Significant Interference with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Pandemic and Classical Strain Replication in Small-Intestine Epithelial Cells Using an shRNA Expression Vector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viral Propagation and Titer Assays
2.2. Plasmid Construction
2.3. Plasmid DNA Preparation
2.4. Cell Transfection and Antiviral Activity In Vitro
2.5. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blots
2.6. Cell Viability Assays
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
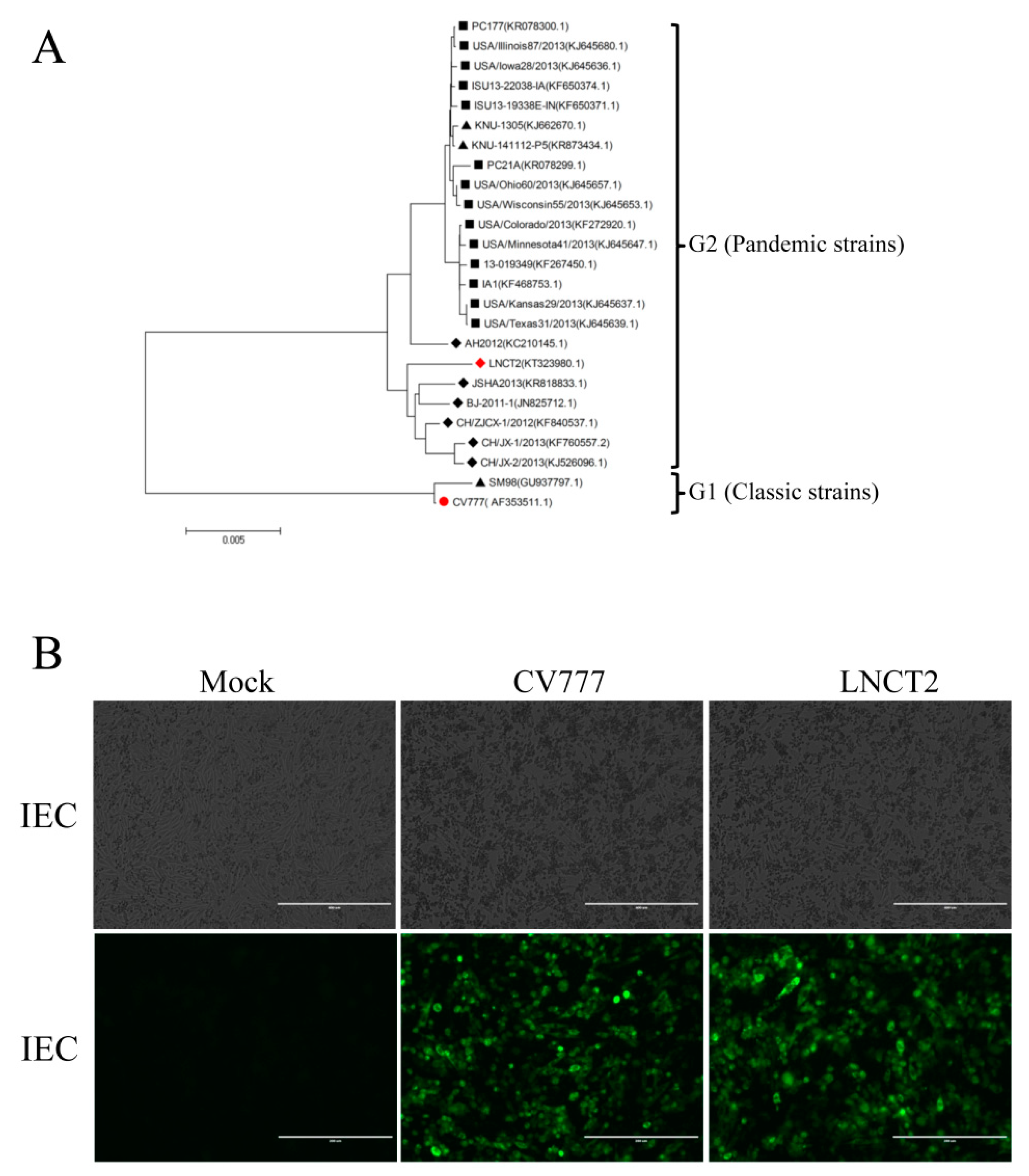
3.1. IEC Cells and PEDV Infection
3.2. Selection of Targeted Sites for N Gene-Specific shRNAs
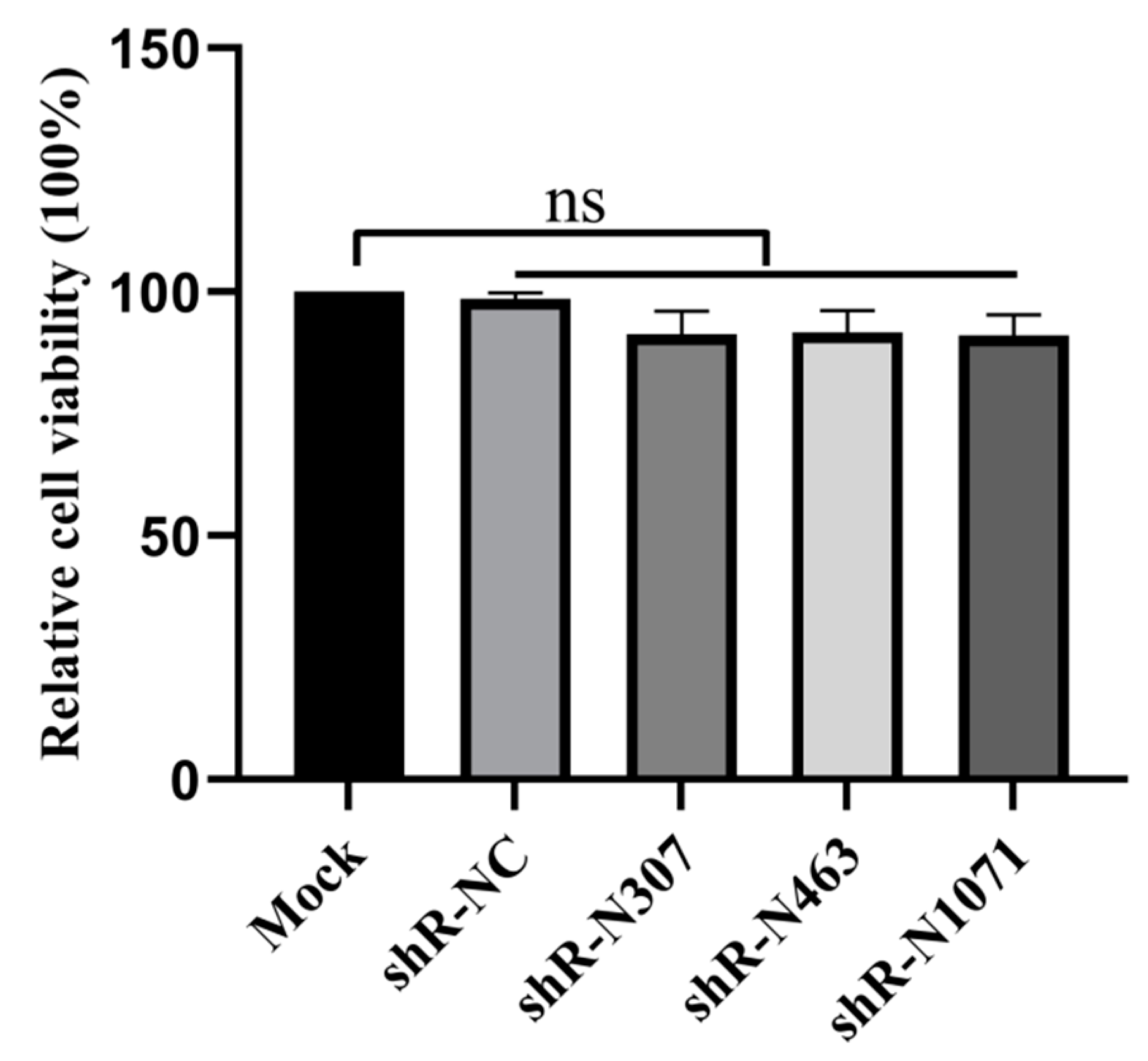
3.3. Cell Viability Is Not Affected by Plasmids with shRNAs
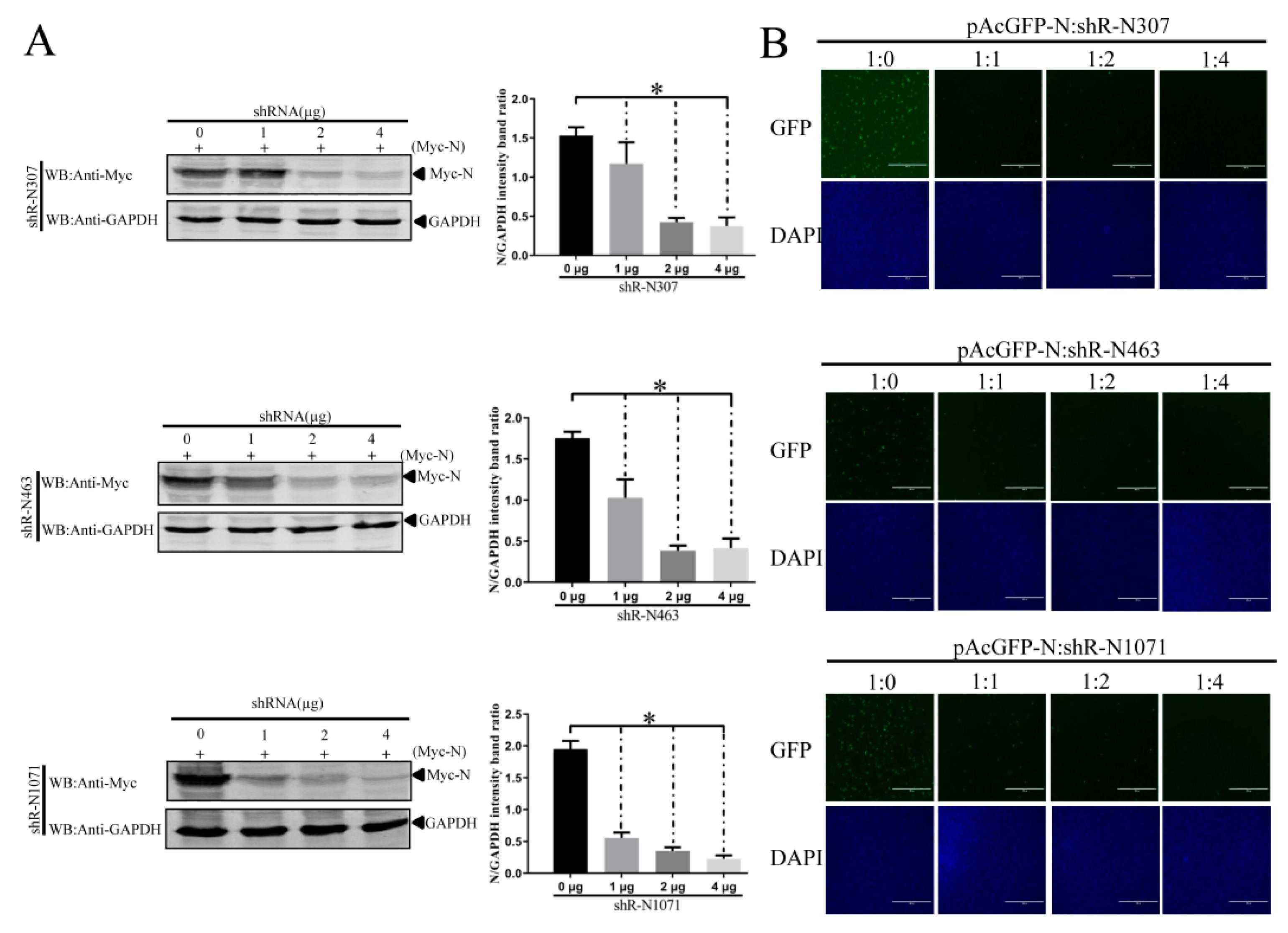
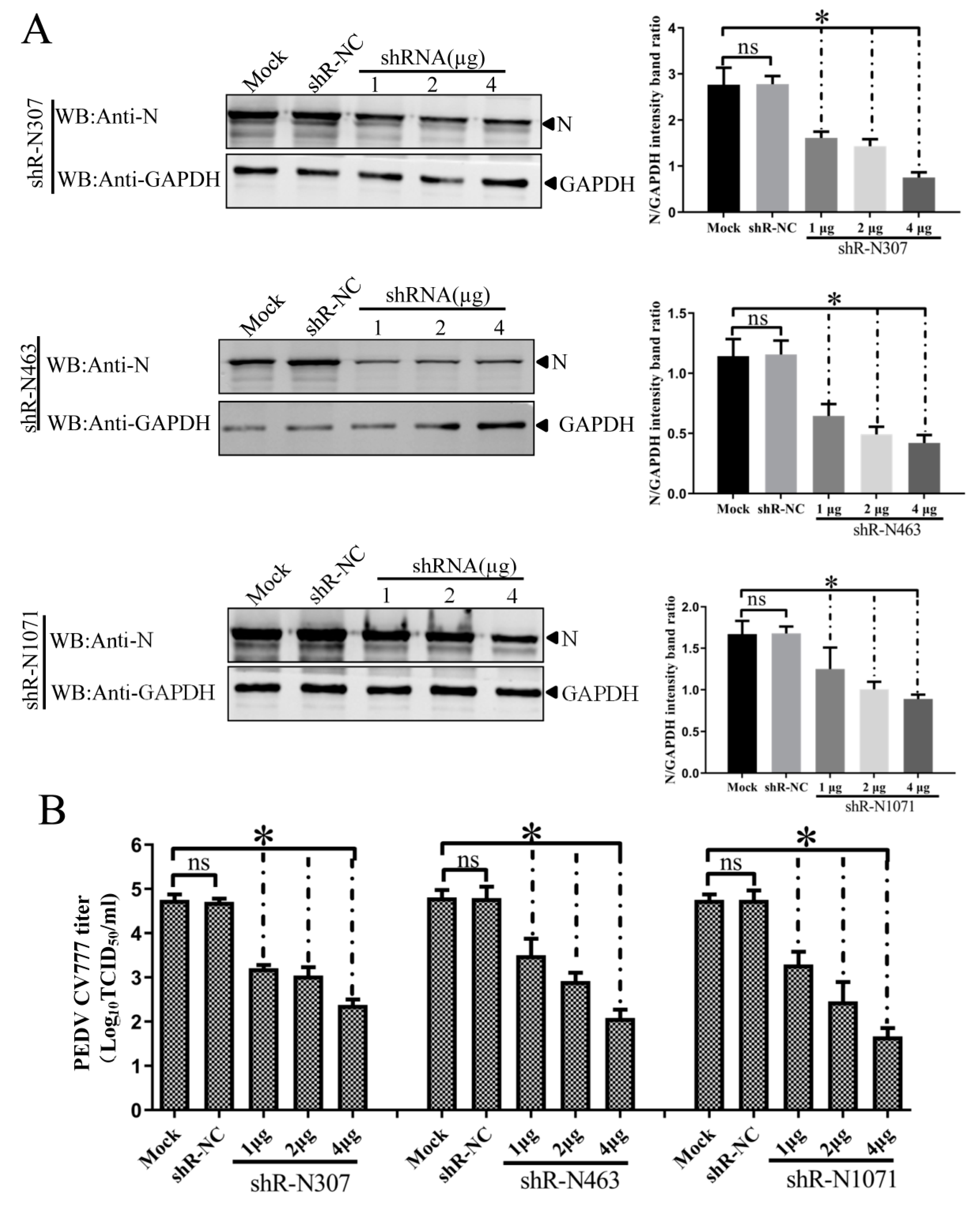
3.4. Efficient Inhibition of PEDV Myc-N or AcGFP-N Expression by shRNA Expression Cassettes
3.5. ShRNA-Mediated Inhibition of N Expression and PEDV Production in Infected IEC Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, D.; Lv, M.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L. Molecular characterizations of subcellular localization signals in the nucleocapsid protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Viruses 2014, 6, 1253–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Hartwig, N.G.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Niemeyer, B.; de Jong, J.C.; Simon, J.H.; Osterhaus, A.D. A previously undescribed coronavirus associated with respiratory disease in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6212–6216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Deng, F.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; He, Q. New variants of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, China, 2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.L.; Shi, W.F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, Q.M.; Mani, S.; et al. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.M.; Cavanagh, D. The molecular biology of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 1997, 48, 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Duenas-Carrera, S.; Alvarez-Lajonchere, L.; Alvarez, J.C.; Ramos, T.; Pichardo, D.; Morales, J. Repeated administration of hepatitis C virus core-encoding plasmid to mice does not necessarily increase the immune response generated against this antigen. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2001, 33, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, C.R.; Finegold, M.J.; Slagle, B.L. Expression of hepatitis B virus X protein does not alter the accumulation of spontaneous mutations in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5266–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifenberg, K.; Deutschle, T.; Wild, J.; Hanano, R.; Gastrock-Balitsch, I.; Schirmbeck, R.; Schlicht, H.J. The hepatitis B virus e antigen cannot pass the murine placenta efficiently and does not induce CTL immune tolerance in H-2(b) mice in utero. Virology 1998, 243, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reifenberg, K.; Lohler, J.; Pudollek, H.P.; Schmitteckert, E.; Spindler, G.; Kock, J.; Schlicht, H.J. Long-term expression of the hepatitis B virus core-e- and X-proteins does not cause pathologic changes in transgenic mice. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Chi, Y.; Feng, L. Detection and molecular diversity of spike gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China. Viruses 2013, 5, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, S.; Feng, L. Immunogenicity and antigenic relationships among spike proteins of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus subtypes G1 and G2. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aagaard, L.; Rossi, J.J. RNAi therapeutics: Principles, prospects and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistella, M.; Marsden, P.A. Advances, Nuances, and Potential Pitfalls When Exploiting the Therapeutic Potential of RNA Interference. Clin Pharm. Ther. 2015, 97, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummelkamp, T.R.; Bernards, R.; Agami, R. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science 2002, 296, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, D.; Wang, L.; Lee, J.S.; Schurmann, N.; Gu, S.; Borner, K.; Storm, T.A.; Kay, M.A. Argonaute proteins are key determinants of RNAi efficacy, toxicity, and persistence in the adult mouse liver. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3106–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, S.M. Dicing and slicing: The core machinery of the RNA interference pathway. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5822–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontiveros, E.; Kuo, L.L.; Masters, P.S.; Perlman, S. Inactivation of expression of gene 4 of mouse hepatitis virus strain JHM does not affect virulence in the murine CNS. Virology 2001, 289, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S. Porcine epidemic diarrhea in China. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Sun, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; Liu, J.; Cao, L.; et al. Nucleocapsid Interacts with NPM1 and Protects it from Proteolytic Cleavage, Enhancing Cell Survival, and is Involved in PEDV Growth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingerote, R.J.; Cruz, B.M.; Gorczynski, R.M.; Fung, L.S.; Hubbell, H.R.; Suhadolnik, R.J.; Levy, G.A. A 2′,5′-Oligoadenylate Analog Inhibits Murine Hepatitis-Virus Strain-3 (Mhv-3) Replication in-Vitro but Does Not Reduce Mhv-3-Related Mortality or Induction of Procoagulant Activity in Susceptible Mice. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BLOCK-iT™ RNAi Designer. Available online: http://rnaidesigner.thermofisher.com/rnaiexpress/ (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST (accessed on 19 October 2019).
- Tokuriki, N.; Oldfield, C.J.; Uversky, V.N.; Berezovsky, I.N.; Tawfik, D.S. Do viral proteins possess unique biophysical features? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2009, 34, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, C.; Guo, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J. Effective inhibition of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus by RNA interference in vitro. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.; Hurst-Hess, K.R.; Koetzner, C.A.; Masters, P.S. Analyses of Coronavirus Assembly Interactions with Interspecies Membrane and Nucleocapsid Protein Chimeras. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4357–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Saif, L.J.; Marthaler, D.; Wang, Q. Evolution, antigenicity and pathogenicity of global porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Feng, L.; Wang, Y. Characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infectivity in human embryonic kidney cells. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2415–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, G.; Wen, K.; Bui, T.; Cao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L. Porcine small intestinal epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) of rotavirus infection as a new model for the study of innate immune responses to rotaviruses and probiotics. Viral Immunol. 2010, 23, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffenberger, E.; Sigl, R.; Geley, S. Conditional RNAi Using the Lentiviral GLTR System. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1448, 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Betel, D.; Miller, M.L.; Sander, C.; Leslie, C.S.; Marks, D.S. Transfection of small RNAs globally perturbs gene regulation by endogenous microRNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejniczak, M.; Polak, K.; Galka-Marciniak, P.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Recent advances in understanding of the immunological off-target effects of siRNA. Curr. Gene Ther. 2011, 11, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
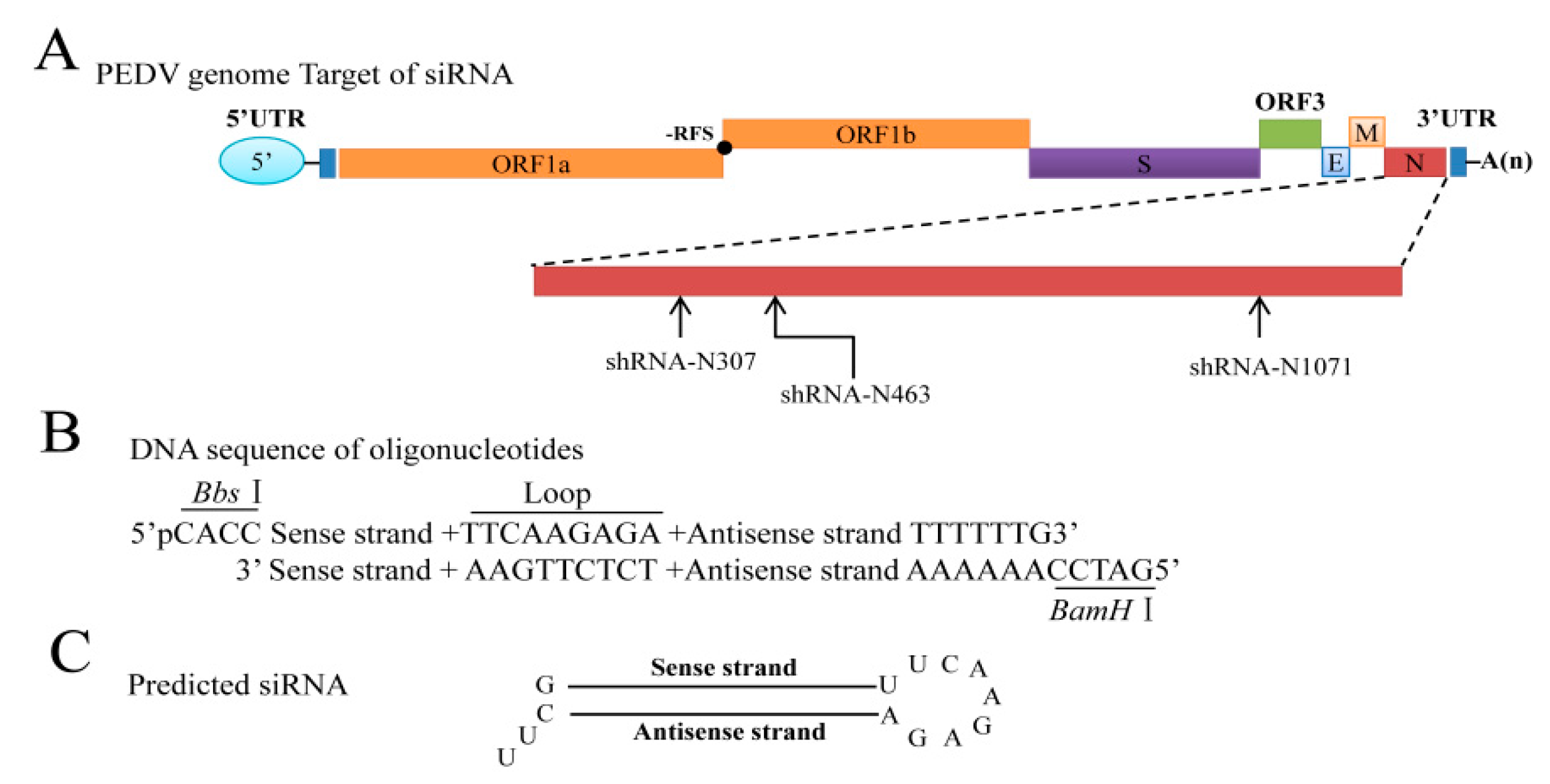

| shRNA | Sequence | Position |
|---|---|---|
| shRNA-N307 | GCAAAGACTGAACCCACTAAC | Position in N gene sequence: 307–327 |
| shRNA-N463 | GGCAACAACAGGTCCAGATCT | Position in N gene sequence: 463–483 |
| shRNA-N1071 | GCCAAAGTCTGATCCAAATGT | Position in N gene sequence: 1071–1091 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; et al. Significant Interference with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Pandemic and Classical Strain Replication in Small-Intestine Epithelial Cells Using an shRNA Expression Vector. Vaccines 2019, 7, 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040173
Shi D, Wang X, Shi H, Zhang J, Han Y, Chen J, Zhang X, Liu J, Zhang J, Ji Z, et al. Significant Interference with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Pandemic and Classical Strain Replication in Small-Intestine Epithelial Cells Using an shRNA Expression Vector. Vaccines. 2019; 7(4):173. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040173
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Da, Xiaobo Wang, Hongyan Shi, Jiyu Zhang, Yuru Han, Jianfei Chen, Xin Zhang, Jianbo Liu, Jialin Zhang, Zhaoyang Ji, and et al. 2019. "Significant Interference with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Pandemic and Classical Strain Replication in Small-Intestine Epithelial Cells Using an shRNA Expression Vector" Vaccines 7, no. 4: 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040173
APA StyleShi, D., Wang, X., Shi, H., Zhang, J., Han, Y., Chen, J., Zhang, X., Liu, J., Zhang, J., Ji, Z., Jing, Z., & Feng, L. (2019). Significant Interference with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Pandemic and Classical Strain Replication in Small-Intestine Epithelial Cells Using an shRNA Expression Vector. Vaccines, 7(4), 173. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines7040173





