Abstract
Due to the low populations of Bacteroides sp. in the gut microbiota of sows compared to nursed piglets, sows may not represent an ideal source of Bacteroides sp. for newborn piglets. In this study, we therefore tested the effect of oral administration of a mixture of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus, Bacteroides fragilis and Bacteroides xylanisolvens on the microbiota development of newborn piglets. Oral administration of such a mixture to piglets within 12 h after parturition did not result in any adverse effects. Sequencing of 16S rRNA showed that 4 days after administration, these species formed approx. 20% of total faecal microbiota and affected the development of gut microbiota in treated piglets. The treatment resulted in an increased abundance of Veillonella caviae, Fusobacterium gastrosuis, Dialister sp., Clostridium jeddahitimonense, C. cadaveris, Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum, Actinobacillus indolicus, A. minor, Streptococcus pasteurianus, S. parasuis, S. equinus, S. pluranimalium, S. thoraltensis and S. suis. On the other hand, administration of the Bacteroides mixture suppressed piglet colonisation by C. disporicum and multiple species from family Prevotellaceae. Bacteroides-treated piglets exhibited significantly higher body weight than untreated controls at 3 months of age. Administration of a mixture of Bacteroides shaped the development of gut microbiota in nursed piglets, which resulted in improved parameters at the end of the pre-fattening period.
1. Introduction
Mammals are born nearly sterile, and microbial colonisation of their bodies begins immediately after birth. The densest microbial populations can be found in the intestinal tract, which changes from nearly zero bacterial counts at birth to 1010 CFU/g only a few days later. Previous studies on the gut microbiota of omnivorous, warm-blooded animals reported that around one thousand different bacterial species colonise the intestinal tract [1,2,3], the vast majority of which are commensal or even beneficial for its host. Despite this, if live bacterial cultures are tested as probiotics, findings on the diversity of gut microbiota are ignored and only a small subset of gut microbiota members such as Lactobacilli, Bifidobacteria, Enterococci, or Bacilli are tested repeatedly [4,5,6,7,8]. However, there is no reason why the remaining gut microbiota members should not be tested for their probiotic potential as well, and the first reports of this type have begun to appear in pigs [9] and chickens [10].
In our earlier studies, we characterised the microbiota of sows and nursed and weaned piglets and found that the first colonisers of newborn piglets included E. coli and Fusobacterium [11,12]. Clostridium perfringens was also a common coloniser of newborn, one-day-old piglets. Within a few days during the first week of life, representatives of genus Bacteroides appear [11] and remain present until weaning, when these are replaced with taxonomically related Prevotella species [13,14,15]. This indicates that breast milk feeding supports Bacteroides colonisation while conventional feed formula supports the proliferation of Prevotella species. As a consequence, Bacteroides are present at a low abundance in adult pigs, including sows, which therefore do not represent an ideal source of Bacteroides for newborn piglets. It can be argued that sows colonised with Bacteroides at a low abundance may still act as a source of Bacteroides, especially if these are then positively selected by a milk diet. However, if Bacteroides were administered to newborn piglets experimentally immediately after birth, Bacteroides colonisation could be accelerated, all piglets in the litter would be equally colonised from the first hours of their life and the whole litter would develop uniformly. In addition, when we retrospectively checked previously published data, we noticed that when Clostridium perfringens formed around 10% of total microbiota of one-day-old piglets, Bacteroides species were present at a low abundance. However, when Bacteroides abundance increased to 20% of total microbiota in four-day-old piglets, C. perfringens decreased to approx. 1% of total microbiota [11]. This observation led to the current study, in which we tested a mixture of Bacteroides species as probiotics for newborn piglets. Besides specific interest in Bacteroides species as probiotics, this study has been designed also as a proof of concept, assessing whether other bacterial species from the intestinal tract can be considered as novel types of probiotics in addition to the traditional lactic acid bacteria.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
The handling of animals in this study was performed in accordance with current Czech legislation (Animal Protection and Welfare Act No. 246/1992 Coll. of the Government of the Czech Republic). The specific experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Veterinary Research Institute, followed by the Committee for Animal Welfare of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic on 3 March 2023 (permit number MZe 2406).
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture
To obtain bacterial strains for this study, rectal swabs were collected from piglets 1–7 days of age at farm A, where the majority of subsequent experiments were performed, and transported on ice to the laboratory for further processing within one hour. The swabs were resuspended in 5 mL of PRAS (0.1 g magnesium sulphate heptahydrate, 0.2 g monobasic potassium phosphate, 0.2 g potassium chloride, 1.15 g dibasic sodium phosphate, 3.0 g sodium chloride, 1.0 g sodium thioglycolate, 0.5 g L-cysteine and 1000 mL distilled water; final pH 7.5 ± 0.2 at 25 °C) in an anaerobic chamber. In the next step, the samples were serially diluted and plated on Wilkins-Chalgren anaerobe agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) supplemented with 5 mg/L hemin, 1 mg/L cellobiose, 0.5 g/L soluble starch, 1 mg/mL maltose, 0.2 mL vitamin K1 solution (0.1 mL of filter sterilized vitamin K1 in 20 mL 95% ethanol) and 0.5 mg/mL L-cysteine. The plates were incubated in an anaerobic chamber under an atmosphere consisting of 10% CO2, 5% H2 and 85% N2 at 37 °C for 48 h. Approx. 10 well-separated colonies of different morphology were selected from each agar plate, subcultured and tested for growth under aerobic conditions. Aerobically growing colonies were discarded and isolates of strict anaerobes were stored at −70 °C in BHI medium (Oxoid, Basingstoke, UK) containing glycerol at 10% concentration. To assign obtained isolates to bacterial species, DNA purified from strict anaerobes using a DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) was used as a template in the PCR amplifying over the whole 16S rRNA gene using forward TGAAGAGTTTGATCATGGCTCAG and reverse AGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA primers. The resulting PCR products were subjected to Sanger sequencing with the forward primer. Obtained sequences were BLAST compared with the GenBank database (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 10 October 2025) and isolates belonging to genus Bacteroides, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium were identified. DNA from such isolates was then subjected to whole genome sequencing using an external service.
The whole genomic sequences were annotated with RAST [16] and genomes of individual Bacteroides species were searched for the most frequent antibiotic resistances, i.e., tetQ and linA [17,18]. Presence of tetQ in the genome of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron An878 was the reason for its replacement with Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ET42 (see below). Later, the search for horizontally acquired antibiotic resistance genes was expanded using ABRicate and combined results of the ARGANNOT, CARD, MEGARES, NCBI and RESFINDER databases [19,20,21,22]. After such analysis, isolates of B. thetaiotaomicron, Bacteroides vulgatus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, Bifidobacterium boum, Lactobacillus ruminis, Lactobacillus salivarius and Lactobacillus mucosae were selected for subsequent experiments.
2.3. Animal Experiments
The first three tests were performed at the same farm from which all Bacteroides strains were cultured and the tests focused on the ability of the used strains to colonise and their safety. This farm routinely used intramuscular amoxycillin administration to control neonatal diarrhoea. The fourth experiment was performed at another farm which did not use antibiotics when testing the Bacteroides probiotic product.
The first test was performed with 15 piglets, five of which were orally inoculated with a mixture of Bacteroides, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, five piglets which were given a mixture of Bacteroides, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium together with amoxycillin treatment and the remaining five piglets were treated with amoxycillin only. When performing the first experiment, Bacteroides fragilis used in later experiments was not yet available so the piglets were treated with a mixture of 3 Bacteroides species only, i.e., B. thetaiotaomicron An878, B. vulgatus An905 and B. xylanisolvens An931 and Bifido. boum An918, L. ruminis An917, L. salivarius An879 and L. mucosae An939 (Table 1).

Table 1.
List of strains used in individual experiments of this study.
In the second experiment, 15 piglets were treated with amoxycillin, 5 piglets were treated with both Bacteroides mixture and amoxycillin and 9 piglets were treated with the Bacteroides mixture only. The original B. thetaiotaomicron An878 was replaced with another strain of the same species, B. thetaiotaomicron ET42, because of the absence of the tetQ gene in the genome of the ET42 strain (Table 2). In addition, since B. fragilis ET48 was obtained in the meantime, these piglets were treated with a mixture of 4 Bacteroides species, i.e., B. thetaiotaomicron ET42, B. vulgatus An905, B. xylanisolvens An931 and B. fragilis ET48. Since none of the tested Lactobacilli and Bifido. boum colonised piglets in the first experiment (see below), these strains were skipped from the remaining tests. The same mixture of 4 different Bacteroides species was then used in all remaining experiments.

Table 2.
Presence of antibiotic resistance genes in the genomes of strains used in this study.
In experiment 3, the microbiota of 12 piglets treated with amoxycillin, 3 piglets treated with both a Bacteroides mixture and amoxycillin and 12 piglets treated with a Bacteroides mixture only was characterised.
Experiment 4 was performed on another farm in which 40 piglets were treated with a Bacteroides mixture and 50 piglets were used as controls without any treatment. Piglets were born in weekly intervals at this farm and 10 piglets born within one week were treated with a mixture of Bacteroides. One week later, all piglets remained untreated and 10 piglets were again treated in the following week, etc. Since the whole test was started and finished with non-treated piglets, we compared 5 production weeks of control piglets without any treatment with 4 production weeks of piglets treated with a Bacteroides mixture. Out of all piglets, only 11 Bacteroides-treated and 10 control piglets were sampled for microbiota composition, while the rest of the piglets were used for comparison of production parameters at the end of the pre-fattening period when the piglets were 3 months of age.
To prepare probiotic mixtures for newborn piglets, all Bacteroides, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species were grown individually in BHI Vegan medium (HiMedia, Thane, Maharashtra, India) in an anaerobic cabinet at 37 °C for 48 h. When the culture was completed, bacterial counts were approx. 1 × 108 CFU/mL. Equal volumes of each of the 4 cultures (7 cultures in the first experiment) were mixed and immediately delivered to the farm in multiple aliquots. The mixtures were kept at 4 °C for a maximum of 5 days and any opened aliquot was used completely. Approx. 10 h old piglets were treated individually by oral administration of 1 mL of the mixture of all strains. Efficiency of colonisation was tested by collecting rectal swabs of 4-day-old piglets.
2.4. 16S rRNA Sequencing
The samples were homogenized in a MagNALyzer (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Following homogenization, the DNA was extracted using a QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and the DNA concentration was determined spectrophotometrically. DNA samples were diluted to 5 ng/mL and were used as a template in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with forward primer 5′-TCG TCG GCA GCG TCA GAT GTG TAT AAG AGA CAG-MID-GTC CTA CGG GNG GCW GCA G-3′ and reverse primer 5′-GTC TCG TGG GCT CGG AGA TGT GTA TAA GAG ACA G-MID-GTG ACT ACH VGG GTA TCT AAT CC-3′. MIDs shown above represent different sequences 5, 6, 7 or 9 base pairs in length that were used to identify individual samples within the sequencing groups. PCR amplification was performed using a HotStarTaq Plus Master Mix kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and the resulting PCR products were purified using AMPure beads (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). In the next step, the concentration of PCR products was determined spectrophotometrically, the DNA was diluted to 100 ng/µL and groups of 14 PCR products with different MID sequences were indexed with the same indices using a Nextera XT Index Kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Prior to sequencing, the concentration of differently indexed samples was determined using a KAPA Library Quantification Complete kit (Kapa Biosystems, Wilmington, MA, USA). All indexed samples were diluted to 4 ng/µL and 20 pM phiX DNA was added to a final concentration of 5% (v/v). Sequencing was performed using a MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 and MiSeq apparatus (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
Analysis of sequencing data was performed with QIIME 2 [23]. Raw sequence data were demultiplexed, quality filtered and sequencing primers were clipped using Je [24] and fastp [25]. The resulting sequences were denoised with DADA2 [26]. Taxonomy was assigned to ASVs using the q2-feature-classifier [27] and classify-sklearn naïve Bayes taxonomy classifier against the Silva 138 [28]. All the software tools were used with default settings.
2.5. Statistics
To identify key events following Bacteroides mixture administration, 5 different groups of piglets were defined for downstream analyses. The first group was formed by all amoxycillin treated piglets at farm A, hereafter designated as ATB (antibiotic treated). The second group comprised all piglets from farm A treated both with Bacteroides mixture and amoxycillin, hereafter called PA (probiotics and antibiotics). The third group comprised piglets from farm A treated with Bacteroides mixture only, hereafter called P1 (probiotics 1). Two groups of piglets from farm B were designated as CTRL (control, i.e., no antibiotics or probiotics) and P2 for piglets provided probiotic Bacteroides mixture at farm B.
Identification of differently abundant taxa was performed by PERMANOVA with 10,000 permutations and using Euclidian matrix distances (R-project, package vegan, Adonis function followed by pairwise comparisons). Only ASVs which formed more than 0.1% of total microbiota in at least one piglet and which were present in at least 15 piglets (out of 93 subjected to 16S rRNA sequencing in the study) were subjected to PERMANOVA analysis. Following PERMANOVA, significant differences (p < 0.05) were picked up from comparisons between ATB and PA groups, ATB and P1 groups and CTRL and P2 groups. Differences in microbiota composition between PA and P1 groups were considered as well.
3. Results
3.1. Safety of the Tested Mixtures
Oral administration of tested Bacteroides mixtures to newborn piglets did not lead to any adverse responses and all strains tested in this study can be therefore considered as safe.
3.2. Gut Microbiota Composition Following Administration of a Bacteroides Mixture
Microbiota composition in 32 piglets in the ATB group, 14 piglets in the PA group, 26 piglets in the P1 group, 10 piglets in the P2 group and 11 piglets in the CTRL group was characterised by 16S rRNA sequencing. The sample with the lowest coverage was characterised by 28,402 sequences, while 239,953 sequences were available for the sample with the highest coverage. Microbiota composition at the phylum level showed a distribution typical for the age group [11], i.e., dominating Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes, followed by Proteobacteria and Fusobacteria, and administration of Bacteroides product did not lead to extensive differences in the composition of gut microbiota at the phylum level (Figure 1A).
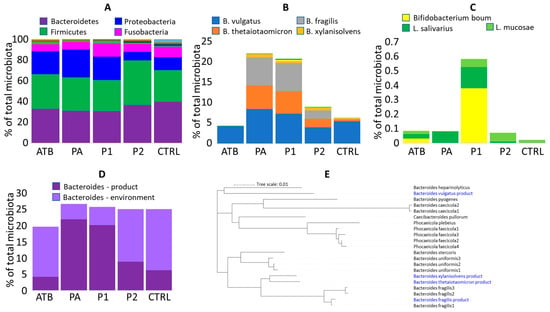
Figure 1.
Colonisation of newborn piglets. (A) Microbiota composition of ATB, PA and P1 piglets from farm A and P2 and CTRL piglets from farm B at phylum level. (B) Abundance of used strains in rectal microbiota of 4-day-old piglets. (C) Zoom in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium colonisation. Mind the Y axis scaling in (B,C). Apparently, the increased abundance of Bifido. boum in P1 piglets was affected by a single highly positive piglet. (D) Summed abundance of Bacteroides species from the used mixture and those of environmental origin. (E) Relatedness of Bacteroides strains used in the mixture and those of environmental origin found in control piglets.
3.3. Ability of Used Strains to Colonise
Except for B. vulgatus, the remaining Bacteroides strains were detected in the treated piglets at a significantly higher abundance than in the non-treated controls (Figure 1B). Absence of significant colonisation of B. vulgatus was caused by a high abundance of B. vulgatus of environmental origin also in the microbiota of ATB and CTRL piglets. B. xylanisolvens was always the least abundant, forming approx. 1% of total microbiota and the remaining Bacteroides species were similarly abundant, each forming 5 to 10% of total microbiota (Figure 1B). Intramuscular amoxycillin administration did not affect Bacteroides colonisation. The presence of antibiotic resistance genes in the genomes of all used strains was therefore checked and although all strains, except for B. thetaiotaomicron, harboured antibiotic resistance genes, only B. fragilis encoded carbapenemase cfiA gene [29] (Table 2). The tetQ gene present in B. vulgatus differed in sequence from tetQ genes, which we recorded in Bacteroides sp. using RAST annotation [17] and B. xylanisolvens harboured strA, strB and sul2 genes common in E. coli or Salmonella [30,31]. Genes at the same contig upstream and downstream from strA, strB and sul2 were manually BLAST-compared with GenBank and these were similar to different Bacteroides sequences excluding any sequencing error.
3.4. Other Bacteroides Species of Environmental Origin Present in Gut Microbiota of 4-Day-Old Piglets
Absence of a significant difference in the colonisation of experimental and control piglets by B. vulgatus indicated that newborn piglets were colonised also by Bacteroides of environmental origin (Figure 1D). The additional Bacteroides species, which were common in the microbiota of control 4-day-old piglets, included B. uniformis, B. heparinolyticus, B. plebeius, B. pyogenes, Phocaeicola (Bacteroides) faecicola and additional sequence variants of B. fragilis. The aggregated sum of alternative Bacteroides species was lower in gut microbiota of the Bacteroides mixture-treated piglets than in the non-treated controls. Having the sequences of each ASV, the distribution of used Bacteroides species and those of environmental origin was compared. B. vulgatus from the product represented one of the two main branches, while B. thetaiotaomicron, B. xylanisolvens and B. fragilis belonged to another main branch (Figure 1E).
Unlike Bacteroides, Bifido. boum, L. ruminis, L. salivarius and L. mucosae used in the first experiment did not colonise piglets during the first days of their life (Figure 1B,C).
3.5. Consequences of Early Colonisation on the Remaining of Microbiota Members
Out of 269 ASVs passing the selection criteria and excluding the strains used for experimental inoculation, 64 ASVs were differently abundant when the microbiota of ATB and P1 piglets was compared, 25 ASVs when the microbiota of ATB and PA piglets was compared and 13 ASVs when the microbiota of CTRL and P2 piglets was compared. This shows a moderate effect of Bacteroides mixture administration on the rest of the microbiota and an additional effect of intramuscularly administered amoxycillin. Since some ASVs were differently abundant in multiple comparisons, altogether 73 ASVs were differently abundant in at least one of the comparisons (Table S1). Some ASVs provided conflicting results, e.g., being more abundant in P1 than in ATB piglets and also more abundant in CTRL than in P2 piglets. Such ASVs were excluded from further considerations. Among the remaining ASVs, Bacteroides administration promoted colonisation of newborn piglets by Veillonella caviae, Fusobacterium gastrosuis, Dialister sp., Clostridium jeddahitimonense, Clostridium cadaveris, Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum, Actinobacillus indolicus and Actinobacillus minor. Bacteroides mixture resulted also in a higher abundance of multiple Streptococcus species incl. S. pasteurianus, S. parasuis, S. equinus, S. pluranimalium, S. thoraltensis and S. suis (Figure 2). On the other hand, administration of Bacteroides mixture acted against piglet colonisation by different species from the Prevotellaceae family and Clostridium disporicum. In Prevotellaceae and Clostridium disporicum, the highest colonisation was recorded in amoxycillin-treated piglets, intermediate in PA piglets and the lowest in P1 piglets indicating the combined effect of antibiotic treatment and Bacteroides mixture administration (Figure 2).
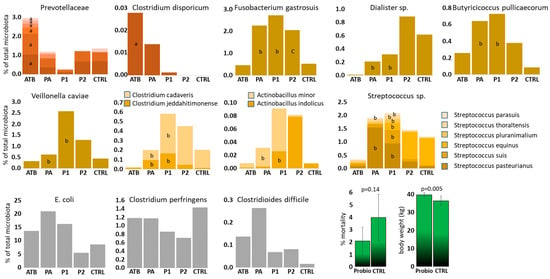
Figure 2.
ASVs affected by Bacteroides product administration. Brownish, yellow and grey columns, gut microbiota members affected by Bacteroides mixture administration. Green columns—consequences of Bacteroides mixture treatment of newborn piglets on production parameters during and at the end of pre-fattening period. a—different from P1 group, b—different from ATB group, c—different from CTRL group.
Piglet colonisation by E. coli, C. perfringens and Cl. difficile, i.e., the original target species, was not significantly affected by Bacteroides mixture administration. Despite this, numerically the highest abundance of C. perfringens was recorded in control piglets without any treatment and the lowest in both groups of probiotic treated piglets (Figure 2).
3.6. Administration of Bacteroides Mixture and the Effect on Body Weight at the End of the Pre-Fattening Period
In the last experiment, we monitored the performance of the piglets treated with Bacteroides mixture till the end of the pre-fattening period 2 months after weaning. There was a lower number of mortalities without reaching statistical significance during the pre-fatting period in Bacteroides mixture-treated piglets than in the non-treated controls. Body weight at the end of the pre-fattening period was significantly higher in Bacteroides mixture-treated pigs than in non-treated controls (Figure 2).
4. Discussion
The gut microbiota consists of hundreds of different bacterial species, which may considerably affect the behaviour of its host [32]. Despite this, bacterial products, which are used to improve the overall status of the host, are limited to a few bacterial genera such as Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, Bifidobacterium or Bacillus, while there is no real reason why other non-pathogenic taxa cannot be tested as well. In this study, we therefore tested a mixture of Bacteroides species in four independent tests, in one case together with Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium. The tests started with individual litters at a farm from which the used strains originated. The species were selected based on the earlier observation of apparent mutual exclusion of Bacteroides sp. and C. perfringens [11]. Orally administered Bacteroides efficiently colonised piglets from day 1 of life without any adverse effects. On the other hand, when three different Lactobacillus species and Bifido. boum were included in the first test, these failed to colonise after a single-dose administration. These observations are similar to those in chickens [33,34] and their ability to colonise is likely inversely associated with the ability of prolonged survival of the used bacteria under aerobic conditions [35,36].
Though the administration of Bacteroides resulted in efficient colonisation, non-treated control piglets were also positive for Bacteroides. This is not surprising as such a colonisation pattern is characteristic for 4-day-old nursed piglets [11]. It can be argued that experimental administration of Bacteroides is then of minimal relevance. However, since experimentally administered Bacteroides dominated over those of environmental origin, these must have been the first ones to colonise. Treated piglets were therefore colonised earlier and all piglets in the litter were colonised uniformly not leaving any piglet with delayed colonisation by Bacteroides species. The presence of additional Bacteroides species in the microbiota of control piglets only confirms that experimental administration of Bacteroides mimicked and sped up the otherwise natural process of piglet gut colonisation.
Bacteroides administration was not effective against original targets such as C. perfringens, Cl. difficile or E. coli. Despite this, we observed that in the case of C. perfringens, the piglets with the highest C. perfringens abundance belonged to the groups not treated with the Bacteroides mixture. The treatment thus prevented C. perfringens overgrowth and reduced exposure of littermates to this agent which is shed by highly positive reservoir piglets.
Bacteroides treatment affected the intestinal abundance of several other taxa. Bacteroides treatment resulted in increased abundance of Veillonella caviae. Co-selection of Veillonella caviae and Bacteroides sp. prevented the formation of attaching and effacing lesions in ligated intestinal loops inoculated with E. coli O157:H7 [37] suggesting that these two taxa may indeed protect piglets against pathogens. Bacteroides treatment also increased abundance of six different Streptococcus species, including pathogenic S. suis. This was rather unexpected since the farmers who tested the Bacteroides mixture reported reduced need for antibiotic treatment of S. suis infections. Bacteroides treatment also positively affected the abundance of Fusobacterium gastrosuis. F. gastrosuis was first identified as pig stomach coloniser [38]. F. gastrosuis was also detected as increasing in tonsilar microbiota in Streptococcus suis-infected pigs [39]. This suggests that the high abundance of Streptococci due to Bacteroides-mixture administration might have caused an increased abundance of F. gastrosuis.
Different representatives of Prevotellaceae were more abundant in amoxycillin-treated than in Bacteroides-mixture-treated piglets. It is likely that antibiotic therapy, despite intramuscular administration, partially affected gut microbiota development, though not the used Bacteroides strains. Piglets with suboptimal gut microbiota were then continuously exposed to Prevotellaceae from their sows, in fact an opposite scenario to the Bacteroides administration. Rapid development of gut microbiota towards an adult type in nursed piglets has been shown to have a negative effect on the occurrence of postweaning diarrhoea [14]. Inappropriate microbiota development in the early days of life can then be associated not only with postweaning diarrhoea but also with lower body weight at the end of the pre-fattening period.
Mechanisms why Bacteroides may positively affect gut health of newborn piglets have not been addressed in this study. However, B. thetaiotaomicron may forage on mucins of host origin, thus facilitating mucin turnover and its availability for other microbiota members [40]. In chickens, bacterial mixtures containing different Bacteroides species considerably affected composition of low molecular weight compounds in the caecum which can affect both grow of other microbiota members and host performance [41].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we showed that Bacteroides sp. can be used as safe probiotics for newborn piglets. Although one must be aware of the occurrence of unusual clones, e.g., as in otherwise commensal E. coli, isolates of genus Bacteroides can be considered as safe for that sensitive model as newborn piglets are.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microorganisms13102356/s1, Table S1: List of ASVs recorded in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.M. (Jitka Matiasovicova) and I.R.; methodology, J.M. (Jitka Matiasovicova), K.N., J.V., J.M. (Jan Matiasovic) and A.S.; software, D.K. and V.B.; investigation, D.K., A.S. and J.V.; resources, K.N. and J.M. (Jan Matiasovic); writing—original draft preparation, I.R.; writing—review and editing, I.R. and J.M. (Jitka Matiasovicova); funding acquisition, I.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic grant numbers RO0523 and QK23020036.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The handling of animals in the study was performed in accordance with current Czech legislation (Animal Protection and Welfare Act No. 246/1992 Coll. of the Government of the Czech Republic). The specific experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Veterinary Research Institute followed by the Committee for Animal Welfare of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic on 3 March 2023 (permit number MZe 2406).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw sequencing data have been deposited in GenBank under accession number PRJNA1309669.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Peter Eggenhuizen for the English language corrections.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Patil, Y.; Gooneratne, R.; Ju, X.H. Interactions between host and gut microbiota in domestic pigs: A review. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 310–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R.E. The pig gut microbial diversity: Understanding the pig gut microbial ecology through the next generation high throughput sequencing. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 177, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajarillo, E.A.; Chae, J.P.; Balolong, M.P.; Kim, H.B.; Seo, K.S.; Kang, D.K. Pyrosequencing-based analysis of fecal microbial communities in three purebred pig lines. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Shen, J.; Liu, C.; Yan, J.; Ma, X. Dietary Bacillus velezensis improves piglet intestinal health and antioxidant capacity via regulating the gut microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongkool, K.; Taweechotipatr, M.; Payungporn, S.; Sawaswong, V.; Lertworapreecha, M. Characterization and evaluation of Lactobacillus plantarum LC5.2 isolated from thai native pigs for its probiotic potential in gut microbiota modulation and immune enhancement. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 35, e2503028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo Zuniga, J.; Fresno Rueda, A.M.; Samuel, R.S.; St-Pierre, B.; Levesque, C.L. Impact of Lactobacillus- and Bifidobacterium-based direct-fed microbials on the performance, intestinal morphology, and fecal bacterial populations of nursery pigs. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Kim, I. Enterococcus faecium supplementation in sows during gestation and lactation improves the performance of sucking piglets. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, R.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, J.K.; Song, J.H.; Hwang, I.C.; Kim, I.H.; Kang, D.K. Multispecies probiotic supplementation in diet with reduced crude protein levels altered the composition and function of gut microbiome and restored microbiome-derived metabolites in growing pigs. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1192249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Guo, T.; He, Y.; Gao, S.; Su, J.; Pan, H.; Li, A. Parabacteroides goldsteinii alleviates intestinal inflammation in dextran sulfate sodium-treated pigs. Animals 2025, 15, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, J.; Faldynova, M.; Matiasovicova, J.; Sebkova, A.; Karasova, D.; Prikrylova, H.; Havlickova, H.; Rychlik, I. Probiotic mixtures consisting of representatives of Bacteroidetes and Selenomonadales increase resistance of newly hatched chicks to Salmonella Enteritidis infection. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasova, T.; Davidova-Gerzova, L.; Merlot, E.; Medvecky, M.; Polansky, O.; Gardan-Salmon, D.; Quesnel, H.; Rychlik, I. Housing systems influence gut microbiota composition of sows but not of their piglets. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubasova, T.; Davidova-Gerzova, L.; Babak, V.; Cejkova, D.; Montagne, L.; Le-Floc’h, N.; Rychlik, I. Effects of host genetics and environmental conditions on fecal microbiota composition of pigs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerzova, L.; Babak, V.; Sedlar, K.; Faldynova, M.; Videnska, P.; Cejkova, D.; Jensen, A.N.; Denis, M.; Kerouanton, A.; Ricci, A.; et al. Characterization of antibiotic resistance gene abundance and microbiota composition in feces of organic and conventional pigs from four EU countries. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasova, D.; Crhanova, M.; Babak, V.; Jerabek, M.; Brzobohaty, L.; Matesova, Z.; Rychlik, I. Development of piglet gut microbiota at the time of weaning influences development of postweaning diarrhea—A field study. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, V.; Luise, D.; Bosi, P.; Trevisi, P. Faecal microbiota shift during weaning transition in piglets and evaluation of AO blood types as shaping factor for the bacterial community profile. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollarcikova, M.; Faldynova, M.; Matiasovicova, J.; Jahodarova, E.; Kubasova, T.; Seidlerova, Z.; Babak, V.; Videnska, P.; Cizek, A.; Rychlik, I. Different Bacteroides species colonise human and chicken intestinal tract. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juricova, H.; Matiasovicova, J.; Kubasova, T.; Cejkova, D.; Rychlik, I. The distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in chicken gut microbiota commensals. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Padmanabhan, B.R.; Diene, S.M.; Lopez-Rojas, R.; Kempf, M.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.M. ARG-ANNOT, a new bioinformatic tool to discover antibiotic resistance genes in bacterial genomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonin, N.; Doster, E.; Worley, H.; Pinnell, L.J.; Bravo, J.E.; Ferm, P.; Marini, S.; Prosperi, M.; Noyes, N.; Morley, P.S.; et al. MEGARes and AMR++, v3.0: An updated comprehensive database of antimicrobial resistance determinants and an improved software pipeline for classification using high-throughput sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D744–D752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Raphenya, A.R.; Lau, T.T.Y.; Tsang, K.K.; Bouchard, M.; Edalatmand, A.; Huynh, W.; Nguyen, A.V.; Cheng, A.A.; Liu, S.; et al. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D517–D525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857, Erratum in Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardot, C.; Scholtalbers, J.; Sauer, S.; Su, S.Y.; Furlong, E.E. Je, a versatile suite to handle multiplexed NGS libraries with unique molecular identifiers. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.S.; Malamy, M.H. Sequencing the gene for an imipenem-cefoxitin-hydrolyzing enzyme (CfiA) from Bacteroides fragilis TAL2480 reveals strong similarity between CfiA and Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase II. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejska, M.; Senk, D.; Cizek, A.; Rybarikova, J.; Sychra, O.; Literak, I. Antimicrobial resistant Escherichia coli isolates in cattle and house sparrows on two Czech dairy farms. Res. Vet. Sci. 2008, 85, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faldynova, M.; Pravcova, M.; Sisak, F.; Havlickova, H.; Kolackova, I.; Cizek, A.; Karpiskova, R.; Rychlik, I. Evolution of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium strains isolated in the Czech Republic between 1984 and 2002. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2002–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraimi, N.; Dawkins, M.; Gebhardt-Henrich, S.G.; Velge, P.; Rychlik, I.; Volf, J.; Creach, P.; Smith, A.; Colles, F.; Leterrier, C. Influence of the microbiota-gut-brain axis on behavior and welfare in farm animals: A review. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 210, 112658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubasova, T.; Kollarcikova, M.; Crhanova, M.; Karasova, D.; Cejkova, D.; Sebkova, A.; Matiasovicova, J.; Faldynova, M.; Sisak, F.; Babak, V.; et al. Gut anaerobes capable of chicken caecum colonisation. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcolla, C.S.; Ju, T.; Willing, B.P. Cecal microbiota development and physiological responses of broilers following early life microbial inoculation using different delivery methods and microbial sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0027123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubasova, T.; Seidlerova, Z.; Rychlik, I. Ecological adaptations of gut microbiota members and their consequences for use as a new generation of probiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasova, D.; Faldynova, M.; Matiasovicova, J.; Sebkova, A.; Crhanova, M.; Kubasova, T.; Seidlerova, Z.; Prikrylova, H.; Volf, J.; Zeman, M.; et al. Host species adaptation of obligate gut anaerobes is dependent on their environmental survival. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yin, X.; Yu, H.; Feng, Y.; Ying, X.; Gong, J.; Gyles, C.L. Alteration of the Microbiota and Virulence Gene Expression in E. coli O157:H7 in Pig Ligated Intestine with and without AE Lesions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Witte, C.; Flahou, B.; Ducatelle, R.; Smet, A.; De Bruyne, E.; Cnockaert, M.; Taminiau, B.; Daube, G.; Vandamme, P.; Haesebrouck, F. Detection, isolation and characterization of Fusobacterium gastrosuis sp. nov. colonizing the stomach of pigs. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 40, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredriksen, S.; Neila-Ibanez, C.; Hennig-Pauka, I.; Guan, X.; Dunkelberger, J.; de Oliveira, I.F.; Ferrando, M.L.; Correa-Fiz, F.; Aragon, V.; Boekhorst, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis infection on European farms is associated with an altered tonsil microbiome and resistome. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjdia, A.; Martens, E.C.; Gordon, J.I.; Berteau, O. Sulfatases and a radical S-adenosyl-L-methionine (AdoMet) enzyme are key for mucosal foraging and fitness of the prominent human gut symbiont, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25973–25982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasatikova, L.; Zeman, M.; Crhanova, M.; Matiasovicova, J.; Karasova, D.; Faldynova, M.; Prikrylova, H.; Sebkova, A.; Rychlik, I. Colonization of chickens with competitive exclusion products results in extensive differences in metabolite composition in cecal digesta. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).