Abstract
The leaves and stems of Bauhinia guianensis Aubl. are used in traditional Amazonian phytotherapy for the treatment of pain and inflammation. This study investigates the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. leaves and stems (HELBg and HESBg, respectively) in vivo models of inflammation and hyperalgesia. Danio rerio experimental animals were submitted to the acute inflammation test, induced by intraperitoneal (ip.) administration of carrageenan 20 μg/animal (abdominal edema); the groups were previously treated orally with saline solution 2 μL/animal (SS), dimethyl sulfoxide 2 μL/animal (DMSO), indomethacin 10 mg/kg, HELBg 100 mg/kg and HESBg 100 mg/kg, n = 12 per experimental group to evaluate the inhibition of edema and alteration histopathology of the liver, intestine and kidney of these animals. The antinociceptive effect was observed from the body curvature index and the behavioral responses of Danio rerio, after an experimental protocol for the induction of hyperalgesia, by ip. administration of 10 μL/animal of 2.5% acetic acid; the animals were orally treated orally with saline solution 2 μL/animal (SS), dimethyl sulfoxide 2 μL/animal (DMSO), morphine 2.5 mg/kg, HELBg 100 mg/kg and HESBg 100 mg/kg, and n = 5 per experimental group. In carrageenan-induced edema, the group treated with HESBg inhibited edema formation over the 3 h of the experiment. Maximum edema was inhibited by 54% (p < 0.05) when compared to the control group. Both HELBg and HESBg prevented body curvature index changes (t(df=3,8) = 6.96 and t(df=3,8) = 6.61, respectively, both p < 0.0001). In the behavioral parameters sensitive to antinociceptive pharmacological modulation, due to the abdominal constriction induced by acetic acid, the administration of HELBg and HESBg resulted in an improvement in swimming activity, with the following results: increase in distance covered (F(df=3,16) = 6.50 and F(df=3,16) = 7.72, respectively, both p < 0.0001), decrease in freezing time (F(df=3,16) = 2.04 and F(df=3,16) = 1.28, respectively, both p < 0.0059), increase in the number of ascents to the upper area of the tank (F(df=3,16) = 33.02 and F(df=3,16) = 35.62, respectively, both p < 0.0009) and decreased time spent in that area (F(df=3,16) = 101.19 and F(df=3,16) = 103.59, respectively, both p < 0.0038). It is reasonable to suppose that both extracts modulated the variations induced by carrageenan and acetic acid through the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis, thereby decreasing the release of inflammatory mediators, the sensitization of peripheral nociceptors, and, consequently, the perception of pain. These results suggest that HELBg and HESBg have anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities, likely of peripheral origin and associated with the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis.
1. Introduction
The centuries-old use of native plant species reflects the valuable resources available to traditional peoples and communities in the Amazon, especially those living in remote areas and dense forests, who rely on native medicinal flora due to the essential components disseminated through ethnomedicinal practices [1,2,3]. A growing body of evidence describes the promising role of natural compounds to reduce pain and inflammation [4]. A bioprospecting approach that reinforces these popular perceptions should be strongly encouraged in pharmacological research [5].
Although significant efforts have been made to develop synthetic drugs in recent years, with anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive actions, the importance of ethnopharmacology as a valuable source of therapeutic compounds is recognized due to the vast biosynthetic capacity derived from constituent phytochemicals [6]. In the Amazonian socioeconomic scenario, the availability of pharmaceutical products is not always accessible, which forces communities to depend solely on traditional medicine for everyday needs [5,7].
In this context, the species Bauhinia guianensis Aubl. (B. guianensis Aubl.), from the Fabaceae family, is considered. It is a spontaneous plant, usually known as “tortoise ladder”, due to the growth of the stem lianas in a flattened, twisted shape, with alternating curves that resemble a ladder. This species of liana is native to the Amazon Biome, being found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Guyana, French Guiana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. In Brazil, it occurs mainly in the North Region; however, it has also been identified in the State of Maranhão and in remnants of the Atlantic Forest Biome in the State of São Paulo [5].
Historically, the stems and leaves of B. guianensis Aubl. have been widely used in Amazonian ethnomedicinal practices to relieve abdominal pain and treat inflammatory processes [8]. Despite numerous reports of the widespread medicinal use of B. guianensis Aubl. in the Amazon, few scientific studies have described its toxicity potential, phytochemical characterization [5,9,10], and pharmacological potential [8,9,11].
Among the studies evaluating the bioprospecting potential of the species, Carvalho et al. [9] investigated the methanolic extract of the stem bark of B. guianensis Aubl. (100 mg/kg) in Swiss mice with the induction of paw edema by carrageenan, a significant inhibition of edema formation was observed in animals treated with the extract when compared to the control group. This study also tested the dichloromethane extract of B. guianensis Aubl. in Swiss mice. The authors observed a significant inhibition of the algogenic process, produced by inducing abdominal contortions with acetic acid.
Previous studies have identified several bioactive compounds in the hydroethanolic extracts of B. guianensis, with a focus on zebrafish at the embryonic development stage and in adults. These compounds, including flavonoids, proanthocyanidins, and tannins—known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties—have demonstrated activities that suggest the modulation of inflammatory processes and pain reduction. Possibly, the procyanidins present in B. guianensis can modulate the inflammatory response mainly by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6), in addition to pro-inflammatory enzymes such as cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Procyanidins suppress Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) activation and, consequently, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages, thereby reducing the expression of numerous inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2, and iNOS [5,10,12].
In this context, inflammation is a necessary and beneficial process for the body, which helps restore homeostasis and return tissue to normal [13]. It acts as a defense and repair strategy; however, this mechanism can be compromised in the intense and uncomfortable presence of acute clinical manifestations (heat, redness, edema, and pain), subacute, extensive systemic or chronic repercussions, with manifestations of disabling symptomatic conditions and cumulative tissue damage, e.g., deformities and functional losses [14,15,16].
The inflammatory process is extensively studied due to its pathophysiological relevance. Faced with the complex series of restorative and protective responses to tissue injury, there are anti-inflammatory agents: steroidal and non-steroidal (NSAIDs) [17]. Currently used anti-inflammatory agents, such as NSAIDs, inhibit cyclooxygenase and therefore prostaglandin synthesis. These compounds also exhibit antinociceptive activity, as prostaglandins are implicated in mediating nociception [18]. However, NSAIDs can cause undesirable side effects [19]. Although widely available on the market, they are not necessarily accessible to Amazonian populations, who seek native plant sources to relieve inflammation. Research on substances or medications that offer fewer adverse effects and can prevent or mitigate the successive events of inflammation is strongly encouraged [20].
In terms of biomedical research, there is a significant amount of work on inflammation in the experimental model Danio rerio [21]. This animal model has been widely used in tests for drug discovery due to its characteristics, such as easy genetic manipulation, high prolificity, external fertilization, rapid development, and transparent embryo [22,23], in addition to the advantages of providing quickly translatable data in a spectrum of tissues, organs, and systems. It exhibits high genetic homology with mammals, robust phenotypes, and high-throughput genetic and chemical screening, making it a powerful tool for evaluating in vivo natural and synthetic substances [24].
In addition, the small size, associated with the low body weight of the adult Danio rerio, allows for the use of reduced amounts of the compound tested, as calculated by the dose, making it an advantageous and relevant model for screening new anti-inflammatory substances [23,25]. This is because it is possible to assess behavioral and tissue alterations, edema formation, accumulation of inflammatory cells in the exudate, mediators, signaling pathways, gene expression, and the production of specific proteins [4]. However, little information is available on the immunomodulatory role of procyanidins in the carrageenan-induced inflammation model in Danio rerio. Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. leaves and stems in models of inflammation and hyperalgesia in vivo, reinforcing the traditional Amazonian use, which is particularly important in the decision-making process for the tested activities.
2. Results
2.1. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of HESBg and HELBg in the Inhibition of Edema by Carrageenan in Danio rerio
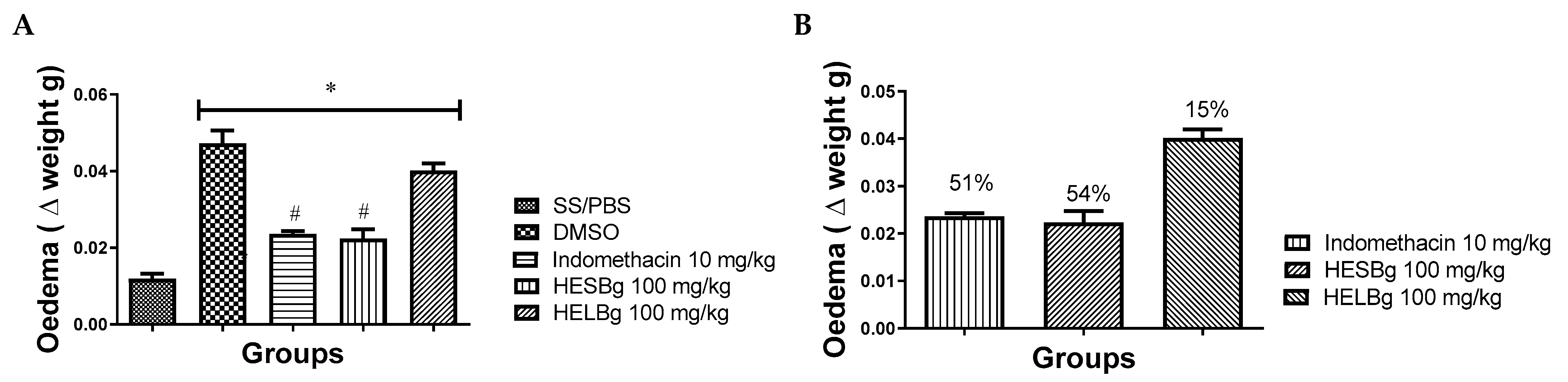
The first group studied received saline orally and PBS ip. (SS/PBS) therefore, there was no induction of inflammatory edema. In the other groups, the administration of carrageenan in the peritoneum of Danio rerio produced visible edema, reaching a maximum peak after the third hour of the stimulus, mainly in the group that received only the DMSO extract diluent. The group treated with HESBg showed considerable inhibition of swelling over the 3 monitored hours. The percentage of inhibition was approximately 15% in the HELBg group, and the group treated with HESBg had a 54% reduction in edema volume, compared to 51% in the control group (indomethacin) (p < 0.05), as shown in Figure 1.
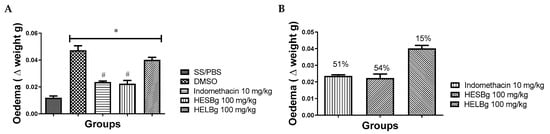
Figure 1.
Effect of oral administration of saline solution and phosphate-buffered saline (SS/PBS, 2 µL), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO 2 µL), indomethacin 10 mg/kg, hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. stems (HESBg 100 mg/kg) and hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. leaves (HELBg 100 mg/kg) on carrageenan-induced edema (20 µg/animal). (A) Edema (Δ weight g) in different groups. * p < 0.05 vs. SS/PBS; # p < 0.05 vs. DMSO (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test, n = 12). (B) Percentage inhibition obtained with oral treatment of indomethacin, HESBg, and HELBg doses in carrageenan edema.
2.2. Histopathological Evaluation of the Inflammation Test in Danio rerio
2.2.1. Histopathological Evaluation of the Liver
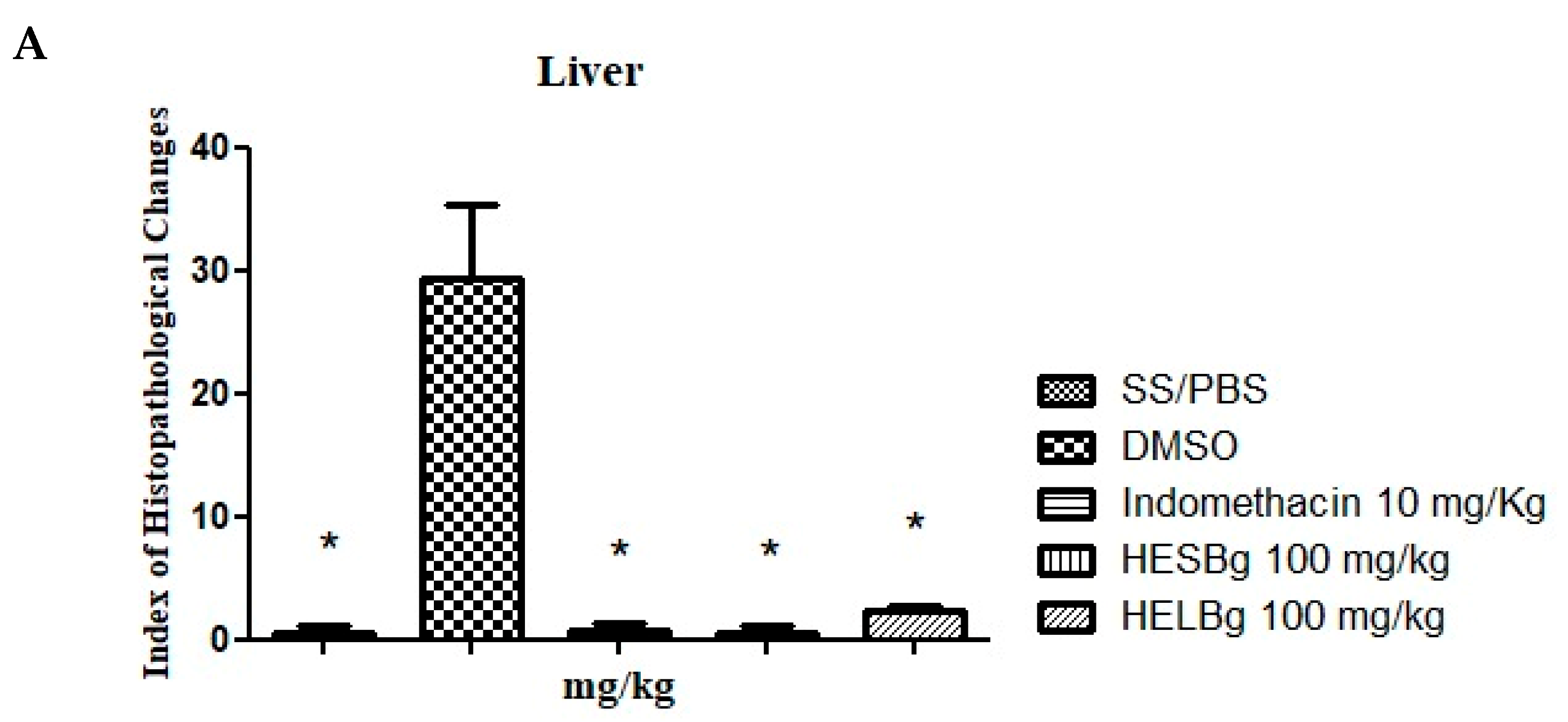
In the histopathological analysis of the animals’ livers (Figure 2A), the Index Histopathological Change (IHA) of the SS and HESBg groups was 0.5 ± 0.288, indomethacin; 0.75 ± 0.250 (Figure 2A), indicating a normal state of the organ after the application of PBS and carrageenan in the indomethacin and HESBg groups. Microscopic examination of the slides revealed only grade I changes, including cytoplasmic vacuolation (Figure 3A).
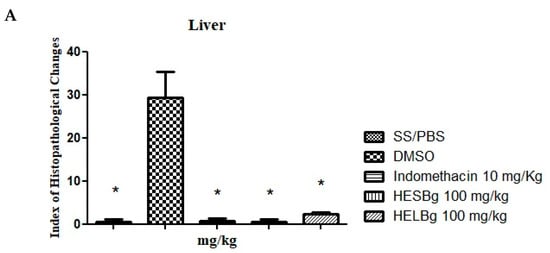
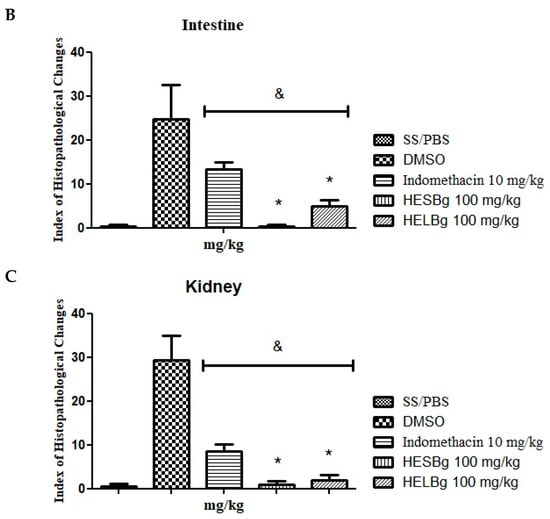
Figure 2.
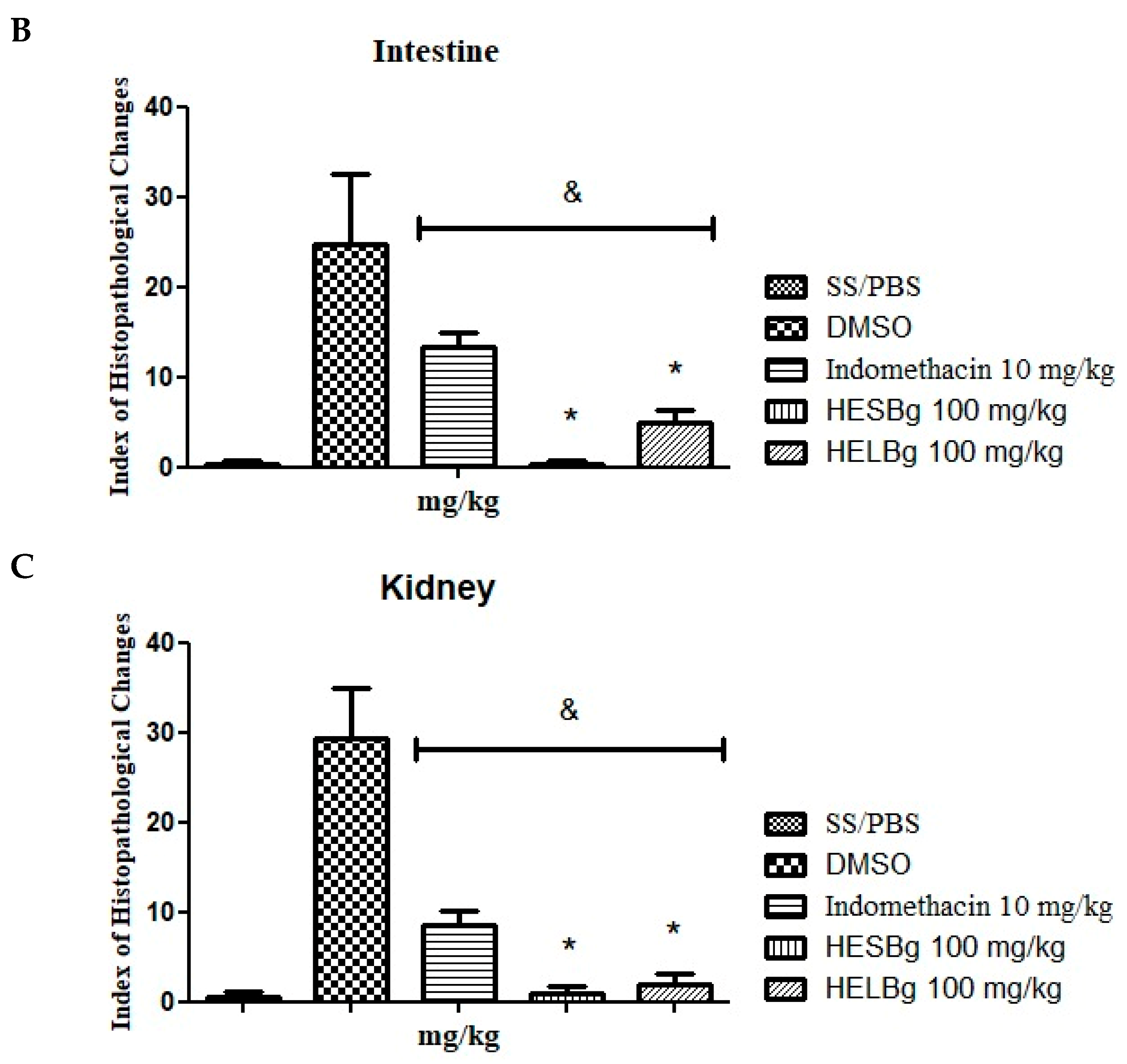
Effect of oral administration of saline solution and phosphate-buffered saline (SS/PBS, 2 μL), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO 2 μL), indomethacin 10 mg/kg, hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. stems (HESBg 100 mg/kg) and hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. leaves (HELBg 100 mg/kg) on the Index of Histopathological Changes in the liver (A), intestine (B), and kidney (C) of Danio rerio with the application of carrageenan (20 μg/animal). Index Histopathological Change (IHA): HESBg and HELBg were not organ toxic. & p < 0.05 in relation to DMSO and * p < 0.05 in relation to indomethacin. ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test, n = 12.
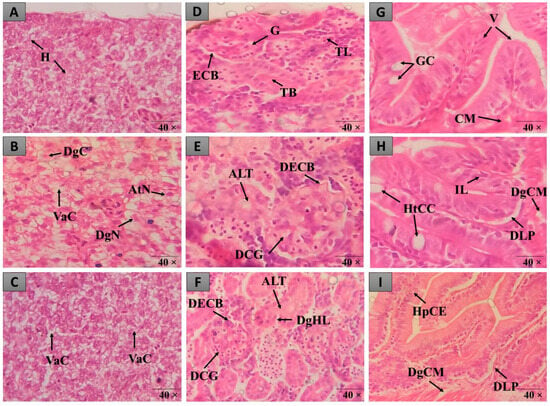
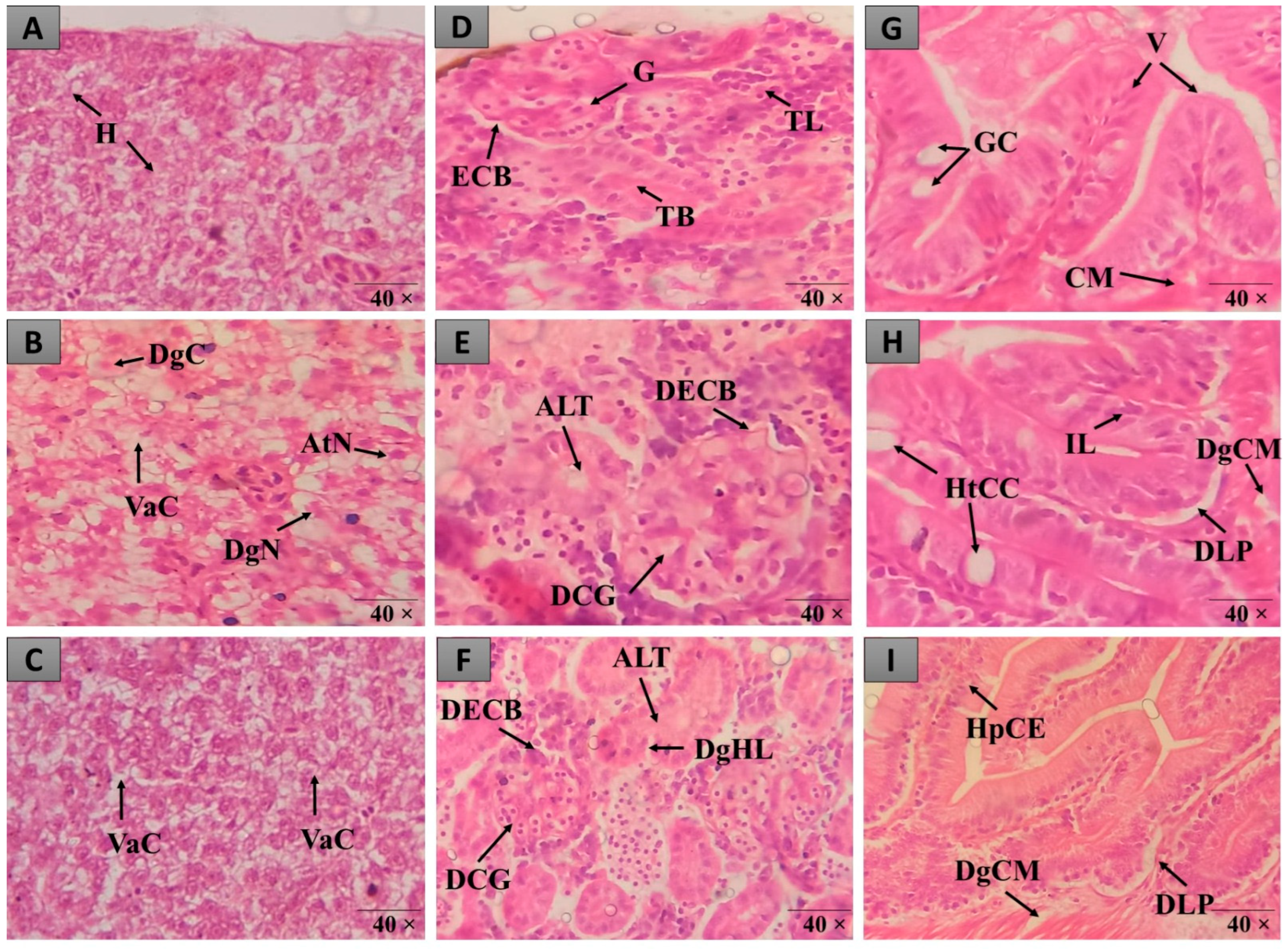
Figure 3.
Histopathological alterations observed in the liver, intestine and kidneys of zebrafish in the different treatments. In (A–C), liver tissue with normal hepatocytes (H), cytoplasmic vacuolation (VaC), nuclear atypia (AtN), nuclear degeneration (DgN) and cellular degeneration (DgC) is observed. In (D–F), there is renal tissue with normal glomerulus (G), Bowman’s capsule space (ECB), tubules (TB), lymphoid tissue (TL), increased tubular lumen (ALT), dilated capillaries of glomerulus (DCG), Bowman’s capsule space narrowing (BDEC) and mild tubular hyaline degeneration (DgHL). In (G–I), intestinal tissue with normal goblet cells (GC), lymphocytic infiltration (IL), villi (V), goblet cell hypertrophy (HtCC), muscle layer degeneration (DgCM) and epithelial cell hyperplasia (HpCE) is observed. Staining (H&E).
The DMSO group had an IHA of 29.25 ± 3.065 (Figure 2A), with significant alterations classified as moderate to severe (levels I, II, and III), including nuclear atypia (I), nuclear degeneration (II), and cellular degeneration (III) (Figure 3B,C). The animals in the HELBg group exhibited liver tissue with an IHA of 2.25 ± 0.25, which classifies this organ as functionally normal (Figure 2A). The histopathological changes observed were cytoplasmic vacuolation (I) and nuclear atypia (I) (Figure 3A,B).
2.2.2. Histopathological Evaluation of the Intestine
The intestinal tissue of the SS and HESBg groups obtained an IHA of 0.25 ± 0.250, and of the HELBg 5.00 ± 0.707, classifying the organs as normal (Figure 2B), that is, with the presence of grade I alterations, such as lymphocytic infiltration and goblet cell hypertrophy (Figure 3G,H). The DMSO group had an IHA of 24.75 ± 3.924 and classification of changes from moderate to severe (Figure 2B), namely, lymphocytic infiltration, hypertrophy of goblet cells (I), and degeneration of the muscle layer (III) (Figure 3G–I). The indomethacin control group had an IHA of 13.25 ± 0.853, classifying the organs as having mild to moderate alterations (Figure 2B), including epithelial cell hyperplasia (I) (Figure 3G,H).
2.2.3. Histopathological Evaluation of the Kidneys
The changes registered in the renal tissue of the groups treated with SS, HESBg, HELBg, and indomethacin were classified with an IHA of 0.5 ± 0.288, 1.0 ± 0.408, 2.0 ± 0.577, and 8.5 ± 0.866, respectively, demonstrating a functionally normal organ (Figure 2C). In the histopathological analysis, these kidneys exhibited grade I alterations, characterized by an increase in the tubular lumen and dilation of the glomerular capillaries (Figure 3D–F).
2.3. Antinociceptive Potential of HESBg and HELBg in the Modulation of Behavioral Phenotypes After Intraperitoneal Injection of Acetic Acid in Danio rerio
The first group studied received saline orally and PBS ip. (SS/PBS)Therefore, PBS alone did not alter the body curvature index (t(df=3) = 3.50, p < 0.0001). The administration of acetic acid (2.5%, ip.) affected the Danio rerio body curvature index (t(df=3) = 13.83, p < 0.0001) compared to its baseline conditions (t(df=3) = 3.29, p < 0.0001) and/or compared to the control (PBS). DMSO does not influence the measured abdominal constriction behavior, as shown in Figure 4.
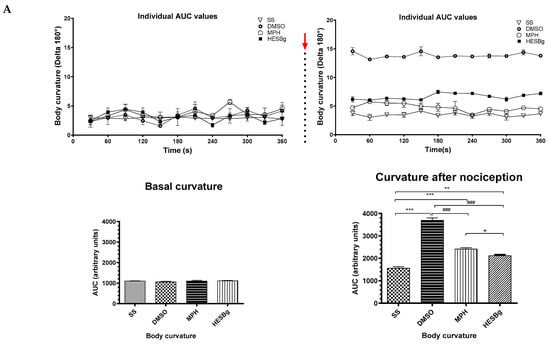
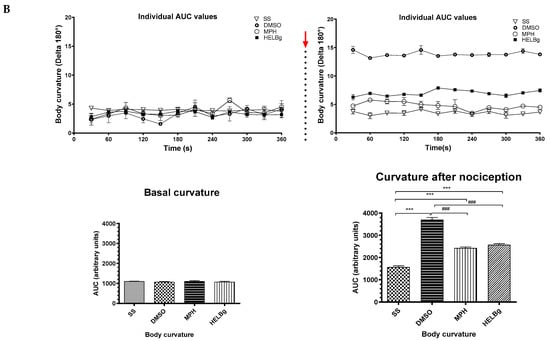
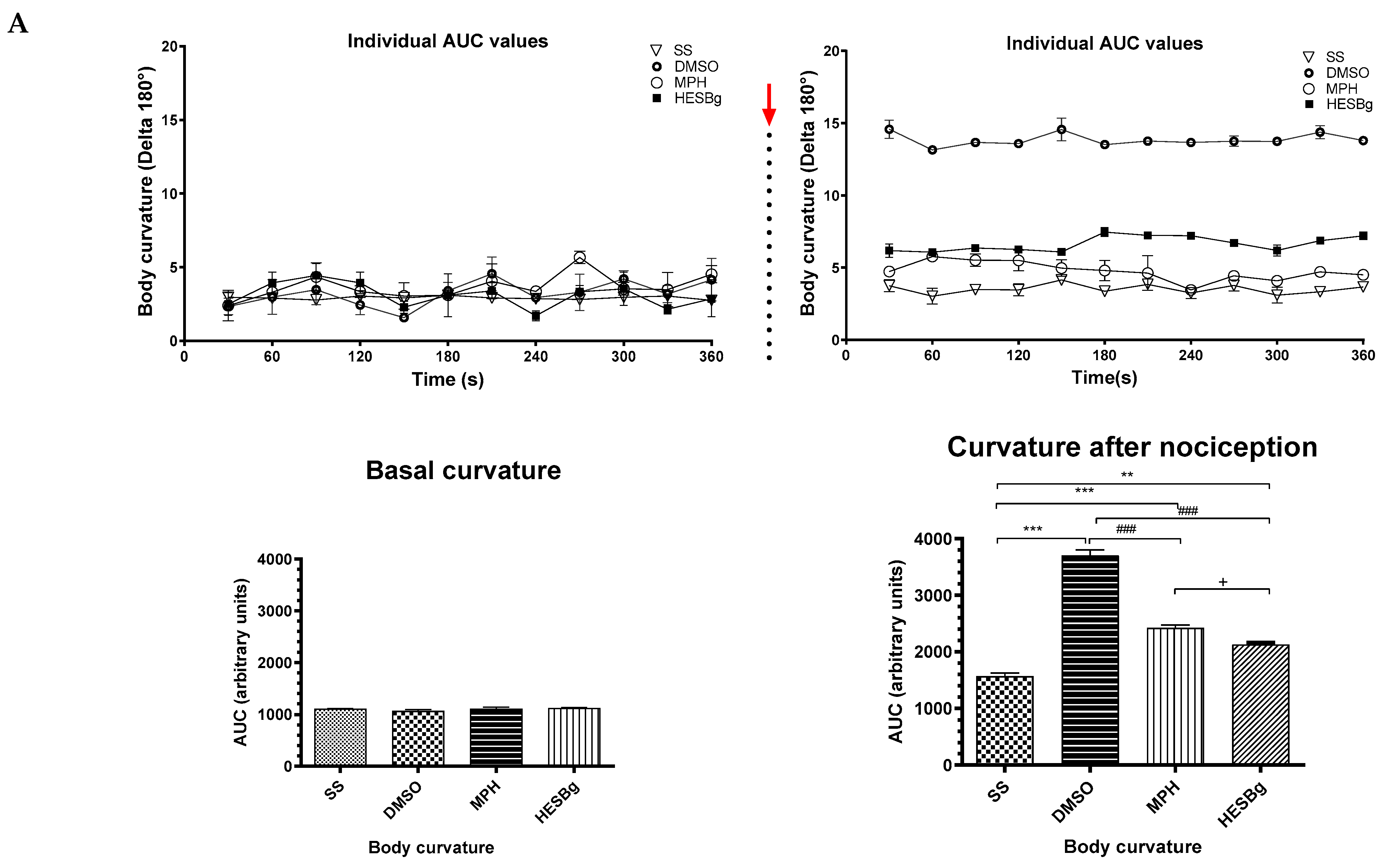
Figure 4.
Behavioral phenotypes (body curvature index) at baseline and after intraperitoneal injection of 2.5% acetic acid in Danio rerio with different treatments (saline solution—SS 2 μL, dimethyl sulfoxide—DMSO 2 μL, morphine—MPH 2.5 mg/kg, hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. stems—HESBg 100 mg/kg, B hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. leaves—HELBg 100 mg/kg). Results expressed as mean ± S.E.M were analyzed using one-way Analysis of Variance (one-way ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s post-test of multiple comparisons, n = 5. Statistical significance for both (A,B) is indicated as: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 (vs. SS); ### p < 0.001 (vs. DMSO); + p < 0.05 (vs. MPH). The red arrow indicates the time point of acetic acid injection.
Oral treatments, such as Morphine, HESBg, and HELBg, standard, prevented changes in body curvature index after intraperitoneal injection of acetic acid (t(df=3,8) = 4.83, 6.61, 6.96; p < 0.0001), as shown in Figure 4. In Figure 5, animals that received PBS ip. demonstrated baseline behaviors, such as locomotion (F(3,16) = 8.12, p < 0.0001), duration of the animal’s freezing behavior (F(3,16) = 0.66, p < 0.0059), transitions to the upper area of the tank (F(3,16) = 38.68, p < 0.0009) and time spent in this area (F(3,16) = 98.64, p < 0.0038).
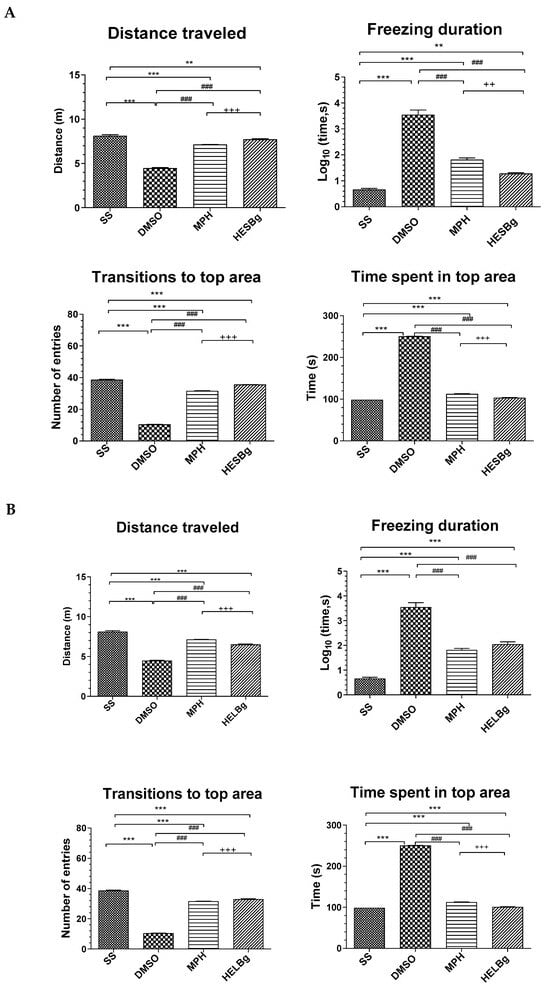
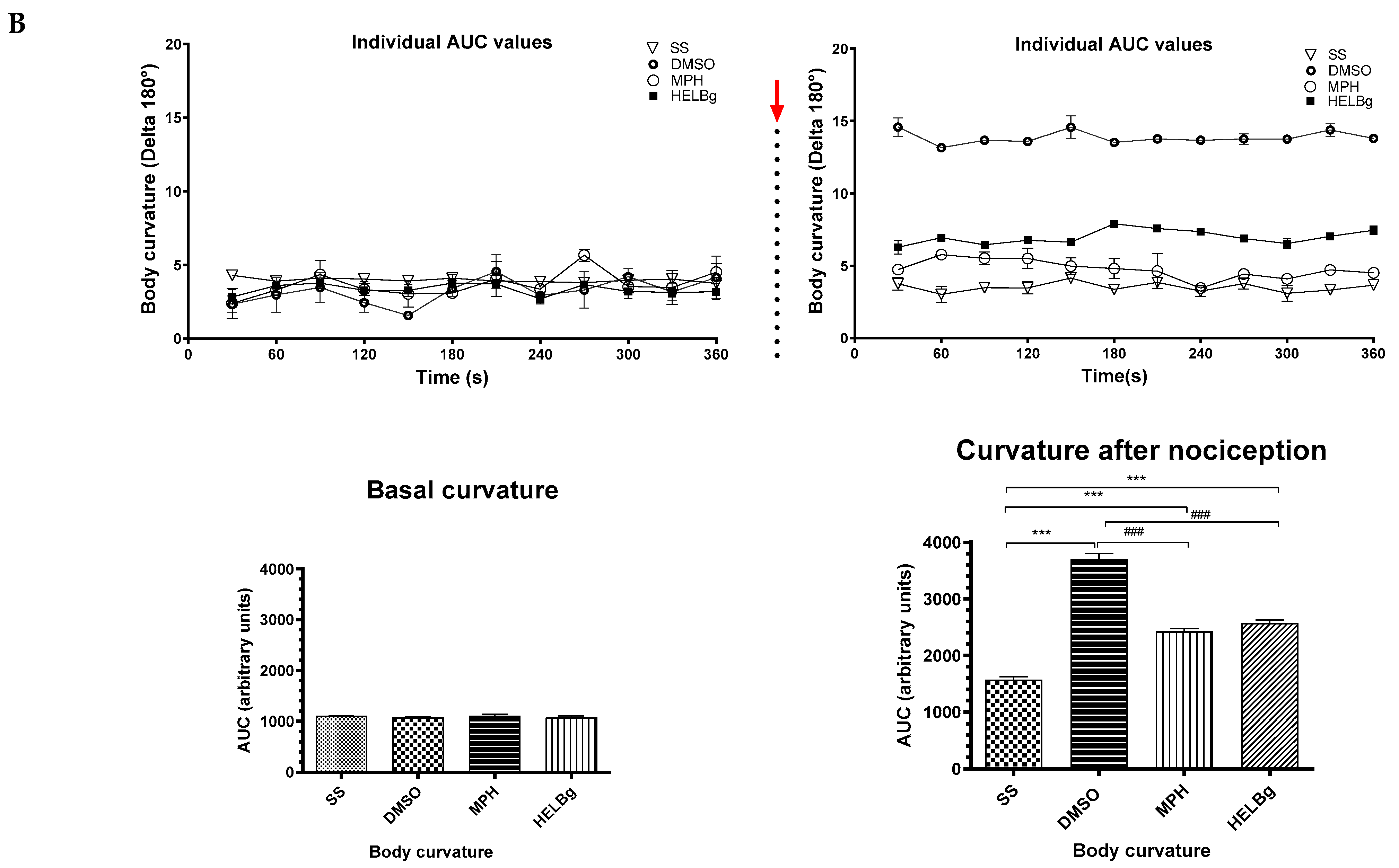
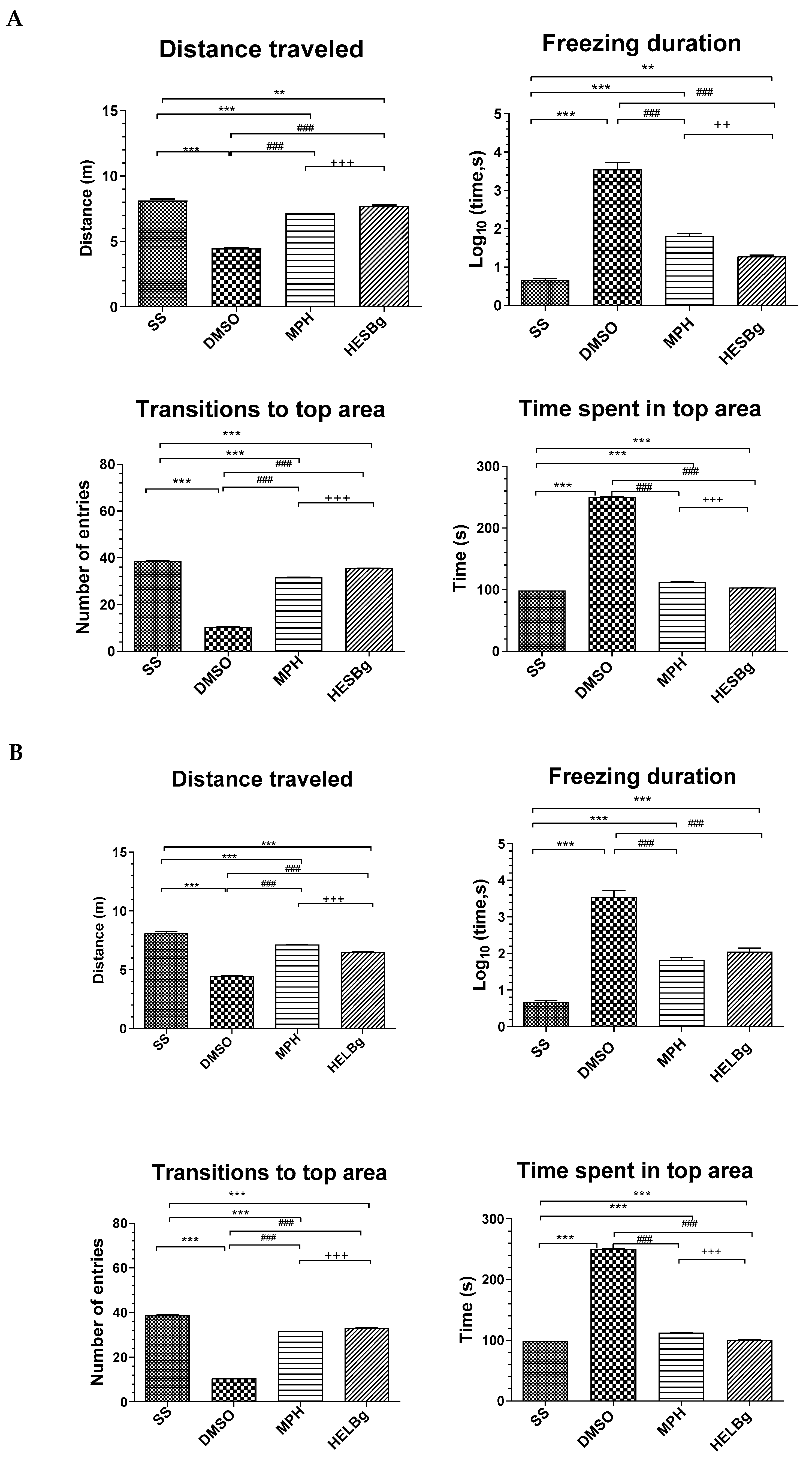
Figure 5.
Behavioral phenotypes (locomotor and exploratory endpoints were assessed by distance walked, freezing duration, number of entries, and time spent in the upper area) after intraperitoneal injection of 2.5% acetic acid in Danio rerio with different treatments (saline solution—SS 2 μL, dimethyl sulfoxide—DMSO 2 μL, Morphine—MPH 2.5 mg/kg, hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. stems—HESBg 100 mg/kg, B hydroethanolic extracts from B. guianensis Aubl. leaves—HELBg 100 mg/kg). (A) Distance traveled, freezing duration, transitions to the top area, and time spent in the top area for the HESBg group. (B) Distance traveled, freezing duration, transitions to the top area, and time spent in the top area for the HELBg group. Results expressed as mean ± S.E.M. were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s post-test of multiple comparisons, n = 5. Statistical significance for both (A,B) is indicated as: ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 (vs. SS); ### p < 0.001 (vs. DMSO); ++ p < 0.01, +++ p < 0.001 (vs. MPH).
The other animals, such as the DMSO group, when receiving acetic acid ip., were observed to see how this influenced the behavior, as it reduced locomotion (F(3,16) = 4.47, p < 0.0001) and transitions to the upper area (F(3,16) = 10.52, p < 0.0009). In addition, it increased the duration of the animal’s freezing behavior (F(3,16) = 3.54, p < 0.0059) and the time spent in the upper area of the tank (F(3,16) = 250.71, p < 0.0038).
While fish treated with morphine, HESBg and HELBg had an improvement in swimming activity, with the following results: increase in the distance covered (F(3,16) = 7.14; 7.72; 6.50, p < 0.0001); decrease in freezing time (F(3,16) = 1.82; 1.28; 2.04, p < 0.0059); increase in the number of ascents to the upper area of the tank (F(3,16) = 31.63; 35.62; 33.02, p < 0.0009); and decrease in time spent in this area (F(3,16) = 112.61; 103.59; 101.19, p < 0.0038).
3. Discussion
In the investigation of the anti-inflammatory effect of B. guianensis Aubl., saline solution (SS), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), indomethacin, HELBg, and HESBg were used as treatment protocols, administered orally 60 min before the acute inflammatory induction by carrageenan [4]. Consequently, abdominal edema formed, a response characterized by inflammatory swelling due to the local accumulation of low-molecular-weight catabolic products and extra fluid, resulting from increased tissue osmotic pressure [26].
In the absence of treatment, and in extreme cases, inflammation can lead to serious complications and death [16]. The induction of edema by the usual method of administering the bioproduct carrageenan, derived from seaweed, involves immunological sensitization, cell migration, and the consequent inflammatory response [27]. The evaluation of substances with anti-inflammatory potential, based on this methodology, is considered an excellent alternative for screening promising compounds [16].
The acute anti-inflammatory activity of B. guianensis Aubl. was previously described by Carvalho et al. [9] in the evaluation of paw edema induced by carrageenan in albino Wistar rats. This study demonstrated that, at a dose of 100 mg/kg body weight, the methanolic extract of the species significantly inhibited the in vivo edema model. The bioactive compounds of this plant species have been examined only in rodent models; however, the present study utilized a Danio rerio model, which simplifies the procedure itself, thereby enhancing the experimental design as a whole [15].
The SS control group did not receive the carrageenan dose, serving as a comparison to receiving only the saline solution orally and PBS intraperitoneally (i.p.), which is a carrageenan-solubilizing extender. The DMSO negative control group was treated with this organic solvent to rule out any anti-inflammatory effects that might be associated with the extracts used.
The animals that received the standard drug, indomethacin, had a decrease in edema. This non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug is widely used as a positive control in the screening of new anti-inflammatory molecules [28], as evidenced by other studies that have obtained similar inhibitory responses to inflammation in Danio rerio [21,29]. It is noted that the HESBg achieved a higher percentage of inhibition of abdominal edema than the anti-inflammatory used, and HELBg, even with a lower rate of inhibition than the control, also showed an inhibitory effect against edema. When evaluating substances with anti-inflammatory potential, similar mechanisms should be considered. Although the compounds differ in their specific mechanisms of action, their effects are concentrated in various inflammatory mediators. For example, NSAIDs inhibit cyclooxygenase and therefore prostaglandin synthesis [14].
It is believed that the results of this analysis suggest anti-inflammatory activity in the extracts obtained from the species B. guianensis Aubl., due to the presence of procyanidins (PCs), which are formed by the condensation of the flavan-3-ol subunits (catechin and epicatechin) and are important secondary metabolites of the flavonoid class [30], with numerous pharmacological properties, including anti-inflammatory, antiallergic [9,31] and antioxidant effects, for stabilizing cell membranes [32].
Several studies have reported the therapeutic potential of these compounds. Sun et al. [33] evaluated the cytoprotection of PCs against H2O2-induced oxidative cellular toxicity in tendon-derived stem cells. Kim et al. [34] demonstrated that PCs present in ethanolic grape seed extracts improved collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in mice, negatively regulating the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), phosphorylated synovial protein IκBα, and the inhibition of nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunits (p65 and p50) in an in vivo model of experimental arthritis. Ma et al. [35] investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of PCs and the mechanism underlying these effects in bovine mammary epithelial cells (MAC-T) stimulated by lipopolysaccharides (LPSs), demonstrating a decrease in inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α) and oxidative stress indicators (cyclooxygenase 2—COX-2 and iNOS) after LPS induction in MAC-T cells.
The potential of flavonoids to inhibit enzymes that metabolize arachidonic acid (AA) has been described since 1980 [36]. Since then, the regulation of the AA pathway has been recognized as one of the main mechanisms by which flavonoids, such as procyanidins, exert their anti-inflammatory effects [37]. During inflammation, COX-2 is essential, as its modulation regulates the inflammatory response. At the transcriptional level, COX-2 can be regulated by pro-inflammatory stimuli, including LPS, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and growth factors, which stimulate the MAPK and NF-κB pathways, leading to the consequent transcription of the COX-2 gene [18]. In this context, procyanidins inhibit COX-2 either by gene transcription, protein expression, or enzymatic activity. Thus, the literature demonstrates that extracts rich in procyanidin are dose-dependent inhibitors of COX-2 protein expression [38,39].
Consequently, if COX-2 is inhibited, there will be low production of prostaglandin (PG) [30]. Therefore, there is strong evidence of the inhibitory potential of PCs on COX-2 activity and gene and protein expression, consistent with the reduction in PG secretion, as reported by Martinez-Micaelo et al. [40] and Terra et al. [41], when evaluating PCs in primary human macrophages.
The histopathology results of the present study showed that the induction of acute inflammation ip. caused alterations in key organs, including the liver, intestine, and kidneys. Danio rerio is a well-established model for addressing multiple systems. The ability to test liver responses to a multitude of toxins enables high-throughput detection, screening, and drug discovery of toxicity [42]. Furthermore, several intestinal functions and immune genes are conserved between Danio rerio and mammals, making this teleost an interesting organism to investigate for investigating the fundamental processes underlying intestinal inflammation and injury [43]. This model organism has been instrumental in the analysis of organogenesis and kidney disease, including kidney-related ciliopathies and acute kidney injury, as well as in the search for new therapies due to the structural and functional simplicity of the kidney [44].
Animals in the SS group exhibited similar observations to those reported by Borges et al. [4]. The second group received the DMSO extender; thus, the solvent’s inertia in preventing tissue damage led to tissue changes arising from the inflammatory process. The histopathological alterations observed in the liver, intestine, and kidneys of this negative control group can be attributed to different factors, such as oxidative stress, accumulation of toxic substances, or lack of adequate supply of nutrients; direct damage to the muscles; and accumulation of proteins and other materials inside the tubules, respectively [4,21].
The third group received a standard drug, indomethacin, bodily functions, which induced histopathological alterations that did not affect Danio rerio liver, as intestinal functions could compromise other bodily functions. Indomethacin is a non-selective COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor. When used in a study with Danio rerio during the larval phase, Westhoff et al. [45] showed serious dose-dependent renal side effects by analyzing histological sections of larvae treated with indomethacin, which resulted in alterations in renal development during nephrogenesis.
The groups of plant extracts studied did not develop histopathological alterations that could influence the functioning of the organs, suggesting that the components present in these tested bioproducts may explain the specific mechanisms of action of secondary metabolites derived from the stem and leaves of B. guianensis Aubl. In terms of the modulation of the inflammatory response, it is thought that the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effects found may be related to the presence of procyanidins, which, among other activities, are responsible for modulating several fundamental pathways for the regulation of inflammation, including cellular homeostasis, such as the AA pathway (through the regulation of eicosanoid-generating enzymes); the production and secretion of inflammatory mediators, such as cytokines or nitric oxide; and the modulation of MAPKs and NF-κB pathways [10,30].
In the context of inflammation, pro-inflammatory mediators can be produced by tissue infiltration and immune cells. These pro-inflammatory mediators can induce pain [46]. Thus, the present study also investigated the antinociceptive effect of B. guianensis Aubl., using SS/PBS as a treatment protocol; DMSO, morphine, HELBg, and HESBg were administered orally 30 min before the induction of hyperalgesia by intraperitoneal injection of acetic acid. Consequently, the injection of acetic acid resulted in modifications in the curvature index and the behavioral phenotypes of Danio rerio. This response was characterized by a notable abnormal abdominal constriction, which justifies the observed locomotor alterations [47].
Pain is a common symptom in various human disorders. It occurs when nociceptors, present in primary afferent nerve fibers, transmit painful signals in response to harmful mechanical, thermal, or chemical stimuli, which activate the central nervous system (CNS) for pain perception and behavioral responses to pain [48]. While acute pain is temporary, has a protective purpose, and is beneficial, when it becomes chronic, it lacks the protective purpose and severely degrades the quality of life of patients [49]. It is considered a public health problem due to its prevalence and impact on quality of life and health systems [46].
In the midst of experimental models used to study evolutionarily conserved mechanisms underlying nociception, Danio rerio emerges as a promising organism to study nociceptive-type responses. Among homologues with humans, Danio rerio exhibits Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) ion channels, such as TRPV1 and TRPA1, as well as acid-sensing ion channels (ASICs) and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) [50].
The induction of hyperalgesia by noxious stimuli such as acetic acid ip. in Danio rerio consists of increased sensitivity to pain, with changes in curvature and behavior, suggesting a local nociceptive effect. The evaluation of substances with antinociceptive potential, based on this methodology, is particularly viable for studying new compounds with antinociceptive properties, as Danio rerio possesses physiological and neuroanatomical structures for nociceptive responses similar to those of mammals [51,52].
The species B. guianensis Aubl. it is widely used in experimental models to study the underlying processes of nociception and pain. It was reported for its pain-modulating effect in a model of abdominal writhing induced by acetic acid in mice treated with the methanolic extract of the species [9]. Cechinel Filho et al. [53] demonstrated a considerable analgesic effect in hydroalcoholic and ethyl acetate extracts (10 mg/kg) of the leaves, stems, bark, and roots of the species in the model of pain caused by 0.6% acetic acid in mice; the extracts exhibited greater efficacy compared to controls (aspirin and paracetamol). Willain Filho et al. [54] observed inhibition of abdominal constriction caused by both acetic acid and formalin in rodents treated with the hydroalcoholic extract of B. guianensis Aubl. The authors proposed that the mechanism of action of the extract would be related to the modulation of opioid receptors.
A similar species of the genus Bauhinia (Bauhinia microstachya) has also been described in the literature for its antinociceptive and antihyperalgesic activity. When hydroalcoholic extracts of aerial parts of B. microstachya were tested in models of pain induced by intraplantar injection of capsaicin and acetic acid ip. in mice, in addition to hyperalgesia induced by intraplantar injection of various phlogistic agents: carrageenan, bradykinin, capsaicin, substance P and adrenaline, there was a significant antinociceptive effect of extracts obtained from B. microstachya on chemical nociception induced by capsaicin and acetic acid in mice. Moreover, the extract of this species reduced the hyperalgesia induced by phlogistic agents in rats, which are substances involved in the transmission of pain [55].
The SS control group did not receive the dose of acetic acid; that is, it represented a comparison by receiving only the saline solution orally, BPS ip., and a diluent of acetic acid, demonstrating the behavior and body curvature common to the baseline [52].
The DMSO negative control group was thus treated to avoid a bias in the association of the organic solvent of the extracts with any effects [56]. Acetic acid provided a consistent reduction in locomotion, reflecting less exploratory activity, to the point of hypolocomotion of the animal for a prolonged period. It also decreased the behavior of climbing to the top of the tank, and when it was at the top, it stayed longer, which may be inferred from the stress factor caused by the pain reflex [57,58].
Notably, locomotor deficits are usually associated with animal welfare. The positive control group, treated with morphine, exhibited antinociceptive activity on ip. acetic acid-induced nociception. It is possible that the activation of opioid receptors in Danio rerio has negatively modulated variations in the body curvature index and mitigated other behaviors [47].
The present study demonstrated that the administration of HESBg and HELBg exhibited antinociceptive activity in the nociception induced by a harmful agent in an adult Danio rerio model, with HESBg showing greater significance, as it negatively modulated nociception; therefore, it demonstrated better effects in the index behavior and body curvature compared to controls. Given the effectiveness of the extracts in preventing nociceptive responses, a relationship is inferred between this endpoint and nociception, based on its good predictive validity.
This result may be associated with the procyanidins present in the extracts of B. guianensis Aubl. due to the suppression of the development of peripheral and central sensitization in the animals. As described by Cady et al. [59] when investigating the effects of extracts rich in procyanidins, obtained from grape seeds, on neurons and glial cells, in the trigeminal ganglia and the caudal trigeminal nucleus, in response to persistent inflammation of the temporomandibular joint induced in Sprague Dawley rats, the extracts suppressed the inflammatory reactions caused by prolonged stimulation of the trigeminal nerves. They significantly increased the basal expression of MKP-1 in neurons and glial cells within the trigeminal ganglia, as well as in neurons and glia in the caudal nucleus trigeminal.
Grape extracts rich in procyanidins were also examined in a model of pain and structural alterations of osteoarthritis, produced by monosodium iodoacetate (MIA) in the knee joint of rats, in which it was demonstrated that the treatment with the extracts attenuates the pain induced by MIA and the histological changes in the knee joint. For the authors, the antinociceptive and antiarthritic effects of the extracts were mediated by the inhibition of cartilage damage, synovitis, and subchondral bone fracture, as well as a reduction in the production of nitrotyrosine and matrix metalloproteinase-13, and the suppression of osteoclastogenesis [60].
The effectiveness of the administration of HESBg and HELBg, in a model of inflammation and pain (Danio rerio) in the activities observed in the present study, revealed that such extracts offer an excellent opportunity for the study of relevant biomarkers of the mechanisms involved; thus, more sensitive tests may be necessary to evaluate the cellular response and the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effects found, for example, the evaluation of cytokines or nitric oxide and the modulation of MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. Additionally, the results in the pain model can be further evaluated through relevant pain-related biomarkers to track the responses of molecular and physiological changes underlying the behavioral and curvature reactions observed in the Danio rerio model, which may involve anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive mechanisms triggered by procyanidins present in B. guianensis Aubl.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
Leaves and stems of B. guianensis were dried, ground, and macerated in a 70% hydroethanolic solution (1:10 m/v) for ten days at room temperature. After filtration, concentration, freezing, and lyophilization, extracts were obtained with yields of 7.73% (stem) and 18.53% (leaf). The extracts of B. guianensis Aubl. (HESBg and HELBg) were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), with a dose selected in the toxicity test and based on previous studies [9,10], with the following parameters: concentration of 0.02% m/v; 0.9% saline solution (SS); 300 μg kappa carrageenan, solubilized in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2, 0.128 mg/mL); indomethacin 10 mg; 2.5% acetic acid [47]; morphine 2.5 mg; ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA); alcohol 70, 80, 90 and 100%; 100% xylol; paraffin; hematoxylin and eosin dyes [4,9,25]. The reagents used were purchased from Sigma Chemical Company (St. Louis, Millstone, MO, USA).
4.2. Experimental Animals
Females and males of the Danio rerio (50) species (zebrafish), wild lineage AB, adults approximately six months old, 3.7 to 4 cm long, weighing around 550 mg, supplied by Power Fish Piscicultura, Itaguaí, were used (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). They were maintained on the Zebrafish Platform of the Drug Research Laboratory, Department of Biological and Health Sciences, Federal University of Amapá (UNIFAP), Macapá, Brazil. The animals remained in an adaptation period (40 days), a circadian cycle of 12 h (light from 7:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m.), temperature 23 ± 2 °C, and were fed twice a day with commercial flake feed (Alcon Colors, Santa Catarina, Brazil). The aquariums were monitored under ideal conditions (pH 6.0–8.0; conductivity 8.2 ± 0.2; hardness ranging from 5 to 20 dGH; calcium levels of 20–100 mg/L; magnesium levels of 10–50 mg/L; sodium levels of 10–50 mg/L; potassium levels of 1–5 mg/L; and dissolved oxygen levels above 5 mg/L; daily cleaning of the recirculation water system) [22,25]. The experiments adhered to the established guidelines for animal care and were approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Use (CEUA) at UNIFAP, with protocol number 007/2020.
Treatment Groups and Routes of Administration
The animals were fasted for 24 h before the experiments, and the groups were treated with different substances, as shown in Table 1, according to the specific test.

Table 1.
List of drugs used in experiments, concentrations, and potential effects in adults Danio rerio.
Inflammation: Control group (SS + PBS, SS 2 μL/animal p.o. + PBS 20 µL ip., carrageenan extender), negative control group (DMSO + CAR, DMSO 2 μL/animal p.o. + carrageenan 20 µL ip.), positive control group (indomethacin 10 mg/kg animal p.o. + carrageenan 20 µL ip.), groups treated with HELBg and HESBg (100 mg/kg animal p.o. + carrageenan 20 µL ip.), triplicate, with n = 12 animals per experimental group. The treatments were administered by the gavage method 60 min before the administration of carrageenan, as described by Borges et al. [4].
Hyperalgesia: Control group (SS + PBS, SS 2 μL/animal p.o. + PBS 10 µL ip., acetic acid diluent), negative control group (DMSO + AAC, DMSO 2 μL/animal p.o. + AAC 10 µL ip.), control group positive (Morphine 2.5 mg/kg animal p.o. + AAC 10 µL ip.), groups treated with HELBg and HESBg (100 mg/kg animal p.o. + AAC 10 µL ip.), n = 5 per experimental group, adhering to the 3R principles of ethical animal experimentation. Oral treatments were administered 30 min before the application of acetic acid, as described by Costa et al. [47].
For the treatments by the gavage method, a volumetric pipette (HTL Lab Solutions Co., São Paulo, Brazil) was used. The process of injecting substances into the peritoneum was performed with the aid of a BD Ultra-fine™ 30U syringe (needle size 6 mm × 0.25 mm).
4.3. Inflammation Induction Protocol with Carrageenan and Measurement of Inflammatory Edema Danio rerio
The process followed the protocol by Borges et al. [4], in which individually weighed animals (beginning and end of the trial, initial weight-Wi and final weight-Wf) on an analytical scale (FA2104N, Bioprecisa Co., São Paulo, Brazil) received a thermal shock as anesthesia, in water at 8–10 °C (the marked opening of the caps and the reduced swimming rhythm indicated the anesthetized state)—this method was preferred over other known anesthetic methods to avoid any additional drug being factored in concomitantly with the effects of the examined compounds.
Subsequently, they were placed on a damp sponge with a hollow center to hold the animal, positioning it so that the abdomen faced upwards to receive the injection. The needle was inserted at a 45° angle in the midline of the abdomen, between the pelvic and pectoral fins. Intraperitoneal administration took an average of 10 s. Then the animals were placed in separate tanks under the same environmental conditions as the system (25 ± 2 °C) for recovery from anesthesia and observation of edema formation. It is important to emphasize that this protocol allowed a rapid evaluation of the animal’s resistance through the return of swimming activity; otherwise, it could be replaced by another animal.
Inflammation Inhibition (II) was evaluated based on the difference in body weight (≠BW = Wf - Wi) of each animal, subsequently calculating the percentage of inflammation inhibition (% II) [21], according to Equation (1):
At the end of the experiment (5 h after the carrageenan injection), the animals were photographed with a digital camera (Canon T7 rebel, EEFS 55–250 mm lens, macro 1.1 m/3.6 ft, Nagasaki, Japan) and, after euthanasia in cold water (<−2 °C), were immediately stored in Bouin’s solution for tissue fixation.
4.3.1. Histopathological Analysis of the Inflammation Test in Danio rerio
For embedding, the animals were fixed in Bouin’s solution for 24 h and then decalcified in EDTA solution for an additional 24 h. Subsequently, they received treatment for tissue dehydration, in a progressive series of alcohol concentrations (70, 80, 90, and 100%) for 1 h each, followed by diaphanization with impregnation in xylol and inclusion in paraffin. The blocks were sectioned into 5 µm cuts using a microtome (Brand Rotary Microtome Cut 6062, Slee Medical, Nieder-Olm, Germany) and placed on glass slides for tissue staining with hematoxylin and eosin [25]. Histopathological analyses of the liver, intestine, and kidneys were performed blindly by a specialist using an Olympus BX41-Micronal Microscope and photographed with a digital camera (MDCE-5C USB 2.0, Qingdao, China).
4.3.2. Evaluation of Histopathological Alterations of the Inflammation Test in Danio rerio
The index of histopathological alterations (IHA) was defined by the extension of the tissue alterations observed in the liver, intestine and kidneys, classified as stages I, II and III: IHA = 0 to 10 (healthy organ), 11 to 20 (mild to moderate changes), 21 to 50 (moderate to severe changes) or >100 (irreversible changes) [22,61]. The index was calculated according to the following equation:
a: first stage alterations; b: second stage alterations; c: third-stage alterations; na: number of alterations considered as a first stage; nb: number of alterations considered as second stage; nc: number of alterations considered as the third stage; N: number of fish analyzed per treatment.
4.4. Hyperalgesia Induction Protocol with Acetic Acid and Behavioral Analysis
The animals were randomly selected and placed individually in observation tanks (15 × 13 × 10 cm, length × height × width), with 10 cm of water depth, in environmental conditions similar to those on the platform. The basal behavioral activity of the fish was recorded during 6 min, with a digital camera (Canon T7 rebel, EEFS 55–250 mm lens, macro 1.1 m/3.6 ft, Nagasaki, Japan). Then, the oral treatments were administered according to the group (SS, DMSO, MORPHINE, HELBg, and HESBg). After 30 min, the i.p. injection of PBS was performed in the control group (SS), and acetic acid was injected in the other groups. The treatment with morphine defined in this study was chosen because it is a classic opioid analgesic, clinically validated and potent, recognized in experimental models of pain, with sensitivity previously described in Danio rerio [47].
The animals were gently handled with a damp sponge having a hollow center, with the animal positioned in such a way that its abdomen faced upwards to receive the AAC injection. The needle was inserted at a 45° angle, in the midline of the abdomen, between the pelvic and pectoral fins. After the protocol, the fish were returned to the water, allowing for a more accurate analysis of their swimming activity and acute pain responses. The behavioral recordings [47] were recorded for 6 min using a digital camera. All behavioral tests in this study were performed between 9:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m. After the experimental procedures, the animals were immediately euthanized in ice water (<−2 °C).
Behavioral Parameters
Possible swimming behaviors related to nociception in Danio rerio were recorded 6 min before (baseline values) and after i.p. injection of AAC, as demonstrated in [47]. All recorded behaviors were analyzed in automated video tracking software (ToxTrac version 2.61, Umeå University, San Diego, CA, USA) at 30 frames/sec to quantify distance traveled (m), freeze duration (sec), transitions for the upper area (number of entries), and time spent in the upper area of the tank (s). The said program is optimized using an algorithm for tracking animals, such as fish, insects, and rodents [62].
Freezing was defined as the complete immobility of the animal (≥2 s), except for the eyes and brachial arches. The body curvature index observed Hyperalgesia, similar to abdominal constriction. Frontal fingerprints were taken every 30 s (totaling 24 photos per fish). Body curvature was measured using ImageJ 1.45 software for Windows (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
To establish the curvature of the body, three points were used on the animal: frontal (front of the head), central (middle of the body—between the anal and dorsal fins), and a posterior point (caudal fin). To calculate the value of the body curvature index, the average curvature angle of the 180° group was subtracted. Double-blind trained observers observed temporal variations in the body curvature index (inter-rater reliability > 0.90) and expressed them as the area under the curve (AUC). Both observers and data analysts were unaware of the treatment groups. Only the person who treated the animals was aware of these conditions, but did not analyze the data.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
The normality of the data and the homogeneity of the variances of the induction of hyperalgesia and inflammation were analyzed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov and Bartlett tests. The significance of the results obtained in inflammatory activity was determined using the one-way ANOVA test (analysis of variance), followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The IHA was evaluated using one-way ANOVA (Kruskal–Wallis) and the Student–Newman–Keuls test, comparing the means between the control and treatment groups, with significant values set at p < 0.05 [4] and highly significant values at p < 0.01. Data were expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (S.E.M.).
Changes in body curvature index and behavioral activity were analyzed by paired Student’s t-test and one-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA). Differences between groups were further assessed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test for significant ANOVA data. The results were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.), and non-parametric data (freezing duration) were previously transformed into log values. The significance level was set at p ≤ 0.05 in all analyses. Graph Pad Prism® 5.03 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) was used.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the potential anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects of hydroethanolic extracts of the leaves (HELBg) and stems (HESBg) of Bauhinia guianensis Aubl., a plant widely used in traditional Amazonian medicine to treat pain and inflammation, using the experimental model in zebrafish (Danio rerio). The results obtained corroborate the widespread use of this species and provide scientific evidence of its pharmacological activity.
In the model of acute inflammation induced by carrageenan, HESBg demonstrated a remarkable anti-inflammatory capacity, significantly inhibiting the formation of abdominal edema at levels comparable to the positive control, indomethacin. HELBg also showed an inhibitory effect, although to a lesser extent. It is important to emphasize that the histopathological analysis of the vital organs (liver, intestine, and kidney) of the animals treated with both extracts revealed no significant changes, suggesting a favorable safety profile at the dose tested.
Regarding antinociceptive activity, assessed by the acetic acid-induced hyperalgesia model, both HELBg and HESBg were effective in preventing changes in the body curvature index and positively modulating behavioral parameters associated with pain. The extracts promoted improvements in swimming activity, reduced freezing time, and altered tank exploration patterns, indicating a decrease in nociceptive perception, with effects comparable to those observed with morphine in some parameters.
The mechanisms underlying these activities appear to be related to the inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis, key mediators in inflammatory processes and nociceptor sensitization. The presence of bioactive compounds, such as procyanidins, previously identified in B. guianensis extracts and known for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, likely contributes to the observed effects, possibly through the modulation of pathways like arachidonic acid (COX) inhibition and NF-κB signaling. These results reinforce the potential of this Amazonian species as a source of new therapeutic agents.
Author Contributions
R.d.C.R.K., study design and wrote the manuscript based on the results obtained; R.d.C.R.K., A.M.F. and G.C.d.S. implemented the inflammation and pain methodologies; A.A.d.S. and P.F.S. performed the statistical tests; J.C.T.C. coordinated and supervised the research project. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank the PROPESPG from the Federal University of Amapá, through the Publication Assistance Program, which made this publication possible in open access format.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals at the Federal University of Amapá approved, in a meeting held on 28 December 2020, the final decision on Protocol 007/2020.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lisa, S.R.; Islam, M.K.; Qais, N. Plants and Plant Constituents with Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities: A Systematic Review. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 19, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conegundes, J.L.M.; da Silva, J.M.; de Freitas Mendes, R.; Fernandes, M.F.; de Castro Campos Pinto, N.; de Almeida, M.A.; Dib, P.R.B.; de Oliveira Andrade, R.; Rodrigues, M.N.; Castañon, M.C.M.N.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activity of Siparuna guianensis Aublet, an Amazonian Plant Traditionally Used by Indigenous Communities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, A.C.B.; Lana, T.N.; Perfeito, J.P.S.; Silveira, D. The Brazilian Market of Herbal Medicinal Products and the Impacts of the New Legislation on Traditional Medicines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 212, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Keita, H.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; dos Santos Sampaio, T.I.; Ferreira, I.M.; Lima, E.S.; de Jesus Amazonas da Silva, M.; Fernandes, C.P.; de Faria Mota Oliveira, A.E.M.; da Conceição, E.C.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Nanoemulsions of Essential Oil from Rosmarinus officinalis L.: In Vitro and in Zebrafish Studies. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Rocha Koga, R.; de Lima Teixeira dos Santos, A.V.T.; do Socorro Ferreira Rodrigues Sarquis, R.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Bauhinia guianensis Aubl., a Plant from Amazon Biome with Promising Biologically Active Properties: A Systematic Review. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2021, 15, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Ribnicky, D.M.; Poulev, A.; Logendra, S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Raskin, I. A Natural History of Botanical Therapeutics. Metabolism 2008, 57, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.N.; Sekar, M.; Fuloria, S.; Gan, S.H.; Rani, N.N.I.M.; Ravi, S.; Begum, M.Y.; Chidambaram, K.; Sathasivam, K.V.; Jeyabalan, S.; et al. Kirenol: A Potential Natural Lead Molecule for a New Drug Design, Development, and Therapy for Inflammation. Molecules 2022, 27, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C. Medicinal Knowledge and Plant Utilization in an Amazonian Coastal Community of Marudá, Pará State (Brazil). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Santos, L.S.; Viana, E.P.; de Almeida, S.S.M.S.; Marconato, E.; Rodrigues, M.; Ferreira, L.R.; Van de Kamp, A. Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of the Crude Extracts from Stem Bark of Bauhinia guianensis. Pharm. Biol. 1999, 37, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, R.C.R.; Souza, G.C.; Teixeira, A.V.T.L.; Ferreira, A.M.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Silva Abreu, L.S.; Tavares, J.F.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Hydroethanolic Extracts from Bauhinia guianensis: A Study on Acute Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryos and Adults. Pharm. Biol. 2024, 62, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintans-Júnior, L.; Almeida, R.; Falcão, A.; de Fátima Agra, M.; Sousa Maria de Fátima Vanderlei; de Fátima Vanderlei de Sousa e José Maria Barbosa-Filho, M. Avaliação Da Atividade Anticonvulsivante de Plantas Do Nordeste Brasileiro. Acta Farm. Bonaer. 2002, 21, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T. Pharmacological Effects of Polyphenol Phytochemicals on the Intestinal Inflammation via Targeting TLR4/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehnlein, O.; Lindbom, L. Phagocyte Partnership during the Onset and Resolution of Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanandrea, R.; Bonan, C.D.; Campos, M.M. Zebrafish as a Model for Inflammation and Drug Discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. Zebrafish: Model for the Study of Inflammation and the Innate Immune Response to Infectious Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 946, 253–275. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Feng, C.-W.; Hung, H.-C.; Chakraborty, C.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Jean, Y.-H.; Wang, H.-M.D.; Sung, C.-S.; Sun, Y.-M.; et al. A Novel Zebrafish Model to Provide Mechanistic Insights into the Inflammatory Events in Carrageenan-Induced Abdominal Edema. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatoo, M.I.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Saxena, A.; Parray, O.R.; Tufani, N.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Tiwari, R.; Dhama, K.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Herbs with Special Emphasis on Herbal Medicines for Countering Inflammatory Diseases and Disorders-A Review. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2018, 12, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Wingerd, B.A.; Arakawa, T.; Smith, W.L. Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene Transcription in a Macrophage Model of Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 8111–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlouni, M. Anti-Inflamatórios Não Esteroides: Efeitos Cardiovasculares, Cérebro-Vasculares e Renais. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2010, 94, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, R.S.; Lima, E.S.; Keita, H.; Ferreira, I.M.; Fernandes, C.P.; Cruz, R.A.S.; Duarte, J.L.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; Castro, A.N.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antialgic Actions of a Nanoemulsion of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Essential Oil and a Molecular Docking Study of Its Major Chemical Constituents. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holanda, F.H.; Ribeiro, A.N.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; de Souza, G.C.; Borges, S.F.; Ferreira, A.M.; Florentino, A.C.; Yoshioka, S.A.; Moraes, L.S.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Baicalein Combined with Silk Fibroin Protein in a Zebrafish Model (Danio rerio). Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 45, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.C.T.; Keita, H.; Santana, G.R.; de Souza, G.C.; dos Santos, I.V.F.; Amado, J.R.R.; Kourouma, A.; Prada, A.L.; de Oliveira Carvalho, H.; Silva, M.L. Effects of Bothrops Alternatus Venom in Zebrafish: A Histopathological Study. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.; Souza, G.; Santana, G.; Duarte, J.; Fernandes, C.; Keita, H.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.; Navarrete, A.; Ferreira, I.; Carvalho, H.; et al. Histopathology in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) to Evaluate the Toxicity of Medicine: An Anti-Inflammatory Phytomedicine with Janaguba Milk (Himatanthus Drasticus Plumel). In Histopathology—An Update; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- de Sá Hyacienth, B.M.; Tavares Picanço, K.R.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Barros Silva, L.; Matias Pereira, A.C.; Machado Góes, L.D.; Sousa Borges, R.; Cardoso Ataíde, R.; dos Santos, C.B.R.; de Oliveira Carvalho, H.; et al. Hydroethanolic Extract from Endopleurauchi (Huber) Cuatrecasas and Its Marker Bergenin: Toxicological and Pharmacokinetic Studies in silico and in vivo on Zebrafish. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, G.; Duarte, J.; Fernandes, C.; Moyado, J.; Navarrete, A.; Carvalho, J. Obtainment and Study of the Toxicity of Perillyl Alcohol Nanoemulsion on Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Nanomed. Res. 2016, 4, 00093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankov, S.V. Definition of Inflammation, Causes of Inflammation and Possible Anti-Inflammatory Strategies. Open Inflamm. J. 2012, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekambaram, S.P.; Perumal, S.S.; Pavadai, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Naravelia zeylanica DC via Suppression of Inflammatory Mediators in Carrageenan-Induced Abdominal Oedema in Zebrafish Model. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 25, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalho, P.G.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; Maurer-Morelli, C.V. Indomethacin Treatment Prior to Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Seizures Downregulates the Expression of il1b and Cox2 and Decreases Seizure-like Behavior in Zebrafish Larvae. BMC Neurosci. 2016, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quitian-Useche, Y.F.; Sánchez-Ortiz, B.L.; Borges, S.F.; Ramos, B.; de Souza, G.C.; Batista, M.A.; da Silva Hage Melim, L.I.; Ferreira, I.M.; Carvalho, J.C.T.; Borges, R.S. Fatty Ethanolamide of Bertholletia Excelsa Triglycerides (Brazil Nuts): Anti-Inflammatory Action and Acute Toxicity Evaluation in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 1519–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Micaelo, N.; González-Abuín, N.; Ardèvol, A.; Pinent, M.; Blay, M.T. Procyanidins and Inflammation: Molecular Targets and Health Implications. BioFactors 2012, 38, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J. Fitoterápicos Anti-Inflamatórios, 2nd ed.; Pharmabooks: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017; ISBN 139788589731805. [Google Scholar]
- David, J.; Barreiros, A.; David, J. Antioxidantes de Fontes Naturais. In Fitoterápicos Anti-Inflamatórios; Pharmabooks: São Paulo, Brazil, 2017; pp. 105–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Qian, H.; Chen, W.; Tong, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Proanthocyanidins Attenuation of H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in Tendon-Derived Stem Cells via Upregulating Nrf-2 Signaling Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7529104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Bang, J.; Son, C.-N.; Baek, W.-K.; Kim, J.-M. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Ameliorates Murine Autoimmune Arthritis through Regulation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, S.; Lu, G.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, C. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Oligomeric Proanthocyanidins Via Inhibition of NF-ΚB and MAPK in LPS-Stimulated MAC-T Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, J.; Bruchhausen, F.v.; Wurm, G. Flavonoids and Related Compounds as Inhibitors of Arachidonic Acid Peroxidation. Prostaglandins 1980, 20, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, M.; Nieminen, R.; Asmawi, M.; Vuorela, P.; Vapaatalo, H.; Moilanen, E. Effects of Flavonoids on Prostaglandin E 2 Production and on COX-2 and MPGES-1 Expressions in Activated Macrophages. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.J.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, D.E.; Rogozin, E.A.; Bode, A.M.; Lee, H.J.; Dong, Z. Cocoa Procyanidins Suppress Transformation by Inhibiting Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 20664–20673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, J.K.; Na, H.-K.; Chun, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-K.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, O.-S.; Sim, Y.-C.; Surh, Y.-J. Inhibition of Phorbol Ester–Induced COX-2 Expression by Epigallocatechin Gallate in Mouse Skin and Cultured Human Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3805S–3810S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Micaelo, N.; González-Abuín, N.; Terra, X.; Richart, C.; Ardèvol, A.; Pinent, M.; Blay, M. Omega-3 Docosahexaenoic Acid and Procyanidins Inhibit Cyclo-Oxygenase Activity and Attenuate NF-ΚB Activation through a P105/P50 Regulatory Mechanism in Macrophage Inflammation. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, X.; Valls, J.; Vitrac, X.; Mérrillon, J.-M.; Arola, L.; Ardèvol, A.; Bladé, C.; Fernández-Larrea, J.; Pujadas, G.; Salvadó, J.; et al. Grape-Seed Procyanidins Act as Antiinflammatory Agents in Endotoxin-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Inhibiting NFkB Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4357–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.; Sadler, K.C. New School in Liver Development: Lessons from Zebrafish. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugman, S. The Zebrafish as a Model to Study Intestinal Inflammation. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 64, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanhart, L.M.; Cosentino, C.C.; Diep, C.Q.; Davidson, A.J.; de Caestecker, M.; Hukriede, N.A. Zebrafish Kidney Development: Basic Science to Translational Research. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2011, 93, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhoff, J.H.; Giselbrecht, S.; Schmidts, M.; Schindler, S.; Beales, P.L.; Tönshoff, B.; Liebel, U.; Gehrig, J. Development of an Automated Imaging Pipeline for the Analysis of the Zebrafish Larval Kidney. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Yuan, M.; Ji, R.-R. Inflammation and Pain. In Neuroimmune Interactions in Pain; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 17–41. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, F.V.; Rosa, L.V.; Quadros, V.A.; Santos, A.R.S.; Kalueff, A.V.; Rosemberg, D.B. Understanding Nociception-Related Phenotypes in Adult Zebrafish: Behavioral and Pharmacological Characterization Using a New Acetic Acid Model. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, A.; Andersson, D.; Shoenfeld, Y. The Biology of Symptom-Based Disorders–Time to Act. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S. Inflammation and Pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Nunez, V.; Rodriguez, R.E. The Zebrafish: A Model to Study the Endogenous Mechanisms of Pain. ILAR J. 2009, 50, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Gupta, P.K.; Gupta, P.; Garabadu, D. Antinociceptive Activity of Standardized Extract of Bacopa Monnieri in Different Pain Models of Zebrafish. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, P.J.; Bardine, N. Antinociceptive Effects of Buprenorphine in Zebrafish Larvae: An Alternative for Rodent Models to Study Pain and Nociception? Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2014, 152, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cechinel Filho, V.; Breviglieri, E.; Willain Filho, A.; Santos, A.R.S. Estudo Fitoquímico e Avaliação Preliminar Da Atividade Analgésica de Bauhinia Splendens. Rev. Bras. Farmacol. 1995, 76, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Willain Filho, A.; Breviglieri, E.; Filho, V.C.; Santos, A.R.S. Antinociceptive Effect of the Hydroalcoholic Extract of Bauhinia splendens Stems in Mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 49, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadotti, V.M.; Santos, A.R.S.; Meyre-Silva, C.; Schmeling, L.O.; Machado, C.; Liz, F.H.; Filho, V.C. Antinociceptive Action of the Extract and the Flavonoid Quercitrin Isolated from Bauhinia microstachya Leaves. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Luna, J.; Al-Jubouri, Q.; Al-Nuaimy, W.; Sneddon, L.U. Impact of Stress, Fear and Anxiety on the Nociceptive Responses of Larval Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding Behavioral and Physiological Phenotypes of Stress and Anxiety in Zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, E.L.; Pinto, A.M.; Baima, C.L.B.; da Silva, H.R.; da Silva Sena, I.; Sanchez-Ortiz, B.L.; de Lima Teixeira, A.V.T.; Pereira, A.C.M.; da Silva Barbosa, R.; Carvalho, H.O.; et al. Evaluation of the in Vitro Release of Isoflavones from Soybean Germ Associated with Kefir Culture in the Gastrointestinal Tract and Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Actions in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cady, R.J.; Hirst, J.J.; Durham, P.L. Dietary Grape Seed Polyphenols Repress Neuron and Glia Activation in Trigeminal Ganglion and Trigeminal Nucleus Caudalis. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.J.; Joo, Y.B.; Jung, Y.O.; Ju, J.H.; Cho, L.M.; Oh, H.J.; Jhun, J.Y.; Park, M.K.; Park, J.S.; Kang, C.M.; et al. Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Ameliorates Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poleksic, V.; Mitrovic-Tutundzic, V. Fish Gills as a Monitor of Sublethal and Chronic Effects of Pollution. In Sublethal and Chronic Effects of Pollutants on Freshwater Fish; Fishing New Books: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.; Zhang, H.; Klaminder, J.; Brodin, T.; Andersson, P.L.; Andersson, M. ToxTrac: A Fast and Robust Software for Tracking Organisms. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2018, 9, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).