- Article
Structure–Property Relationships Governing Rheological, Damping, and Thermal Behaviour of Immiscible Natural Rubber/Nitrile Rubber Blend Nanocomposites
- Martin George Thomas,
- Sanitha Vasudevan and
- Sabu Thomas
- + 4 authors
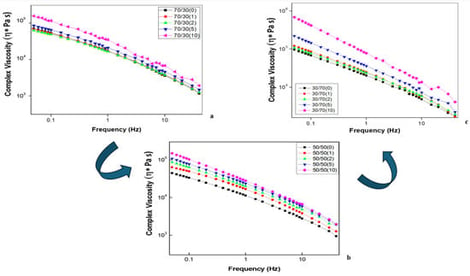
Polymer nanocomposites have been attracting significant interest over the last three decades. One of the most intriguing applications is related to the preparation of clay-filled nanocomposites based on rubber blend matrices. Although several studies already exist on the subject, there is limited information available regarding their rheological, thermal, and, particularly, damping behaviour of rubber blend systems. In this work, the rheological, viscoelastic, and thermal behaviour of a natural rubber/nitrile rubber (NR/NBR) blend nanocomposite containing organically modified nanoclay was systematically investigated, and the damping characteristics were also assessed. At a lower nanoclay concentration (5 phr), network formation through filler–filler and filler–polymer interactions led to partial immobilization of polymer chains, resulting in a pronounced increase in viscosity and enhanced viscoelastic response. In contrast, at higher nanoclay loading (10 phr), strong agglomeration of filler particles occurred, corresponding to a stacked clay morphology, which hindered effective filler–filler network formation and weakened filler–polymer interactions, leading to lower viscosity and reduced damping efficiency. The blend composition and filler content were found to significantly influence the investigated properties, especially the hysteresis loss and the thermal conductivity, which is explained by matrix–filler interactions and the resulting morphology of the system.
7 February 2026