative stability was not specifically assessed in this study. The emulsions were prepared freshly, stored in closed containers protected from light, and evaluated up to 30 days, during which no visible signs of phase separation or sensory deterioration were detected. Considering the high content of unsaturated fatty acids in plant oils within the continuous phase of W/O systems, susceptibility to oxidation remains a relevant issue for long-term product performance that needs to be investigated in future. In addition, batch-to-batch variability of plant oils was not evaluated in the present study. Given the natural variability in plant oil composition, this factor may influence emulsion stability and rheological behavior and should be considered in future work. Eventually, as previously discussed, oil-specific effects were evaluated relative to a control formulation with a different total oil phase fraction, and the observed results should thus be interpreted as formulation-level responses rather than isolated compositional effects of individual oils.
5. Conclusions
The stable W/O cosmetic emulsions for topical application were successfully formulated in this study. Both the plant oil type and concentration had a noticeable impact on the rheological properties of the formulations, which demonstrated shear-thinning and time-dependent flow behavior. Formulations containing 30% plant oil exhibited higher SPF value than their 15% counterparts. However, only emulsions containing 30% olive oil, avocado oil and flaxseed oil reached SPF > 1. Furthermore, all examined formulations showed high occlusive factor values, which may have a beneficial effect on skin hydration during sun exposure, but also impair their cosmetic acceptability, due to the potentially heavy feeling on the skin resulting from a pronounced occlusion. Based on the results, formulation F8 containing 30% flaxseed oil exhibited most favorable overall properties.
Although plant oils are not recognized as approved UV filters, in light of the increased demand for sustainability in cosmetics, they hold significant potential as added-value ingredients in photoprotective formulations. In this context, future work may focus on combining plant oils that demonstrated supportive UV-protective potential in the present study, particularly olive, avocado, and flaxseed oils, with low concentrations of approved lipophilic UV filters. Such combinations may enable optimization of SPF and photostability while maintaining favorable rheological behavior and sensory attributes in sustainable W/O formulations. Furthermore, to enhance cosmetic elegance and consumer appeal, advanced oil-containing dosage forms may also be considered.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cosmetics13010023/s1, Figure S1: Flow curves (shear stress vs. shear rate) of the emulsions: (a) F1–F5 and (b) F6–F10, each compared with the control formulation F0.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.P.; methodology, K.Ž. and D.Z.; software, N.P. and J.M.; validation, D.Z. and D.Ć.; formal analysis, K.Ž. and D.Z.; investigation, N.P., K.Ž. and D.Z.; resources, N.P.; data curation, J.M. and V.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Z. and J.M.; writing—review and editing, N.P., D.Ć. and V.K.; visualization, N.P. and J.M.; supervision, N.P. and V.K.; project administration, N.P.; funding acquisition, N.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Provincial Secretariat for Higher Education and Science, Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, Republic of Serbia (project No. 003877177 2025 09418 003 000 000 001).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgment of AI-Assisted Language Editing. The authors used generative AI tools solely to assist with minor language editing (grammar and phrasing). The scientific content, including study design, data generation, analysis, and interpretation, was created entirely by the authors without any AI assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Egambaram, O.P.; Kesavan Pillai, S.; Ray, S.S. Materials Science Challenges in Skin UV Protection: A Review. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y. Biomarkers, oxidative stress and autophagy in skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 59, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L. Recent global patterns in skin cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence. Chin. Med. J. 2025, 138, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roky, A.H.; Islam, M.M.; Ahasan, A.M.F.; Mostaq, M.S.; Mahmud, M.Z.; Amin, M.N.; Mahmud, M.A. Overview of skin cancer types and prevalence rates across continents. Cancer Pathog. Ther. 2025, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lergenmuller, S.; Rueegg, C.S.; Perrier, F.; Robsahm, T.E.; Green, A.C.; Lund, E.; Ghiasvand, R.; Veierød, M.B. Lifetime Sunburn Trajectories and Associated Risks of Cutaneous Melanoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma Among a Cohort of Norwegian Women. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, L.K.; Vanbeek, M.J.; Beane Freeman, L.E.; Smith, B.J.; Dawson, D.V.; Coughlin, J.A. Sunburns and risk of cutaneous melanoma: Does age matter? A comprehensive meta-analysis. Ann. Epidemiol. 2008, 18, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.C.; Williams, G.M.; Logan, V.; Strutton, G.M. Reduced melanoma after regular sunscreen use: Randomized trial follow-up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, L.T.N.; Tran, V.V.; Moon, J.-Y.; Chae, M.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Recent Trends of Sunscreen Cosmetic: An Update Review. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, S.; Karrer, S.; Berneburg, M. Modern sun protection. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 46, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesus, A.; Sousa, E.; Cruz, M.T.; Cidade, H.; Lobo, J.M.S.; Almeida, I.F. UV Filters: Challenges and Prospects. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ácsová, A.; Hojerová, J.; Janotková, L.; Bendová, H.; Jedličková, L.; Hamranová, V.; Martiniaková, S. The real UVB photoprotective efficacy of vegetable oils: In vitro and in vivo studies. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2021, 20, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeager, D.G.; Lim, H.W. What’s New in Photoprotection: A Review of New Concepts and Controversies. Dermatol. Clin. 2019, 37, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazipura, M.; McGowan, R.; Arslan, A.; Hossain, T. Exposure to benzophenone-3 and reproductive toxicity: A systematic review of human and animal studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorigo, M.; Mariana, M.; Cairrao, E. Photoprotection of ultraviolet-B filters: Updated review of endocrine disrupting properties. Steroids 2018, 131, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.L.; Lim, H.W.; Mohammad, T.F. Sunscreens and Photoaging: A Review of Current Literature. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 22, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breakell, T.; Kowalski, I.; Foerster, Y.; Kramer, R.; Erdmann, M.; Berking, C.; Heppt, M.V. Ultraviolet Filters: Dissecting Current Facts and Myths. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lungu, C.; Gradinaru, A.C.; Ivanescu, B. Plant-Based Sunscreens: Innovations and New Formulations. In Cosmetic Industry—Trends, Products and Quality Control; Kartal, S.P., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Badea, G.; Lăcătuşu, I.; Badea, N.; Ott, C.; Meghea, A. Use of various vegetable oils in designing photoprotective nanostructured formulations for UV protection and antioxidant activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, M.; Farhadian, N.; Golmohammadzadeh, S.; Karimi, M.; Ebrahimi, M. Formulation, clinical and histopathological assessment of microemulsion based hydrogel for UV protection of skin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 179, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, C.D.; Saraf, S. In vitro sun protection factor determination of herbal oils used in cosmetics. Pharmacogn. Res. 2010, 2, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Lademann, J.; Richter, H.; Darvin, M.E.; Schanzer, S.; Thiede, G.; Sterry, W.; Vergou, T.; Hauser, M. In vivo investigations on the penetration of various oils and their influence on the skin barrier. Skin. Res. Technol. 2012, 18, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanhole, R.C.; Fava, A.L.M.; Tundisi, L.L.; Macedo, L.M.; Santos, É.M.D.; Ataide, J.A.; Mazzola, P.G. Unplanned absorption of sunscreen ingredients: Impact of formulation and evaluation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 591, 120013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, J.P. Sunscreen Formulation: Optimising Aesthetic Elements for Twenty-First-Century Consumers. In Principles and Practice of Photoprotection; Wang, S.Q., Lim, H.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 289–302. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro, L.; Santagati, L.M. Use of Vegetable Oils to Improve the Sun Protection Factor of Sunscreen Formulations. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, A.; Garcia, A.G.; Young, L.K.; Szoboszlai, M.; Liberatore, M.W.; Baki, G. Measurements meet perceptions: Rheology-texture-sensory relations when using green, bio-derived emollients in cosmetic emulsions. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estanqueiro, M.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Comparison between sensory and instrumental characterization of topical formulations: Impact of thickening agents. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smadi, K.; Ali, M.; Zhu, J.; Abdoh, A.; Phan, K.; Mohammed, Y. Advances in Characterization of Transdermal and Topical Products using Texture Analyzer Systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 2025, 26, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.S.; Pham, C.V.; Myung, C.S.; Cho, C.W. Tadalafil-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers using permeation enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, A.; Verma, A.; Hema, G.; Pathak, K. Topical Delivery of Geranium/Calendula Essential Oil-Entrapped Ethanolic Lipid Vesicular Cream to Combat Skin Aging. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4593759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutmann, J.; Passeron, T.; Gilaberte, Y.; Granger, C.; Leone, G.; Narda, M.; Schalka, S.; Trullas, C.; Masson, P.; Lim, H.W. Photoprotection of the future: Challenges and opportunities. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhag, S.; Nayak, A.; Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y. Anti-aging and Sunscreens: Paradigm Shift in Cosmetics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rücker, J.; Leonhardt, J.; Wild, C. Effects of three sunscreens on the ecophysiology of hard and soft corals from the Maldives. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 219, 118316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamta; Prakash, G. Publication trends and green cosmetics buying behaviour: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, H.; Patel, S.; Kundu, R.V. Cost and quality in consumer sunscreen preferences. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Final Administrative Order OTC000006_M020-Sunscreen Drug Products for OTC Human Use. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/omuf/index.cfm?event=OrderDetail&orderid=OTC000006 (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Geoffrey, K.; Mwangi, A.N.; Maru, S.M. Sunscreen products: Rationale for use, formulation development and regulatory considerations. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, M.A.; Fița, A.C.; Nițulescu, G.; Ozon, E.A.; Stancu, E.; Baltă, M.D.; Balaci, T.; Lupuliasa, D.; Popescu, I.A. Sunscreen topical products—From conventional to novel formulations. Farmacia 2024, 72, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Qi, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Lu, H. pH-Switchable W/O Polymer Emulsion: A Promising Strategy for Rapid Dissolution of Drag Reducers. Langmuir 2023, 39, 13976–13985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, K.; Pei, X.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xu, K.; Wang, P. Water-in-oil Pickering emulsion polymerization of N-isopropyl acrylamide using starch-based nanoparticles as emulsifier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Brandvik, A.; Alvarado, V. Probing Interfacial Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion Stability Controls Using Electrorheology. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 6359–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembyla, M.; Murray, B.S.; Sarkar, A. Water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by surfactants, biopolymers and/or particles: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Kwa, M.; Agarwal, A.; Rademaker, A.; Kundu, R.V. Sunscreen Product Performance and Other Determinants of Consumer Preferences. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weig, E.A.; Tull, R.; Chung, J.; Brown-Joel, Z.O.; Majee, R.; Ferguson, N.N. Assessing factors affecting sunscreen use and barriers to compliance: A cross-sectional survey-based study. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lu, J.; Potanin, A.; Boyke, C. Prediction of Tactile Sensory Attributes of Facial Moisturizers by Rheology and Tribology. Biotribology 2021, 28, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic, M.; Jaksic, I.; Krstonosic, V.; Dokic, L.; Savic, S. Effect of Small Change in Oil Phase Composition on Rheological and Textural Properties of w/o Emulsion. J. Texture Stud. 2013, 44, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, L.; Savary, G.; Grisel, M.; Picard, C. Predicting sensory texture properties of cosmetic emulsions by physical measurements. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2013, 124, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herazo, M.; Ciro-Velásquez, H.J.; Márquez, C.J. Rheological and thermal study of structured oils: Avocado (Persea americana) and sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) systems. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinov, J.; Krstonošić, V.; Ćirin, D.; Hadnađev, M.; Đanić, M.; Pavlović, N. Development and evaluation of quercetin topical emulgels: Physicochemical and rheological properties, stability and sun protective potential. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 417, 126568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstonošić, V.; Pavlović, N.; Nikolić, I.; Milutinov, J.; Ćirin, D. Physicochemical properties and stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by soy protein isolate and xanthan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryscio, D.; Sathe, P.; Lionberger, R.; Yu, L.; Bell, M.; Jay, M.; Hilt, J. Spreadability Measurements to Assess Structural Equivalence (Q3) of Topical Formulations—A Technical Note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, B.; Oh, H.; Lee, J.B.; Park, K.; Yi, Y.; Park, C.; Park, J.D. Predictive model for the spreadability of cosmetic formulations based on large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS) and machine learning. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Aggarwal, D.; Garg, S.; Singla, A.K. Spreading of semisolid formulations: An update. Pharm. Technol. N. Am. 2002, 26, 84–105. [Google Scholar]
- Terukina, T.; Uchiyama, Y.; Kikuma, F.; Fukumitsu, S.; Iwata, N.; Kanazawa, T.; Kondo, H. A New Approach for Characterizing the Thixotropic Properties of Gel Formulations as Sprayable Agents Based on Rheological Analysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapcharoenkun, C.; Klamchuen, A.; Kasamechonchung, P.; Iemsam-arng, J. Role of rheological behavior of sunscreens containing nanoparticles on thin film preparation. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 259, 114608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaklan, D.; Davidović, N.; Milutinov, J.; Ćirin, D.; Krstonošić, V.; Pavlović, N. Influence of Talc Substitution with Starches from Different Botanical Origins on Rheological and Absorption Properties of Stiff Zinc Oxide Paste Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, S. Elastoviscoplastic rheology and aging in a simplified soft glassy constitutive model. J. Rheol. 2020, 64, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, G.C. Simple shear flow of a Herschel-Bulkley fluid with wall slip above a threshold stress. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2021, 8, 100068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, S. Yield stress fluids solidifying in capillary imbibition. J. Fluid. Mech. 2024, 996, A48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A.; Walters, K. The yield stress myth? Rheol. Acta 1985, 24, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, C.; Moussa, A. Dynamic driving eliminates volume fraction inhomogeneity and apparent yield stress in flowing dense non-Brownian suspensions. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 083338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priani, S.E.; Humanisya, H.; Darusman, F. Development of sunscreen emulgel containing Cinnamomum burmannii stem bark extract. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2014, 3, 2338–2339. [Google Scholar]
- Souto, A.; Zhang, J.; Aragón, A.M.; Velikov, K.P.; Coulais, C. Edible mechanical metamaterials with designed fracture for mouthfeel control. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 2910–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.K.; Zhong, L.; Santiago, J.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Barrier Repair Effects of Topical Application of Some Plant Oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Franco, E.; de Aquino, C.M.; de Medeiros, P.L.; Evêncio, L.B.; da Silva Góes, A.J.; de Souza Maia, M.B. Effect of a Semisolid Formulation of Linum usitatissimum L. (Linseed) Oil on the Repair of Skin Wounds. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 270752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Corona, J.; Aragón-Vargas, L. Sunscreen Use and Sweat Production in Men and Women. J. Athl. Train. 2016, 51, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou-Yang, H.; Meyer, K.; Houser, T.; Grove, G. Sunscreen formulations do not interfere with sweat cooling during exercise. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2018, 40, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarzi, F.; Knudsen, N.; Komjani, N.M.; Ebbesen, M.F.; Brewer, J.R.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Thormann, E. Enhancing the sweat resistance of sunscreens. Skin. Res. Technol. 2022, 28, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, M.J.F.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Vieira, I.R.S.; Neves, G.A.; Menezes, R.R.; Gonçalves, E.; Pires, M.C.C. Development and characterization of a babassu nut oil-based moisturizing cosmetic emulsion with a high sun protection factor. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26268–26276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Um, J.Y.; Chung, B.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.C.; Park, C.W.; Kim, H.O. Moisturizer in Patients with Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Medicina 2022, 58, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Carbone, C.; Condorelli, G.; Drago, R.; Puglisi, G. Effect of oil phase lipophilicity on in vitro drug release from o/w microemulsions with low surfactant content. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2006, 32, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đekić, L.; Ćirić, A.; Milinković, S.; Budinčić, J.M.; Fraj, J.; Petrović, L. Film-Forming Microemulsions with Essential Oils: Elucidating Relationships Between Formulation Parameters, Thermodynamic Stability, and Quality Attributes. Processes 2025, 13, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, M.; Pierzak, M.; Kręcisz, B.; Suliga, E. Bioactive Compounds for Skin Health: A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljšak, N.; Kočevar Glavač, N. Vegetable Butters and Oils as Therapeutically and Cosmetically Active Ingredients for Dermal Use: A Review of Clinical Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 868461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C.; Nyam, K.L. Application of seed oils and its bioactive compounds in sunscreen formulations. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2021, 98, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addor, F.A.S.; Barcaui, C.B.; Gomes, E.E.; Lupi, O.; Marçon, C.R.; Miot, H.A. Sunscreen lotions in the dermatological prescription: Review of concepts and controversies. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2022, 97, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 24444:2019; Cosmetics—Sun Protection Test Methods—In Vivo Determination of the Sun Protection Factor (SPF). International Organization for Standardization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:24444:ed-2:v1:en (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- ISO 23675:2024; Cosmetics—Sun Protection Test Methods—In Vitro Determination of Sun Protection Factor (SPF). International Organization for Standardization: Geneve, Switzerland, 2024. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:23675:ed-1:v1:en (accessed on 2 November 2025).
- Hermund, D.B.; Torsteinsen, H.; Vega, J.; Figueroa, F.L.; Jacobsen, C. Screening for New Cosmeceuticals from Brown Algae Fucus vesiculosus with Antioxidant and Photo-Protecting Properties. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Lohani, A.; Mishra, A.K.; Verma, A. Formulation and evaluation of carrot seed oil-based cosmetic emulsions. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2019, 21, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.